Spirit Airlines Bundle
Who Really Owns Spirit Airlines?
The saga of Spirit Airlines, from its trucking roots to its current status as a major ultra-low-cost carrier, is a compelling tale of strategic shifts and market dominance. The failed JetBlue acquisition attempt in early 2024 highlighted the critical role of ownership in shaping an airline's destiny and its impact on the competitive landscape. But who exactly holds the reins of this aviation disruptor?

Understanding the Spirit Airlines SWOT Analysis is crucial, as its ownership structure dictates its strategic direction, financial performance, and ability to navigate the turbulent skies of the airline industry. This exploration will uncover the Spirit Airlines ownership details, including its Spirit Airlines parent company, major shareholders, and the individuals who ultimately control its operations. Discover the Spirit Airlines history and the evolution of its ownership, from its humble beginnings to its current position, providing insights into who owns Spirit Airlines.
Who Founded Spirit Airlines?
The story of Spirit Airlines begins in 1964, not as an airline, but as Clippert Trucking Company, founded by Ned Homfeld. This trucking business set the stage for the future airline, marking the initial phase of what would eventually become a major player in the aviation industry. The transition from trucking to air travel reflects a strategic evolution in response to market opportunities.
The transformation into an airline started in 1990 when the company, then known as Charter One, began offering charter vacation packages. This marked the initial foray into the travel sector, focusing on destinations such as the Bahamas and Las Vegas. The acquisition of its first jet aircraft in 1992 was a pivotal moment, leading to the rebranding as Spirit Airlines, and a shift from charter services to scheduled passenger flights.
Information regarding the specific equity split or shareholding percentages of Ned Homfeld or other early backers at the company's inception as Charter One or Spirit Airlines is not readily available in public records from that early period. Early funding likely came from Homfeld himself and potentially private investors interested in the nascent charter and low-cost travel market. There is no widely publicized information about early agreements such as vesting schedules, buy-sell clauses, or founder exits, nor any notable initial ownership disputes or buyouts from this formative period. The founding vision, however, was clearly centered on providing accessible travel, a principle that has remained central to Spirit's business model.
Understanding the early ownership of Spirit Airlines provides context to its current structure. The shift from charter services to scheduled flights in 1992 was a crucial strategic move. The early ownership structure is not fully detailed in public records from that time, but the focus was on accessible travel.
- The company's journey began with Clippert Trucking Company in 1964, founded by Ned Homfeld.
- Charter One started offering charter vacation packages in 1990.
- The acquisition of its first jet aircraft in 1992 led to the rebranding as Spirit Airlines.
- Early funding likely came from Homfeld and private investors.
For more details on how Spirit Airlines generates revenue and its business model, you can read Revenue Streams & Business Model of Spirit Airlines.
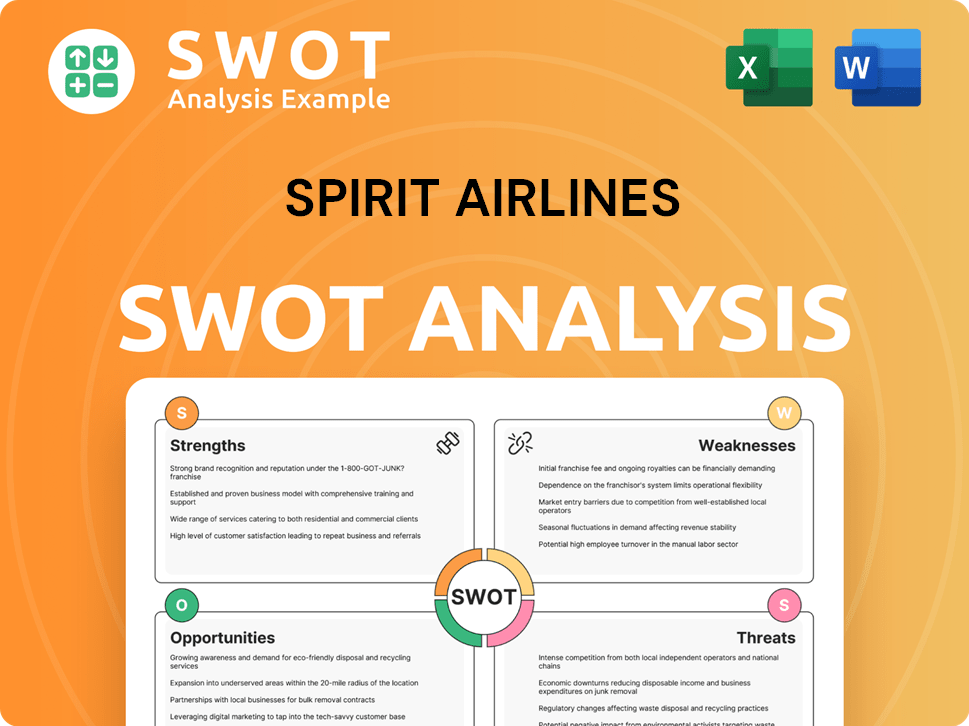
Spirit Airlines SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
How Has Spirit Airlines’s Ownership Changed Over Time?
The journey of Spirit Airlines from a privately held entity to a publicly traded company is a pivotal aspect of understanding its ownership. The airline's Initial Public Offering (IPO) on November 11, 2011, marked a significant shift, with shares listed on the NASDAQ exchange under the ticker 'SAVE.' The IPO saw the sale of approximately 15.6 million shares at $12 each, raising around $187 million and establishing an initial market capitalization of about $800 million. This event opened the door for broader investor participation and set the stage for the ownership structure it has today.
Since its IPO, the ownership of Spirit Airlines has largely transitioned to institutional investors. As of early 2024, a substantial portion of Spirit's outstanding shares is held by these institutions, reflecting a common trend in the airline industry. Key institutional investors include major asset management firms, mutual funds, and index funds. For example, as of March 29, 2024, The Vanguard Group Inc. held 12.18% of the shares, BlackRock Inc. held 11.23%, and State Street Corp. held 5.09%. Other significant holders include Renaissance Technologies LLC, Geode Capital Management, LLC, and Norges Bank.
| Shareholder | Percentage of Shares (as of March 29, 2024) | Type of Investor |
|---|---|---|
| The Vanguard Group Inc. | 12.18% | Institutional |
| BlackRock Inc. | 11.23% | Institutional |
| State Street Corp. | 5.09% | Institutional |
The attempted acquisition by JetBlue, which began with an offer in April 2022 and was ultimately blocked by a federal court in January 2024, significantly impacted the company's trajectory. This proposed merger would have fundamentally changed Spirit's ownership and market position. The termination of the merger agreement solidified Spirit's stand-alone status, at least for the near future, highlighting the influence of shareholders and regulatory bodies on the company's strategic direction.
Spirit Airlines is a publicly traded company, with institutional investors holding a significant portion of shares. Key shareholders include The Vanguard Group, BlackRock, and State Street Corp. The failed merger with JetBlue was a major event affecting the company's ownership structure.
- Institutional investors hold the majority of shares.
- The IPO occurred in November 2011.
- The JetBlue merger was blocked in January 2024.
- The current CEO of Spirit Airlines is Ted Christie.
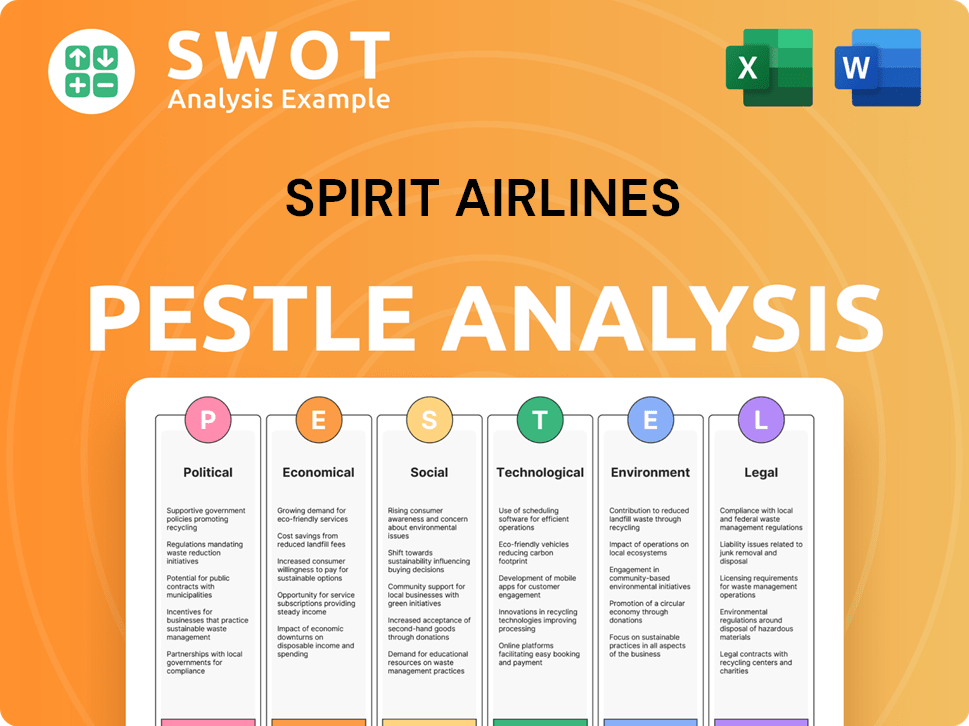
Spirit Airlines PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
Who Sits on Spirit Airlines’s Board?
As of early 2024, the Board of Directors of Spirit Airlines is responsible for overseeing the company's strategic direction and representing shareholder interests. The board is composed of a mix of independent directors and those with executive roles within the company. For example, the board includes members like Ted Christie, who serves as the President and CEO, along with independent directors who bring expertise in finance, aviation, and other relevant fields. Details about the board's composition, including which members represent major shareholders, are available in the company's annual proxy statements filed with the SEC. These directors primarily serve in a fiduciary capacity, representing the interests of the broader shareholder base rather than any specific major investor.
The Board's role has been particularly significant during major corporate events. For instance, during the proposed merger with JetBlue, the Board played a crucial role in evaluating offers and recommending a course of action to shareholders. While there were no public proxy battles in the traditional sense, the competing bids from Frontier Airlines and JetBlue led to significant shareholder engagement. The Board's decisions during this period were subject to intense scrutiny, highlighting its accountability to the company's diverse ownership base. Understanding the Competitors Landscape of Spirit Airlines is crucial for assessing its position and the impact of strategic decisions.
| Board Member | Title | Relevant Experience |
|---|---|---|
| Ted Christie | President and CEO | Extensive experience in airline operations and finance. |
| Robert L. Fornaro | Lead Independent Director | Former CEO of Spirit Airlines, significant aviation industry experience. |
| Other Independent Directors | Various | Backgrounds in finance, aviation, and related industries. |
Spirit Airlines operates under a one-share-one-vote structure. This means that each outstanding common share typically grants its holder one vote on matters presented to shareholders, such as the election of directors or approval of corporate actions. This structure promotes a more democratic governance model among shareholders. There are no indications of dual-class shares or special voting rights that would grant outsized control to any single individual or entity. This structure ensures a more equitable distribution of voting power among shareholders.
Spirit Airlines' governance structure is designed to be shareholder-friendly, with each share generally carrying equal voting rights. This approach ensures that all shareholders have a proportional say in the company's direction. The Board of Directors is responsible for representing the interests of all shareholders.
- One-share-one-vote structure.
- Board oversees strategic direction.
- Independent directors provide oversight.
- Shareholder votes on major decisions.
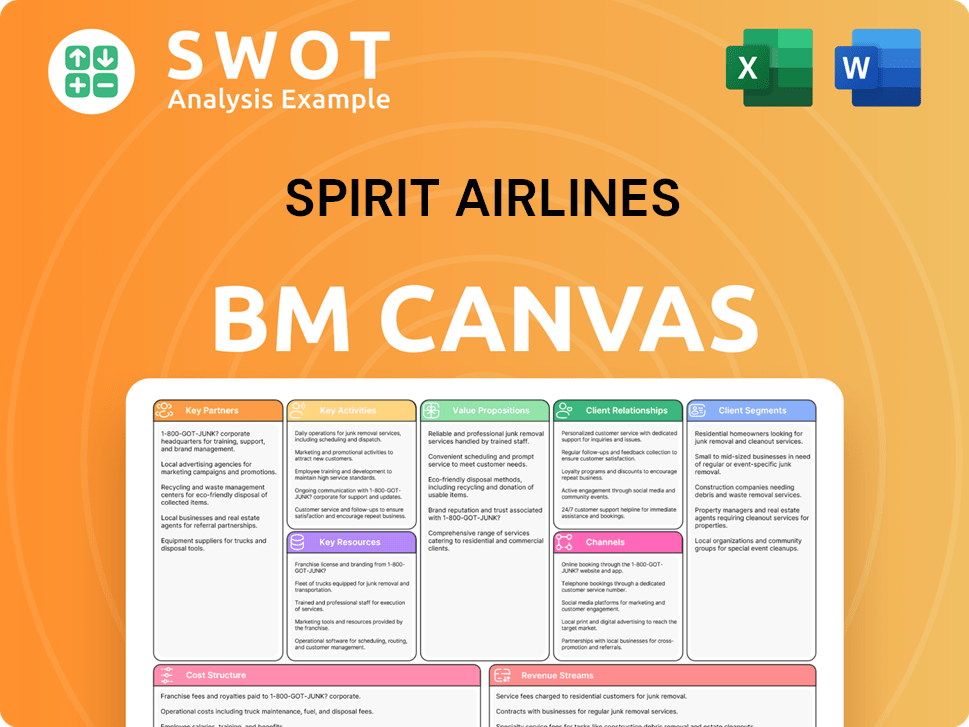
Spirit Airlines Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
What Recent Changes Have Shaped Spirit Airlines’s Ownership Landscape?
Over the past few years, the ownership structure of Spirit Airlines has been significantly impacted by industry dynamics and strategic moves. A major event was the attempted acquisition by JetBlue Airways, which began in April 2022. This deal, however, was blocked by a federal court in January 2024 due to antitrust concerns. This outcome created volatility in the company's stock and drew the attention of many institutional investors and arbitrageurs.
Following the failed merger, Spirit Airlines' stock experienced a decline, reflecting the market's re-evaluation of its standalone prospects. The airline industry, including ultra-low-cost carriers (ULCCs) like Spirit, has seen an increase in institutional ownership. Large asset managers hold significant stakes in various airlines. This can influence the focus on financial results and shareholder returns. While the company is now largely dispersed among institutional investors, its ownership is no longer concentrated in the hands of the founders.
| Metric | Details | Year |
|---|---|---|
| Stock Performance Post-Merger Termination | Significant decline | 2024 |
| Institutional Ownership | Increased presence | 2024-2025 |
| Merger Attempt | JetBlue acquisition attempt blocked | 2022-2024 |
Looking ahead, Spirit Airlines is focused on navigating a competitive market as an independent entity. The company's leadership has expressed intentions to strengthen its standalone business. This includes optimizing operations and improving profitability. The company's success in demonstrating sustained profitability and growth will be crucial for attracting and retaining investor confidence. For more insights, you can read about the Growth Strategy of Spirit Airlines.
The failed merger with JetBlue was a major catalyst for changes in Spirit Airlines' stock performance. This has led to increased scrutiny from institutional investors. The airline's ability to maintain investor confidence will depend on its ability to demonstrate financial stability and growth.
The airline industry is dynamic, with strategic realignments possible. Spirit Airlines faces the challenge of operating independently in a competitive market. The company's focus is on optimizing its operations and enhancing profitability.
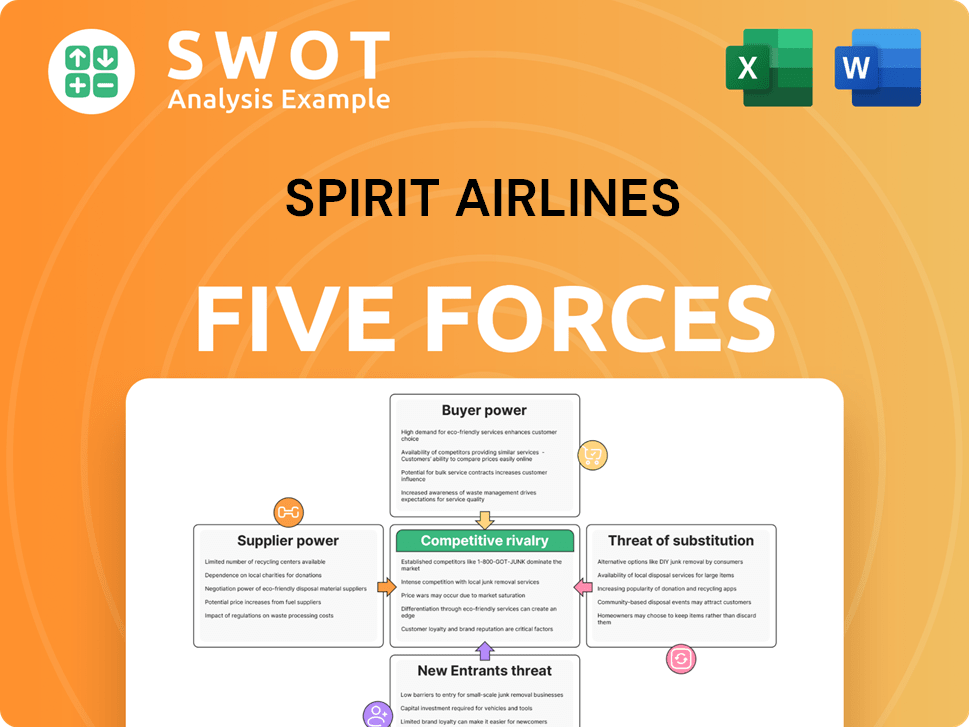
Spirit Airlines Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What are Mission Vision & Core Values of Spirit Airlines Company?
- What is Competitive Landscape of Spirit Airlines Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of Spirit Airlines Company?
- How Does Spirit Airlines Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of Spirit Airlines Company?
- What is Brief History of Spirit Airlines Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of Spirit Airlines Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.