Sumitomo Bakelite Bundle
How has Sumitomo Bakelite Shaped the Plastics Industry?
Journey back in time to explore the fascinating Sumitomo Bakelite SWOT Analysis and the remarkable story of Sumitomo Bakelite Company, a true pioneer in the world of plastics. From its origins in 1932, this Japanese company has been at the forefront of innovation, transforming industries with its groundbreaking materials. Discover how this legacy of innovation continues to drive the company's success in the global market.
The brief history of Sumitomo Bakelite, from its roots in phenolic resin to its current status as a global leader, reflects a commitment to excellence and adaptability. This exploration will uncover the key milestones that shaped Sumitomo Bakelite's trajectory, highlighting its impact on plastic manufacturing and its enduring legacy. Understanding the Sumitomo Bakelite Company's journey provides valuable insights for investors and business strategists alike.
What is the Sumitomo Bakelite Founding Story?
The story of Sumitomo Bakelite Company, a prominent
This pivotal move followed Sankyo Company's acquisition of exclusive Japanese patent rights for 'Bakelite' in 1911. Developed by Dr. Leo Baekeland in 1907, Bakelite was a groundbreaking synthetic resin. Trial production of phenolic resin commenced at Sankyo Company's Shinagawa Plant, which effectively launched Japan's plastics industry.
In 1955, Nippon Bakelite Co., Ltd. merged with Sumitomo Synthetic Resin Industries, Ltd., a synthetic resin molding business within the Sumitomo Group. This merger officially formed Sumitomo Bakelite Co., Ltd. This consolidation integrated pioneering plastics technology with the broader Sumitomo Group's business principles. The company's name, 'Bakelite,' reflects its legacy in the industry.
Sumitomo Bakelite's history is marked by strategic developments and technological advancements.
- 1911: Sankyo Company secures exclusive rights to 'Bakelite' in Japan.
- 1932: Nippon Bakelite Co., Ltd. is established, separating from Sankyo.
- 1955: Sumitomo Bakelite Co., Ltd. is officially formed through a merger.
- Early 20th Century: Bakelite, the world's first synthetic plastic, is invented.
Sumitomo Bakelite SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
What Drove the Early Growth of Sumitomo Bakelite?
Following its establishment in 1955, through the merger of Nippon Bakelite and Sumitomo Synthetic Resin Industries, Sumitomo Bakelite Company began a period of significant early growth and expansion. This Japanese company quickly diversified its product portfolio, introducing new materials and expanding its reach across various sectors. These early product launches were crucial for its future prominence in diverse sectors, including electronics and packaging.
Between 1956 and 1981, Sumitomo Bakelite introduced several key products. These included rigid polyvinyl chloride sheets, known as SUMILITE® VSS, and epoxy molding compounds for semiconductor encapsulation, SUMIKON® EME. This diversification into different materials like phenolic resin and plastics laid the groundwork for its expansion.
Sumitomo Bakelite's expansion extended beyond Japan. The company established its first international subsidiary in Singapore. Further international growth included the acquisition of Vyncolit N.V. in Belgium and Vyncolit North America, Inc. in the USA from Perstorp AB of Sweden in 2005, and the establishment of Sumitomo Bakelite (Nantong) Co., Ltd. in China in 2007.
The company expanded its reach through strategic acquisitions and the establishment of joint ventures. In 1999, Sumitomo Bakelite (Taiwan) Co., Ltd. was founded as a joint venture with Chang Chun Plastics Co., Ltd., focusing on producing epoxy molding compounds. These moves helped strengthen its global supply chain and market presence. For more insights into the company's strategic growth, see the Growth Strategy of Sumitomo Bakelite.
In 2021, Sumitomo Bakelite standardized its disparate ERP systems at four major Asian bases onto Oracle Fusion Cloud ERP and SCM applications. This unified finance, purchasing, inventory, and other back-office processes. This facilitated timelier management decisions, reflecting the company's commitment to technological innovation.
Sumitomo Bakelite PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
What are the key Milestones in Sumitomo Bakelite history?
The Sumitomo Bakelite Company has a rich Bakelite history, marked by significant milestones in the plastic manufacturing industry. This Japanese company has consistently pushed boundaries, contributing substantially to the evolution of plastic and phenolic resin technologies.
| Year | Milestone |
|---|---|
| Ongoing | Holds the world's top market share in epoxy molding compounds for semiconductor encapsulation, accounting for approximately 40% of the global market. |
| 2010 | Initiated research and development into plant-based plastics, focusing on producing compounds like phenol from inedible plant resources. |
| 2024 | Introduced the SUMILITERESIN® PRZ Series, a new additive polymer (COP) and copolymerized cyclo-olefin polymer (COC), for diverse applications. |
| Fiscal 2024 | Aimed to introduce thermosetting resin solutions for automotive battery components, targeting adoption in Europe, the United States, and Japan. |
| April 2025 | Secured a total of 25,415 patents, reflecting a strong commitment to continuous research and development. |
| February 2025 | Earned a Gold Medal in the EcoVadis sustainability assessment, placing it among the top 5% of all evaluated companies. |
Sumitomo Bakelite has consistently focused on innovations, particularly in the realm of plastic manufacturing and phenolic resin development. The company's advancements include the development of plant-based plastics and the introduction of new additive polymers.
Sumitomo Bakelite's epoxy molding compounds are used in semiconductor encapsulation, holding a substantial market share.
Research began in 2010 to develop plant-based plastics, aiming to replace petroleum-derived raw materials.
In 2024, the company introduced the SUMILITERESIN® PRZ Series, a new additive polymer with high transparency and other beneficial properties.
The company developed a solution using thermosetting resin for automotive battery components to reduce weight and enhance manufacturing efficiency for electric vehicles (EVs).
The company has secured a substantial number of patents, with a total of 25,415 patents as of April 2025, reflecting its continuous commitment to research and development.
Sumitomo Bakelite has received prestigious recognition for its sustainability efforts, earning a Gold Medal in the EcoVadis sustainability assessment in February 2025.
Despite its achievements, Sumitomo Bakelite has faced challenges, including market fluctuations and the need for strategic adjustments. The company has demonstrated resilience by adapting its business model and focusing on high-value-added products.
The company has navigated market downturns, requiring strategic pivots to maintain its position.
In response to geopolitical risks, the company adjusted its financial targets.
The company focuses on high-value-added products in niche markets.
The company raised its fiscal 2023 sales revenue target to 300 billion yen and business profit to 30 billion yen.
The company's commitment to creating an environment for generating new ideas and its willingness to invest in strategic areas like sustainable materials and e-mobility applications demonstrate its resilience and forward-thinking approach.
Achieved record sales revenue, business profit, and earnings in fiscal 2023.
Sumitomo Bakelite Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
What is the Timeline of Key Events for Sumitomo Bakelite?
The Sumitomo Bakelite Company has a rich Bakelite history, marked by significant milestones in the plastic manufacturing industry. From its early days producing phenolic resin to its current focus on sustainable materials and e-mobility, the company's evolution reflects its commitment to innovation and market adaptation. The Japanese company has consistently expanded its operations and product offerings, establishing itself as a key player in the global materials market.
| Year | Key Event |
|---|---|
| 1907 | Phenolic resin, 'Bakelite,' was developed by Dr. Leo Baekeland. |
| 1911 | Sankyo Company secured exclusive patent rights for Bakelite in Japan and began trial production of phenolic resin. |
| 1932 | Nippon Bakelite Co., Ltd. was established, separating the phenolic resin business from Sankyo Company. |
| 1955 | Nippon Bakelite Co., Ltd. merged with Sumitomo Synthetic Resin Industries, Ltd. to form Sumitomo Bakelite Co., Ltd. |
| 1956-1981 | Introduction of rigid polyvinyl chloride sheets (SUMILITE® VSS) and epoxy molding compounds for semiconductors (SUMIKON® EME). |
| 1993 | The 'Vyncolite' material production department spun off into Vyncolit NV, later becoming part of Sumitomo Bakelite Europe (Ghent) NV. |
| 1999 | Sumitomo Bakelite (Taiwan) Co., Ltd. was founded as a joint venture for semiconductor packaging materials. |
| 2005 | Acquisition of Vyncolit N.V. in Belgium and Vyncolit North America, Inc. in the USA. |
| 2007 | Sumitomo Bakelite (Nantong) Co., Ltd. was established in China. |
| 2010 | Sumitomo Bakelite began researching the production of plastics from plant-based raw materials. |
| 2018 | Green Phenol Development Co., Ltd. (GPD) changed its name to Green Chemicals Co., Ltd. (GCC) for commercialization of plant-based plastics. |
| 2023 | Sumitomo Bakelite Europe (Ghent) NV finalized construction of a 600-panel photovoltaic installation and a new production line, focusing on e-mobility. |
| February 2025 | Sumitomo Bakelite received a Gold Medal in the EcoVadis sustainability assessment. |
| April 2025 | Launch of a 'Project Team to Prepare for Mass Production of Functional Membranes for Hydrogen Production.' |
| May 2025 | Announced year-end commemorative dividend for the fiscal year ended March 31, 2025. |
Sumitomo Bakelite is actively working towards carbon neutrality within the chemical industry. This includes significant investments in developing and cultivating plant-based plastics as a key part of their sustainability strategy.
The company is targeting growth in the e-mobility sector, with new composite materials designed for electric vehicle applications. They are developing thermosetting resins for automotive battery components.
In April 2025, Sumitomo Bakelite launched a project team to prepare for mass production of functional membranes for hydrogen production, demonstrating its commitment to green technologies.
For the fiscal year ending March 31, 2026, the company projects sales of 310.00 billion yen, a 1.7% increase, and an operating profit of 31.00 billion yen, a 25.0% increase. The company reported trailing 12-month revenue of $2 billion as of March 31, 2025.
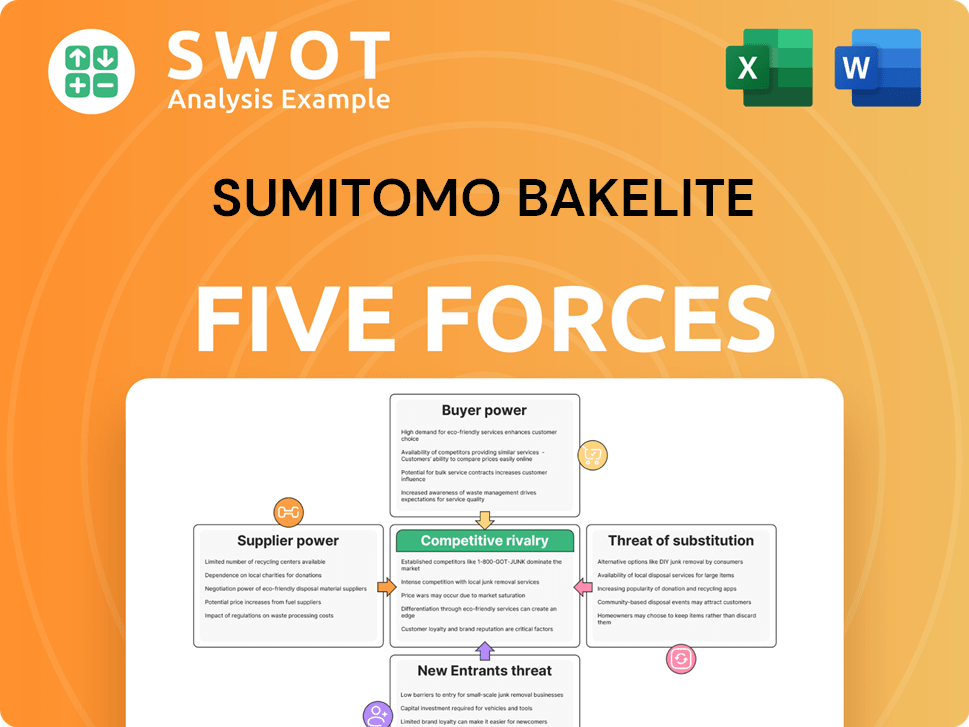
Sumitomo Bakelite Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What is Competitive Landscape of Sumitomo Bakelite Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of Sumitomo Bakelite Company?
- How Does Sumitomo Bakelite Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of Sumitomo Bakelite Company?
- What is Brief History of Sumitomo Bakelite Company?
- Who Owns Sumitomo Bakelite Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of Sumitomo Bakelite Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.