Toyota Motor Bundle
How did a Japanese car manufacturer become a global automotive giant?
Embark on a journey through the Toyota Motor SWOT Analysis, a story of innovation and resilience. From its origins as an automatic loom manufacturer, Toyota's transformation is a masterclass in strategic foresight. Discover how this company, founded on a vision of accessible and reliable vehicles, reshaped the global automotive landscape.
The brief history of Toyota Motor Company reveals a fascinating Toyota timeline, starting with its establishment in 1937. The early years of Toyota Motor Company saw the company evolve from a small Japanese car manufacturer into a global powerhouse. This journey, marked by key milestones in Toyota's history, showcases the legacy of Kiichiro Toyoda, the Toyota founder, and the company's impact on the global car market through innovative Toyota models and manufacturing techniques.
What is the Toyota Motor Founding Story?
The Toyota Motor Company, a giant in the global automotive industry, has a rich history rooted in innovation and strategic vision. The company's origins trace back to a pivotal moment in Japanese industrial development, driven by a desire to establish a domestic automotive manufacturing capability.
Officially established on August 28, 1937, Toyota Motor Corporation emerged as a spin-off from Toyota Industries Corporation. This marked a significant step towards self-sufficiency and economic growth for Japan. Kiichiro Toyoda's vision was instrumental in shaping the company's early direction, influenced by his engineering background and observations of the evolving automotive landscape.
The Competitors Landscape of Toyota Motor highlights the company's journey from its inception to its current position as a global leader.
Kiichiro Toyoda, the son of Sakichi Toyoda, spearheaded the creation of Toyota Motor Company, aiming to establish an independent automotive manufacturer in Japan. The company's initial focus was on mass-producing passenger cars and trucks, contributing to Japan's economic development.
- In 1929, the sale of Sakichi Toyoda's automatic loom patent to a British company provided the initial funding for the automotive venture.
- The A1 passenger car prototype in 1935 and the G1 truck were among the company's first models.
- The name 'Toyota' was chosen for its auspiciousness and aesthetic appeal in Japanese script.
- The pre-World War II era in Japan, with its emphasis on industrialization, provided a conducive environment for Toyota's establishment.
Toyota Motor SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
What Drove the Early Growth of Toyota Motor?
The early growth and expansion of the Toyota Motor Company, a prominent Japanese car manufacturer, showcases a strategic approach to product development and market understanding. The company's initial focus was on the burgeoning Japanese market, with the launch of its first production passenger cars. Expansion involved building a dedicated automotive facility and assembling a skilled workforce, laying the groundwork for future success.
Following its formal establishment, the company launched its first production passenger car, the Model AA, in 1936, and the Model BA in 1940. These early Toyota models were crucial in establishing a foundation for future mass production. The company's initial team expansion focused on engineers and skilled laborers, many of whom transferred from Toyota Industries, bringing with them a culture of meticulous craftsmanship and innovation.
The outbreak of World War II significantly impacted Toyota's trajectory, with the company shifting its focus to truck production for military purposes. Post-war, Toyota faced immense challenges, including material shortages and economic instability, but quickly pivoted back to civilian vehicle production. The first dedicated automotive facility was the Koromo Plant, which began operations in 1938.
The 1950s marked a pivotal period of growth for the company. In 1950, the company faced a severe financial crisis, leading to significant restructuring and the implementation of the 'Toyota Production System' (TPS), a revolutionary manufacturing philosophy focused on eliminating waste and continuous improvement (Kaizen). This system, developed by Taiichi Ohno, became a cornerstone of Toyota's operational excellence. By 2024, the TPS is still a key element of the company's efficiency.
Toyota's entry into international markets began tentatively in the late 1950s, with the Toyopet Crown being the first Japanese car exported to the United States in 1958. The 1960s saw significant expansion, with the launch of iconic models like the Corolla in 1966, which quickly became a global best-seller. Toyota also established its first overseas manufacturing plant in Brazil in 1958, marking its commitment to global production. In 2024, the company has manufacturing plants in over 20 countries.
Toyota Motor PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
What are the key Milestones in Toyota Motor history?
The Toyota Motor Company has a rich Toyota timeline marked by significant achievements and a lasting impact on the automotive industry. From its origins as a small Japanese car manufacturer to its current status as a global leader, Toyota's history is a testament to its adaptability and innovation. Understanding the key milestones provides insight into the company's evolution and its enduring influence on the global car market.
| Year | Milestone |
|---|---|
| 1937 | Kiichiro Toyoda founded the Toyota Motor Company, initially as a division of Toyoda Automatic Loom Works. |
| 1947 | The first post-war Toyota models, the Model SA, was introduced, marking a return to vehicle production after WWII. |
| 1966 | The Toyota Corolla was launched, eventually becoming the world's best-selling car. |
| 1997 | The Prius, a pioneer in hybrid technology, was introduced, showcasing Toyota's commitment to environmental sustainability. |
| 2000s | Toyota expanded its global presence, becoming a major player in North America and other international markets. |
| 2023 | Toyota announced plans to accelerate its EV strategy, aiming to sell 3.5 million BEVs annually by 2030. |
Toyota has consistently been at the forefront of automotive innovation. The development of the Toyota Production System (TPS) revolutionized manufacturing processes, emphasizing efficiency and quality. This system, with its 'Just-in-Time' and 'Jidoka' principles, has become a global benchmark.
The TPS, developed post-World War II, focused on eliminating waste and improving efficiency. It is a cornerstone of Toyota's manufacturing prowess. This system has been adopted by numerous industries worldwide.
Toyota pioneered hybrid technology with the Prius, leading the way in fuel-efficient vehicles. The Prius has secured numerous patents in hybrid technology.
Toyota implemented rigorous quality control measures throughout its manufacturing processes. These systems ensure high standards of reliability and customer satisfaction. These measures are continuously updated and improved.
Toyota strategically expanded its operations globally, establishing manufacturing plants and sales networks worldwide. This expansion increased market share and brand recognition. This has led to a strong presence in North America, Europe, and Asia.
Toyota is investing in a diverse range of powertrain technologies, including hydrogen fuel cells and solid-state batteries. This reflects a long-term vision for sustainable mobility. This includes exploring various alternative fuel options.
Toyota constantly refines its vehicle designs and engineering to meet evolving consumer demands and technological advancements. This includes continuous improvements in safety and performance. This also involves integrating the latest technologies.
Despite its successes, Toyota Motor Company has faced significant challenges. The recalls in the late 2000s, due to safety issues, significantly impacted the company's reputation and led to extensive investigations and fines. The transition to electric vehicles (EVs) presents another challenge, with Toyota needing to accelerate its adoption of battery electric vehicles to remain competitive.
The recalls in the late 2000s damaged Toyota's reputation for quality and reliability. This led to increased scrutiny and the need for improved safety measures. This also resulted in significant financial penalties.
Toyota faces the challenge of transitioning to EVs and competing with other manufacturers in this rapidly growing market. The company is investing heavily in diverse powertrain technologies. This includes hydrogen fuel cells and solid-state batteries.
Toyota, like other automakers, has faced supply chain disruptions, impacting production and sales. These disruptions have highlighted the need for resilient supply chain strategies. This includes diversifying suppliers and improving logistics.
Toyota's performance is influenced by global economic conditions, including inflation, interest rates, and currency fluctuations. Economic downturns can reduce consumer demand. This requires strategic financial planning and market adjustments.
Toyota must comply with increasingly stringent environmental regulations and emission standards worldwide. This includes investing in cleaner technologies. This also involves adapting to changing consumer preferences.
Toyota faces intense competition from both established and emerging automotive manufacturers. This requires continuous innovation and differentiation. This includes adapting to changing consumer preferences.
For a deeper understanding of Toyota's strategic approach, consider exploring the Marketing Strategy of Toyota Motor. Toyota's ability to adapt, innovate, and learn from its challenges has solidified its position as a major player in the global automotive industry.
Toyota Motor Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
What is the Timeline of Key Events for Toyota Motor?
The Revenue Streams & Business Model of Toyota Motor is a story of innovation and global expansion. From its roots in Japan to its current status as a leading global car manufacturer, the company has consistently adapted and evolved. The history of Toyota reflects a commitment to quality, efficiency, and customer satisfaction.
| Year | Key Event |
|---|---|
| 1937 | Kiichiro Toyoda founded Toyota Motor Company, separating from Toyoda Automatic Loom Works. |
| 1936 | The first prototype passenger car, the Model AA, was created. |
| 1957 | Toyota began exporting vehicles to the United States. |
| 1966 | The launch of the Corolla marked a significant milestone, becoming one of the world's best-selling cars. |
| 1980s | Toyota expanded its global presence, establishing manufacturing plants in North America. |
| 1997 | Toyota launched the Prius, revolutionizing the automotive industry with hybrid technology. |
| 2000s | The company focused on sustainable practices and advanced technologies, including electric vehicles and autonomous driving. |
The company plans to significantly increase its electric vehicle offerings. This includes new models and expanding production capacity to meet growing demand. The focus is on providing a diverse range of EVs to cater to different consumer needs and preferences. This expansion aligns with global trends towards sustainable transportation and reduced emissions.
Research and development in battery technology are crucial for future growth. The goal is to improve the range, charging times, and overall performance of EVs. Innovations in solid-state batteries are a key area of focus, with the potential to revolutionize the EV market. These advancements will enhance the competitiveness of Toyota's electric vehicles.
The company is committed to reducing its environmental footprint through sustainable manufacturing practices. This includes using renewable energy sources in its factories and minimizing waste. The aim is to create a more environmentally friendly production process. These efforts contribute to the long-term sustainability of the company and the industry.
Toyota continues to expand its presence in emerging markets. This includes establishing new manufacturing facilities and adapting its products to meet local consumer demands. Strategic partnerships and collaborations are essential for entering new markets. The goal is to increase market share and strengthen its position as a global leader in the automotive industry.
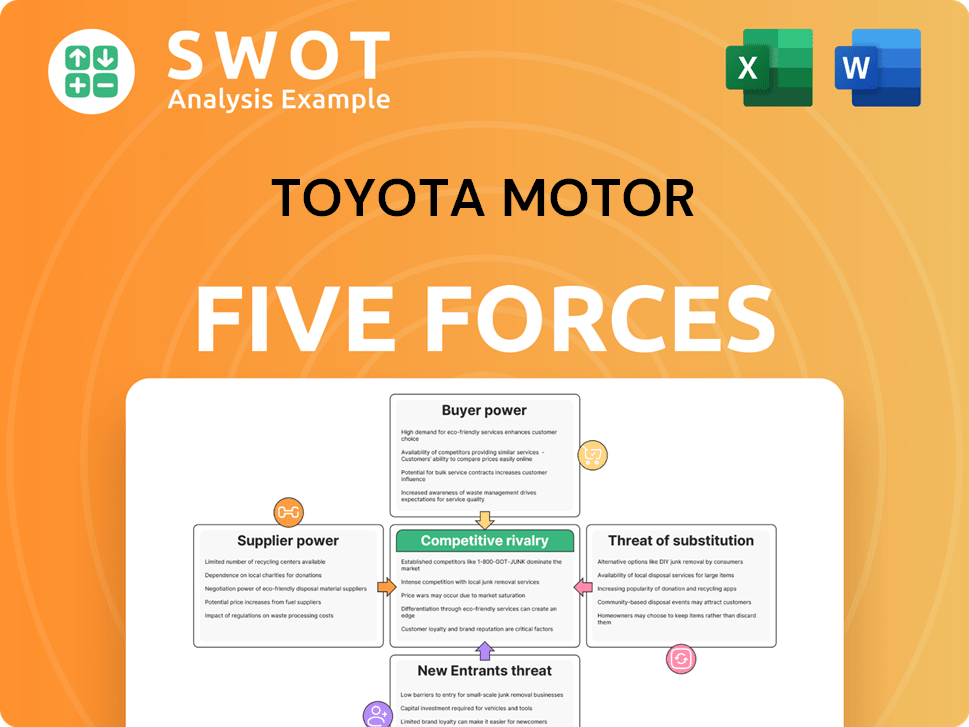
Toyota Motor Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What is Competitive Landscape of Toyota Motor Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of Toyota Motor Company?
- How Does Toyota Motor Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of Toyota Motor Company?
- What is Brief History of Toyota Motor Company?
- Who Owns Toyota Motor Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of Toyota Motor Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.