Zoom Video Communications Bundle
How Did Zoom Video Communications Conquer the World?
The world changed dramatically in the early 2020s, and at the forefront of this transformation was Zoom Video Communications. Founded in 2011 by Eric Yuan, Zoom emerged as a vital tool for remote work and learning. This Zoom Video Communications SWOT Analysis will help you understand its journey.
From its origins in San Jose, California, the Zoom platform quickly gained popularity, offering a user-friendly and reliable video conferencing service. Zoom's initial public offering in 2019 marked a significant milestone in the company's history. This brief history of Zoom explores how a startup became a leading force in the video conferencing market, impacting how we communicate and collaborate globally.
What is the Zoom Video Communications Founding Story?
The story of Zoom Video Communications, or Zoom, begins with its founder, Eric Yuan. Yuan established the company on April 21, 2011. His vision was to create a more streamlined and user-friendly video conferencing experience, a stark contrast to the existing technologies at the time. This ambition led to the creation of the Zoom platform, which would soon revolutionize how people communicate.
Before launching Zoom, Yuan held the position of corporate vice president of engineering at Cisco Webex. His experience there, particularly his dissatisfaction with the complexities of Webex's video conferencing tools, fueled his desire to build something better. Yuan's goal was to make video communication accessible and easy for everyone, a concept that would become central to Zoom's design and functionality.
The early days of Zoom were marked by a focus on mobile-first solutions, recognizing the increasing use of smartphones. The company adopted a freemium business model, providing a basic free service alongside paid subscriptions that offered enhanced features and larger meeting capacities. This strategy allowed Zoom to attract a broad user base. The company secured its initial funding through a Series A round in June 2011, raising $3 million. Investors included Subrah Iyar, the founder of Webex, and Dan Scheinman, a former Cisco executive. This funding enabled Yuan to build a team of engineers, many of whom had previously worked with him at Webex, and begin developing the platform.
Zoom's journey began with Eric Yuan's vision to simplify video conferencing.
- Founded on April 21, 2011.
- Eric Yuan, the founder, previously worked at Cisco Webex.
- Initial funding of $3 million in June 2011.
- Focus on a mobile-first, freemium business model.
- Built with a team of engineers, many from Webex.
The early success of Zoom was built on its ease of use and reliability, which quickly gained traction among users. Zoom's user-friendly interface and robust performance set it apart from competitors. This focus on user experience helped drive the company's early growth. The company's commitment to innovation and accessibility is further detailed in the article about Mission, Vision & Core Values of Zoom Video Communications, which highlights the company's core principles.
Zoom's initial public offering (IPO) occurred on April 18, 2019. The IPO price was set at $36 per share. The company's valuation at the time was approximately $9.2 billion. Zoom's stock began trading on the NASDAQ under the ticker symbol ZM. The IPO provided Zoom with significant capital to expand its operations and further develop its platform. The IPO's success was a testament to the company's growth and potential in the video conferencing market. By the end of 2019, Zoom had approximately 37,000 customers with more than ten employees.
As of 2024, Zoom continues to be a leading player in the video conferencing market. The company has expanded its services to include features such as Zoom Rooms, Zoom Phone, and Zoom Webinars. Zoom's revenue for the fiscal year 2024 was approximately $4.4 billion. Zoom's market capitalization as of May 2024 is approximately $16.5 billion. The company's global presence and continuous innovation ensure its relevance in the evolving landscape of digital communication.
Zoom Video Communications SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
What Drove the Early Growth of Zoom Video Communications?
The early growth of the Zoom company was marked by a strong focus on product development and attracting users through word-of-mouth and a freemium model. The Zoom platform officially launched in January 2013, quickly gaining popularity due to its user-friendliness and reliability compared to competitors. This period saw significant milestones and funding rounds that fueled its rapid expansion, setting the stage for its future success.
By June 2014, the Zoom platform had reached 10 million participants, and by the end of 2014, it surpassed 30 million participants. This rapid growth demonstrated the platform's appeal and effectiveness in the video conferencing market. The ease of use and reliability of the Zoom platform were key factors in attracting a large user base quickly.
In 2015, the introduction of Zoom Rooms expanded its offerings to conference room systems. The launch of Zoom Phone in 2019 further diversified its communication solutions. These new products expanded the company's reach and provided more comprehensive communication tools for businesses and individuals.
The company secured a Series B round of $6.5 million in 2013 and a Series C round of $30 million in 2015. These investments were crucial for scaling infrastructure, expanding the engineering team, and increasing marketing efforts. These investments helped the company grow rapidly and compete in the video conferencing market.
By the time of its initial public offering (IPO) in April 2019, the company was valued at nearly $9 billion. This valuation highlighted its strong market reception and growth trajectory. The IPO marked a significant milestone, reflecting the company's success and potential for future growth. To learn more about the company's strategies, read about the Growth Strategy of Zoom Video Communications.
Zoom Video Communications PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
What are the key Milestones in Zoom Video Communications history?
The Zoom company has a history marked by significant achievements and pivotal moments that have shaped its trajectory in the video conferencing industry. Its journey began with its founding by Eric Yuan, and it quickly evolved into a leading platform for virtual communication.
| Year | Milestone |
|---|---|
| 2011 | Eric Yuan founded the company. |
| 2015 | Launched Zoom Rooms, expanding its offerings to conference spaces. |
| April 2019 | The company's initial public offering (IPO) raised $751 million, valuing the company at nearly $9 billion. |
| 2019 | Introduced Zoom Phone, a cloud-based voice communication service. |
| April 2020 | Reached over 300 million daily meeting participants during the peak of the pandemic. |
The Zoom platform has consistently introduced innovative features to enhance user experience and expand its services. These innovations have been crucial in maintaining its competitive edge in the rapidly evolving video conferencing market.
Zoom Rooms transformed conference rooms into integrated video conferencing hubs, improving collaboration. This feature facilitated seamless meetings in physical spaces, enhancing productivity.
Zoom Phone provided cloud-based voice communication, integrating phone services directly into the platform. This offered a unified communication solution, streamlining business operations.
The company implemented end-to-end encryption and waiting rooms to address security concerns. These enhancements were crucial in building user trust and protecting sensitive information.
Virtual backgrounds and filters improved user engagement and customization during meetings. These features added a layer of personalization, making meetings more enjoyable.
The Zoom company integrated with various third-party apps to enhance functionality. This integration streamlined workflows and improved overall user experience.
The platform expanded its capabilities to support webinars and large meetings. This allowed the platform to cater to a broader range of communication needs.
Despite its success, Zoom Video Communications has faced several challenges, particularly concerning security and competition. Addressing these issues has been vital for the company's sustained growth and market position.
Early on, the platform faced significant scrutiny regarding security vulnerabilities and privacy breaches. The company had to quickly implement measures to enhance security protocols.
The rise of 'Zoom-bombing' incidents highlighted the need for improved access controls and security features. The company responded by adding waiting rooms and enhanced encryption.
The company faced intense competition from established tech giants like Microsoft Teams and Google Meet. This required continuous innovation and strategic partnerships.
Rapid user growth during the pandemic strained the platform's infrastructure and support systems. The company had to scale its operations to meet increased demand.
Addressing security concerns and privacy issues was crucial for maintaining user trust. The company invested in transparency and user-friendly security settings.
Keeping up with evolving market demands and user expectations required constant adaptation. This included adding new features and improving existing services.
To understand more about the company's financial aspects, you can explore the Revenue Streams & Business Model of Zoom Video Communications.
Zoom Video Communications Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
What is the Timeline of Key Events for Zoom Video Communications?
The Zoom Video Communications journey began in 2011 when Eric Yuan founded the company, and it quickly became a leader in the video conferencing industry. The Zoom platform launched in 2013, and by 2014, it had already reached 10 million participants. Significant milestones include achieving unicorn status in 2017 and going public on NASDAQ in 2019. The COVID-19 pandemic spurred unprecedented growth, with over 300 million daily meeting participants by April 2020. Recent developments include AI integration and the acquisition of Workvivo in April 2024, showcasing Zoom's commitment to innovation and platform expansion. For more insights, explore the Marketing Strategy of Zoom Video Communications.
| Year | Key Event |
|---|---|
| 2011 | Eric Yuan founded the company. |
| 2013 | The Zoom platform launched. |
| 2014 | Reached 10 million participants. |
| 2015 | Introduced Zoom Rooms. |
| 2017 | Achieved unicorn status. |
| 2019 | Zoom Phone launched and went public on NASDAQ (ZM). |
| 2020 | Experienced massive growth during the pandemic, reaching over 300 million daily meeting participants by April. |
| 2021 | Attempted to acquire cloud contact center software provider Five9 for $14.7 billion, but the deal was terminated. |
| 2022 | Introduced new features like Zoom Whiteboard and Zoom IQ for Sales. |
| 2023 | Focused on AI integration and platform extensibility. |
| March 22, 2024 | Announced new AI Companion capabilities for education. |
| March 28, 2024 | Announced new Zoom Workplace and AI Companion innovations. |
| April 12, 2024 | Acquired Workvivo, an employee experience platform. |
Zoom is heavily investing in artificial intelligence to enhance its platform. The introduction of AI Companion capabilities in March 2024 aims to improve productivity and collaboration. This includes features designed to assist with meeting summaries, smart recordings, and intelligent scheduling, reflecting a strategic move to integrate AI across its offerings.
The company is expanding beyond traditional video conferencing with the introduction of Zoom Workplace. This AI-powered collaboration platform is designed to optimize hybrid work environments. The acquisition of Workvivo in April 2024 further demonstrates its commitment to providing broader communication solutions and enhancing employee experience.
Analyst predictions suggest continued growth in the unified communications as a service (UCaaS) market. Zoom is a key player in this market. Leadership emphasizes a focus on innovation, platform expansion, and delivering a seamless, intelligent collaboration experience, positioning the company for sustained success.
Zoom's strategic initiatives include a strong emphasis on innovation and platform expansion. The company aims to solidify its position as an indispensable tool for the evolving landscape of work. This forward-looking approach aligns with its founding vision of frictionless communication and positions it for continued relevance.
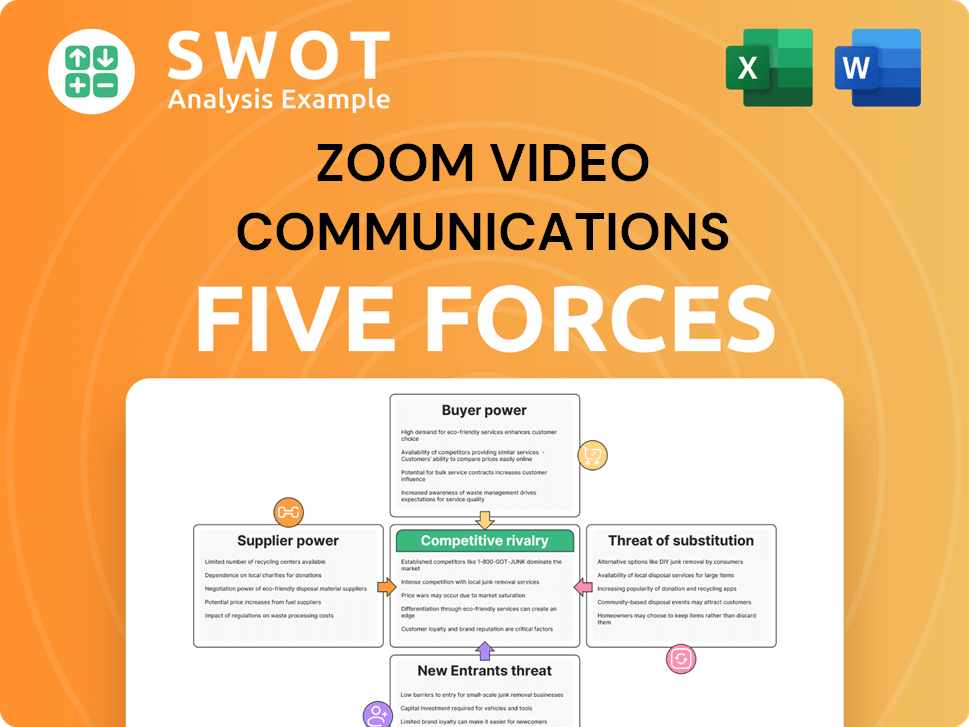
Zoom Video Communications Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What is Competitive Landscape of Zoom Video Communications Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of Zoom Video Communications Company?
- How Does Zoom Video Communications Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of Zoom Video Communications Company?
- What is Brief History of Zoom Video Communications Company?
- Who Owns Zoom Video Communications Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of Zoom Video Communications Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.