First Republic Bank Bundle
What Secrets Fueled First Republic Bank's Rise and Fall?
First Republic Bank (FRB) was once a beacon in the financial services industry, known for its personalized approach to private banking and wealth management. Focusing on high-net-worth clients, the bank cultivated a reputation for exceptional service, achieving an impressive Net Promoter Score of 80 in 2022. But how did First Republic Bank make money, and what ultimately led to its dramatic downfall?

Understanding the operational intricacies of First Republic is vital for anyone interested in the banking sector, especially given its prominent role in the 2023 banking crisis. Its rapid expansion, with assets soaring to $212.6 billion, highlights the bank's influence and the potential risks associated with its model. To gain a deeper understanding, consider exploring a First Republic Bank SWOT Analysis to uncover the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats that shaped its trajectory.
What Are the Key Operations Driving First Republic Bank’s Success?
First Republic Bank (FRB) centered its core operations on a relationship-based, client-focused approach. The bank offered personalized private banking, private business banking, and wealth management services. This strategy was designed to cater to high-net-worth individuals, families, and businesses, including those in the venture capital and technology sectors.
Key offerings included residential real estate lending, particularly nonconforming jumbo mortgages, to attract affluent clients. Beyond lending, FRB expanded relationships by providing a comprehensive suite of services such as private banking, business banking, wealth management, trust, and brokerage services. The bank's focus on personalized service and technological integration set it apart in the financial services industry.
FRB's value proposition lay in its ability to provide tailored financial solutions and build strong client loyalty. This was achieved through a combination of specialized expertise in serving affluent clients, a commitment to exceptional service, and technological integration. This approach allowed FRB to maintain a loyal customer base, with a significant portion of new deposits and loan originations coming from existing clients.
FRB prioritized a 'high-touch' service model, fostering strong client satisfaction. This personalized approach encouraged repeat business and referrals. The bank's ability to gather low-cost core deposits, often through expanding relationships with existing clients, was a crucial aspect of its funding strategy.
FRB offered a comprehensive suite of services, including private banking, business banking, wealth management, trust, and brokerage services. Residential real estate lending, especially jumbo mortgages, was a key offering. This diverse range of services helped attract and retain a high-net-worth clientele.
FRB utilized digital banking platforms for convenient account access and transactions. The bank invested in innovative technologies like AI, machine learning, and blockchain to enhance products, automate processes, and ensure robust security protocols. This technological integration supported its client-focused model.
A crucial aspect was the ability to gather low-cost core deposits. FRB often expanded relationships with existing clients to achieve this. This strategy helped maintain financial stability and support its lending activities. The bank's funding strategy was key to its success.
FRB's operational uniqueness combined specialized expertise with exceptional service and technological integration. This approach translated into tailored financial solutions and strong client loyalty. In 2022, more than half of new deposits and 64% of new loan originations came from existing clients.
- Relationship-based banking model.
- Focus on high-net-worth clients.
- Comprehensive service offerings.
- Emphasis on technological innovation.
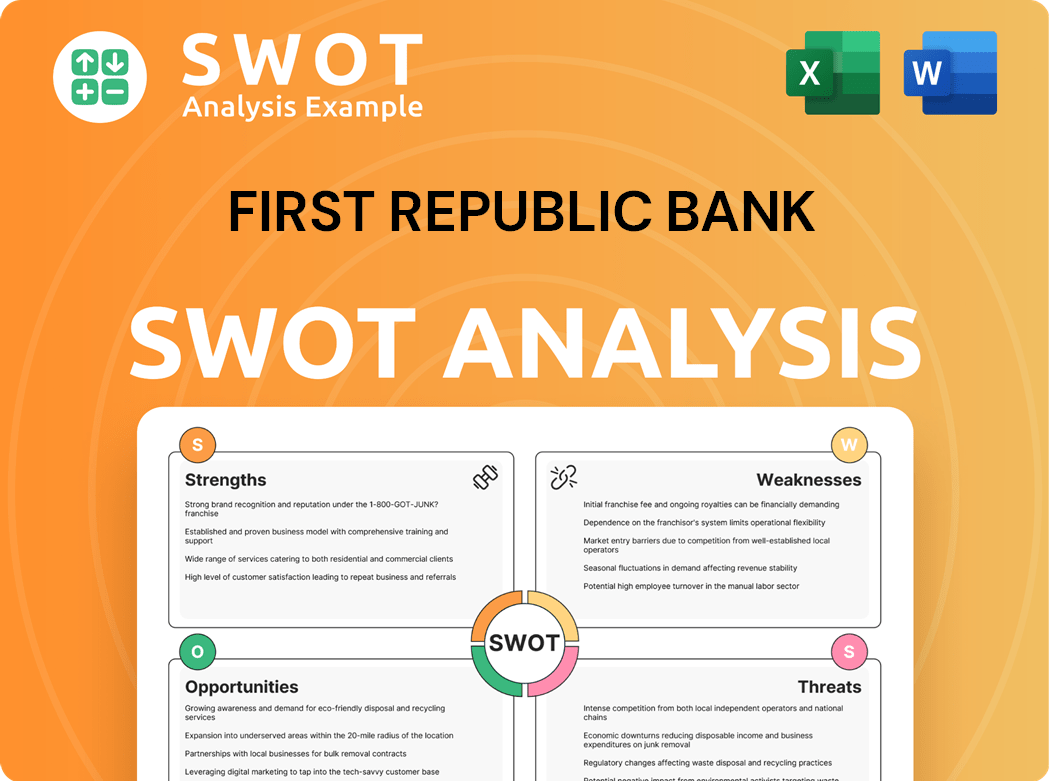
First Republic Bank SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
How Does First Republic Bank Make Money?
The primary revenue streams for First Republic Bank (FRB) were net interest income and non-interest income, with a strong emphasis on lending activities and wealth management. The bank focused on attracting high-net-worth clients and cross-selling them a range of financial products and services. This strategy aimed to broaden client relationships and generate additional revenue through diverse offerings.
For the full year 2022, First Republic reported total revenues of $5.9 billion, reflecting a 16.5% increase compared to the previous year. Net interest income was the major revenue source, reaching $4.8 billion in 2022, up 17.5% year-over-year, primarily driven by substantial loan growth.
Non-interest income, mainly from wealth management fees, also significantly contributed to the bank's revenue. In 2022, wealth management revenues totaled $877 million, accounting for approximately 15.0% of the bank's total revenues.
Net interest income, the difference between interest earned on loans and interest paid on deposits, was a key revenue driver for First Republic. In 2022, this income reached $4.8 billion, showing a 17.5% increase year-over-year.
First Republic's loan portfolio was heavily concentrated in residential mortgages, including jumbo mortgages. By the end of 2022, total loans reached $166.9 billion, an increase of 23.6%.
Wealth management services generated significant non-interest income for the bank. Wealth management revenues totaled $877 million in 2022, representing a 15.4% increase. Wealth management assets stood at $271.2 billion at the end of 2022.
The bank's strategy involved attracting high-net-worth clients with competitive loan terms and cross-selling additional services. This approach aimed to expand client relationships and increase revenue through a diverse range of offerings.
Other non-interest income sources included investment management, brokerage, insurance, trust, and foreign exchange fee income. These additional services contributed to the bank's overall revenue diversification.
First Republic Bank experienced revenue growth, with total revenues reaching $5.9 billion in 2022. This growth was supported by increased net interest income and wealth management fees.
The bank's business model centered on providing personalized services to affluent clients, which included competitive loan products and comprehensive wealth management solutions. The Growth Strategy of First Republic Bank involved expanding its client base and offering a wide array of financial services to increase revenue streams. This approach helped FRB to build strong client relationships and generate sustainable income.
First Republic Bank's revenue model was primarily based on two key components: net interest income and non-interest income, with a strong emphasis on wealth management.
- Net Interest Income: This was the largest revenue source, derived from the difference between interest earned on loans and interest paid on deposits.
- Wealth Management Fees: Significant non-interest income was generated from wealth management services, including investment management, brokerage, and other related fees.
- Loan Portfolio: The bank's loan portfolio, particularly residential mortgages, played a crucial role in generating interest income.
- Cross-Selling Strategy: FRB focused on attracting high-net-worth clients and offering them a range of financial products and services.
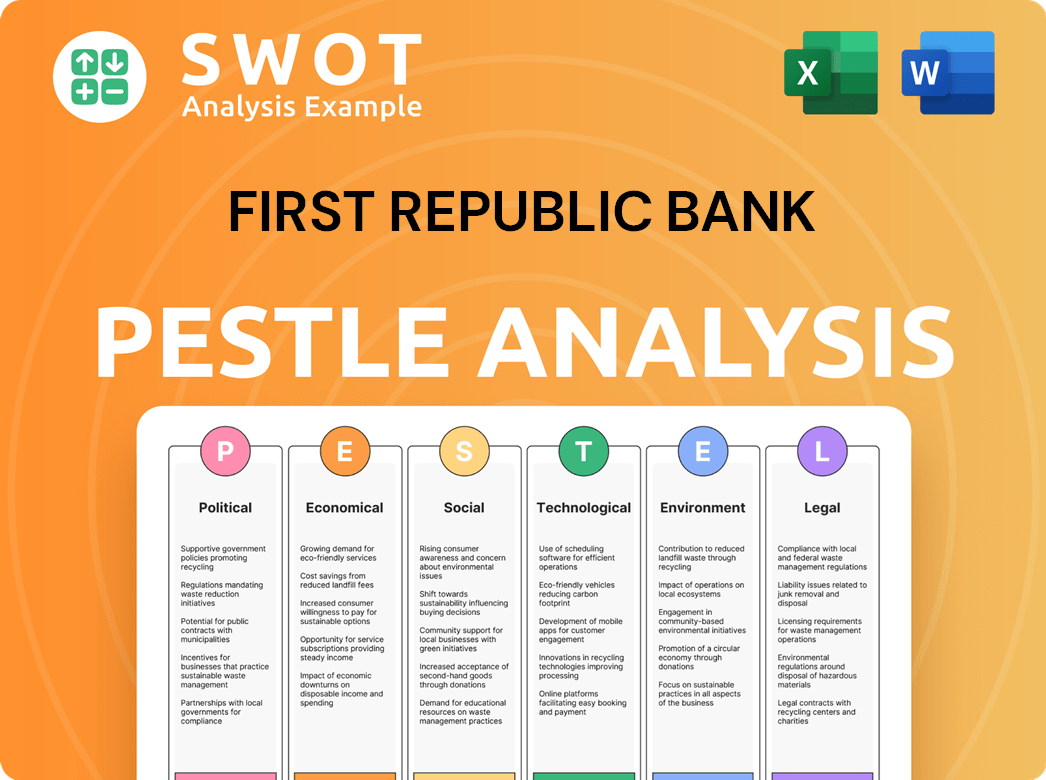
First Republic Bank PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
Which Strategic Decisions Have Shaped First Republic Bank’s Business Model?
Founded in 1985, First Republic Bank (FRB) quickly established itself in the financial sector. A key milestone was its initial public offering (IPO) on the Nasdaq in August 1986. The bank later went independent again in December 2010, after being acquired by Merrill Lynch in 2007, marking a significant shift in its operational structure.
Throughout its history, First Republic's strategic focus remained on serving high-net-worth individuals and businesses. This 'client-centric' model, emphasizing personalized service, was a core tenet of its operations. The bank's dedication to this approach led to high client satisfaction and referrals, as evidenced by a Net Promoter Score of 80 in 2022.
The bank's competitive edge was built on a strong brand reputation, specialized expertise in serving affluent clients, and technological innovation. First Republic integrated digital banking solutions and explored technologies like AI to enhance the client experience. Operationally, the bank focused on growing core deposits to provide a stable funding source. For more information about the target market of FRB, you can read this article about Target Market of First Republic Bank.
FRB's IPO occurred in August 1986, and the bank was re-established as an independent public entity in December 2010. These milestones reflect the bank's evolution and strategic shifts over time. These changes were critical to its growth and market positioning.
The bank's strategy centered on serving high-net-worth clients with personalized service. This approach, combined with technological advancements, aimed to enhance client experience and operational efficiency. The bank also focused on growing core deposits to maintain a stable funding base.
FRB's competitive advantage came from its strong brand reputation and exceptional customer service. Its specialized expertise in wealth management and innovative use of technology further enhanced its position. These factors helped to differentiate FRB in the competitive financial services market.
FRB faced challenges, including rapid growth and concentration in uninsured deposits. Rising interest rates in 2022 and the impact of the failures of Silicon Valley Bank and Signature Bank in March 2023 led to a deposit run. JPMorgan Chase acquired FRB in May 2023.
At the end of 2022, uninsured deposits accounted for 67% of FRB's total deposits. The acquisition by JPMorgan Chase in May 2023 involved approximately $173 billion of loans, $30 billion of securities, and the assumption of $92 billion of deposits.
- Rapid deposit outflows during periods of market stress.
- Asset-liability mismatch with long-duration, low-yielding fixed-rate loans.
- Contagion effect from the failures of Silicon Valley Bank and Signature Bank.
- JPMorgan Chase acquired FRB in May 2023.
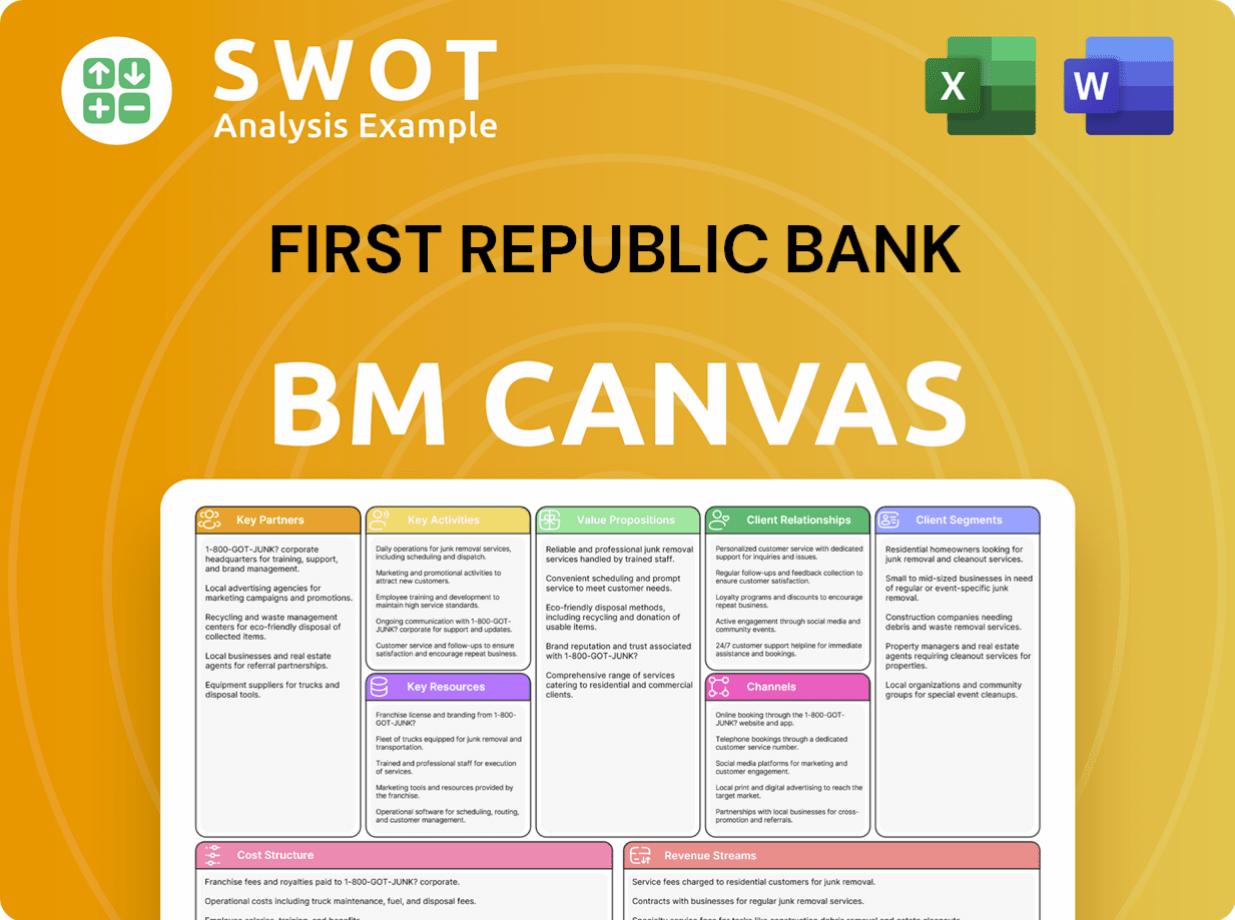
First Republic Bank Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
How Is First Republic Bank Positioning Itself for Continued Success?
Prior to its collapse, First Republic Bank (FRB) held a notable position in the U.S. banking sector, especially in private banking and wealth management for high-net-worth individuals. In 2022, it was the 14th largest lender in the U.S. Its market share among high-net-worth households (with $10 million or more in investable assets) was approximately 20%. The bank's focus on personalized service helped build strong customer loyalty.
However, FRB faced significant risks that led to its failure. A key risk was its reliance on uninsured deposits, which made the bank vulnerable to rapid outflows. Rising interest rates in 2022 also significantly impacted the fair value of its loan portfolio, resulting in substantial unrealized losses. Regulatory changes and the contagion effect from other bank failures also posed challenges. To learn more about the bank's beginnings, read the Brief History of First Republic Bank.
FRB focused on private banking and wealth management. It was the 14th largest lender in the U.S. in 2022. The bank had a market share of about 20% in its target demographic.
Overreliance on uninsured deposits was a major risk. Rising interest rates led to significant unrealized losses. Regulatory changes and the impact of other bank failures added to the challenges.
JPMorgan Chase acquired FRB's assets and assumed deposits. JPMorgan Chase has integrated FRB's businesses. The focus is now on retaining clients and expanding wealth management.
Uninsured deposits were about 68% of total deposits in 2022. Unrealized losses on the loan portfolio were $22.2 billion by the end of 2022. JPMorgan Chase acquired approximately $173 billion of loans.
JPMorgan Chase's acquisition of FRB included a substantial portion of its assets and deposits. The integration of FRB's businesses is expected to be modestly accretive to earnings. The acquisition aims to sustain and expand client relationships within JPMorgan Chase.
- JPMorgan Chase acquired approximately $173 billion of loans.
- Around 75% of advisors and clients were retained.
- The acquisition is expected to generate over $500 million of incremental net income per year.
- The future outlook is under the strategic direction of JPMorgan Chase.
First Republic Bank Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked

Related Blogs
- What are Mission Vision & Core Values of First Republic Bank Company?
- What is Competitive Landscape of First Republic Bank Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of First Republic Bank Company?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of First Republic Bank Company?
- What is Brief History of First Republic Bank Company?
- Who Owns First Republic Bank Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of First Republic Bank Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.