AECOM Bundle
Who Really Owns AECOM?
Unraveling the AECOM SWOT Analysis reveals more than just market strategies; it highlights the critical importance of understanding who controls this global infrastructure giant. From its humble beginnings to its current status as a publicly traded entity, AECOM's ownership has undergone a fascinating evolution. Understanding the AECOM ownership structure is key to grasping its strategic direction and future prospects.

This deep dive into AECOM company ownership will examine the shift from employee ownership to a publicly traded model, exploring the influence of major AECOM shareholders and the roles of AECOM executives. We will trace the AECOM history to understand how its ownership structure impacts its operations, financial performance, and overall market position, providing a comprehensive view of who owns AECOM and its implications.
Who Founded AECOM?
The initial ownership structure of the AECOM company differed from that of typical startups. It emerged not from individual founders, but from a spin-off and consolidation of engineering and design firms that were subsidiaries of Ashland Oil, Inc. (now Ashland Inc.). Key firms included Daniel, Mann, Johnson & Mendenhall (DMJM), Frederic R. Harris, and Holmes & Narver. Richard G. Newman played a significant role in the formation of AECOM, transitioning it from a division of Ashland Oil to an independent company.
Initially, AECOM was primarily employee-owned. This employee ownership model was crucial for its early growth. By 2007, before its IPO, approximately 75% of the company's stock was employee-owned, supported by an 18% company stock match for employees. Private equity investors held a smaller portion. This structure meant that control was broadly distributed among the workforce, highlighting the influence of employee-shareholders.
In 1990, the company changed its name to AECOM Technology Corporation. By 1998, AECOM became 100% employee-owned. The company's attempt at an IPO in 2003 was postponed due to market conditions and employee reluctance, which underscored the significance of employee ownership at the time. For more insights, you can explore the Marketing Strategy of AECOM.
The early ownership structure of AECOM was unique, with a focus on employee ownership rather than individual founders.
- Formed through the consolidation of several engineering and design firms.
- Richard G. Newman played a pivotal role in the company's formation.
- Employee ownership was the primary source of capital for early growth.
- The company was approximately 75% employee-owned before its IPO in 2007.
- By 1998, AECOM had achieved 100% employee ownership.
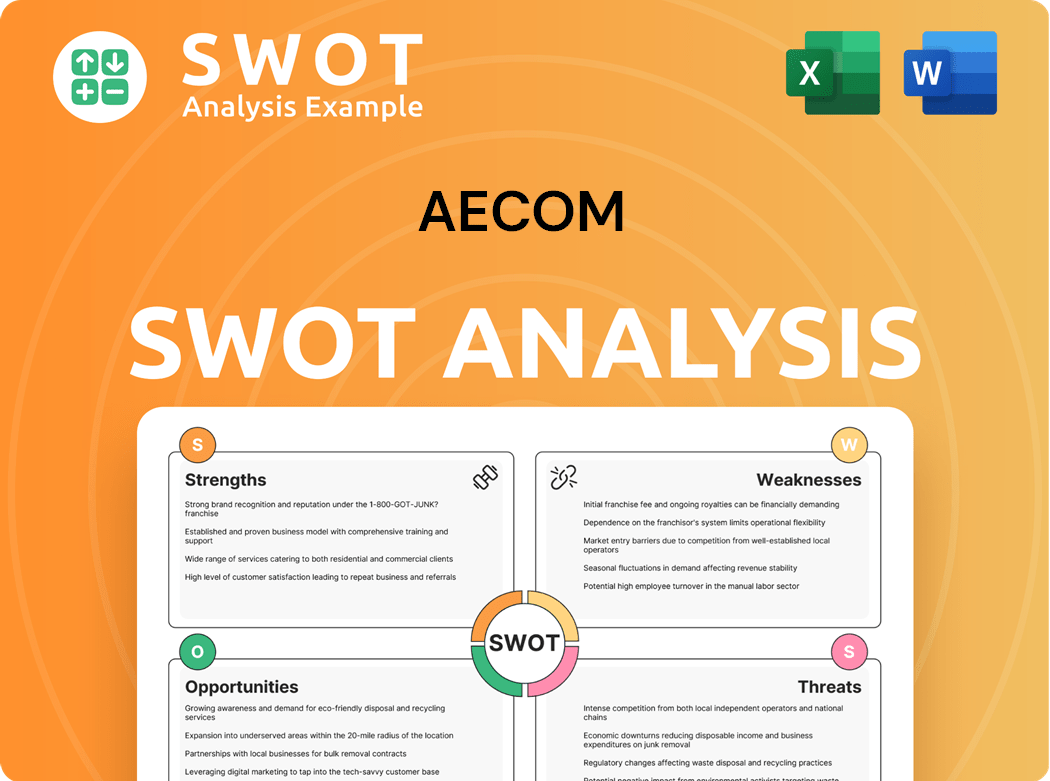
AECOM SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
How Has AECOM’s Ownership Changed Over Time?
The evolution of AECOM's ownership has been marked by significant transitions, most notably with its Initial Public Offering (IPO) in May 2007. This event shifted the company from being largely employee-owned to a publicly traded entity. The IPO, which priced shares at $20.00 each, provided the company with $468.3 million and opened the door for institutional investors to acquire substantial stakes. Before the IPO, around 75% of the company was employee-owned, with private equity holding a smaller portion. Following the IPO, employees still held over half the stock, but mutual funds, pension funds, and other institutional investors gained significant ownership.
Another crucial event was the acquisition of URS Corporation in October 2014. This $4 billion deal, involving both cash and stock, changed the ownership distribution, with AECOM shareholders owning approximately 65% and URS shareholders owning about 35% of the combined company. This merger significantly expanded AECOM's market presence, adding expertise in sectors like oil & gas, power, and government services, thus reshaping the company's strategic direction and governance.
| Ownership Milestone | Details | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Pre-IPO | Primarily employee-owned, with private equity involvement. | Limited access to capital markets. |
| IPO (May 2007) | Transition to a publicly traded company on the NYSE. | Increased access to capital, facilitated acquisitions. |
| URS Acquisition (October 2014) | AECOM shareholders held ~65%, URS shareholders held ~35% of the combined entity. | Diversified market presence, expanded service offerings. |
As of late 2024 and early 2025, AECOM operates as a publicly traded corporation, listed on the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) under the ticker symbol ACM. The majority of AECOM's shares are held by institutional investors. Approximately 87.17% to 92.0% of the company's shares are held by institutions as of May 2025. Key institutional shareholders include BlackRock, Inc. (11.35% as of March 2025), Vanguard Group Inc. (9.64% as of March 2025), PRIMECAP Management Company (7.648%), and State Street Corp (3.904%). The top 11 shareholders collectively own 51% of the company. This high level of institutional ownership indicates a significant influence on the company's share price and board decisions.
AECOM's ownership structure has evolved significantly, transitioning from employee-owned to a publicly traded model. Key milestones include the 2007 IPO and the 2014 URS acquisition.
- Publicly traded on NYSE under ACM.
- Institutional investors hold a significant majority of shares.
- Major shareholders include BlackRock and Vanguard.
- Ownership changes impact strategy and governance.
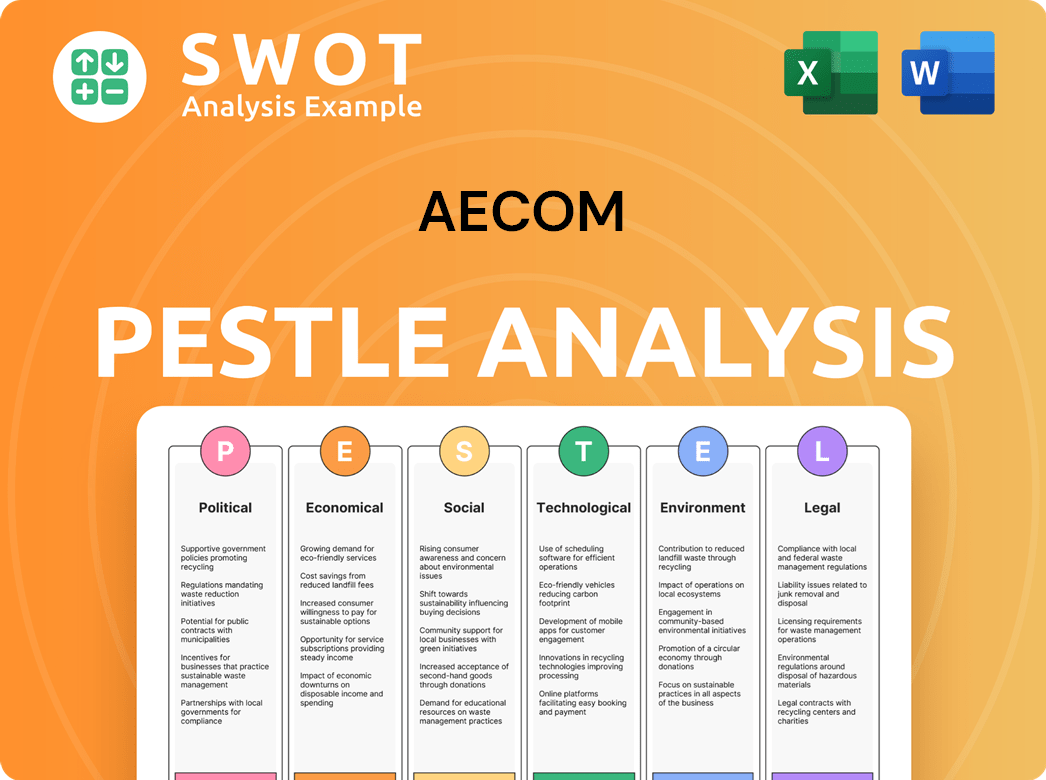
AECOM PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
Who Sits on AECOM’s Board?
As of early 2025, the Board of Directors of the AECOM company plays a critical role in guiding the company's strategic direction and overseeing its governance. The Board currently consists of 12 directors, with all, except Carl B. Webb, up for election at the 2025 Annual Meeting. Sarah A. Slusser is also a new director nominee for the 2025 election.
While specific details on the representation of major shareholders or founders by each board member are not explicitly provided in the available information for 2024-2025, the Board's composition includes a mix of individuals, some of whom may represent significant shareholder interests, alongside independent directors. For instance, in 2020, a Starboard Value board member resigned, highlighting the influence of activist investors on board decisions. Understanding the Target Market of AECOM can also shed light on the strategic direction influenced by the board.
| Board Member | Role | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Carl B. Webb | Director | Remains on the board |
| Sarah A. Slusser | Director Nominee | Nominated for the 2025 election |
| Other Directors | Directors | Up for election at the 2025 Annual Meeting |
AECOM's voting structure generally follows a one-share-one-vote principle for its common stock. The company does not appear to have dual-class shares or special voting rights that would grant outsized control to specific entities. Stockholders of record as of March 24, 2025, were eligible to vote at the annual meeting. The Board's recommendations on proposals, such as director elections and executive compensation, are typically followed, unless shareholders vote differently. The Board also recommends voting 'FOR' the ratification of Ernst & Young LLP as the independent registered public accounting firm for fiscal year 2024. Executive compensation is subject to an annual advisory vote by stockholders. A policy prohibits directors, executive officers, and employees from buying shares on margin and pledging company securities, with limited exceptions.
The Board of Directors guides AECOM's strategic direction. The voting structure is based on one-share-one-vote. Stockholders of record as of March 24, 2025, were eligible to vote.
- The Board consists of 12 directors as of early 2025.
- All directors, except Carl B. Webb, were up for election at the 2025 Annual Meeting.
- Sarah A. Slusser is a new director nominee for the 2025 election.
- Executive compensation is subject to an annual advisory vote by stockholders.
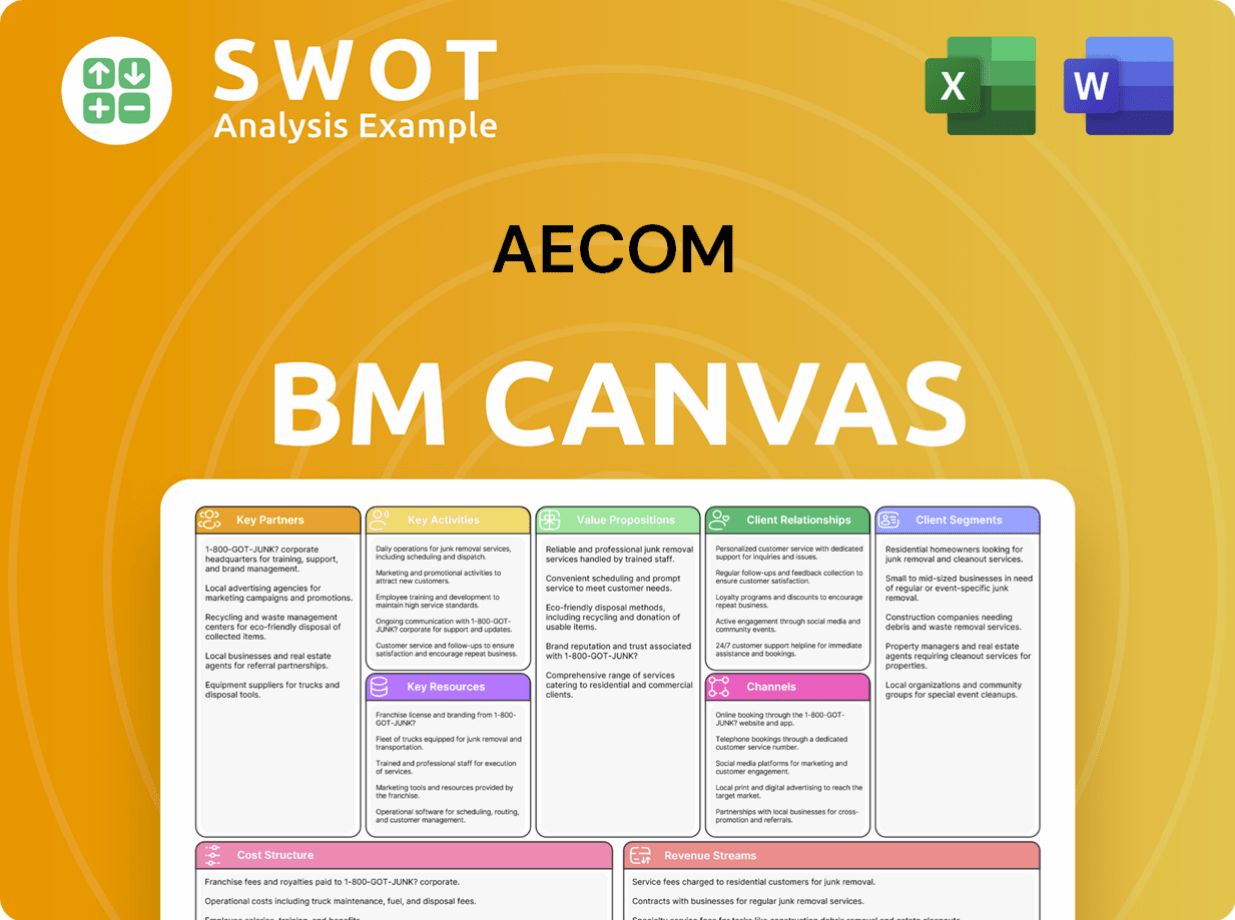
AECOM Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
What Recent Changes Have Shaped AECOM’s Ownership Landscape?
Over the past few years, the AECOM company has actively managed its ownership profile, primarily through strategies aimed at returning value to shareholders. Since September 2020, AECOM has repurchased over $2.3 billion worth of stock, which has led to a 21% reduction in outstanding shares. As of March 2025, the company's 6-Month Share Buyback Ratio stood at 0.40%. Furthermore, in November 2024, the Board of Directors approved an increase in the share repurchase authorization to $1 billion and an 18% increase to the quarterly dividend, reaching $0.26 per share. This followed a 22% increase in the quarterly dividend to $0.22 per share in November 2023. These actions demonstrate a strong commitment to enhancing shareholder value through consistent returns.
Industry trends indicate increased institutional ownership for companies like AECOM. As of May 2025, institutional investors hold a substantial portion of AECOM's shares, ranging from 87.17% to 90.92%. This concentration among institutional holders, including BlackRock, Inc., Vanguard Group Inc., and PRIMECAP Management Company, highlights their significant influence on the company's share price and strategic decisions. While institutional ownership is high, individual insiders' holdings remain relatively low, approximately 0.49% to 0.56% as of May 2025. The general public holds about a 9.16% stake, reflecting the distribution of AECOM ownership.
Leadership transitions and strategic divestitures have also shaped AECOM's trajectory. W. Troy Rudd was appointed CEO in October 2020, succeeding Michael S. Burke, with Lara Poloni becoming the new president. The sale of the Management Services business (now Amentum) in January 2020, followed by the Power and Civil construction businesses in late 2020 and early 2021, reflects a strategic shift toward a higher-margin, lower-risk professional services business. These changes have streamlined the company's focus and influenced its financial profile, impacting investor interest and ownership patterns.
AECOM's ownership is primarily characterized by significant institutional holdings, indicating a strong influence from large investment firms. Individual insider ownership remains relatively low, with a small percentage held by company executives and insiders. The general public holds a notable stake, reflecting the company's publicly traded status and the distribution of shares among various investors.
AECOM has actively pursued strategies to enhance shareholder value, including significant stock repurchases and consistent dividend increases. These actions demonstrate a commitment to returning capital to shareholders and increasing the overall value of their investments. The company's financial performance and strategic decisions directly impact shareholder returns.
Institutional investors, such as BlackRock and Vanguard, hold a substantial portion of AECOM's shares, giving them considerable influence over the company's strategic direction. Their investment decisions and voting power can significantly impact the company's share price and overall market performance. This ownership structure highlights the importance of institutional investor relations.
AECOM's strategic divestitures and leadership changes have played a crucial role in reshaping its business model and influencing investor confidence. These moves have streamlined the company's focus and impacted its financial profile, which can affect investor interest. These changes reflect the company's adaptability and strategic vision.
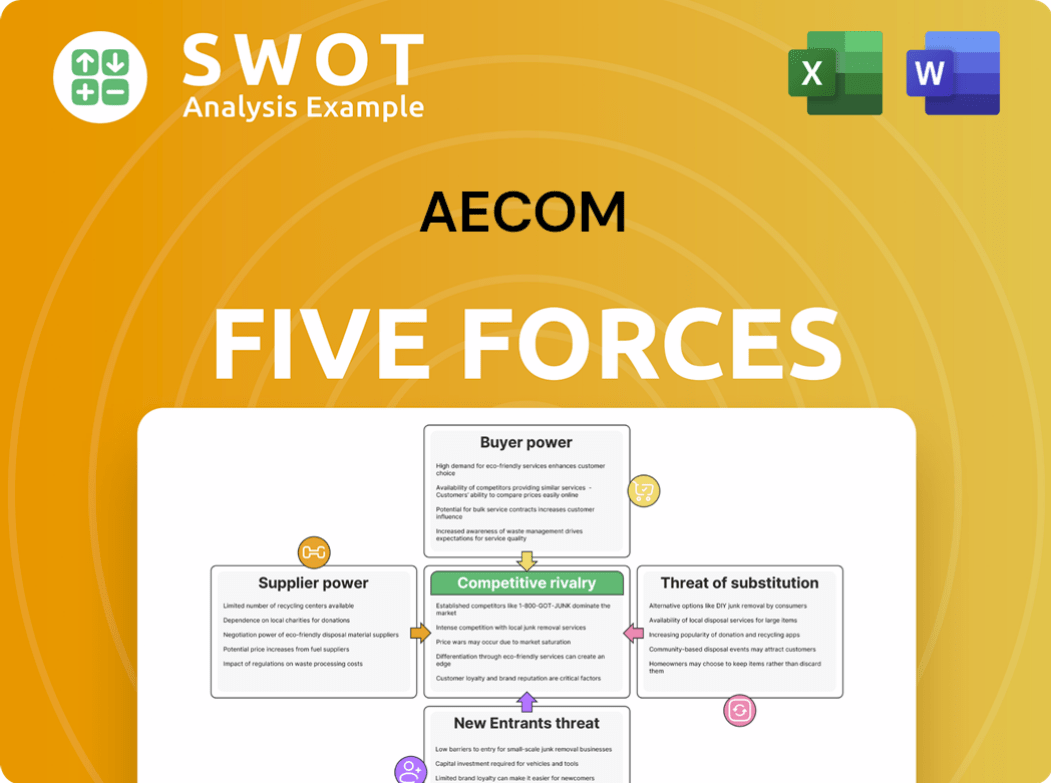
AECOM Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What are Mission Vision & Core Values of AECOM Company?
- What is Competitive Landscape of AECOM Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of AECOM Company?
- How Does AECOM Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of AECOM Company?
- What is Brief History of AECOM Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of AECOM Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.