Amsted Industries Bundle
Who Really Owns Amsted Industries?
Understanding a company's ownership structure is crucial for grasping its strategic direction and market position. Amsted Industries, a major player in industrial manufacturing, presents a fascinating case study in corporate ownership evolution. From its origins as a publicly traded entity to its current unique structure, the story of Amsted's ownership offers valuable insights.
Amsted Industries' journey from a publicly traded company to a 100% employee-owned entity through an Employee Stock Ownership Plan (ESOP) is a compelling narrative. This transformation, completed by 1998, significantly altered the company's trajectory. This article will delve into the Amsted Industries SWOT Analysis, exploring the implications of its ownership on its operations, financial performance, and future prospects, providing a comprehensive Amsted Industries company profile.
Who Founded Amsted Industries?
The story of Amsted Industries began on June 26, 1902, under the name American Steel Foundries (ASF). This marked the consolidation of several steel companies, setting the stage for a major player in the industrial sector. The formation of ASF was a strategic move, bringing together key figures and resources to enhance competitiveness.
Key individuals played pivotal roles in the early days of American Steel Foundries. Judge Elbert H. Gary, who also chaired U.S. Steel's executive committee, was instrumental. Edward Shearson, comptroller of U.S. Steel and later founder of Shearson-Hammill brokerage house, also contributed. Charles M. Schwab, who would later establish Bethlehem Steel, was another significant figure.
Other notable figures included Dan Eagan, president of the American Steel Casting Company; W. D. Sargent, head of the Sargent Steel Company; and Edward F. Goltra and George B. Leighton, who controlled steel interests in St. Louis, Missouri. These individuals brought a wealth of experience and resources to the newly formed company, which initially focused on finishing steel products.
American Steel Foundries significantly increased its capitalization in its first year.
The initial headquarters for American Steel Foundries was located in New York City.
Early operations concentrated on finishing steel products.
Amsted Industries was established on June 26, 1902.
Judge Elbert H. Gary, Edward Shearson, and Charles M. Schwab were key figures.
The initial capitalization was $9 million, which grew to $40 million.
Understanding the early ownership and formation of Amsted Industries provides context for its later development. The company's initial capitalization jump from $9 million to $40 million within its first year highlights its rapid growth. While specific equity splits among the founders aren't publicly detailed, the consolidation of resources aimed to strengthen the company's position in the market. The focus on finishing steel products, rather than primary steel production, was a key operational strategy.
- The merger of several steel companies created American Steel Foundries.
- Key figures included Judge Elbert H. Gary and Charles M. Schwab.
- The company's capitalization increased substantially in its first year.
- Early operations focused on finishing steel products.
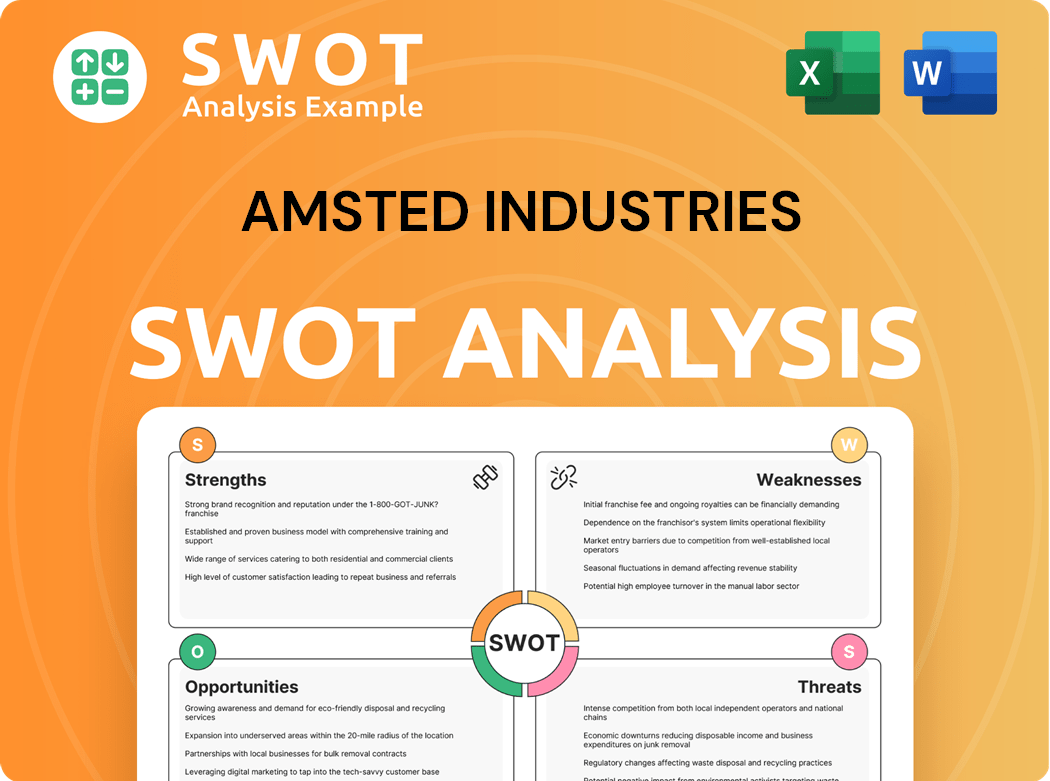
Amsted Industries SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
How Has Amsted Industries’s Ownership Changed Over Time?
The ownership structure of Amsted Industries has seen a significant shift over time. Initially a publicly traded entity, the company transitioned to a wholly employee-owned model. This change was solidified in 1986 when Amsted Industries was taken private through an employee stock ownership buyout, valued at $529 million. This move established its Employee Stock Ownership Plan (ESOP), a pivotal moment in the company's history.
By 1998, Amsted Industries achieved full employee ownership, a structure that continues to define its operations. This transition from public to private ownership has profoundly influenced Amsted's corporate strategy and governance. Understanding the evolution of Amsted Industries' marketing strategy requires recognizing this unique ownership model and its impact on the company's long-term goals.
| Event | Date | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Public to Private Transition | 1986 | Employee stock ownership buyout for $529 million, establishing ESOP. |
| Full Employee Ownership | 1998 | Amsted Industries became 100% employee-owned. |
| Current Ownership | Ongoing | Employees are the primary stakeholders through the ESOP, with shares distributed annually. |
As an ESOP-owned company, Amsted's employees are its primary stakeholders. Shares are allocated into individual retirement accounts at the end of each fiscal year. This structure distinguishes Amsted from publicly traded companies that have diverse institutional and individual investors. While primarily employee-owned, some institutional investors hold debt instruments of Amsted Industries Inc. For example, Six Circles Trust - Six Circles Credit Opportunities Fund, XHYI - BondBloxx USD High Yield Bond Industrial Sector ETF, and XBB - BondBloxx BB Rated USD High Yield Corporate Bond ETF, hold a total of 3,091,000 shares as of recent filings.
Amsted Industries is primarily owned by its employees through an ESOP.
- The ESOP model fosters a 'Spirit of Ownership' among the workforce.
- Employee interests are aligned with the company's long-term success.
- The ESOP serves as a retirement savings vehicle for U.S. employee-owners.
- Institutional investors hold debt instruments, not equity.
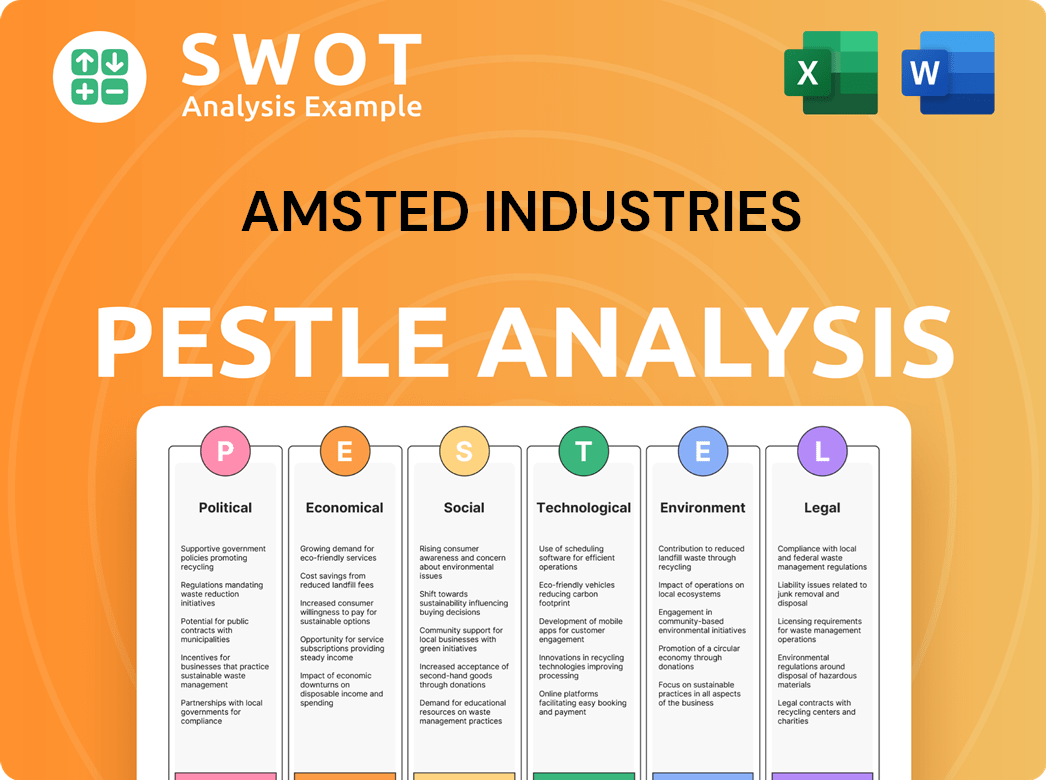
Amsted Industries PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
Who Sits on Amsted Industries’s Board?
The governance structure of Amsted Industries, a 100% employee-owned company, is unique. While specific details about the current board members and their affiliations aren't extensively available due to its private status, the board of directors guides the company. This board is responsible for considering the interests of various stakeholders, including employees, senior management, customers, suppliers, and the community. The company's structure, as detailed in an article about Growth Strategy of Amsted Industries, emphasizes employee involvement.
Amsted Industries' leadership team includes Stephen R. Smith, who serves as Chairman, President, and CEO, a role he has held since 2018. Key members of the leadership team also include Chris P. Meyers (VP, Finance & CFO), Christopher G. Athas (VP, General Counsel & Secretary), Janet Joy (VP, Audit), and Wayne A. Luce (VP, People). This leadership team works within the framework of the ESOP structure, where employee-owners have a direct say in governance.
| Leadership Role | Name | Title |
|---|---|---|
| Chairman, President, and CEO | Stephen R. Smith | Joined Amsted in 2005, became President and CEO in 2017, and Chairman in 2018. |
| VP, Finance & CFO | Chris P. Meyers | Oversees financial operations. |
| VP, General Counsel & Secretary | Christopher G. Athas | Manages legal and corporate governance matters. |
The ESOP structure at Amsted Industries allows all participants to vote on the entire board of directors annually. This direct voting power ensures accountability of the leadership to its employee-owners. This model aims to reward hard work and commitment, allowing employees to share in the company's success. This structure is a key part of the Amsted ownership model, differentiating it from many other companies.
Amsted Industries operates with a unique governance structure due to its employee ownership. The board of directors is responsible for balancing the interests of various stakeholders. Employee-owners have direct voting power, influencing decision-making.
- Employee ownership model.
- Direct voting rights for employees.
- Focus on accountability and shared success.
- Key leadership roles and responsibilities.
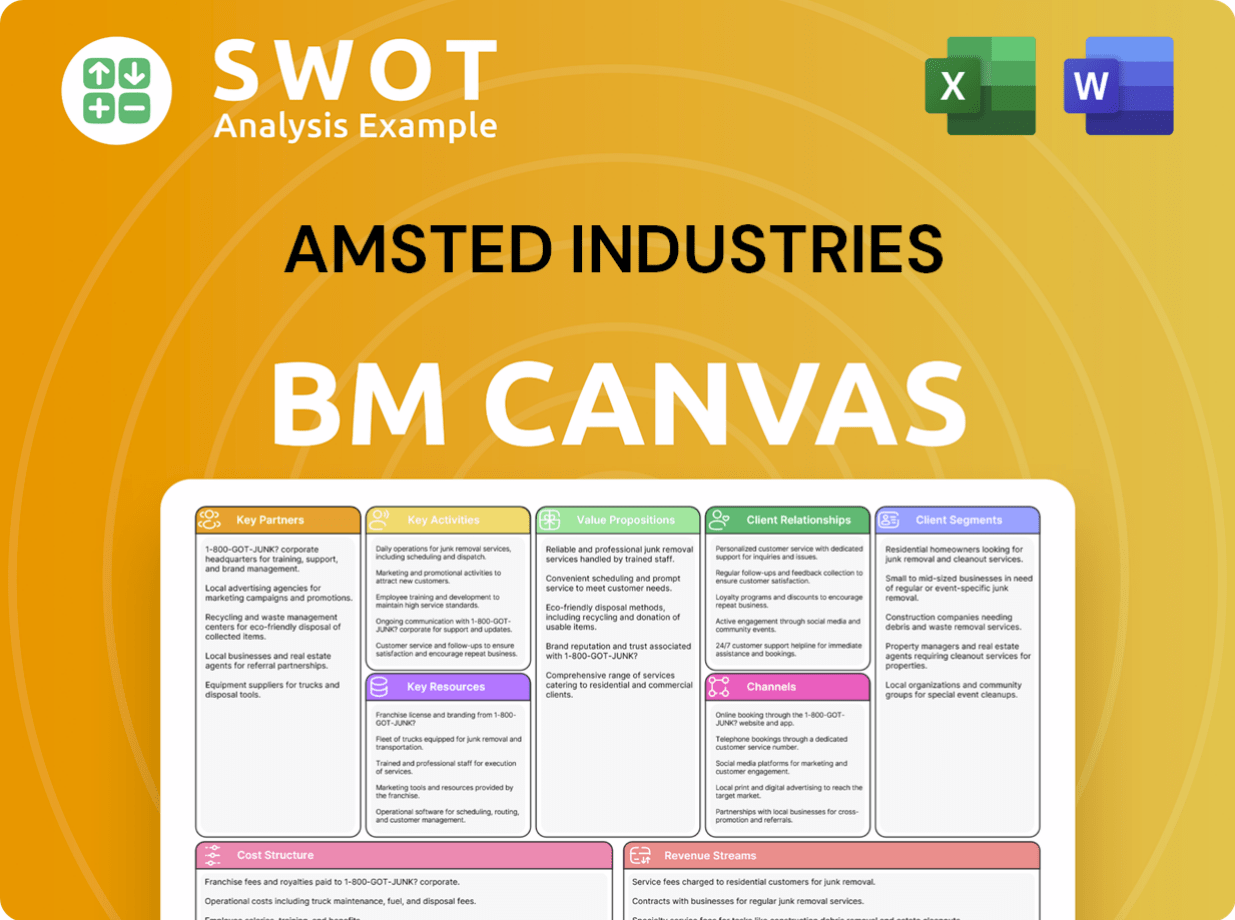
Amsted Industries Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
What Recent Changes Have Shaped Amsted Industries’s Ownership Landscape?
Over the past few years, the ownership of Amsted Industries has remained consistent. The company is 100% employee-owned through an Employee Stock Ownership Plan (ESOP). This structure has been a key part of its operations. Recent financial activities include a significant refinancing in early 2025, involving a $500 million issuance of 6.375% senior notes due 2033, the refinancing of a $1.4 billion credit facility, and the extension of a $225 million AR securitization facility. Furthermore, a tender offer was completed for its outstanding $400 million 5.625% senior notes due 2027. These moves aimed to manage debt and optimize the capital structure.
In 2024, Amsted Industries reported approximately $6.5 billion in revenue. The company has been focusing on innovation, especially within its Amsted Automotive group, which is developing technologies for electric and hybrid vehicles, aligning with the growing e-mobility market. This market is projected to reach $10 billion by 2026. Investments in research and development increased by 15% in 2024. Amsted Rail is also expanding into transit rail, a North American market valued at $10.5 billion in 2024 and projected to reach $12 billion by 2025.
| Financial Activity | Details | Year |
|---|---|---|
| Senior Notes Issuance | $500 million, 6.375% due 2033 | Early 2025 |
| Credit Facility Refinancing | $1.4 billion | Early 2025 |
| AR Securitization Facility Extension | $225 million | Early 2025 |
| Revenue | Approximately $6.5 billion | 2024 |
| R&D Investment Increase | 15% | 2024 |
While the company's ownership structure remains employee-owned, the financial health and strategic initiatives are influenced by its commitment to its employee-owners. The ESOP serves as a retirement savings vehicle, and the company's valuation directly affects employee accounts. For a deeper understanding of the competitive landscape, you can explore the Competitors Landscape of Amsted Industries.
Amsted Industries is 100% employee-owned through an ESOP, a unique aspect of the company structure.
The company reported around $6.5 billion in revenue for 2024, showing strong market positions across its segments.
Amsted is investing in innovation, particularly in automotive technologies for electric and hybrid vehicles.
Amsted Rail is expanding into the transit rail market, which is valued at $10.5 billion in North America in 2024.
Amsted Industries Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What are Mission Vision & Core Values of Amsted Industries Company?
- What is Competitive Landscape of Amsted Industries Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of Amsted Industries Company?
- How Does Amsted Industries Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of Amsted Industries Company?
- What is Brief History of Amsted Industries Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of Amsted Industries Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.