Glencore International Bundle
Unveiling Glencore's Ownership: Who Really Calls the Shots?
Ever wondered who truly controls the global behemoth that is Glencore International? From its inception as a private trading house to its current status as a publicly listed giant, Glencore's ownership structure has undergone a fascinating transformation. Understanding Glencore International SWOT Analysis is key to grasping its strategic moves and market dominance. This deep dive explores the key players and pivotal moments that have shaped Glencore's ownership landscape.

The evolution of Glencore International from a private entity to a publicly traded company in 2011, significantly impacted its ownership dynamics. Knowing "Who owns Glencore" is crucial for investors, analysts, and anyone tracking the company's impact on the global economy. This exploration goes beyond the basics, examining the influence of major Glencore shareholders and the role of the Glencore CEO in shaping the company's future, providing a comprehensive view of Glencore's ownership and control.
Who Founded Glencore International?
The origins of Glencore trace back to 1974 with the founding of Marc Rich + Co AG by Marc Rich. The initial ownership structure was predominantly private, with Marc Rich holding a significant controlling stake. Rich, a pioneer in the global oil spot market, built the company on aggressive trading strategies and a vast network of global contacts. His background in commodities trading significantly influenced the early ethos and operational model of the firm.
Early ownership was concentrated among Rich and a core group of traders and executives. These key individuals were instrumental in the company's rapid growth. The company's expansion was primarily fueled by its trading profits and debt financing, rather than external investment rounds. Internal agreements, common in private trading houses, likely included vesting schedules and profit-sharing arrangements designed to retain talent and incentivize aggressive trading.
A pivotal moment in the company's ownership history occurred in 1993. Following legal troubles faced by Marc Rich, he sold his controlling stake to a management buyout. This led to the renaming of the company to Glencore International AG, fundamentally reshaping the ownership structure. This buyout distributed control among a larger group of senior managers and traders, solidifying the employee-partner model.
Founded in 1974 by Marc Rich as Marc Rich + Co AG.
Highly private, with Marc Rich holding a significant controlling stake.
Built on aggressive trading strategies and global contacts, influenced by Rich's background.
Primarily fueled by trading profits and debt financing.
Marc Rich sold his stake, leading to a management buyout and renaming to Glencore International AG.
Control distributed among senior managers and traders, solidifying the employee-partner model.
The early structure of Glencore ownership was designed to incentivize performance. The shift in 1993 marked a significant change, distributing control among a wider group of senior managers. This employee-partner model was a key feature for nearly two decades before the company's IPO. The company's history, including its early ownership, is crucial to understanding its current structure. For more insights into the company's strategies, consider reading the Marketing Strategy of Glencore International.
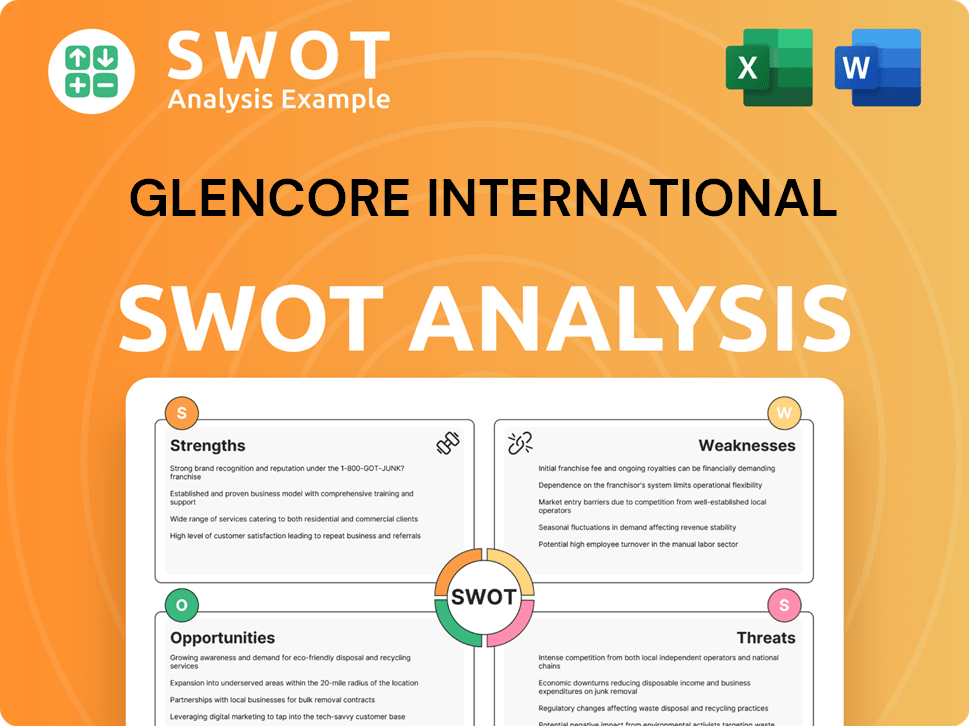
Glencore International SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
How Has Glencore International’s Ownership Changed Over Time?
The most significant shift in the ownership structure of Glencore International occurred with its initial public offering (IPO) on May 19, 2011. This IPO, which listed on the London Stock Exchange and the Hong Kong Stock Exchange, valued the company at roughly $60 billion. This transition marked a substantial change from its previous status as a private, employee-owned entity to a publicly traded company. At the time of the IPO, employees held approximately 80% of the shares, with Glencore CEO Ivan Glasenberg as the largest individual shareholder. The IPO provided an opportunity for many employees to realize the value of their long-held stakes.
Since the IPO, the ownership of Glencore has become more diverse. While no single entity holds a controlling stake, major shareholders include a mix of institutional investors, mutual funds, index funds, and individual insiders. As of early 2025, the Qatar Investment Authority (QIA) is a significant shareholder, holding approximately 9% of the company's shares as of late 2023. BlackRock Inc. and Vanguard Group also hold substantial stakes. Individual insiders, particularly those in executive management and on the board, continue to hold meaningful stakes.
| Event | Impact on Ownership | Date |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Public Offering (IPO) | Transitioned from private, employee-owned to publicly traded; significant diversification of shareholders. | May 19, 2011 |
| Merger with Xstrata | Further diversified asset base; introduced new institutional shareholders. | 2013 |
| Qatar Investment Authority (QIA) Stake Increase | Increased institutional ownership; QIA became a major shareholder. | Post-2016 |
The evolution of Glencore ownership has been influenced by strategic decisions, such as the merger with Xstrata in 2013, which diversified Glencore's asset base and brought in new institutional shareholders. This shift towards public ownership has increased transparency and adherence to corporate governance standards, impacting company strategy. For more insights, explore the Growth Strategy of Glencore International.
Glencore is a publicly traded company with a diversified shareholder base, including institutional investors and individual insiders. The IPO in 2011 was a pivotal moment, transforming the company's ownership structure.
- The Qatar Investment Authority (QIA) is a major institutional investor.
- BlackRock and Vanguard hold substantial passive stakes.
- The merger with Xstrata in 2013 further diversified the shareholder base.
- Glencore shareholders include a mix of institutional and individual investors.
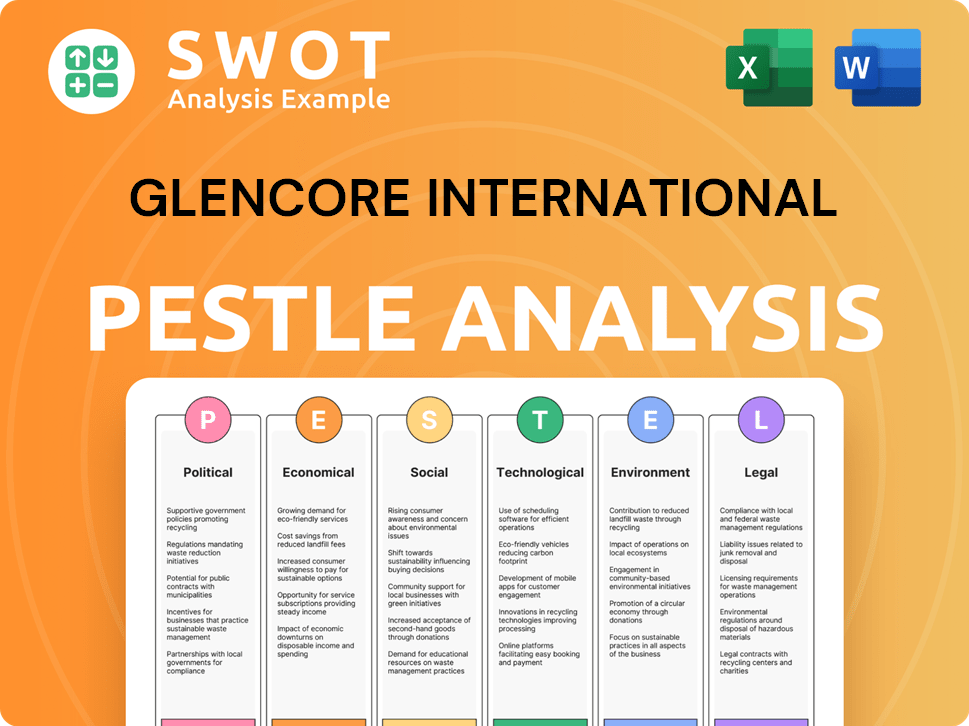
Glencore International PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
Who Sits on Glencore International’s Board?
The current Board of Directors of Glencore plc includes a mix of executive and non-executive directors. As of early 2025, the board typically comprises individuals with extensive experience in mining, commodities, and finance. While specific board members representing major shareholders are not always explicitly stated, representatives from significant institutional investors or those with historical ties to the company's employee-partner structure can influence decision-making. For instance, even though Ivan Glasenberg stepped down as CEO in 2021, his historical influence and continued presence as a significant individual shareholder mean his perspective remains relevant.
The board's composition reflects the company's global operations and its focus on the natural resources sector. The board is responsible for overseeing the company's strategy, risk management, and financial performance. Decisions made by the board have a significant impact on the company's direction and its stakeholders, including shareholders, employees, and the communities in which Glencore operates. The board's structure and the influence of its members are key factors in understanding Glencore's operations and its approach to corporate governance.
| Board Member | Role | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Gary Nagle | CEO | Appointed as CEO in 2021 |
| Peter Freyberg | Chairman | Oversees the board's activities |
| Non-Executive Directors | Various | Represent diverse backgrounds |
Glencore operates primarily on a one-share-one-vote structure, which is common for publicly listed companies. There are no publicly disclosed dual-class shares or special voting rights that would grant outsized control to any specific individual or entity beyond their proportional shareholding. Major institutional investors, by virtue of their large holdings, collectively wield significant voting power, influencing resolutions at annual general meetings (AGMs) concerning executive compensation, board appointments, and strategic initiatives. Understanding Revenue Streams & Business Model of Glencore International is crucial for grasping the company's financial dynamics and the impact of shareholder decisions.
Glencore's ownership is primarily through publicly traded shares, with significant influence from institutional investors. The company's governance structure emphasizes shareholder voting rights.
- One-share-one-vote structure.
- Institutional investors hold significant voting power.
- Focus on ESG matters influences decision-making.
- Shareholder pressure impacts company policies.
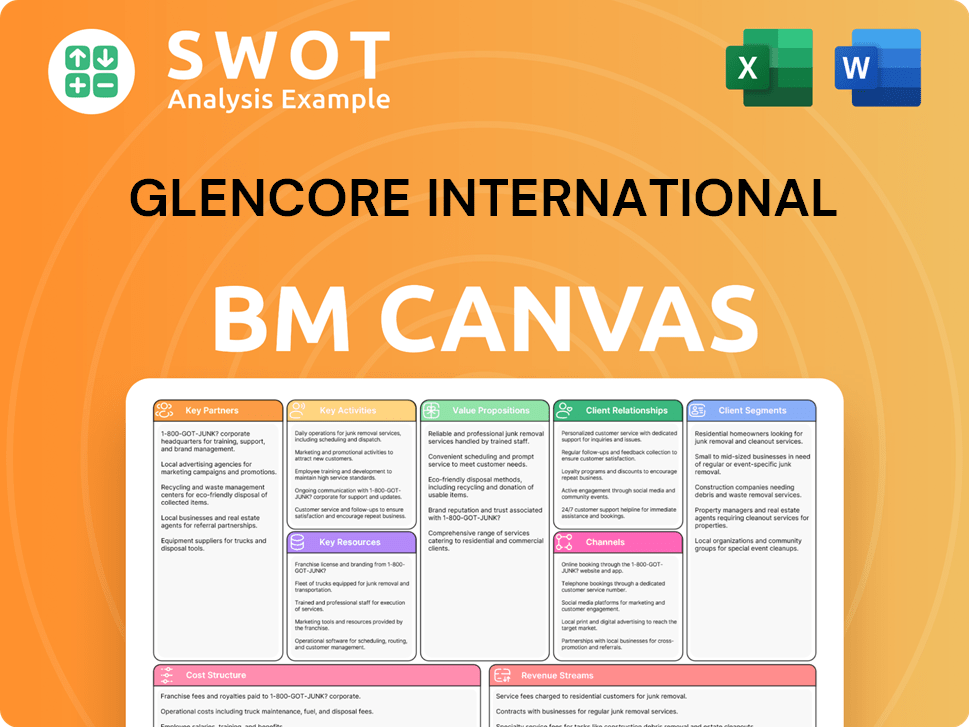
Glencore International Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
What Recent Changes Have Shaped Glencore International’s Ownership Landscape?
Over the past few years, the ownership structure of Glencore International, commonly referred to as Glencore, has seen subtle shifts. Institutional investors remain the dominant force among Glencore shareholders. Share buyback programs, such as the $1.2 billion announced in February 2024, have been a key part of returning value to shareholders, although they haven't drastically changed the core ownership, but rather reduced the total number of outstanding shares, increasing the proportional stake of remaining shareholders.
Leadership transitions have also played a role. The 2021 change in Glencore CEO, with Gary Nagle succeeding Ivan Glasenberg, is a notable example. While Glasenberg remains a significant individual shareholder, his diminished operational influence may lead to a gradual rebalancing of individual insider ownership. The company has not seen major secondary offerings or significant new strategic investors that have dramatically altered the ownership landscape recently. For more information on the competitive landscape, you can review the Competitors Landscape of Glencore International.
Industry trends, such as the increasing focus on ESG investing, have influenced Glencore's actions. The company has enhanced its sustainability reporting and decarbonization efforts to meet the demands of institutional investors. Furthermore, the natural dilution of ownership from former executives and employees, who are gradually reducing their holdings, is also a factor. In 2024, Glencore's management continues to emphasize shareholder returns, indicating a commitment to maintaining a robust and diverse investor base.
Institutional investors are the primary owners of Glencore shares. There are no major changes in the shareholder structure. Share buybacks have reduced the total number of shares outstanding, increasing the stake of existing shareholders.
The transition of the Glencore CEO in 2021 has influenced ownership trends. As former executives divest their shares, the ownership structure may gradually shift. This is a natural process in mature public companies.
ESG investing has increased scrutiny on Glencore's environmental impact. This has led to enhanced sustainability reporting and decarbonization efforts. These efforts influence investment decisions by large funds.
Glencore's management emphasizes shareholder returns. This suggests a commitment to maintaining a diverse investor base. The company's focus remains on providing value to its shareholders.
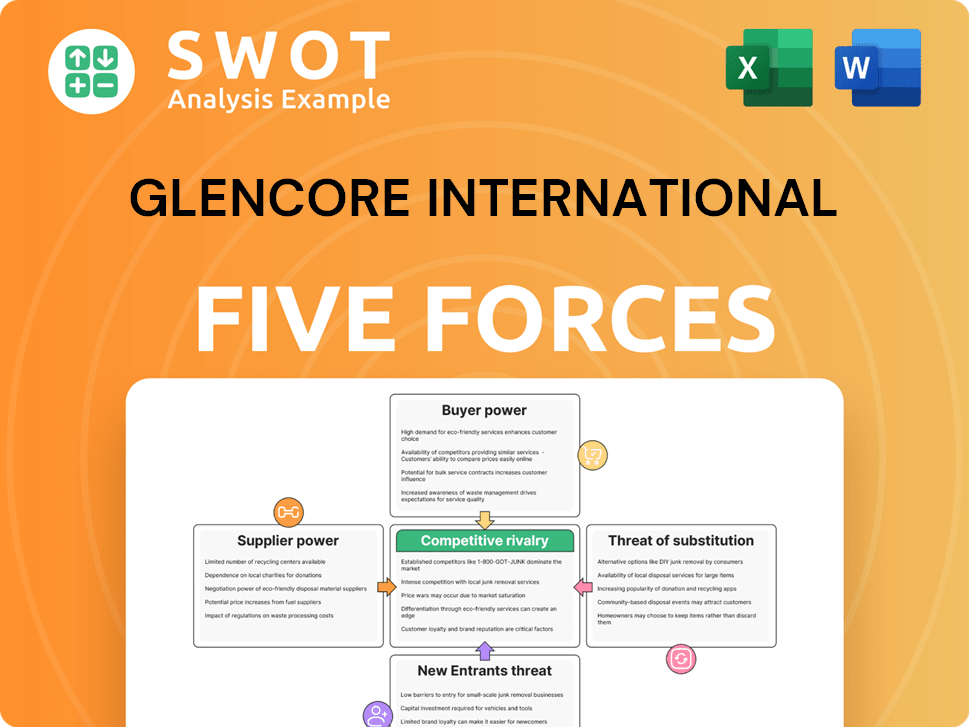
Glencore International Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What are Mission Vision & Core Values of Glencore International Company?
- What is Competitive Landscape of Glencore International Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of Glencore International Company?
- How Does Glencore International Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of Glencore International Company?
- What is Brief History of Glencore International Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of Glencore International Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.