J. Crew Bundle
Who Really Owns J.Crew?
Ever wondered who pulls the strings at J.Crew, the iconic brand known for its preppy style? The J. Crew SWOT Analysis reveals that understanding the company's ownership is key to grasping its strategic direction and future prospects. From its catalog beginnings to its current market position, J.Crew's journey has been marked by significant shifts in ownership, especially after navigating financial challenges. This exploration uncovers the complex web of stakeholders that shape J.Crew's destiny.
The story of J. Crew's ownership is a fascinating case study in corporate finance, detailing how the company's J. Crew SWOT Analysis, history, and financial status have shaped its evolution. From private equity involvement to its emergence from bankruptcy, the identity of the J. Crew parent company and the key players behind it have dramatically influenced its business strategies. Exploring the current ownership structure unveils insights into the company's current financial situation and its path forward in a competitive retail market.
Who Founded J. Crew?
The story of J. Crew's beginnings is rooted in 1983, when Arthur Cinader established Popular Merchandise, Inc. His vision shaped the brand's identity, focusing on a classic American style. While specific details on initial equity splits are not widely available, Cinader's influence was fundamental in setting the direction for the company.
Initially, J. Crew operated as a catalog-based retailer, with the first catalog mailing in 1983. This direct-to-consumer approach was a key part of its early business model. The company expanded in 1989 by opening its first retail store in New York City, marking a significant step beyond its catalog origins. This transition was crucial for the brand's growth and market presence.
During these early years, ownership was largely concentrated within the Cinader family. This structure was typical for a growing business, allowing the founders to maintain control and steer the brand's aesthetic and market positioning. There's no publicly available information about early angel investors or specific details on vesting schedules during this foundational period.
Arthur Cinader founded Popular Merchandise, Inc. in 1983. The company started as a catalog-based retailer.
The first J. Crew catalog was mailed in 1983. This was the primary sales channel initially.
The first retail store opened in New York City in 1989. This marked a significant expansion.
Early ownership was primarily within the Cinader family. This provided stability during the company's formative years.
Specific equity splits and details on early investors are not publicly available. The focus was on building the brand.
The initial business model centered on direct-to-consumer sales. This strategy evolved with the opening of retail stores.
The early history of J. Crew highlights a family-led business with a focus on building a brand. The transition from catalog to retail was a crucial step in its evolution. The ownership structure was designed to support the company's growth and market positioning.
- Arthur Cinader's founding vision shaped the brand's identity.
- The initial focus was on direct-to-consumer sales through catalogs.
- The opening of the first retail store in 1989 marked a significant expansion.
- Ownership was primarily concentrated within the Cinader family during the early years.
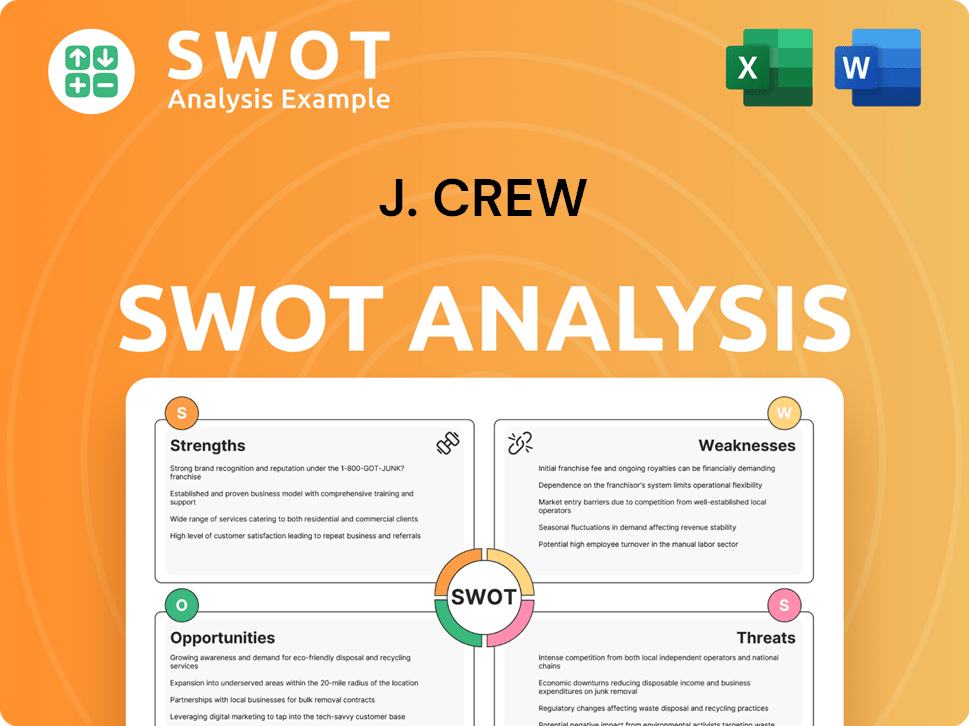
J. Crew SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
How Has J. Crew’s Ownership Changed Over Time?
The evolution of J. Crew's ownership has been marked by significant shifts, particularly involving private equity firms and a major bankruptcy restructuring. In 1997, Texas Pacific Group (TPG) acquired a majority stake in the company, a pivotal move away from family ownership. This acquisition, valued at approximately $500 million, aimed to fuel expansion and modernize operations. TPG later took the company public in 2006.
The most notable change occurred in May 2020 when the company filed for Chapter 11 bankruptcy protection. This was largely due to a heavy debt burden and the economic fallout from the COVID-19 pandemic. The restructuring plan saw lenders taking over ownership, with Anchorage Capital Group, GSO Capital Partners (Blackstone's credit arm), and other investment firms becoming the primary owners. These firms converted roughly $1.6 billion of debt into equity, reshaping the company's financial landscape and ownership structure.
| Year | Event | Impact on Ownership |
|---|---|---|
| 1997 | TPG Acquisition | Shift from family ownership to private equity control. |
| 2006 | Initial Public Offering (IPO) | Company became publicly traded. |
| 2011 | Leveraged Buyout | TPG and Leonard Green & Partners took the company private again. |
| 2020 | Chapter 11 Bankruptcy | Lenders, including Anchorage Capital Group and GSO Capital Partners, took ownership. |
Currently, the primary owners of the company are investment firms that emerged from the bankruptcy restructuring. While specific ownership percentages aren't always public, these entities now hold significant control. This shift has led to a focus on debt reduction, operational efficiency, and a renewed emphasis on core brands. The company's financial status continues to evolve as it navigates the competitive retail landscape.
The company's ownership has changed significantly over time, primarily through private equity involvement and a bankruptcy restructuring. The current ownership structure is dominated by investment firms that took control during the 2020 bankruptcy. The company's financial health and strategic direction are now heavily influenced by these key stakeholders.
- TPG acquired a majority stake in 1997.
- The company went public in 2006.
- The company returned to private ownership in 2011.
- The company filed for bankruptcy in 2020, with lenders taking over ownership.
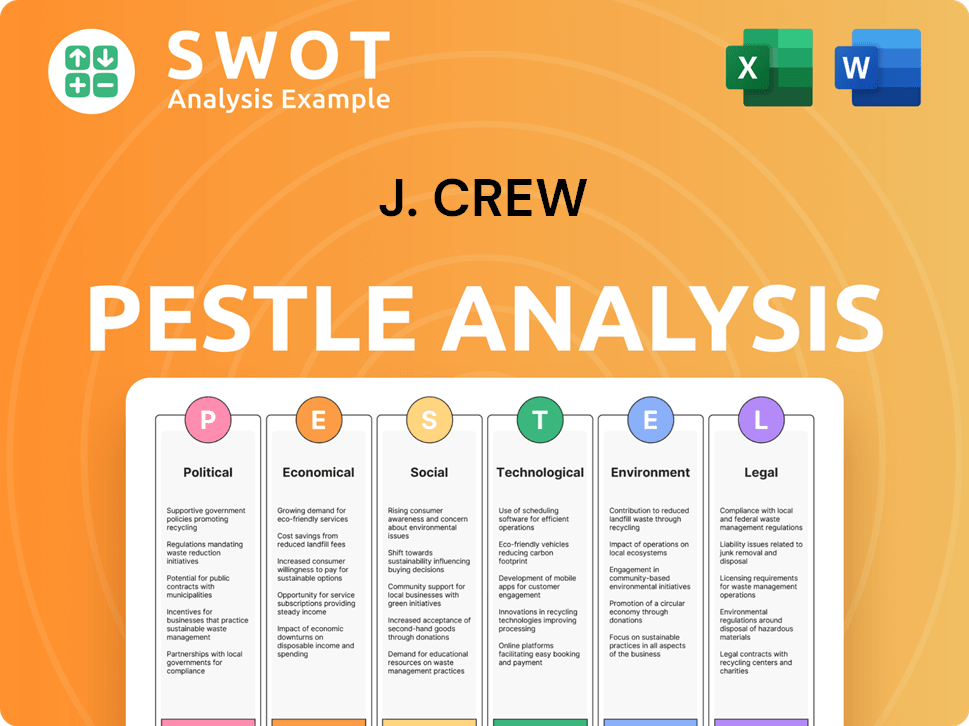
J. Crew PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
Who Sits on J. Crew’s Board?
Following its emergence from bankruptcy in September 2020, the board of directors of the company reflects its new ownership structure. The board primarily consists of representatives from investment firms that converted debt into equity. While a comprehensive, real-time list of all board members and their precise affiliations with specific ownership stakes isn't consistently publicized for a privately held company post-bankruptcy, the board typically includes individuals representing major equity holders.
These representatives are appointed to protect the interests of their respective investment firms, ensuring that strategic decisions align with the objectives of the new owners. These objectives often prioritize financial stability, profitability, and eventual value realization. The board's focus is on guiding the company through its post-bankruptcy phase, optimizing its operations, and strengthening its financial position, with decisions largely driven by the collective interests of its new investment firm owners.
| Board Member | Affiliation | Role |
|---|---|---|
| Representative | Anchorage Capital Group | Board Member |
| Representative | GSO Capital Partners | Board Member |
| Unknown | Other Investors | Board Member |
Given that the company is privately held since its bankruptcy restructuring, the voting structure isn't subject to the same public disclosure requirements as publicly traded entities. Voting power is generally concentrated among the new equity holders based on their proportional ownership stakes. This typically operates on a one-share-one-vote basis, although specific agreements among the investor group could include provisions for certain supermajority votes on critical decisions. There have been no widely reported proxy battles or activist investor campaigns since its emergence from bankruptcy, as the ownership is consolidated among a smaller group of institutional investors who likely maintain a collaborative approach to governance to maximize their investment. To learn more about the company's journey, you can read more about the J. Crew history.
The board of directors is composed of representatives from investment firms that hold equity. Voting power is concentrated among equity holders based on their ownership stakes. The primary focus is on financial stability and profitability.
- Ownership structure is not publicly disclosed.
- Voting typically follows a one-share-one-vote basis.
- The board aims to optimize operations and strengthen the financial position.
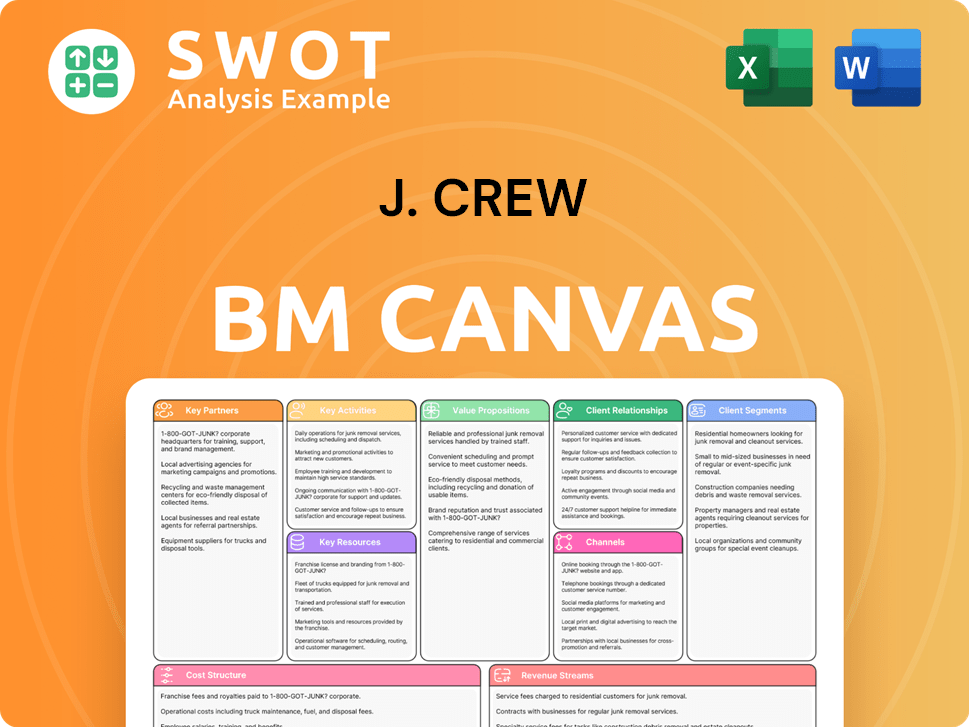
J. Crew Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
What Recent Changes Have Shaped J. Crew’s Ownership Landscape?
In the past few years, the J. Crew ownership landscape has been significantly reshaped. The company's emergence from Chapter 11 bankruptcy in September 2020 marked a pivotal moment, transferring control from private equity firms TPG and Leonard Green & Partners to senior lenders such as Anchorage Capital Group and GSO Capital Partners. This restructuring recapitalized the business, converting roughly $1.6 billion in debt into equity, fundamentally altering the company's financial structure and ownership.
Since the bankruptcy, the ownership of the J. Crew parent company has largely remained consolidated among these investment firms. There have been no major public announcements regarding share buybacks or secondary offerings. The focus has been on stabilizing operations and fostering growth under the new ownership structure. A key leadership change occurred with the departure of CEO Jan Singer in November 2020, succeeded by Libby Wadle, formerly of Madewell. This move signaled a strategic emphasis on leveraging the success of the Madewell brand within the broader J.Crew Group.
The retail industry has seen a rise in institutional ownership, particularly through private equity and distressed debt investors, as companies navigate challenging market conditions. For Who owns J. Crew, the recent ownership change mirrors the trend of creditors gaining control in distressed situations, highlighting the impact of financial leverage on ownership. The long-term goals for the current investment firm owners likely involve enhancing the company's value for a future exit, whether through a sale or a return to public markets, contingent on sustained profitability and favorable market conditions. The headquarters of J.Crew is located in New York City.
J.Crew emerged from bankruptcy in September 2020. Senior lenders, including Anchorage Capital Group and GSO Capital Partners, gained control. This restructuring converted approximately $1.6 billion in debt to equity.
Jan Singer, the CEO, left in November 2020. Libby Wadle, formerly of Madewell, became the new CEO. This shift emphasized leveraging the Madewell brand within the J.Crew Group.
The retail sector shows increased institutional ownership. Private equity and distressed debt investors are common. Creditors often take control in distressed situations, influencing ownership.
The current owners aim to increase company value. Potential exits include sales or a return to public markets. Success depends on sustained profitability and market conditions.
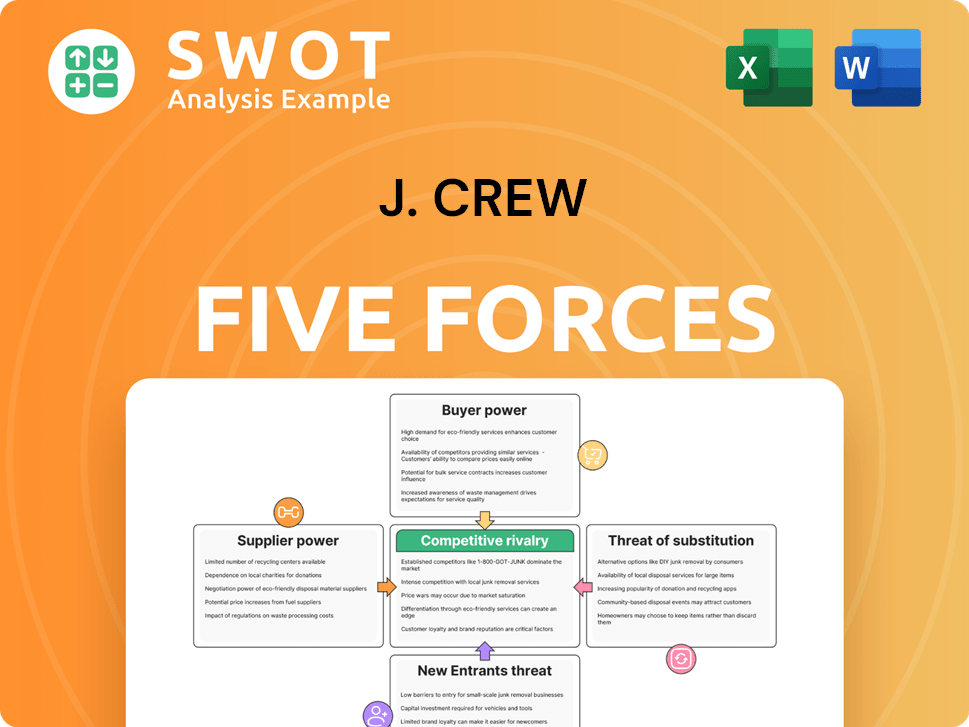
J. Crew Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What are Mission Vision & Core Values of J. Crew Company?
- What is Competitive Landscape of J. Crew Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of J. Crew Company?
- How Does J. Crew Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of J. Crew Company?
- What is Brief History of J. Crew Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of J. Crew Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.