Deutsche Lufthansa Bundle
Who Really Owns Lufthansa?
Ever wondered who steers the flight path of one of Europe's aviation giants? Understanding the Deutsche Lufthansa SWOT Analysis is crucial to grasp its strategic landscape. The ownership structure of Lufthansa, a company with a rich history and global presence, is a dynamic story of government intervention and private enterprise. This exploration unveils the key players behind the scenes.

From its roots to its current status as a publicly traded company, the Lufthansa Group's ownership has seen significant shifts. Knowing who owns Lufthansa provides insight into the company's strategic decisions, particularly in times of economic uncertainty. This in-depth analysis will explore the Lufthansa shareholders, the evolution of its ownership, and the impact of major stakeholders on its operations and financial performance. Discover the answers to questions like: Who is the main shareholder of Lufthansa and who controls Deutsche Lufthansa AG?
Who Founded Deutsche Lufthansa?
The current Deutsche Lufthansa AG, often referred to as Lufthansa, traces its roots back to January 6, 1953, when it was established as Aktiengesellschaft für Luftverkehrsbedarf (Luftag) in Cologne. This marked the re-establishment of a German flag carrier following the liquidation of the original Deutsche Luft Hansa. The name and logo of the liquidated Deutsche Luft Hansa were acquired in 1954, continuing the legacy of German aviation.
The original Deutsche Luft Hansa was founded in Berlin on January 6, 1926, through the merger of Deutscher Aero Lloyd and Junkers Luftverkehr. The re-establishment of Lufthansa in 1953 was a pivotal moment, reflecting post-war efforts to rebuild Germany's infrastructure, including its aviation sector. This involved significant government backing and strategic partnerships.
The early ownership structure of Luftag was primarily composed of the Federal German Government, holding a significant stake, alongside other entities. This setup was crucial in the initial phase, supporting the airline's operations and expansion. The ownership details highlight the strategic importance of Lufthansa to the German economy and its role in international travel.
Deutsche Lufthansa AG was re-established on January 6, 1953, as Luftag. This was a crucial step in rebuilding Germany's aviation sector after the war.
The original Deutsche Luft Hansa existed from 1926, merging two earlier aviation companies. The re-establishment of Lufthansa was a strategic move.
Hans M. Bongers was instrumental in setting up the preparatory airline corporation. Dr. Kurt Weigelt became the president of the refounded entity.
The Federal German Government held a significant stake, alongside the State of North Rhine-Westphalia and Federal German Railways. Smaller holdings were also present.
The initial ownership structure reflected the post-war vision of re-establishing a national airline. This involved significant government backing.
The ownership details highlight the strategic importance of Lufthansa to the German economy. It played a key role in international travel.
The initial ownership of Lufthansa, or Luftag, in 1953 was primarily controlled by the Federal German Government, holding a substantial stake. Other significant shareholders included the State of North Rhine-Westphalia and Federal German Railways, alongside smaller holdings. This structure reflects the post-war strategy to rebuild Germany's aviation sector, with government support playing a crucial role. Understanding the Growth Strategy of Deutsche Lufthansa provides further insights into its development.
- The Federal German Government held approximately 74% of the shares initially.
- The State of North Rhine-Westphalia and Federal German Railways also held shares.
- There were 125 smaller holdings, mainly in travel and transport.
- Hans M. Bongers and Dr. Kurt Weigelt were key figures in the airline's re-establishment.
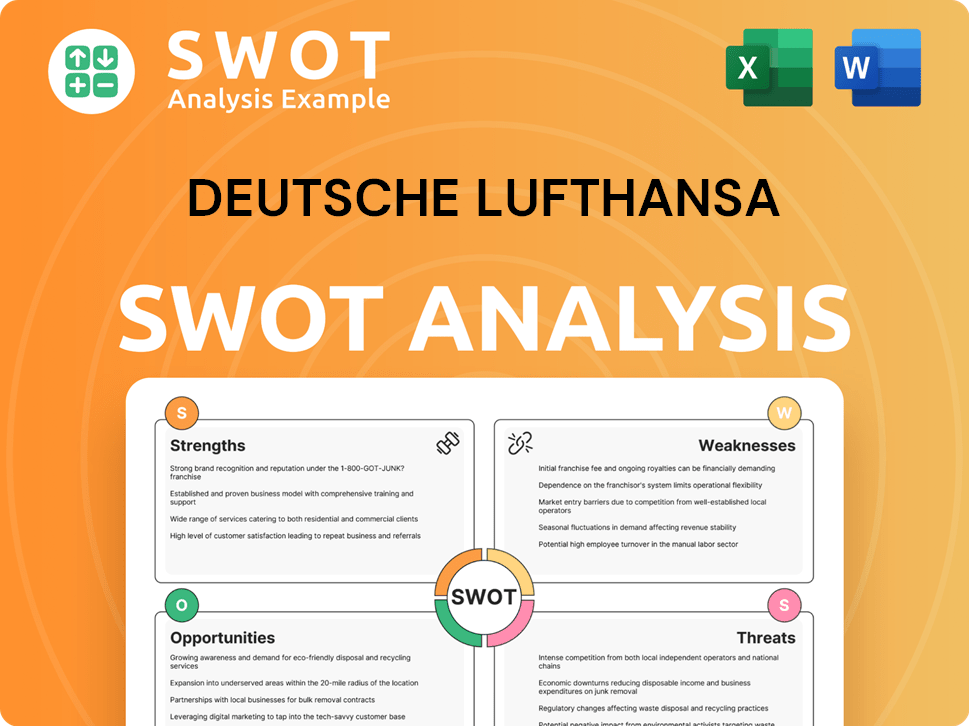
Deutsche Lufthansa SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
How Has Deutsche Lufthansa’s Ownership Changed Over Time?
The evolution of Deutsche Lufthansa AG's ownership reflects significant shifts over time. Initially a state-owned entity, the company transitioned to full privatization in 1997. This transformation marked a pivotal moment, opening the door for broader investor participation and reshaping the company's financial landscape. Understanding the Growth Strategy of Deutsche Lufthansa involves a deep dive into its ownership dynamics.
Key events have significantly impacted the ownership structure of Lufthansa. The COVID-19 crisis in 2020 led to the German government's Economic Stabilisation Fund (WSF) acquiring a 20% stake as part of a bailout. However, by September 2022, the WSF had divested its remaining holdings, returning Lufthansa to full private ownership. These changes highlight the dynamic nature of Lufthansa's ownership, influenced by economic conditions and strategic decisions.
| Ownership Aspect | Details | As of March 31, 2025 |
|---|---|---|
| Nationality of Shareholders | German Investors | 81.3% |
| Nationality of Shareholders | USA Investors | 7.4% |
| Nationality of Shareholders | Ireland Investors | 4.9% |
| Nominal Capital | Total | EUR 3,067,690,682.88 |
| Number of Shares | Total | 1,198,316,673 |
As of March 31, 2025, the ownership structure reveals that German investors hold the majority of shares at 81.3%. The USA holds 7.4% and Ireland holds 4.9%. The nominal capital of the company is EUR 3,067,690,682.88, divided into 1,198,316,673 no-par value registered shares. These figures provide a clear picture of who owns Lufthansa and the distribution of its ownership.
Lufthansa's ownership structure has evolved significantly since its privatization in 1997. The German government's role, through the WSF, was temporary, and the company is now fully privately owned. Key stakeholders include German, US, and Irish investors.
- German investors hold the largest share.
- The WSF's stake was divested in 2022.
- The company's nominal capital is over EUR 3 billion.
- Understanding Lufthansa's ownership is crucial for investors.
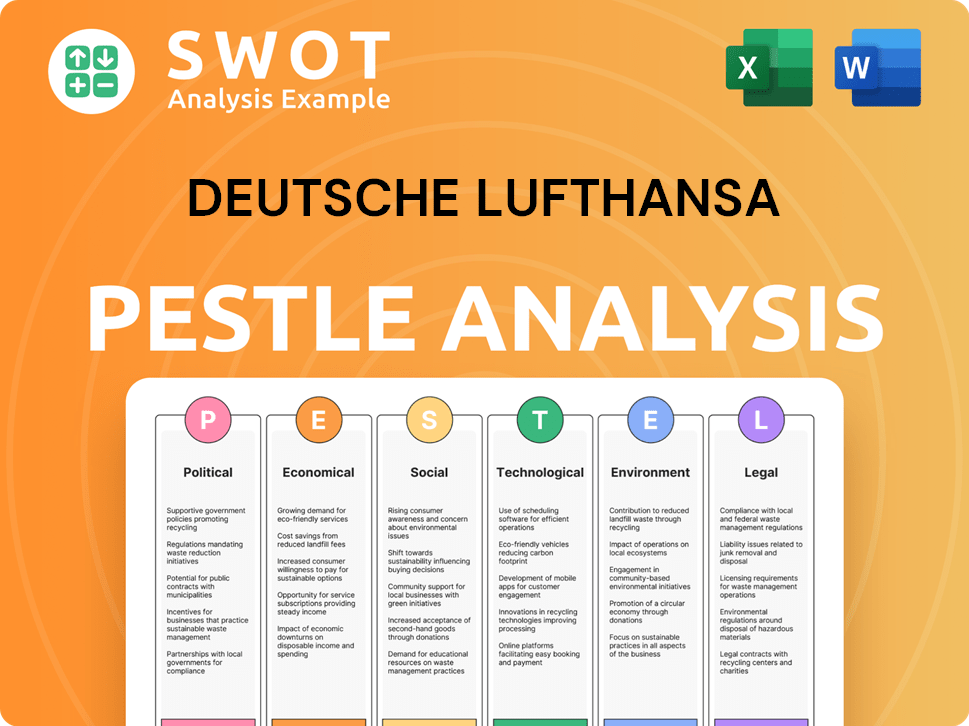
Deutsche Lufthansa PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
Who Sits on Deutsche Lufthansa’s Board?
The Board of Directors of Deutsche Lufthansa AG is key to the company's governance. While a complete list of all board members representing major shareholders or independent seats isn't available in this context, individuals like Dr. Michael Niggemann are part of the Executive Board. Understanding the Deutsche Lufthansa ownership structure requires looking at the composition and roles within the board.
As of December 31, 2024, Deutsche Lufthansa AG held approximately 8.44% of the shares and voting rights in Fraport AG. This illustrates the company's influence and involvement in related businesses. The board's decisions and the voting power of shareholders are essential for the company's strategic direction. The Lufthansa Group's largest airline customer is Fraport AG at Frankfurt Airport.
| Board Member | Role | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Dr. Michael Niggemann | Executive Board Member | Part of the Executive Board of Deutsche Lufthansa AG |
The voting structure for Deutsche Lufthansa AG's shares generally follows a one-share-one-vote principle. However, the company must comply with the German Stock Corporation Act (AktG) and the Aviation Compliance Documentation Act (LuftNaSiG). These regulations ensure that the company remains under German or European control, which is vital for maintaining aviation licenses and rights. The Lufthansa shareholders and their voting power are essential for the company's operations.
Deutsche Lufthansa AG operates under specific regulations, impacting its ownership and control. The German government's role and the influence of major shareholders are key. For more details, you can explore the topic further by reading about Deutsche Lufthansa's financial analysis.
- Compliance with German and European regulations is essential.
- Shareholder voting rights are typically one share, one vote.
- The nationality of shareholders is important for aviation rights.
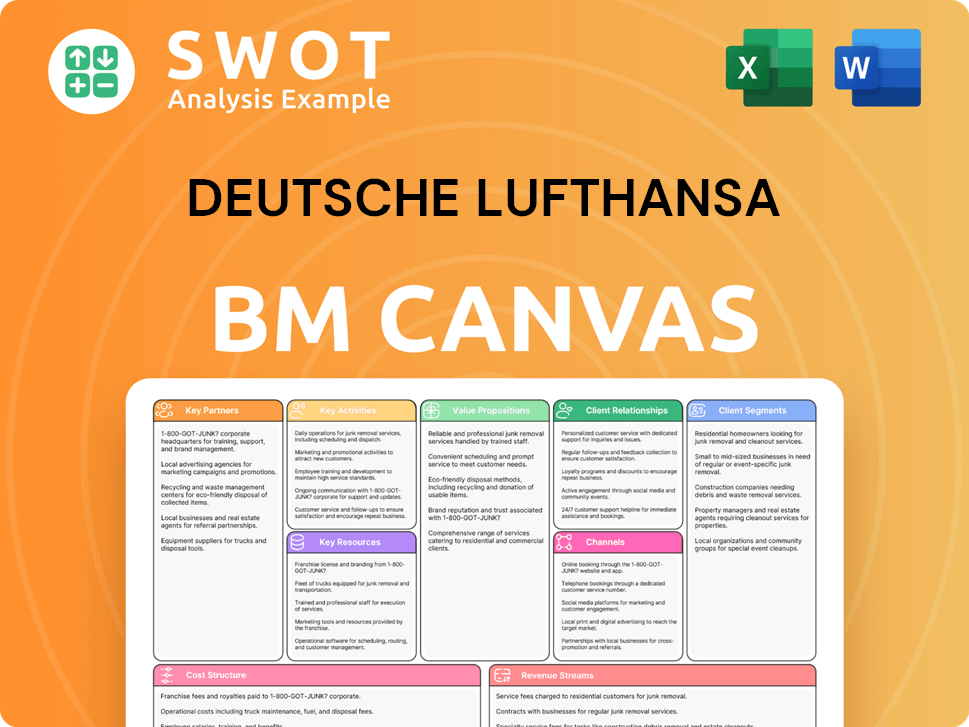
Deutsche Lufthansa Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
What Recent Changes Have Shaped Deutsche Lufthansa’s Ownership Landscape?
Over the past few years, significant shifts have occurred in the ownership of Deutsche Lufthansa AG. A pivotal moment was the German government's intervention during the COVID-19 pandemic. In 2020, the Economic Stabilisation Fund (WSF) acquired a 20% stake in Lufthansa as part of a €9 billion bailout. This stake was progressively reduced, and by September 2022, the WSF had divested its remaining 6.2% holding, returning Lufthansa to full private ownership. This move generated a profit of €760 million for the German government.
Following the government's exit, German billionaire Klaus-Michael Kuehne increased his stake, reaching 17.5% in September 2022. This highlights the influence of individual shareholders. As of March 31, 2025, German investors collectively held 81.3% of the shares, a notable increase from 76.2% in March 2024. This demonstrates a strong domestic investor base. U.S. investors hold 7.4%, Irish investors 4.9%, and Luxembourg investors 1.6%.
| Shareholder Type | March 2024 | March 2025 |
|---|---|---|
| German Investors | 76.2% | 81.3% |
| US Investors | - | 7.4% |
| Irish Investors | - | 4.9% |
| Luxembourg Investors | - | 1.6% |
In terms of share buybacks, the 1-Year Share Buyback Ratio as of March 2025 was -0.10%, and the 3-Month Share Buyback Ratio was 0.00%. This indicates limited share repurchases during these periods. The Executive Board is authorized to purchase up to 10% of the nominal capital in its own shares, providing flexibility for future corporate actions. The strategic direction for Lufthansa in 2025 includes a focus on operational stability, efficiency, and cost reduction, alongside strategic expansion, such as the ongoing integration of ITA Airways. For more insights into the competitive landscape, consider reading about the Competitors Landscape of Deutsche Lufthansa.
The ownership of Lufthansa has evolved significantly, with a strong presence of German investors. Key shareholders include individual investors and institutional investors.
The major shareholders include German investors holding the largest portion of the shares, followed by investors from the US, Ireland, and Luxembourg.
The company reported a record revenue of €37.6 billion in 2024, with an expected adjusted EBIT significantly higher in 2025. Moderate capacity growth of around 4% is anticipated in 2025.
Lufthansa Group is focusing on operational stability, efficiency, and strategic expansion, including the integration of ITA Airways, with synergies expected by 2027.
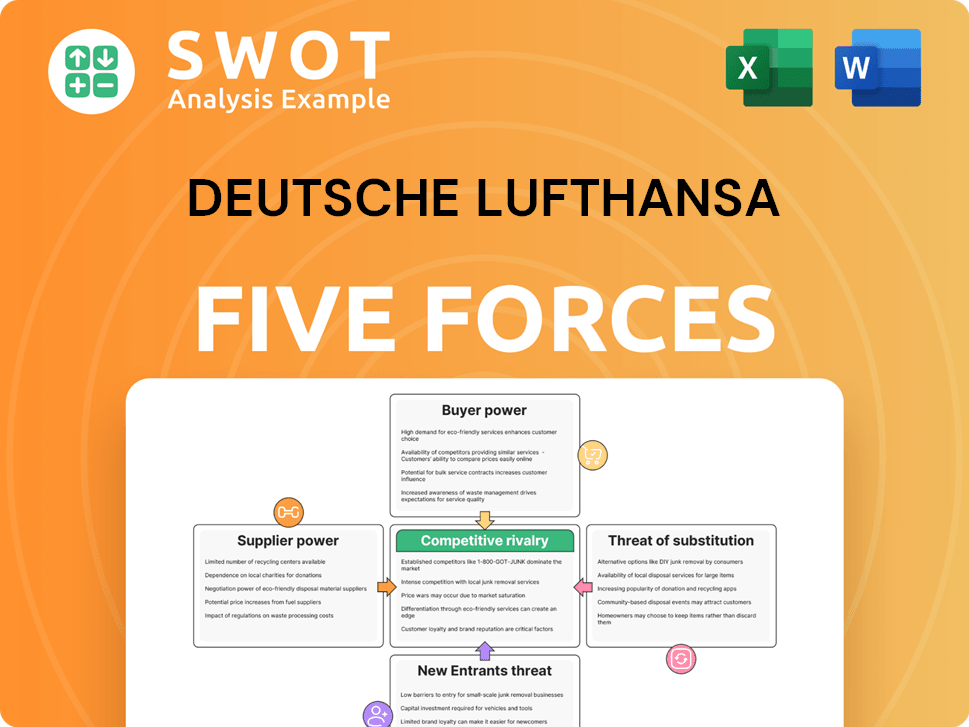
Deutsche Lufthansa Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What are Mission Vision & Core Values of Deutsche Lufthansa Company?
- What is Competitive Landscape of Deutsche Lufthansa Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of Deutsche Lufthansa Company?
- How Does Deutsche Lufthansa Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of Deutsche Lufthansa Company?
- What is Brief History of Deutsche Lufthansa Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of Deutsche Lufthansa Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.