Ping An Insurance Group Bundle
Who Really Controls Ping An Insurance?
Unraveling the ownership of Ping An Insurance Group is crucial for understanding its strategic direction and future potential. This deep dive explores the intricate web of shareholders and influences that shape one of the world's largest financial powerhouses. Discover the key players behind the scenes and how their stakes impact Ping An Insurance Group SWOT Analysis.

Understanding Ping An ownership is essential for investors and analysts alike, providing insights into the Chinese insurance market and the company's long-term strategy. The question of "Who controls Ping An?" is pivotal for anyone evaluating its financial performance and considering investment opportunities. Exploring the history of Ping An Insurance Group Company and its evolving shareholder base reveals the dynamics that drive this financial giant.
Who Founded Ping An Insurance Group?
The genesis of Ping An Insurance Group in 1988 was spearheaded by Ma Mingzhe, who is recognized as the founder. He was the driving force behind the establishment of the company, leveraging his financial expertise and foresight to navigate China's evolving economic landscape.
Early Ping An ownership was primarily held by a select group of individuals and local state-owned entities. This reflected the economic environment of China during the late 1980s, where state involvement and private initiatives often intertwined.
The foundational support provided by institutions like the Industrial and Commercial Bank of China (ICBC) and China Merchants Bank was essential for Ping An Group. These institutions provided the initial capital and credibility needed for the insurance company to begin operations.
Ma Mingzhe was the central figure in the establishment of Ping An Insurance.
ICBC and China Merchants Bank were instrumental in providing capital and support.
Early ownership combined private individuals with state-owned entities.
The initial focus was on establishing and growing the core insurance business.
The early years of Ping An Insurance Group Company were marked by a clear focus on establishing the core insurance business. The structure of the company reflected a blend of private initiative and state support, which was typical of the economic environment in China at the time. The leadership under Ma Mingzhe was central, with key financial institutions providing strategic backing.
- Ma Mingzhe's leadership was pivotal in the company's formation.
- ICBC and China Merchants Bank provided crucial early financial backing.
- The ownership structure combined private and state-backed entities.
- The primary objective was to build and expand the insurance business.
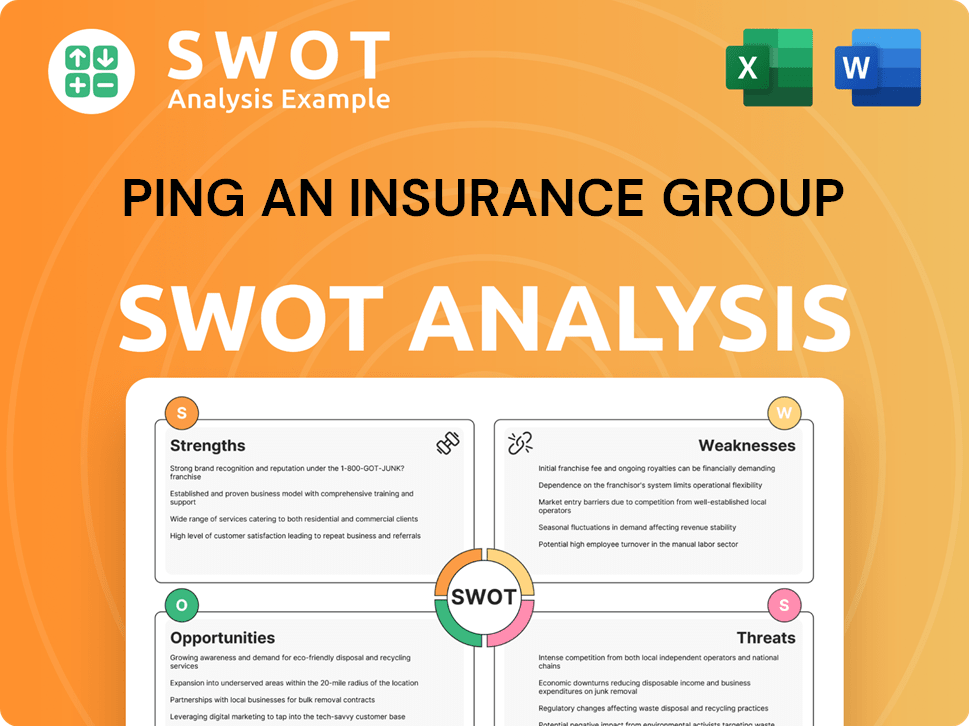
Ping An Insurance Group SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
How Has Ping An Insurance Group’s Ownership Changed Over Time?
The ownership structure of Ping An Insurance Group has changed significantly since its inception. Initially, it was a privately held entity with state support. A major turning point was its initial public offering (IPO) on the Hong Kong Stock Exchange in 2004, followed by a listing on the Shanghai Stock Exchange in 2007. These listings opened the door to a wider range of investors, both institutional and individual, which greatly diversified its ownership.
These public listings were crucial for the growth of Ping An Insurance Group, allowing it to raise capital and expand its operations. They also introduced greater transparency and accountability, as the company became subject to the regulations and scrutiny of public markets. This shift from a more closely held structure to a publicly traded one has had a profound impact on its strategic direction and governance.
| Key Event | Date | Impact on Ownership |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Public Offering (IPO) | 2004 (Hong Kong), 2007 (Shanghai) | Opened the company to a broader investor base, diversifying ownership. |
| Shenzhen Investment Holdings Co., Ltd. | Ongoing | Maintained a significant stake, reflecting the local government's strategic interest. |
| CP Group Acquisition | 2013 | Diversified ownership further, with the Thai conglomerate becoming a major shareholder. |
Currently, Ping An's major shareholders include state-owned enterprises, large institutional investors, and public shareholders. As of late 2024 and early 2025, key shareholders include Shenzhen Investment Holdings Co., Ltd., a state-owned enterprise, and the CP Group (Charoen Pokphand Group), a Thai conglomerate. The CP Group has maintained a notable presence, often holding around 10-15% of the shares. Various mutual funds, index funds, and asset management companies, both domestic and international, also hold significant portions of the company's shares. These shifts in Ping An ownership have fostered a more market-oriented approach while balancing the interests of its diverse shareholder base.
The ownership of Ping An Group has evolved from a privately held entity to a publicly traded company.
- Initial public offerings in Hong Kong and Shanghai broadened the shareholder base.
- State-owned enterprises and institutional investors are significant shareholders.
- CP Group is a major stakeholder, diversifying ownership.
- Understanding the shareholder structure is crucial for investors.
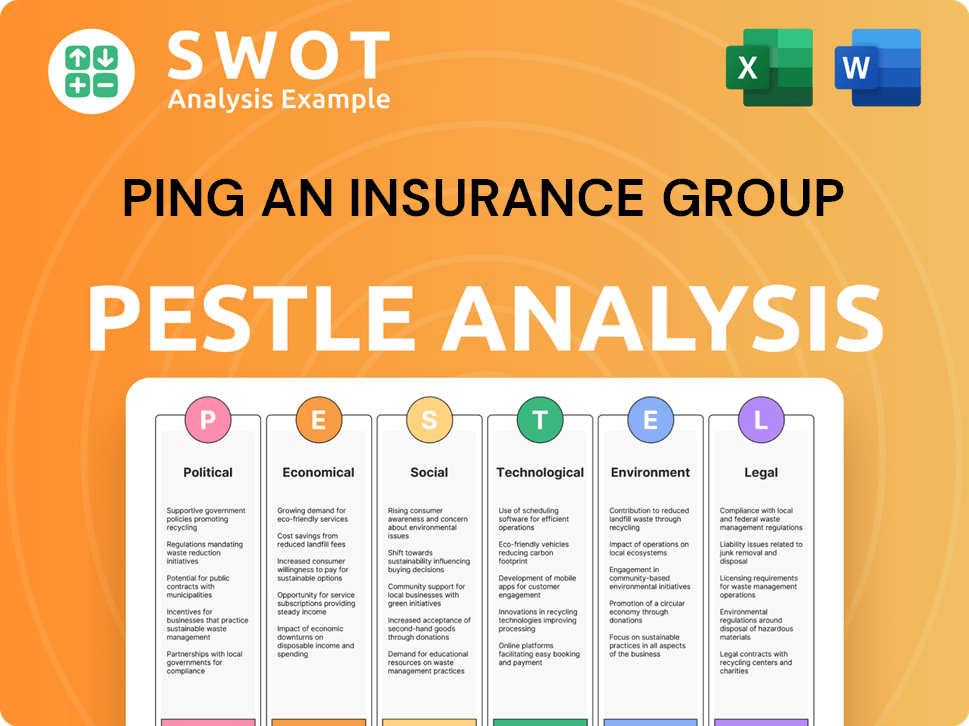
Ping An Insurance Group PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
Who Sits on Ping An Insurance Group’s Board?
The Board of Directors of Ping An Insurance Group, as of early 2025, is composed of executive directors, non-executive directors, and independent non-executive directors. This structure helps balance the interests of the diverse ownership base of the company. Non-executive directors often represent major shareholders, such as Shenzhen Investment Holdings Co., Ltd., or the CP Group, ensuring their perspectives are considered in strategic decisions. Ma Mingzhe, the founding chairman, continues to hold a position of significant influence.
The board's composition is regularly updated in the company's annual reports, reflecting changes in shareholder representation and the addition of independent expertise. This ensures that the board remains aligned with the evolving needs of the company and its stakeholders. The board's structure and the influence of key figures are critical aspects of understanding Ping An Group's governance.
| Director Category | Description | Representative Shareholders |
|---|---|---|
| Executive Directors | Responsible for the day-to-day operations and management. | Typically senior management of Ping An. |
| Non-Executive Directors | Represent major shareholders, ensuring their interests are represented. | Shenzhen Investment Holdings Co., Ltd., CP Group. |
| Independent Non-Executive Directors | Provide independent oversight and expertise. | Individuals with relevant industry or financial experience. |
Ping An operates under a one-share-one-vote structure for both its A-shares (Shanghai) and H-shares (Hong Kong). This means that voting power is directly proportional to share ownership. While there are no special voting rights, the concentration of shares among large institutional and state-backed entities, combined with the influence of the founding chairman, gives these entities significant voting power. The company's governance is subject to mainland China and Hong Kong regulatory frameworks, promoting transparency and accountability. For further insights into the company's strategic direction, consider reading about the Growth Strategy of Ping An Insurance Group.
The board includes executive, non-executive, and independent directors, balancing diverse interests. The Chairman, Ma Mingzhe, holds significant influence due to his founding role. The company uses a one-share-one-vote system, but major shareholders have considerable voting power.
- Board composition reflects a balance of interests.
- Shareholder influence is significant due to share concentration.
- Governance is subject to regulatory oversight in both mainland China and Hong Kong.
- Regular updates in annual reports reflect changes in representation.
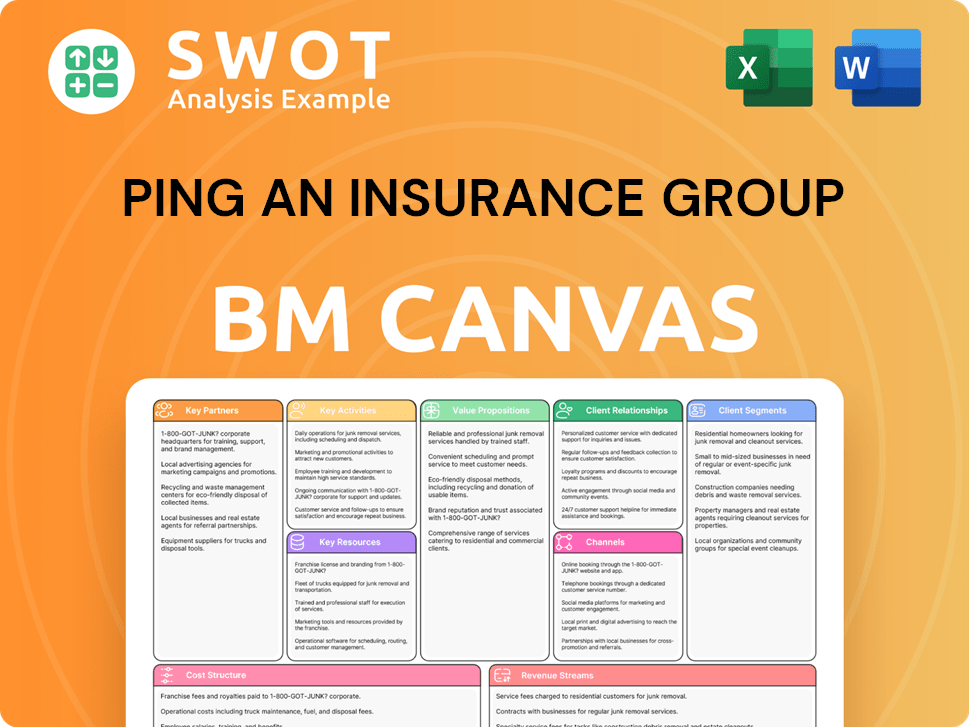
Ping An Insurance Group Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
What Recent Changes Have Shaped Ping An Insurance Group’s Ownership Landscape?
In the past few years, the ownership structure of Ping An Insurance Group has seen continued evolution. There has been a steady increase in institutional ownership. This is a reflection of the broader market's increasing inclusion of Chinese equities in global indices. This trend attracts both passive and active institutional investment. Brief History of Ping An Insurance Group provides further context on the company's development.
While significant share buybacks haven't been a major feature, the company continues to optimize its capital structure. There have been no major mergers or acquisitions that have fundamentally altered its core ownership structure. The company has been actively pursuing strategic investments in fintech and healthcare ventures. These actions, while not directly altering the parent company's ownership, reflect a strategic allocation of capital that can indirectly influence shareholder value.
| Metric | Data | Year |
|---|---|---|
| Market Capitalization (approx.) | $100 billion | 2024 |
| Institutional Ownership (approx.) | Over 60% | 2024 |
| Revenue (approx.) | $170 billion | 2023 |
Industry trends highlight a continuous focus on corporate governance and transparency, particularly for large financial conglomerates like Ping An. There's an increasing emphasis on environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors from regulators and investors. This can influence institutional investment decisions and, consequently, ownership distribution. Future ownership trends are likely to be influenced by China's evolving regulatory environment, the performance of its diverse business segments, and global investor sentiment towards Chinese assets.
Major institutional investors hold significant stakes in Ping An Insurance, reflecting confidence in the company's long-term prospects and its strategic direction. These investors often include global asset management firms and sovereign wealth funds.
ESG considerations are increasingly important for investors, influencing ownership decisions. Ping An's commitment to ESG practices can attract and retain investors. This enhances its appeal in the global market.
Ping An's investments in fintech and healthcare ventures show its strategic allocation of capital. These investments can drive growth and potentially influence shareholder value. They also reflect the company's diversification strategy.
China's regulatory environment plays a vital role in shaping Ping An's ownership landscape. Changes in regulations can affect investor confidence and influence ownership distribution. Compliance and transparency are key.
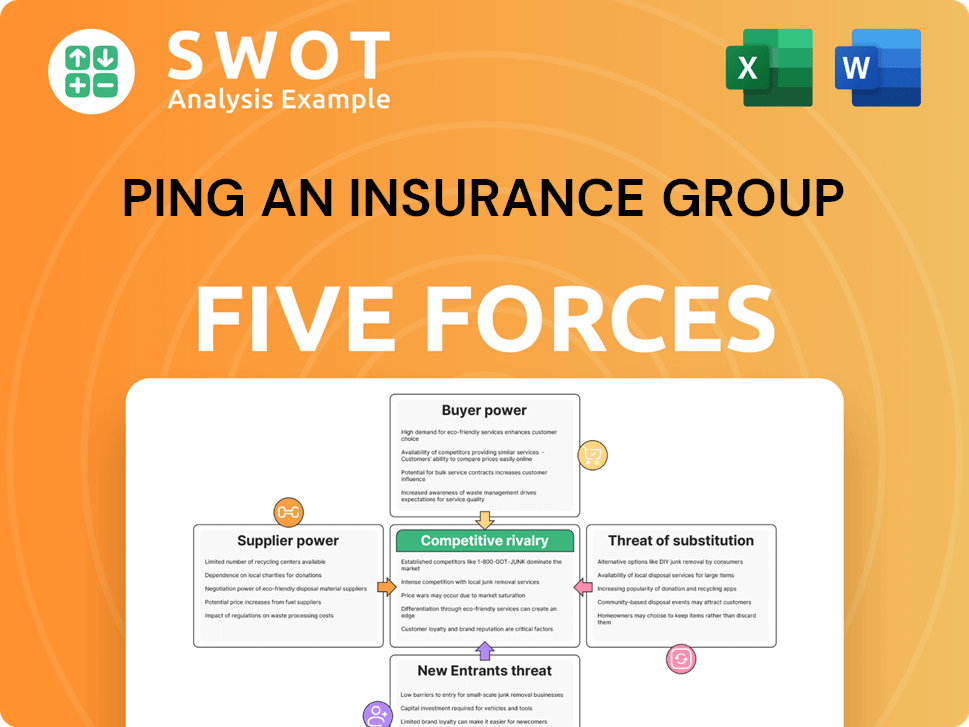
Ping An Insurance Group Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What are Mission Vision & Core Values of Ping An Insurance Group Company?
- What is Competitive Landscape of Ping An Insurance Group Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of Ping An Insurance Group Company?
- How Does Ping An Insurance Group Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of Ping An Insurance Group Company?
- What is Brief History of Ping An Insurance Group Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of Ping An Insurance Group Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.