Singapore Airlines Bundle
Who Really Owns Singapore Airlines?
Understanding the ownership of a global powerhouse like Singapore Airlines (SIA) is crucial for investors and strategists alike. Unraveling the intricacies of Singapore Airlines SWOT Analysis reveals how its ownership structure impacts its strategic decisions and market position. This deep dive explores the key stakeholders that shape the airline's destiny, from its governmental roots to its current public and institutional ownership.

The question of "Who owns Singapore Airlines?" goes beyond a simple shareholder list; it's about understanding the forces that drive this aviation leader. Examining the SIA ownership reveals the significant influence of the Singapore government and its impact on the airline's long-term vision and operational resilience. Exploring the Singapore Airlines parent company and its shareholders provides valuable insights for anyone looking to understand the airline's strategic direction and future prospects. This analysis will clarify whether Singapore Airlines is a publicly traded company and who controls Singapore Airlines.
Who Founded Singapore Airlines?
Understanding the ownership of Singapore Airlines (SIA) begins with its unique origins. Unlike many airlines with individual founders, SIA emerged from the split of Malaysia-Singapore Airlines (MSA) in 1972. This separation led to the creation of two distinct entities, with SIA focusing on Singapore's aviation needs.
The initial ownership structure of Singapore Airlines was straightforward. The Singapore government, through its Ministry of Finance, was the sole owner. This meant that from its inception, SIA was a state-owned enterprise, with the government holding 100% of the shares. This structure was crucial for aligning the airline's development with national strategic objectives.
The early days of Singapore Airlines saw no private investors or external shareholders. The government provided all the necessary capital, ensuring that decisions about fleet expansion, route development, and overall strategy were in line with Singapore's economic and connectivity goals. This centralized control facilitated the rapid establishment of Singapore as a major aviation hub.
The Singapore government was the sole owner at the beginning. This gave the government complete control over the airline's operations and strategy.
There were no early angel investors or private shareholders. All capital came directly from the government.
Government ownership ensured the airline's goals were in line with national development, particularly in establishing Singapore as a key aviation hub.
The government provided the necessary funds for fleet acquisition and network expansion, crucial for SIA's early growth.
The government's direct control allowed for quick decision-making and strategic alignment with national interests.
There were no ownership disputes or buyouts in the initial phase, as the ownership was centralized within the government.
The initial SIA ownership structure was unique because it was a direct result of the split from MSA, with the Singapore government as the sole shareholder. This ownership model was pivotal for aligning the airline's growth with Singapore's national interests. To learn more about the airline's history, you can read Brief History of Singapore Airlines.
- Singapore government ownership: The Singapore government initially owned 100% of Singapore Airlines.
- Strategic importance: This ownership structure was essential for developing Singapore as a key aviation hub.
- No early investors: There were no external shareholders in the initial phase.
- Governmental control: The government's control ensured alignment with national objectives.
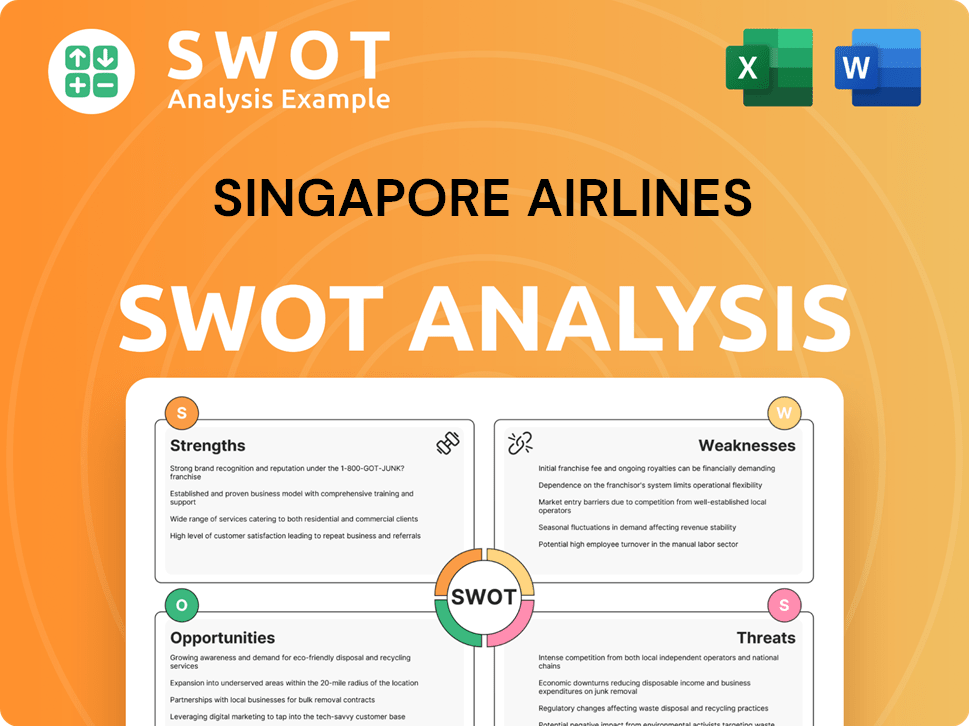
Singapore Airlines SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
How Has Singapore Airlines’s Ownership Changed Over Time?
The evolution of SIA ownership is a crucial aspect of understanding the airline's strategic direction. Initially, the company was fully state-owned. A pivotal shift occurred in 1985 when it was listed on the Singapore Exchange (SGX). This initial public offering (IPO) opened the door for broader public and institutional investor participation, marking a transition from complete government control to a mixed ownership model.
This move towards public ownership allowed for increased capital raising and enhanced market visibility, while still maintaining a significant level of government influence. This blend of public and state ownership has shaped the airline's long-term strategic planning, including major fleet renewal programs and network expansion initiatives, often with a view towards national economic benefits. The current SIA ownership structure reflects a balance between commercial viability and national interests.
| Event | Impact | Year |
|---|---|---|
| Initial State Ownership | Complete government control | Pre-1985 |
| IPO on SGX | Public ownership introduced, broader investor base | 1985 |
| Ongoing Ownership Structure | Majority stake held by Temasek Holdings, other shares held by public shareholders | Ongoing |
Today, the primary stakeholder in Singapore Airlines is Temasek Holdings (Private) Limited, the investment arm of the Singapore government. As of early 2025, Temasek typically holds between 50.9% and 56% of the company's shares. This substantial holding grants the Singapore government, through Temasek, effective control over the airline's strategic decisions. The remaining shares are held by a diverse group of public shareholders, including institutional investors, mutual funds, and individual retail investors. These diverse shareholders provide market liquidity and reflect investor confidence in SIA's performance. The continued majority ownership by Temasek ensures that the airline's strategy remains aligned with national interests, particularly in maintaining Singapore's status as a global aviation hub, while also operating as a commercially viable entity.
Understanding who owns Singapore Airlines is essential for investors and stakeholders. The ownership structure plays a significant role in shaping the company's strategic direction and operational decisions.
- Temasek Holdings: The major shareholder, representing the Singapore government.
- Institutional Investors: Hold a significant portion of the free float, including asset management firms.
- Public Shareholders: Include mutual funds, index funds, and individual investors.
- SIA shareholders: These stakeholders benefit from the airline's performance.
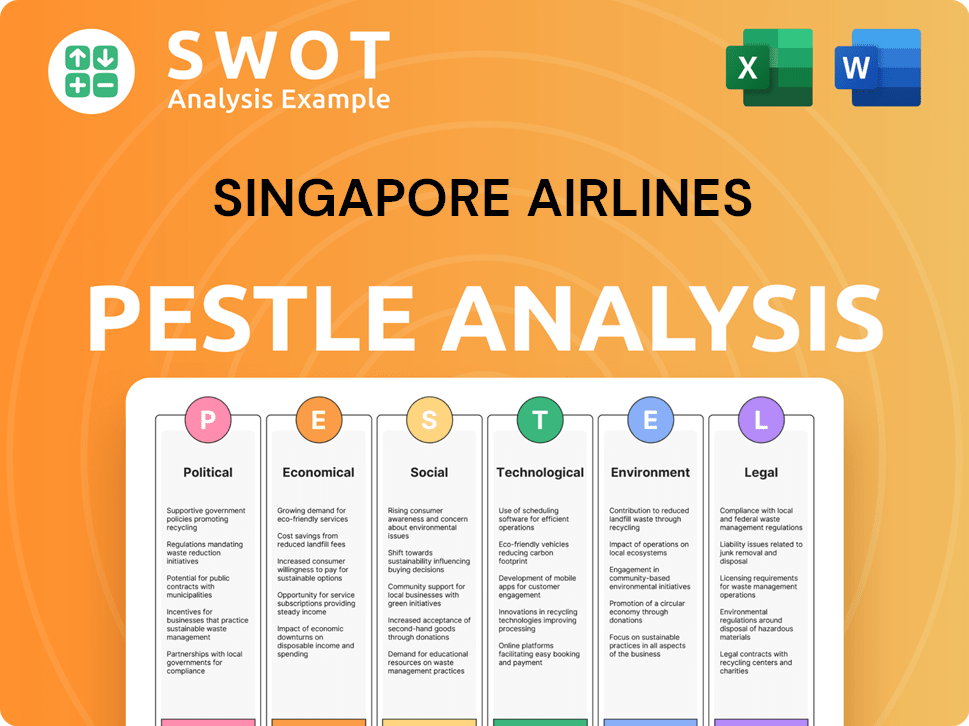
Singapore Airlines PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
Who Sits on Singapore Airlines’s Board?
The Board of Directors of Singapore Airlines (SIA) is pivotal in the company's governance, reflecting its ownership structure. The board typically includes representatives from major shareholders, independent directors, and executive directors. As of early 2025, the major shareholder, Temasek Holdings, often has representatives on the board, ensuring alignment with strategic objectives. The Chairman of the Board is often a prominent figure with strong ties to Singapore's business or governmental landscape. Understanding Competitors Landscape of Singapore Airlines is also crucial for grasping the broader industry dynamics that influence the board's decisions.
The board's composition and specific members can change, but the overall structure reflects the company's commitment to both commercial success and national interests. The board's decisions are subject to scrutiny from shareholders and the public, given the airline's national importance. Governance controversies are rare, reflecting a generally stable and well-managed corporate structure under the oversight of Temasek and the board.
| Board Member | Role | Affiliation |
|---|---|---|
| Goh Choon Phong | Chief Executive Officer | Singapore Airlines |
| Peter Seah | Chairman | Independent Director |
| Gillian Tan | Director | Temasek Holdings Representative |
Singapore Airlines operates primarily under a one-share-one-vote structure. This arrangement means that Temasek Holdings' majority stake directly translates into significant voting power, influencing key decisions. There are no publicly reported dual-class shares or special voting arrangements. The board plays a critical role in balancing commercial objectives with national strategic interests, ensuring the airline's long-term sustainability and competitiveness. As of March 2024, the market capitalization of Singapore Airlines was approximately $14.5 billion.
Temasek Holdings, the majority shareholder, significantly influences Singapore Airlines through board representation and voting power.
- The board balances commercial goals with national strategic interests.
- The one-share-one-vote structure ensures that voting power aligns with shareholding.
- The board's decisions are subject to scrutiny, reflecting the airline's importance.
- Governance is generally stable, with Temasek and the board providing oversight.
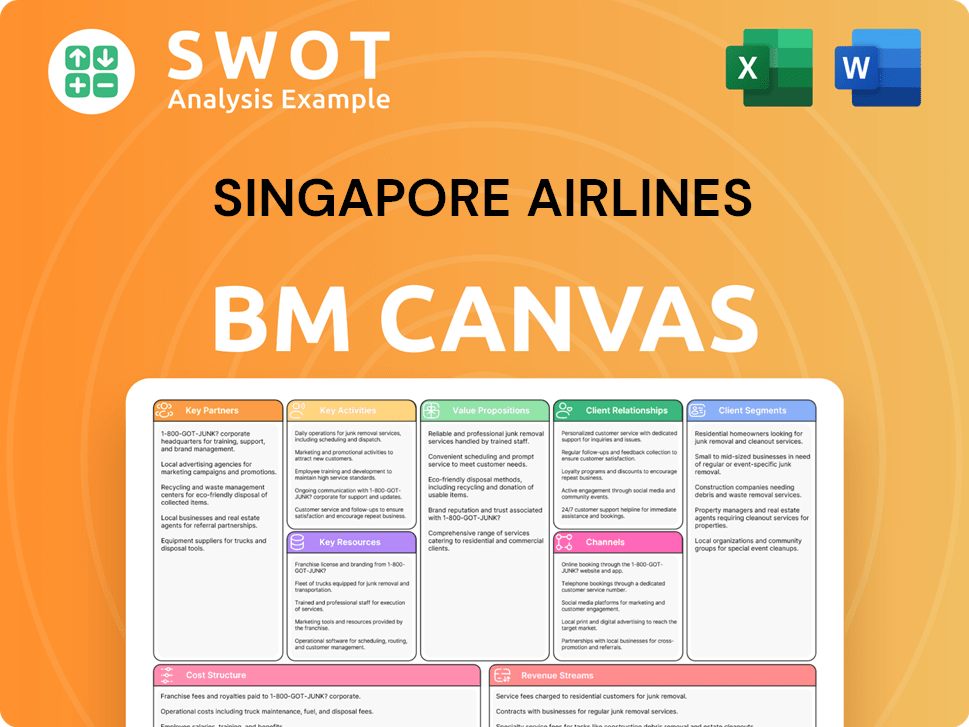
Singapore Airlines Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
What Recent Changes Have Shaped Singapore Airlines’s Ownership Landscape?
Over the past few years, the ownership structure of Singapore Airlines (SIA) has remained relatively stable. The impact of the global pandemic significantly influenced the aviation industry, leading SIA to undertake substantial capital-raising exercises. In 2020, SIA successfully raised approximately S$15 billion through a rights issue and convertible bonds. Temasek Holdings, the primary shareholder, underwrote a significant portion of this, reinforcing its commitment.
More recently, as the aviation industry recovers, SIA has focused on strengthening its balance sheet and resuming growth. While the core ownership structure, with Temasek's dominant position, hasn't seen major shifts, the airline has engaged in strategic partnerships and fleet modernizations. Industry trends show an increasing focus on environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors, which can influence investor behavior. For SIA, this could mean attracting more sustainability-focused investors. The focus remains on strategic growth, network expansion, and maintaining its competitive edge in a recovering market. For more insights, you can explore the Growth Strategy of Singapore Airlines.
| Key Aspect | Details | Recent Data |
|---|---|---|
| Major Shareholder | Temasek Holdings | Majority stake |
| Capital Raising (2020) | Rights issue and convertible bonds | S$15 billion |
| Industry Focus | ESG factors, strategic partnerships | Growing importance |
The SIA ownership structure is primarily characterized by Temasek Holdings' majority stake, reflecting a long-term commitment. The airline's response to the pandemic involved significant capital-raising efforts, with Temasek playing a crucial role. As the aviation sector recovers, SIA is concentrating on financial stability and strategic growth initiatives. There have been no public statements regarding privatization or major founder departures.
The ownership profile of Singapore Airlines has remained relatively stable in recent years, with Temasek Holdings maintaining its majority stake. This stability provides a strong foundation for the airline's strategic initiatives and long-term planning.
In response to the challenges posed by the pandemic, SIA undertook significant capital-raising exercises. Temasek Holdings played a crucial role in these efforts, underwriting a substantial portion of the rights issue and convertible bonds.
As the aviation industry recovers, SIA is focusing on strengthening its balance sheet and resuming growth. There's an increasing focus on environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors, which could influence investor behavior.
The focus remains on strategic growth, network expansion, and maintaining its competitive edge in a recovering market. There have been no public statements about potential privatization or major founder departures.
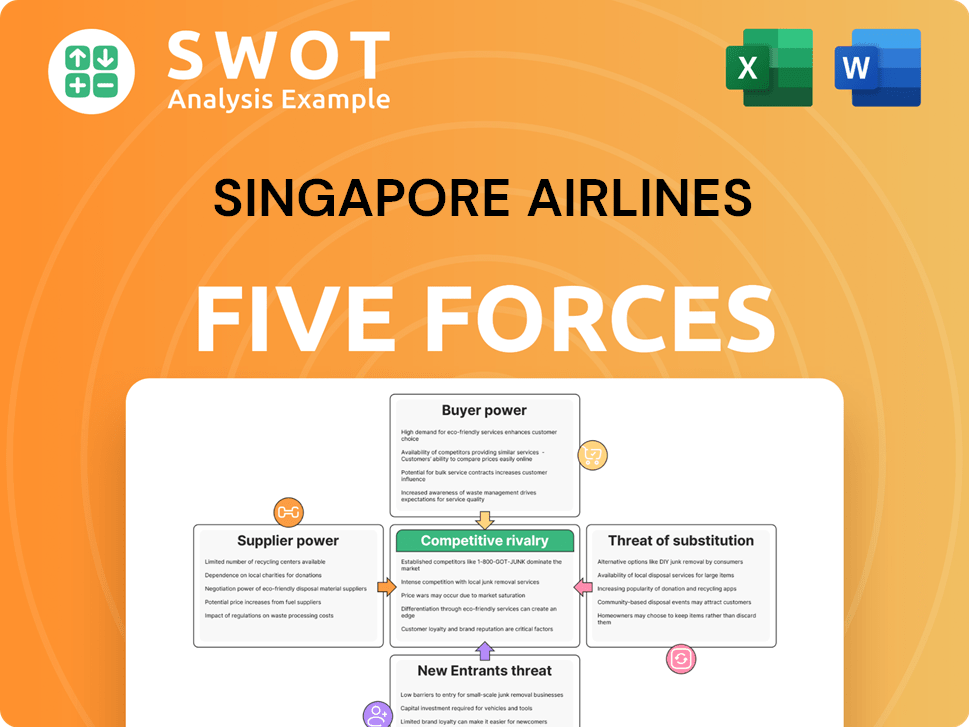
Singapore Airlines Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What are Mission Vision & Core Values of Singapore Airlines Company?
- What is Competitive Landscape of Singapore Airlines Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of Singapore Airlines Company?
- How Does Singapore Airlines Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of Singapore Airlines Company?
- What is Brief History of Singapore Airlines Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of Singapore Airlines Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.