Sumitomo Rubber Industries Bundle
Who Really Owns Sumitomo Rubber Industries?
Understanding a company's ownership structure is crucial for investors and strategists alike. Did you know that Sumitomo Rubber Industries (SRI), a leading tire manufacturer, recently finalized a significant acquisition that reshaped its brand portfolio? This pivotal move underscores the importance of understanding who controls a company and how it impacts its future.
The Sumitomo Rubber Industries SWOT Analysis reveals the intricacies of its corporate structure and strategic direction. As a prominent Japanese company, Sumitomo Rubber Industries's history is deeply intertwined with the Sumitomo Group, influencing its operational policies and strategic decisions. This article explores the evolution of Sumitomo ownership, providing insights into the key stakeholders and the factors shaping the SRI company's trajectory in the global market.
Who Founded Sumitomo Rubber Industries?
The initial ownership structure of Sumitomo Rubber Industries (SRI) is deeply intertwined with the Sumitomo Group. The company's origins trace back to 1909 when the Sumitomo Group invested in Dunlop Japan, a newly established Japanese subsidiary of the British company Dunlop Rubber. This investment marked the beginning of Sumitomo's involvement in the rubber and tire manufacturing sector in Japan.
While specific equity splits or initial shareholding percentages are not readily available, the establishment as a subsidiary of the Sumitomo Group indicates a foundational ownership and strategic direction guided by the larger conglomerate. This early structure set the stage for the future development of the SRI company.
A significant shift in early ownership occurred in 1963 when the Sumitomo Group acquired full control of Dunlop Japan, subsequently renaming it Sumitomo Rubber Industries Ltd. This acquisition solidified the Sumitomo Group's dominance in the company's ownership, reflecting the Sumitomo Group's long-term vision for the rubber industry. Early backers were primarily the Sumitomo Group itself, which, as a prominent keiretsu (conglomerate), facilitated cross-ownership of shares among its associated companies.
Sumitomo Group's investment in Dunlop Japan in 1909 marked the beginning of its involvement.
The Sumitomo Group provided foundational ownership and strategic direction.
In 1963, Sumitomo Group acquired full control of Dunlop Japan.
The Sumitomo Group, a keiretsu, facilitated cross-ownership among its associated companies.
The acquisition reflected the Sumitomo Group's long-term vision for the rubber industry.
Dunlop Japan was renamed Sumitomo Rubber Industries Ltd.
The history of Sumitomo Rubber Industries, a major tire manufacturer, is closely tied to the Sumitomo Group's strategic investments. The Sumitomo Group's initial investment in Dunlop Japan in 1909 marked the beginning of its involvement in the tire industry. The acquisition of full control in 1963 solidified the Sumitomo Group's ownership. For more details, you can read a Brief History of Sumitomo Rubber Industries.
- The Sumitomo Group's influence is central to the SRI company's corporate structure.
- The early ownership was primarily within the Sumitomo Group.
- The renaming to Sumitomo Rubber Industries Ltd. was a key step in its history.
- The Sumitomo Group's keiretsu structure facilitated ownership.
Sumitomo Rubber Industries SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
How Has Sumitomo Rubber Industries’s Ownership Changed Over Time?
The ownership of Sumitomo Rubber Industries (SRI), a prominent tire manufacturer, has evolved since its listing on the Tokyo Stock Exchange (TYO:5110) in 1980. As of June 2025, the company's market capitalization is approximately 432.61 billion JPY (around $3.02 billion USD). The corporate structure reflects a blend of Sumitomo Group influence and diverse institutional investment.
The Sumitomo Group maintains a significant stake in SRI. Sumitomo Electric Industries, Ltd., a key member of the Sumitomo Group, held 28.9% of the shares as of December 31, 2024. This illustrates the ongoing influence of the broader Sumitomo conglomerate. The remaining shares are held by a mix of institutional investors, including The Vanguard Group, Inc., BlackRock, Inc., and Nomura Asset Management Co., Ltd., among others. The top 25 shareholders collectively owned 59.45% of the company as of the end of 2024.
| Shareholder | Percentage of Shares (as of Dec 31, 2024) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Sumitomo Electric Industries, Ltd. | 28.9% | Key member of Sumitomo Group |
| The Vanguard Group, Inc. | Data not available | Institutional Investor |
| BlackRock, Inc. | Data not available | Institutional Investor |
Key events have shaped the ownership landscape of this Japanese company. The acquisition of Dunlop's automobile tire assets in 1985, including the right to use the Dunlop brand, was a pivotal move. More recently, in May 2025, SRI finalized the acquisition of the Dunlop brand rights for four-wheel consumer vehicle tires in Europe, North America, and Oceania from Goodyear. This acquisition, with a total cost of approximately $699 million, including brand rights, transition fees, and inventory, underscores SRI's strategic efforts to consolidate brand control and expand its global presence. For more insights into the company's financial performance, consider reading about the Revenue Streams & Business Model of Sumitomo Rubber Industries.
Sumitomo Electric Industries, Ltd. holds a significant stake in SRI, reflecting the influence of the Sumitomo Group.
- Institutional investors hold a substantial portion of the shares.
- Strategic acquisitions, like the Dunlop brand rights, have reshaped the company's market position.
- The company's market capitalization is approximately $3.02 billion USD as of June 2025.
- SRI continues to be a key player in the global tire industry.
Sumitomo Rubber Industries PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
Who Sits on Sumitomo Rubber Industries’s Board?
The Board of Directors of Sumitomo Rubber Industries (SRI) oversees the company's governance, closely tied to its ownership structure. As of March 2025, the company planned to reduce internal Directors by two and elect a total of 10 Directors to enhance oversight and streamline decision-making. Satoru Yamamoto holds the positions of Representative Director, President, and CEO. This structure is crucial for a major tire manufacturer like SRI, shaping its strategic direction and operational efficiency.
SRI's corporate governance emphasizes shareholder rights and value enhancement through stakeholder collaboration. The Nomination and Remuneration Committee, composed mainly of independent outside officers, carefully evaluates and recommends director candidates. The company's policy on cross-shareholdings aims to improve corporate value and strengthen business relationships. These practices directly impact how Sumitomo ownership influences the company's performance and market position within the Japanese company landscape.
| Director | Title | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Satoru Yamamoto | Representative Director, President, and CEO | |
Regarding voting, SRI exercises its rights for cross-shareholdings to boost the investee's and its own long-term value. In March 2025, Institutional Shareholder Services (ISS) recommended against the re-election of CEO Satoru Yamamoto due to the company's Return on Equity (ROE). The five-year average ROE was 4.1% for the fiscal year ending December 2024. However, excluding a one-time impairment loss, the adjusted ROE would have been 9.4%, and the five-year average would be 5.7%. This illustrates how proxy advisor recommendations can influence shareholder decisions, even within the standard one-share-one-vote voting structure. For more insights into the company's strategic direction, consider reading about the Growth Strategy of Sumitomo Rubber Industries.
SRI's board structure and governance policies are designed to protect shareholder interests and improve corporate value.
- The Nomination and Remuneration Committee plays a key role in selecting directors.
- Cross-shareholding policies are in place to enhance business relationships and long-term value.
- Proxy advisor recommendations can significantly influence shareholder voting decisions.
- Focus on ROE highlights the importance of financial performance in governance.
Sumitomo Rubber Industries Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
What Recent Changes Have Shaped Sumitomo Rubber Industries’s Ownership Landscape?
Over the past few years, Sumitomo Rubber Industries has been reshaping its corporate structure and strategic focus. A significant move was the acquisition of the Dunlop brand trademark rights for four-wheel consumer vehicles in key markets, finalized in May 2025. This strategic acquisition, valued at approximately $701 million, aims to bolster the global expansion of the Dunlop brand under Sumitomo Rubber's complete control. This is expected to significantly impact Sumitomo ownership, with projections of an annual revenue increase of $500 million or more, fully realized in fiscal year 2026 and beyond.
Another notable development is the decision to cease tire production in the U.S. and dissolve Sumitomo Rubber USA, LLC (SRUSA), announced in November 2024. This restructuring, part of a mid-term plan focusing on core business segments, led to a restructuring cost of 11.7 billion yen in fiscal year 2023 and an impairment loss of 69.4 billion yen in fiscal year 2024. Research and development activities previously at SRUSA will be transferred to SRI America, Inc., maintaining its presence in North America. These actions reflect a strategic shift within the SRI company to optimize global production and concentrate resources.
| Fiscal Year | Sales Revenue (Billion Yen) | Business Profit (Billion Yen) |
|---|---|---|
| 2024 | 1,211.9 | 87.9 |
| Q1 2025 | 287.8 | 14.1 |
Financially, Sumitomo Rubber Industries reported record business profits of 87.9 billion yen and sales revenue of 1,211.9 billion yen for the fiscal year ending December 31, 2024. However, net earnings decreased by 73.4% to $65.1 million due to the U.S. factory closure. For the first quarter of 2025, sales revenue was ¥287.8 billion, with a business profit of ¥14.1 billion, although profit attributable to owners of the parent decreased by 85.7% to ¥3.56 billion. The company anticipates a 3.2% sales growth for fiscal year 2025. These financial results influence the strategic decisions regarding Sumitomo ownership and future investments.
Acquisition of Dunlop brand rights for $701 million, aiming for significant revenue growth.
Closure of U.S. tire production and dissolution of SRUSA, impacting financial results.
Record business profit in 2024, but net earnings affected by one-time losses in Q1 2025.
Continued reduction of policy shareholdings, with sales generating 4.8 billion JPY in fiscal year 2024.
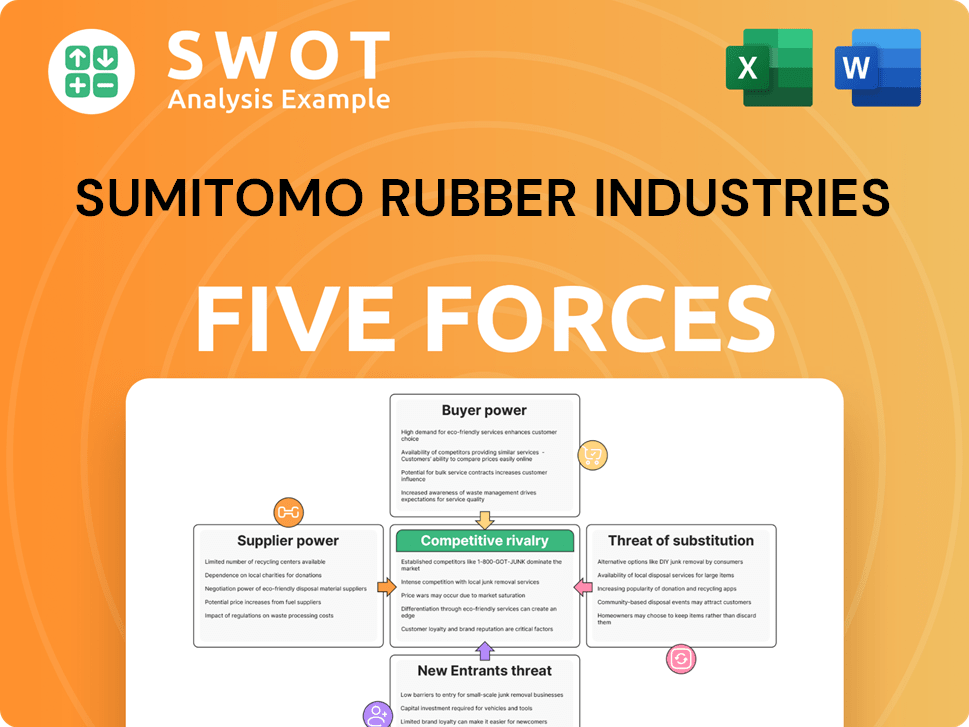
Sumitomo Rubber Industries Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What are Mission Vision & Core Values of Sumitomo Rubber Industries Company?
- What is Competitive Landscape of Sumitomo Rubber Industries Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of Sumitomo Rubber Industries Company?
- How Does Sumitomo Rubber Industries Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of Sumitomo Rubber Industries Company?
- What is Brief History of Sumitomo Rubber Industries Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of Sumitomo Rubber Industries Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.