TC Energy Bundle
Who Really Owns TC Energy?
Understanding the ownership structure of a major TC Energy SWOT Analysis is key to grasping its strategic direction and market influence. With increasing investor focus on environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors, the makeup of a company's shareholder base has never been more critical. This article dives into the ownership of TC Energy, a prominent North American energy infrastructure company, to uncover the key players shaping its future.

From its origins as TransCanada PipeLines Limited in 1951 to its current status, TC Energy's ownership has evolved considerably. Exploring "Who owns TC Energy" reveals a complex interplay of institutional investors, individual shareholders, and a board of directors guiding its path. This exploration of TC Energy ownership will examine the major stakeholders, key events, and recent trends impacting this pipeline company.
Who Founded TC Energy?
The entity now known as TC Energy, originally incorporated as TransCanada PipeLines Limited on October 25, 1951, emerged from a collaborative effort. This initiative involved several Canadian natural gas producers and pipeline companies. Their primary objective was to transport natural gas from Western Canada to markets in the east.
While pinpointing specific individual founders with precise equity splits is challenging due to the nature of the company's formation, the early ownership structure of TC Energy was characterized by a consortium of Canadian energy interests. Companies like Canadian Delhi Oil played a significant role in the early development of Canadian natural gas resources, contributing to the foundational structure of the company.
The initial capitalization of TC Energy was achieved through a combination of equity and debt. This approach reflected the substantial investment required for such a large-scale infrastructure project. Early financial backing primarily came from institutional investors and other energy companies. They recognized the strategic importance of a trans-Canadian pipeline.
The early ownership of TC Energy was a collective effort, involving multiple Canadian energy companies and investors.
The company's initial capital was raised through a combination of equity and debt.
Early backers included institutional investors and other energy companies.
The founding team's vision was to establish a unified Canadian natural gas transmission system.
Early agreements focused on securing capital and regulatory approvals for the pipeline project.
The project garnered broad-based support from various stakeholders in the Canadian energy industry.
The early agreements were crucial for securing the necessary capital and regulatory approvals for the ambitious pipeline project. The vision of the founding team, which aimed to create a unified Canadian natural gas transmission system, was reflected in the widespread backing from various stakeholders within the Canadian energy industry. This broad support was essential to ensure the efficient and reliable delivery of energy across the country. To understand more about the company's financial aspects, you can read about the Revenue Streams & Business Model of TC Energy.
The initial formation of TC Energy involved a consortium of Canadian energy companies and investors, aiming to transport natural gas across Canada. Early funding came from a mix of equity and debt, with institutional investors playing a key role. The company's vision was supported by various stakeholders to ensure reliable energy delivery. As of 2024, the company continues to be a significant player in the North American energy market.
- The company was initially named TransCanada PipeLines Limited.
- Early ownership was characterized by a consortium of Canadian energy interests.
- Initial capital was raised through equity and debt.
- The project aimed to create a unified Canadian natural gas transmission system.
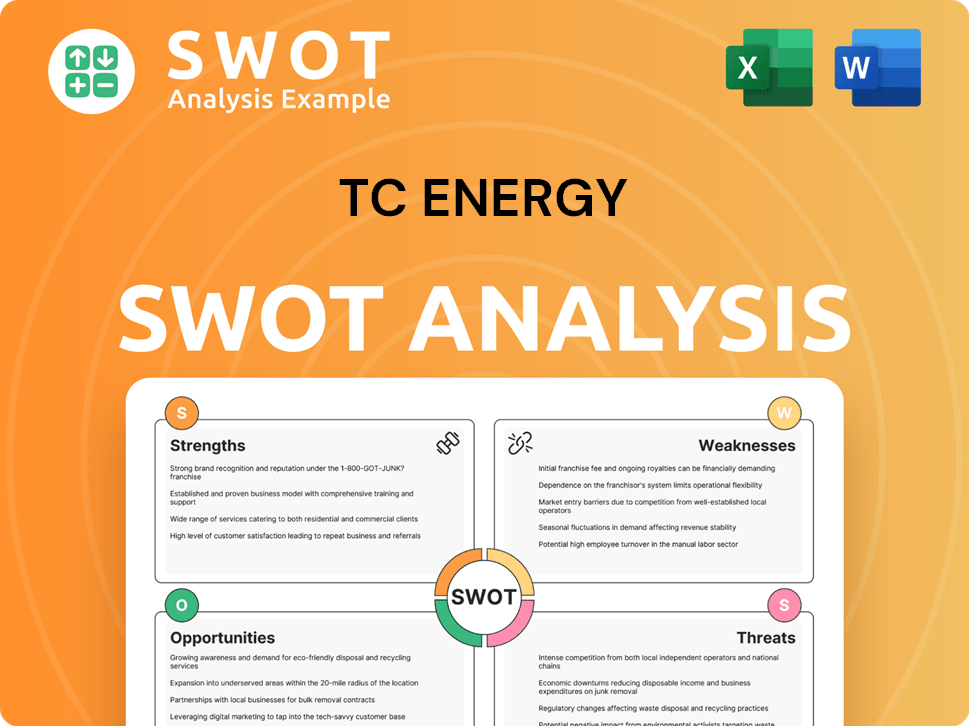
TC Energy SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
How Has TC Energy’s Ownership Changed Over Time?
The evolution of TC Energy's ownership structure has been marked by significant shifts, particularly following its initial public offering (IPO). This transition transformed the company into a publicly traded entity, opening it up to a diverse range of investors. The IPO was a pivotal event, enabling the company to raise capital and expand its operations, which in turn influenced its ownership dynamics over time. As the company grew, its ownership base became increasingly diversified, reflecting the broader market trends and investor preferences.
The current ownership landscape of TC Energy is dominated by institutional investors. These entities, including large asset management firms and index funds, hold a substantial portion of the company's shares. This concentration of ownership among institutional investors has a notable impact on the company's strategic direction and governance practices. The presence of these major shareholders often leads to a greater emphasis on shareholder value, dividend policies, and consistent financial performance. The continuous reporting of institutional holdings, as seen through SEC filings and annual reports, provides ongoing transparency into the evolving shareholder base.
| Shareholder | Percentage of Shares (as of March 31, 2024) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| The Vanguard Group, Inc. | 5.34% | A significant institutional investor. |
| BlackRock Inc. | 4.41% | Another major institutional holder. |
| RBC Global Asset Management Inc. | 2.80% | Part of a large financial institution. |
| BMO Asset Management Inc. | 2.50% | Another major financial institution. |
| Total Institutional Ownership | 60.19% | Reflects the dominance of institutional investors. |
The shift towards institutional ownership, common in large, mature public companies like TC Energy, has several implications. It generally leads to a greater focus on corporate governance and transparency. Institutional investors often have specific requirements and expectations regarding financial performance and strategic direction. This can result in a more disciplined approach to capital allocation, risk management, and overall corporate strategy. The influence of these major shareholders is a key factor in understanding the current dynamics of TC Energy's ownership and its future trajectory.
TC Energy's ownership structure has evolved significantly since its IPO, with institutional investors holding a substantial portion of shares.
- The Vanguard Group, Inc. and BlackRock Inc. are among the major institutional holders.
- Institutional ownership totaled 60.19% as of March 31, 2024.
- This ownership structure influences company strategy and governance.
- Increased focus on shareholder value, dividends, and financial performance.
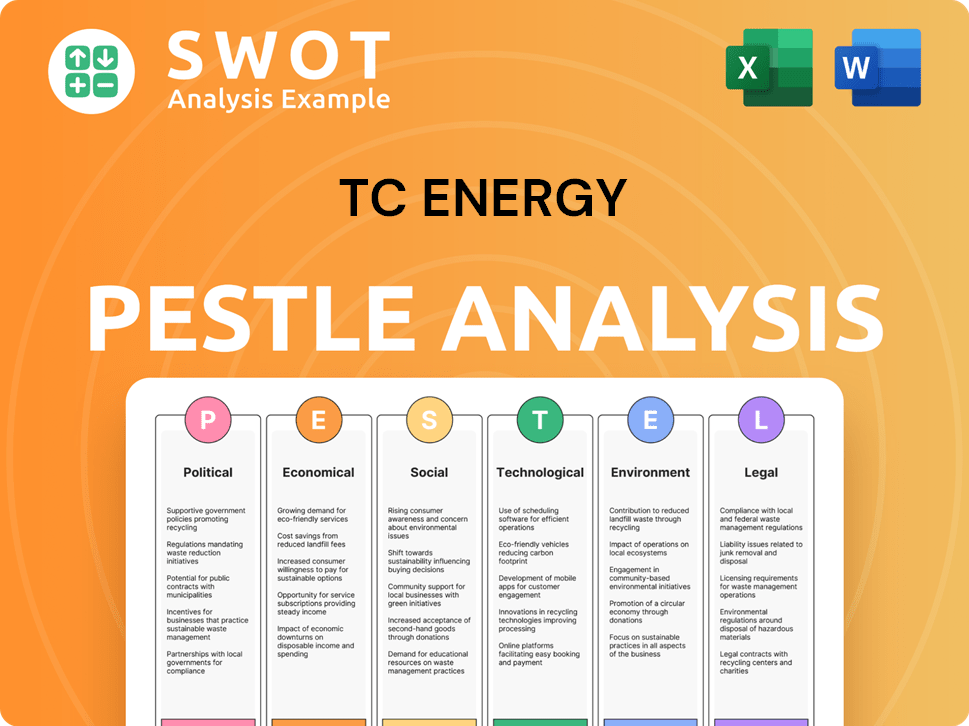
TC Energy PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
Who Sits on TC Energy’s Board?
The Board of Directors of TC Energy plays a vital role in the company's governance and strategic oversight, representing the interests of its shareholders. As of April 2024, the board includes independent directors and those with extensive experience in the energy and finance sectors. The board members include individuals such as Siim A. Vanaselja, who serves as the Chair, and other directors like Una Power and Mary Pat Salomone. The directors are expected to act in the best interests of all shareholders.
The board's composition reflects a commitment to diverse expertise and perspectives, ensuring robust oversight of the company's operations and strategic initiatives. This structure is typical for a publicly traded energy company like TC Energy, which prioritizes both operational excellence and shareholder value. The board's role includes overseeing financial performance, risk management, and compliance with regulatory requirements, ensuring the company's long-term sustainability and success.
| Board Member | Position | Key Experience |
|---|---|---|
| Siim A. Vanaselja | Chair | Extensive experience in finance and corporate governance. |
| Una Power | Director | Experience in the energy sector and financial management. |
| Mary Pat Salomone | Director | Background in corporate strategy and risk management. |
TC Energy generally operates under a one-share-one-vote structure, meaning each common share typically carries one vote. This standard voting arrangement ensures that voting power is directly proportional to the number of shares owned. The company's governance practices are guided by Canadian corporate law and stock exchange regulations, which emphasize transparency and accountability. In recent years, like many large corporations, TC Energy has faced scrutiny regarding its environmental and social performance, which can sometimes lead to activist investor campaigns or proxy battles focused on governance issues or sustainability initiatives.
TC Energy's governance structure is designed to protect shareholder interests and ensure accountability. The company operates under a one-share-one-vote system, granting voting power proportional to share ownership.
- One-share-one-vote structure.
- Board composed of experienced directors.
- Focus on transparency and accountability.
- Compliance with Canadian corporate law.
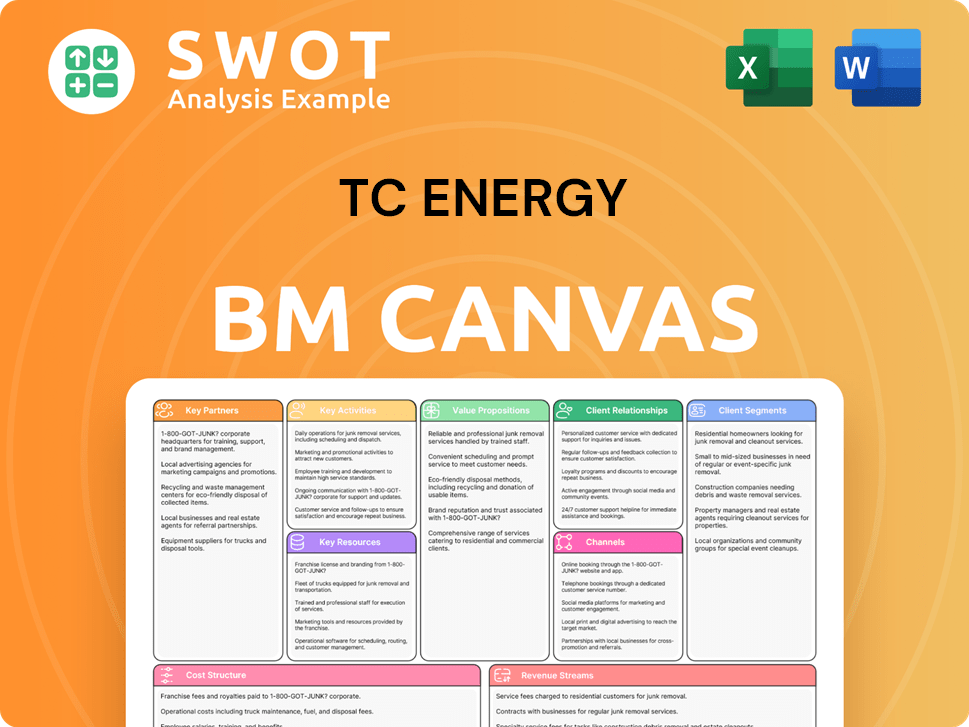
TC Energy Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
What Recent Changes Have Shaped TC Energy’s Ownership Landscape?
Over the past few years, the ownership landscape of TC Energy has been significantly influenced by strategic decisions and broader industry trends. A key development has been the spin-off of its liquids pipeline business, now known as South Bow, which was announced in 2023 and is expected to be completed in mid-2024. This move is set to reshape TC Energy's asset portfolio and potentially its investor base. This will inevitably lead to shifts in TC Energy ownership as investors decide whether to hold shares in both entities.
The energy sector's focus on streamlining operations and core competencies is evident in this strategic move. Other trends impacting TC Energy ownership include the growing influence of ESG-focused institutional investors. These investors are increasingly scrutinizing companies' environmental performance and governance practices. This can lead to shifts in institutional holdings as funds rebalance their portfolios based on sustainability criteria. The company's capital expenditure plans, particularly for its natural gas pipeline projects, will also influence future ownership. The company's commitment to long-term shareholder value, often through strategic divestitures and investments in growth areas, is consistently emphasized in public statements.
| Metric | Details | Recent Data (2024/2025) |
|---|---|---|
| Market Capitalization | Reflects the total value of outstanding shares. | Approximately $45 billion (as of early 2024) |
| Institutional Ownership | Percentage of shares held by institutional investors. | Around 65%-70% |
| ESG Investment Impact | Influence of ESG criteria on investment decisions. | Increasingly significant, with funds allocating more capital based on ESG ratings |
Understanding the evolution of TC Energy ownership requires considering both company-specific actions and broader market dynamics. The spin-off of South Bow is a pivotal event, and the company's commitment to long-term shareholder value will continue to shape its ownership profile. For more insights into the company's history, consider reading Brief History of TC Energy.
TC Energy has been actively managing its portfolio, including the spin-off of its liquids pipeline business. This strategic move allows the company to focus on its core strengths.
ESG factors are increasingly important to institutional investors. TC Energy is likely to be affected by these trends. This can lead to shifts in institutional holdings based on sustainability criteria.
TC Energy's capital expenditure plans for natural gas pipeline projects will influence future ownership structures. These investments are a key part of their business strategy.
The company emphasizes long-term shareholder value through strategic divestitures and investments in growth areas. This is a key focus for TC Energy.
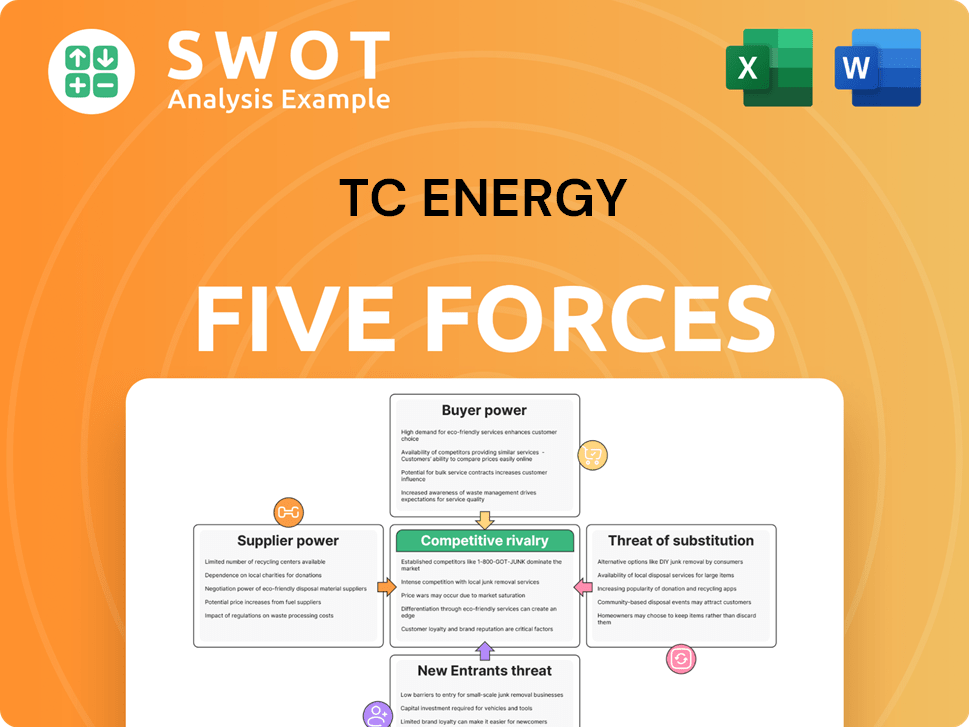
TC Energy Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What are Mission Vision & Core Values of TC Energy Company?
- What is Competitive Landscape of TC Energy Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of TC Energy Company?
- How Does TC Energy Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of TC Energy Company?
- What is Brief History of TC Energy Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of TC Energy Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.