CSX Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
CSX Bundle
What is included in the product
Tailored exclusively for CSX, analyzing its position within its competitive landscape.
Clean, simplified layout—ready to copy into pitch decks or boardroom slides.
Same Document Delivered
CSX Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete CSX Porter's Five Forces analysis—exactly what you’ll download immediately after purchase. It examines industry rivalry, supplier power, buyer power, threat of substitutes, and threat of new entrants. You'll receive a comprehensive, ready-to-use document, meticulously researched and formatted. No revisions needed; it’s ready for your immediate use. The preview accurately reflects the final deliverable.
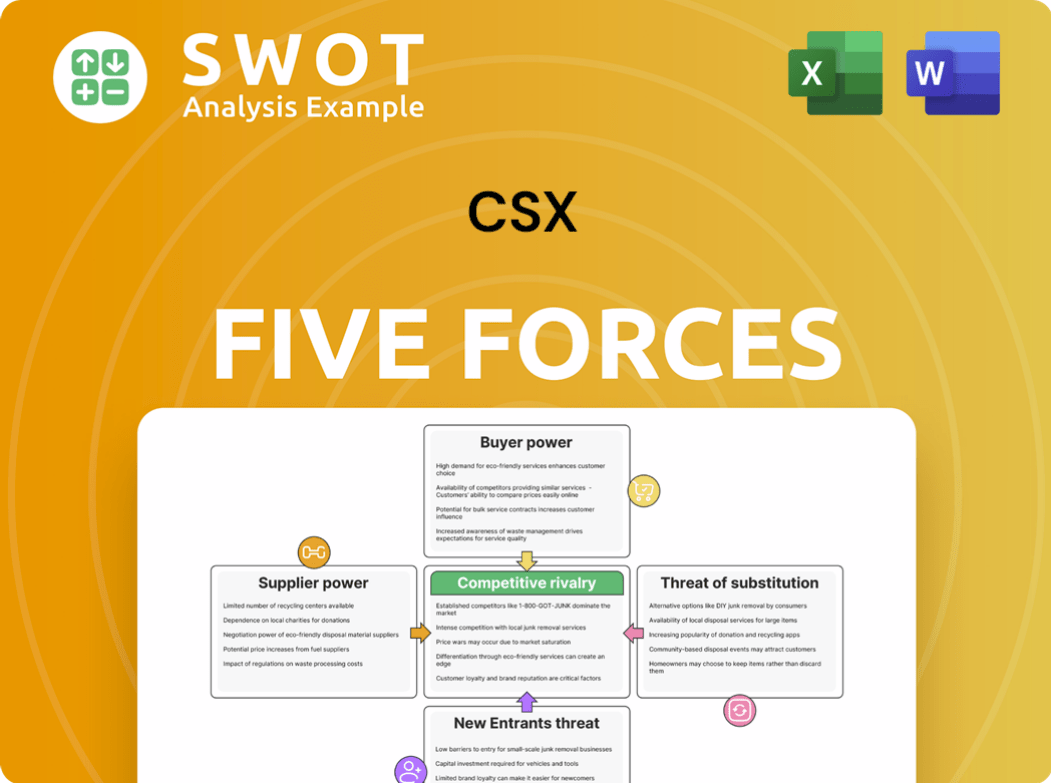
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Template
CSX's industry landscape is shaped by powerful forces. Buyer power, influenced by shipping alternatives, is a key factor. Supplier power, particularly from rail equipment providers, also plays a significant role. The threat of new entrants, though moderate, adds complexity. Competitive rivalry, especially with other railroads, is high. Finally, the threat of substitutes, like trucking, constantly challenges CSX.
Ready to move beyond the basics? Get a full strategic breakdown of CSX’s market position, competitive intensity, and external threats—all in one powerful analysis.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The locomotive market is controlled by a few companies like Wabtec and GE. This concentration gives them strong bargaining power over CSX. For example, in 2024, Wabtec reported revenues of $9.2 billion. CSX depends on these suppliers, making it vulnerable to price hikes and supply issues.
CSX heavily relies on steel for its railway infrastructure, sourcing from suppliers like ArcelorMittal and EVRAZ North America. In 2024, steel prices saw fluctuations, impacting costs. CSX's large procurement volumes enable it to negotiate favorable terms. This helps to offset supplier power, maintaining cost control despite market volatility.
The railway industry relies on specialized, expensive equipment. Locomotives can cost upwards of $2-3 million to replace. Switching suppliers for tracking systems means significant investment and training for CSX.
High switching costs amplify supplier power, decreasing CSX's flexibility. CSX's capital expenditures for 2024 reached $2.11 billion. This makes CSX less likely to switch suppliers frequently.
Concentrated supply chain for critical rail components
The supply chain for essential rail components like brake systems and signal equipment is quite concentrated, giving suppliers significant leverage. CSX faces limited choices for these specialized parts, which strengthens suppliers' bargaining power. This concentration means that any supply disruptions or price hikes from these key suppliers can severely affect CSX's operations and costs. For example, in 2024, the cost of railcar parts increased by approximately 7%, impacting overall operating expenses.
- Concentrated supplier base limits CSX's options.
- Specialized components increase supplier power.
- Disruptions or price hikes directly impact CSX.
- In 2024, railcar parts cost rose by roughly 7%.
Supplier reliance on railroad companies
Suppliers to CSX, such as those providing railcars or maintenance services, often depend on the railroad for a significant portion of their revenue. This reliance typically reduces their bargaining power. CSX's large orders and consistent demand strengthen its position. Maintaining good relationships is crucial for suppliers to secure contracts.
- CSX's 2023 revenue was approximately $14.7 billion, highlighting its market influence.
- Suppliers' ability to switch customers is limited due to industry-specific needs.
- Strong supplier relationships are vital for CSX's operational efficiency.
CSX faces concentrated supplier power from locomotive and specialized component providers. Switching costs and supply chain concentration amplify supplier leverage, impacting operations. In 2024, railcar part costs rose approximately 7%, affecting expenses.
| Supplier Aspect | Impact on CSX | 2024 Data |
|---|---|---|
| Locomotive Market | High supplier power | Wabtec 2024 Revenue: $9.2B |
| Steel Suppliers | Moderate, offset by volume | Steel price fluctuations |
| Switching Costs | Limits flexibility | 2024 CapEx: $2.11B |
Customers Bargaining Power
CSX serves diverse sectors like agriculture, chemicals, and autos. Agriculture is a major freight source, impacting pricing and service. Large clients, such as those in agriculture, can pressure CSX. They negotiate favorable rates due to high shipping volumes. In 2024, agricultural products represented roughly 15% of CSX's total revenue.
Customers of CSX have multiple transportation alternatives, such as trucking, air freight, and intermodal options. Trucking accounts for a substantial portion of U.S. freight transport, holding over 60% market share in 2024. This availability grants customers considerable bargaining power. They can readily shift to alternative modes if CSX's costs are unfavorable or service quality declines.
CSX's customers' price sensitivity fluctuates based on cargo type and transport alternatives. High-value goods shippers might be less sensitive to price changes versus bulk commodity clients. This price sensitivity significantly impacts their negotiation power with CSX. In 2024, CSX's revenue was approximately $14.8 billion. The volume of merchandise transported is also crucial.
Intermodal competition
CSX contends with rivals in intermodal transport. In 2023, intermodal revenue was a significant part of CSX's total. Strong intermodal competition boosts customer power, letting them pick the best deal. Trucking offers a competitive edge, while superior CSX service expands intermodal opportunities.
- 2023 intermodal revenue percentage of total revenue: Approximately 35%.
- Key competitors in intermodal: Norfolk Southern, BNSF Railway.
- Trucking market share of freight transport: Around 69% in 2024.
- CSX's focus: Improving service to attract customers from trucking.
Customer switching costs
Customer switching costs in the transportation industry are generally moderate. Customers can switch between rail and trucking services based on price and service quality. This flexibility gives customers leverage. In 2024, the trucking industry's revenue was approximately $800 billion, highlighting the availability of alternative options. Lower switching costs mean buyers have more power.
- Moderate switching costs empower customers.
- Customers can choose between rail and trucking.
- The trucking industry generated around $800B in revenue in 2024.
- Buyer power increases with easier switching.
Customer bargaining power at CSX is significant due to several factors. Large clients, like those in agriculture (15% of 2024 revenue), can negotiate better rates. They have alternatives, such as trucking (69% market share in 2024), giving them leverage.
| Factor | Impact | 2024 Data |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Size | Higher Power | Agriculture: 15% Revenue |
| Alternatives | Increased Power | Trucking: 69% Market Share |
| Switching Costs | Moderate | Trucking Industry: $800B Revenue |
Rivalry Among Competitors
CSX faces intense competition from Norfolk Southern, a major Class I railroad in the Eastern U.S. These rivals battle for customers and freight across their networks. The competition can drive down prices, impacting profit margins. In 2024, both companies focused on operational efficiency to manage costs amidst the rivalry.
The railroad industry shows a concentrated market, heightening competition among major firms. CSX, along with its rivals, battles for market share, intensifying rivalry. CSX's strategy includes industrial development, boosting its competitive edge. In 2024, CSX reported revenues of $14.79 billion, showcasing its market presence. This reinforces its strategic positioning within the competitive landscape.
Railroads compete by differentiating services, focusing on reliability and network reach. Superior service boosts intermodal opportunities, facing truck competition. CSX's investments in technology and infrastructure aim for reliable delivery. In 2024, CSX's operating ratio was around 60%, reflecting efficiency efforts.
Pricing strategies
Competitive rivalry in the railroad industry, including CSX, often intensifies through aggressive pricing strategies. Railroads typically implement inflation-plus pricing models. However, competitive pressures can squeeze profitability, particularly during economic slowdowns or when freight volumes decline. For example, in 2023, CSX's operating ratio was around 61.9%, which reflects the efficiency of their operations, but pricing strategies can still influence this.
- CSX's 2023 revenue was approximately $14.7 billion.
- The industry's pricing strategies are crucial for maintaining market share.
- Economic downturns intensify pricing pressures.
- Inflation-plus pricing is a common industry practice.
Industry cyclicality
The transportation sector, including rail freight, is set for a cyclical recovery, influencing competitive dynamics. This cyclicality sharpens rivalry, especially during downturns, as companies fight for volume and revenue. Tightening freight conditions are expected to benefit CSX. In 2024, CSX's operating ratio improved, showing efficiency gains amidst fluctuating market conditions.
- Rail traffic experienced volatility in 2024, with fluctuations in carloads and intermodal units.
- CSX's revenue and profitability are closely tied to overall economic activity.
- The cyclical nature demands strategic agility from CSX.
CSX's competitive landscape is significantly influenced by its rivalry with Norfolk Southern. This competition affects pricing and profit margins, compelling both companies to focus on operational efficiency. In 2024, CSX's revenues reached $14.79 billion, showcasing its market presence. CSX's operating ratio in 2024 was approximately 60%, demonstrating its efforts to navigate intense competition.
| Metric | 2023 | 2024 |
|---|---|---|
| Revenue (USD billions) | 14.7 | 14.79 |
| Operating Ratio (%) | 61.9 | ~60 |
| Market Share | Variable | Focused on Growth |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The trucking industry poses a considerable threat to CSX as a substitute. Trucking accounts for a large share of U.S. freight, with over 70% of the total. This dominance is thanks to its flexibility and expansive road network. In 2024, the trucking industry's revenue is projected to be around $800 billion, underscoring its strong position as a substitute.
Barging serves as a substitute for CSX, particularly for bulk commodities using waterways. However, existing barge users likely already utilize this method, diminishing its threat to CSX's current volume. In 2024, barges transported approximately 14% of all U.S. freight. Barging's slower speed restricts its suitability for time-sensitive goods.
Pipelines act as a substitute for CSX, primarily for liquids and gases, like petroleum and natural gas, with a 2024 market share of approximately 20% for freight transportation. They are cost-effective for these specific goods, yet lack the versatility of rail. This limits the overall threat to CSX's diverse freight offerings. However, the competition remains notable in the energy sector. The pipeline industry generated about $140 billion in revenue in 2023.
Air freight
Air freight serves as a substitute for CSX, particularly for high-value or time-critical shipments. The air freight market in the United States generates substantial revenue annually. However, air freight is considerably more expensive than rail transport, which makes it less appealing for many shippers. This cost difference limits the threat posed by air freight to CSX.
- Air freight revenue in the U.S. was approximately $34.5 billion in 2023.
- Air freight is typically 4-5 times more expensive than rail.
- CSX's primary focus is on bulk and intermodal transport.
- Time-sensitive goods are the main target for air freight.
Intermodal competition as substitution
CSX faces substitution threats from intermodal competition, blending transport modes. Intermodal solutions, like combining rail with trucking, pose a significant challenge. CSX's intermodal revenue is a key metric to watch. The viability of these substitutes hinges on cost and service quality. In 2024, CSX's intermodal revenue accounted for a substantial portion of its overall revenue, reflecting its importance.
- Intermodal transport combines rail and trucking.
- CSX's intermodal revenue is vital.
- Cost and service drive substitution.
- Rail historically cheaper than trucking.
CSX faces substitution risks from various modes. Trucking, the dominant substitute, generates around $800 billion in 2024 revenue. Barging and pipelines offer alternatives, particularly for bulk goods and liquids. Air freight, while expensive, targets high-value, time-sensitive shipments.
| Substitute | 2024 Revenue/Market Share | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Trucking | $800B | Flexibility, road network |
| Barging | 14% of U.S. freight | Bulk commodities, slower speed |
| Pipelines | 20% of U.S. freight (approximate) | Liquids and gases, cost-effective |
| Air Freight (2023) | $34.5B | High value/time-critical, expensive |
Entrants Threaten
The railroad industry demands significant initial capital for infrastructure, such as tracks and terminals. Constructing a rail network like CSX's poses a major financial hurdle for newcomers. High capital needs significantly deter new entrants. In 2024, CSX invested billions in capital expenditures, highlighting the financial barrier. This financial burden restricts the number of potential competitors.
The railroad industry faces stringent regulations, making it tough for new players to enter. New entrants must deal with complicated permitting and safety rules. Changes in regulations could hike costs or limit expansion. These regulatory obstacles significantly block new competitors. In 2024, compliance costs for major railroads like CSX are substantial, reflecting the impact of these hurdles.
CSX, a major player in the railroad industry, enjoys significant economies of scale. This advantage allows CSX to distribute its substantial fixed costs, such as infrastructure maintenance, over a large volume of freight. New entrants face a tough challenge in matching CSX's cost structure, which is crucial for profitability. In 2024, CSX reported operating revenues of approximately $14.7 billion, demonstrating its scale.
Access to infrastructure
New entrants face substantial hurdles accessing rail infrastructure, a critical barrier in CSX's industry. Established railroads like CSX control vital routes and terminals, creating a significant disadvantage for potential competitors. Route density gives incumbents a cost advantage, as seen in 2024, with CSX moving around 2.4 million carloads. This advantage makes it difficult for new companies to build a competitive network.
- High infrastructure costs deter new entries.
- Established networks possess superior economies of scale.
- Control of key terminals restricts market access.
- CSX's existing routes offer established advantages.
Brand recognition and customer loyalty
CSX benefits from strong brand recognition and customer loyalty built over decades. These established relationships with shippers provide a significant advantage. The company's reputation and essential services in the North American economy further solidify its position. This makes it challenging for new entrants to compete effectively.
- CSX's strong management team is seen as a key factor for growth.
- Building trust and loyalty with shippers takes a long time.
- Existing railroads have a significant advantage.
- New entrants face challenges.
High capital needs and stringent regulations limit new entrants. Established players, like CSX, benefit from economies of scale and control of essential infrastructure, creating significant barriers. CSX's brand strength further complicates entry. In 2024, new entries faced steep hurdles.
| Factor | Impact on New Entrants | CSX's Advantage |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Costs | High Barrier | Established Infrastructure |
| Regulations | Compliance Challenges | Compliance Expertise |
| Economies of Scale | Difficult to Match | Low Unit Costs |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
CSX's Porter's Five Forces draws on SEC filings, financial news, and industry reports. These diverse sources ensure data-driven evaluations of the competitive landscape.