Financial Institutions Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Financial Institutions Bundle
What is included in the product
Analyzes competitive forces, threats, and market entry to assess Financial Institutions' position.
Customize pressure levels based on new data or evolving market trends.
Same Document Delivered
Financial Institutions Porter's Five Forces Analysis
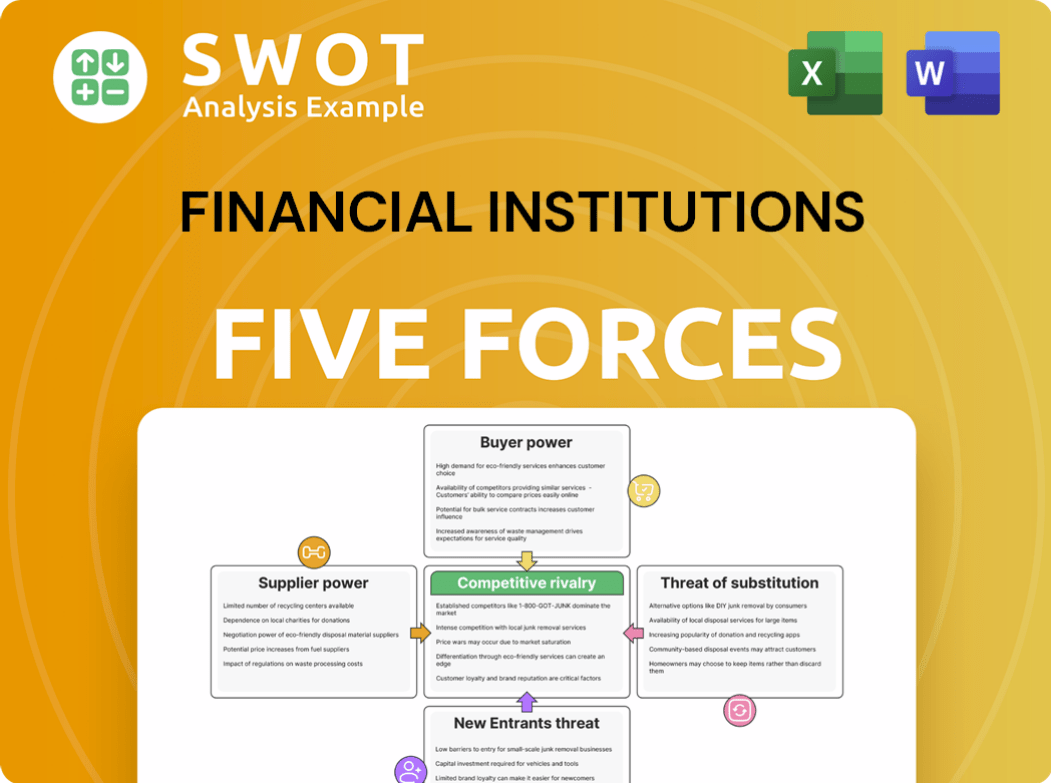
This preview showcases the comprehensive Porter's Five Forces analysis of financial institutions, examining competitive rivalry, threat of new entrants, bargaining power of suppliers, bargaining power of buyers, and threat of substitutes.
The document delves into the specific forces impacting the financial sector.
The analysis provides strategic insights into the competitive landscape.
You’re previewing the final version—precisely the same document that will be available to you instantly after buying.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Template
Financial institutions face dynamic competitive pressures shaped by five forces. Buyer power stems from customer choice and switching costs. Supplier influence comes from fintechs and data providers. New entrants, like digital banks, challenge incumbents. The threat of substitutes, including alternative payment methods, looms. Rivalry among existing players is intense, driven by market share battles.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Financial Institutions’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Suppliers of tech infrastructure and software significantly affect financial institutions' costs. Tech's crucial role means pricing and availability directly influence profitability. Cybersecurity threats increase costs, especially security software. In 2024, global cybersecurity spending is projected to reach $207 billion, highlighting supplier influence.
Service providers, including those handling data processing and IT support, wield considerable influence. Financial institutions depend on them for seamless operations. The bargaining power of these suppliers grows with the specialization and criticality of their services. For example, in 2024, cybersecurity spending by financial institutions reached $27.6 billion, highlighting their reliance. However, long-term contracts can lessen this impact.
The bargaining power of specialized labor, like financial analysts, influences financial institutions. High demand and skills drive up compensation, impacting operational costs. In 2024, the average salary for financial analysts was around $86,000. Strategic talent management is crucial. This includes competitive salaries and benefits to retain key personnel.
Regulatory Compliance Costs
Suppliers of compliance solutions and legal services significantly impact financial institutions' costs, especially with ever-changing regulations. Financial Institutions Inc. (FII) must invest heavily in these services to stay compliant. The complexity of these regulations drives up demand and prices. For example, in 2024, the average cost of regulatory compliance for financial institutions has increased by 15%.
- Increased demand for specialized legal expertise.
- Rising costs for compliance software and consulting.
- Impact of new regulations like Basel III finalization.
- Higher operational expenses due to compliance.
Data Providers' Leverage
Data providers, especially those offering financial data and analytics, wield significant influence. This is because access to timely and accurate data is critical for informed decision-making and client value. The need for real-time data has increased, as evidenced by the 2024 growth in financial data spending, which is expected to reach $35 billion. The more unique and essential the data, the higher the bargaining power of these suppliers.
- Market data providers like Refinitiv and Bloomberg control vast data sets.
- Specialized data sources for ESG or alternative data have increasing leverage.
- The high cost of switching data providers bolsters their power.
- Data quality and regulatory compliance further enhance their position.
Suppliers influence costs through tech, services, and labor. Cybersecurity and compliance expenses are significant. Data providers, like Refinitiv, hold considerable power due to critical data access.
| Supplier Type | Impact | 2024 Data Point |
|---|---|---|
| Tech & Software | Pricing & Availability | Cybersecurity spending: $207B |
| Service Providers | Operational Costs | Compliance cost increase: 15% |
| Data Providers | Decision-Making | Financial data spending: $35B |
Customers Bargaining Power
Customers of financial institutions are highly sensitive to interest rates and fees. They can easily move their business to competitors providing more favorable terms, which impacts the institution's market share. For example, in 2024, the average interest rate on a 30-year fixed mortgage was around 7%, driving many to seek better rates elsewhere. Financial Institutions Inc. must carefully balance profitability with competitive pricing to maintain and grow its customer base.
Customers now expect personalized financial services, boosting their bargaining power. Tailored solutions increase their influence over terms. Financial Institutions Inc. needs robust customer relationship management (CRM) to adapt. In 2024, CRM spending is projected to reach over $28 billion in the US alone.
Switching costs for financial services are generally low, empowering customers. They can effortlessly transfer accounts and investments to other institutions. In 2024, the average time to switch banks is under a week, enhancing mobility. Exceptional service is crucial for financial institutions, as approximately 70% of customers would switch for better rates or service.
Demand for Digital Solutions
Customers' demand for digital solutions impacts their bargaining power within financial institutions. They increasingly expect convenient digital banking and investment platforms. This shift boosts their ability to choose institutions offering seamless online experiences. Financial institutions must invest in technology and user experience to remain competitive, as evidenced by the 2024 surge in mobile banking app usage, with over 70% of consumers regularly using them.
- Mobile banking app usage rose to over 70% in 2024.
- Customers prioritize user experience in financial services.
- Investment in technology is crucial for competitiveness.
- Digital platforms increase customer choice and power.
Transparency and Trust
Customers today are better informed, expecting transparency in fees and services from financial institutions. Their ability to easily compare offerings and switch providers significantly boosts their bargaining power. Financial institutions must prioritize clear communication and build trust to maintain customer loyalty. In 2024, the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB) reported over 15,000 consumer complaints related to banking fees, highlighting the importance of transparency.
- Increased customer awareness of financial products and services.
- Ease of switching between financial institutions.
- Rising demand for lower fees and better service quality.
- The need for clear, trustworthy communication.
Customers' bargaining power in financial institutions stems from their sensitivity to interest rates and fees, enabling them to switch providers easily. Digital platforms enhance their choices and expectations for seamless experiences. Transparency and informed decisions further boost their influence. In 2024, the CFPB reported over 15,000 banking fee complaints, highlighting the need for trust.
| Factor | Impact | 2024 Data |
|---|---|---|
| Interest Rate Sensitivity | Influences customer decisions | Avg. 30-yr mortgage rate ~7% |
| Digital Expectations | Drives demand for digital solutions | Mobile banking app usage >70% |
| Transparency | Affects loyalty | CFPB: 15k+ fee complaints |
Rivalry Among Competitors
The financial services sector is fiercely competitive, with many firms battling for customer attention. Financial Institutions Inc. competes with established banks, credit unions, and digital financial services. In 2024, the top 10 U.S. banks held over 50% of total banking assets, highlighting the concentration and rivalry. Competition drives innovation, but also squeezes profit margins.
Intense rivalry among financial institutions often triggers pricing pressures. This is especially true for standardized services such as loans and deposit accounts. For example, in 2024, the average interest rate on a 30-year fixed mortgage fluctuated, reflecting aggressive competition. Financial Institutions Inc. needs to control expenses and distinguish its services to protect profit margins.
Financial institutions are locked in a technology arms race, with rivals pouring billions into digital upgrades. In 2024, JPMorgan Chase allocated over $14 billion to tech, aiming to streamline services and boost customer satisfaction. This investment surge necessitates that Financial Institutions Inc. match these efforts to maintain its market position. Keeping pace is crucial; otherwise, they risk losing market share to tech-savvy competitors.
Market Consolidation
The financial industry is seeing significant market consolidation, primarily through mergers and acquisitions (M&A). This trend is intensifying the competitive landscape, as larger institutions gain greater market power. Financial Institutions Inc. needs to adjust its strategies to thrive amid these changes. In 2024, M&A activity in the financial sector reached $300 billion globally, a 15% increase from the previous year.
- Increased market share of fewer players.
- Heightened need for innovation to stay competitive.
- Potential for increased pricing pressure.
- Need to assess and adapt to new business models.
Customer Loyalty
Customer loyalty significantly impacts financial institutions in a competitive landscape. Exceptional service and personalized solutions are crucial for retaining customers, especially in 2024. Financial Institutions Inc. must prioritize customer retention strategies to thrive. The financial services industry experiences intense competition, making customer loyalty a key differentiator.
- Customer retention rates in the banking sector average around 70-80% annually.
- Personalized financial advice can increase customer loyalty by up to 20%.
- Banks investing in digital customer service see a 15% increase in customer satisfaction.
- Loyal customers are 5 times more likely to repurchase and 4 times more likely to refer.
Rivalry in financial services is intense, with institutions vying for market share. This competition leads to pricing pressures and a focus on customer loyalty. Tech investment and M&A activity are also significant competitive factors.
| Key Factor | Impact | 2024 Data |
|---|---|---|
| Market Share | Concentration | Top 10 US banks held over 50% of assets. |
| Pricing | Pressure | Mortgage rates fluctuated due to competition. |
| Tech Spend | Investment Race | JPMorgan Chase allocated $14B+ to tech. |
SSubstitutes Threaten
FinTech companies, like Stripe and Square, provide digital payment solutions, representing substitutes for traditional banking services. These alternatives threaten Financial Institutions Inc., with a growing market share. For example, the global fintech market was valued at $112.5 billion in 2023. Financial Institutions Inc. must innovate and adopt new technologies to remain competitive, facing challenges from agile FinTech competitors. The rise of these substitutes necessitates strategic adaptation.
Peer-to-peer (P2P) lending platforms offer a direct alternative to traditional financial institutions, enabling individuals and businesses to borrow and lend money without the involvement of banks. This shift poses a threat to Financial Institutions Inc., as P2P platforms often provide more favorable interest rates and quicker loan approvals. In 2024, the global P2P lending market was valued at approximately $110 billion, demonstrating its increasing popularity and competitive edge. Financial Institutions Inc. must innovate by improving customer service and offering competitive products to compete effectively against these emerging substitutes.
Mobile payment systems and digital wallets pose a growing threat to financial institutions by offering convenient alternatives to traditional banking. Adoption rates are surging; for instance, in 2024, mobile payment transactions in the U.S. reached $1.4 trillion. This shift forces banks to integrate these technologies to remain competitive. Failure to adapt could lead to a significant loss of market share and revenue.
Cryptocurrencies
Cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology present a threat as decentralized alternatives to traditional banking. These solutions could disrupt established financial models. The rise of digital assets like Bitcoin, with a market capitalization exceeding $1 trillion in 2024, poses a competitive challenge. Financial Institutions Inc. must actively explore and integrate these technologies to mitigate risks.
- Bitcoin's market cap surpassed $1 trillion in 2024.
- Decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms are gaining traction.
- Blockchain technology offers secure and transparent transactions.
- Traditional banks face pressure to innovate and adapt.
Alternative Investments
Alternative investments, including real estate crowdfunding, present viable options beyond conventional financial products. These substitutes can lure investors with promises of superior returns, potentially diverting capital from traditional financial institutions. To mitigate this threat, Financial Institutions Inc. must expand and diversify its product offerings. The rise of alternative investments is evident, with the global market size estimated at $14.7 trillion in 2024.
- Real estate crowdfunding grew by 15% in 2024.
- Alternative investments now make up 20% of institutional portfolios.
- Investors are increasingly allocating capital to hedge funds and private equity.
- Financial Institutions Inc. needs to offer similar products.
The threat of substitutes significantly impacts Financial Institutions Inc. FinTech, P2P lending, and mobile payments challenge traditional banking models, with FinTech valued at $112.5B in 2023. Cryptocurrencies and alternative investments also divert capital; Bitcoin's market cap exceeded $1T in 2024. Financial Institutions Inc. must innovate to remain competitive.
| Substitute Type | Impact | 2024 Data |
|---|---|---|
| FinTech | Digital Payment Solutions | Global Market: $120B (est.) |
| P2P Lending | Direct Lending | Market Value: $110B |
| Mobile Payments | Convenience | U.S. Transactions: $1.4T |
Entrants Threaten
The financial sector demands substantial capital for infrastructure and regulatory compliance. This high initial investment acts as a significant barrier, limiting new competitors. Financial Institutions Inc. leverages this, enjoying protection from less-capitalized startups. In 2024, the cost to launch a regional bank could exceed $100 million, deterring many.
Stringent regulations and licensing, like those from the SEC or FDIC, significantly raise the bar for new financial firms. These hurdles, including capital requirements and compliance costs, protect existing institutions. For instance, in 2024, the average cost to comply with regulations increased by 7% for financial firms. Financial Institutions Inc. can use its established compliance infrastructure to its advantage, reducing the impact of these barriers.
Established brands in financial institutions hold a significant edge due to existing customer loyalty. Building brand recognition and trust is costly and time-consuming. Financial Institutions Inc. leverages its established reputation to attract and retain customers. For instance, in 2024, JPMorgan Chase spent $3.2 billion on advertising, reinforcing its brand presence. This advantage makes it difficult for new entrants to compete effectively.
Economies of Scale
Established financial institutions, like JPMorgan Chase & Co., benefit from economies of scale, making it difficult for new entrants to compete on cost. JPMorgan Chase & Co. reported total assets of $3.9 trillion as of December 31, 2023, demonstrating their substantial size. This scale allows them to spread fixed costs over a larger base, reducing per-unit expenses. Financial Institutions Inc. can leverage its operational efficiencies to maintain a competitive edge.
- Lower operating costs per transaction.
- Increased profitability.
- Enhanced pricing power.
- Ability to invest in advanced technology.
Customer Relationships
Established financial institutions benefit from strong customer relationships, built over time. New entrants face the challenge of building trust and loyalty from scratch. Financial Institutions Inc. can leverage its existing customer base to maintain its market position. Customer loyalty, influenced by factors like personalized service and brand reputation, is a significant barrier to entry. In 2024, customer retention rates remain a key metric for financial institutions, often exceeding 80% for established players [1, 2, 3].
- Established institutions have built strong customer relationships.
- New entrants must establish trust and loyalty.
- Financial Institutions Inc. can leverage its existing customer base.
- Customer loyalty is a barrier to entry.
The threat of new entrants in the financial sector is moderate. High capital requirements, like the $100M+ to launch a bank in 2024, and strict regulations act as significant barriers. Established firms benefit from economies of scale and customer loyalty, further deterring new competitors.
| Barrier | Description | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Needs | High startup costs. | Limits new competitors. |
| Regulations | Compliance burdens. | Increases operational costs. |
| Economies of Scale | Existing firms have cost advantages. | Deters competition. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
For our analysis, we incorporate financial statements, regulatory reports, and market share data to accurately score competitive forces.