Microchip Technology Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Microchip Technology Bundle
What is included in the product
Tailored exclusively for Microchip Technology, analyzing its position within its competitive landscape.
Customize pressure levels reflecting Microchip's shifting market dynamics.
Same Document Delivered
Microchip Technology Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact Microchip Technology Porter's Five Forces Analysis document you'll receive. Analyze competitive rivalry, threat of new entrants, supplier/buyer power, and threat of substitutes. This professionally written analysis is ready for immediate download and use after purchase. No changes, what you see is what you get.
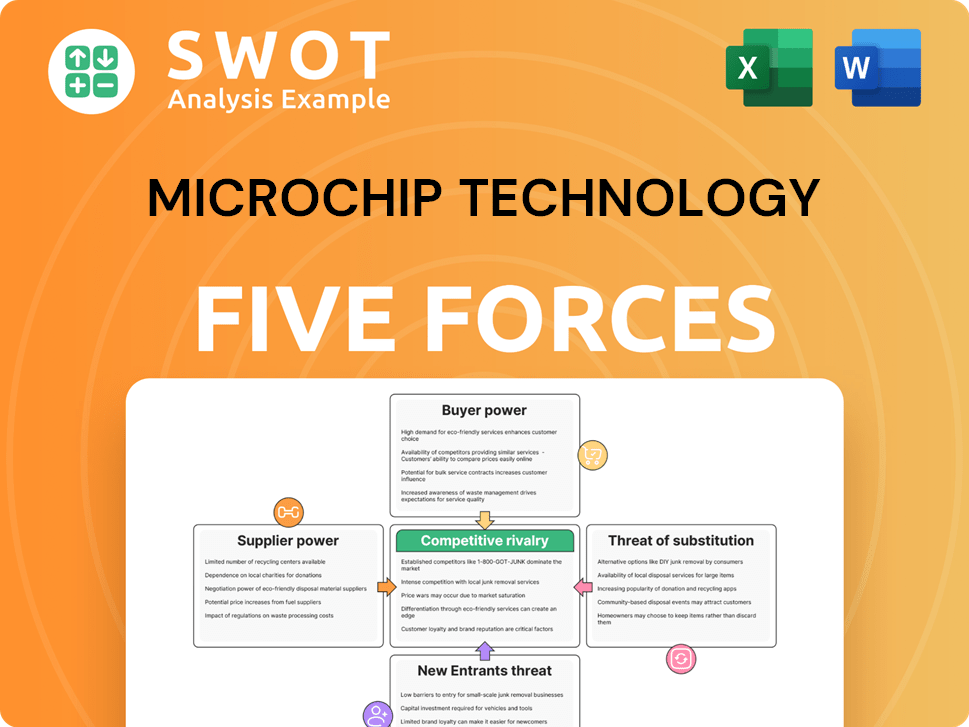
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Template
Microchip Technology faces moderate rivalry, with established competitors in the microcontroller market. Supplier power is notable due to the concentration of certain component manufacturers. Buyer power is relatively high, stemming from diverse customer needs. The threat of new entrants is moderate because of high barriers. Substitutes present a modest threat, given the specialized nature of microcontrollers.
Ready to move beyond the basics? Get a full strategic breakdown of Microchip Technology’s market position, competitive intensity, and external threats—all in one powerful analysis.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The microchip industry's supplier base is diverse, limiting any single supplier's power. Microchip Technology likely sources components from various vendors, reducing reliance. This diversification strengthens Microchip's negotiation position. In 2024, the semiconductor market saw varied supplier contributions, preventing over-reliance. Intel, TSMC, and Samsung are key players.
Microchip Technology benefits from standardized components. This means multiple suppliers offer similar parts. In 2024, the semiconductor industry saw a rise in standardized component usage. Switching suppliers is easy, keeping costs down for Microchip.
Microchip's design expertise allows it to dictate component needs, influencing supplier production. This control enhances its bargaining power. In 2024, Microchip's revenue was approximately $8.7 billion, reflecting its supply chain influence. Thus, they can set terms with suppliers. This strategy helps manage costs.
Long-term supplier relationships
Microchip Technology's ability to build and maintain long-term supplier relationships is crucial. These relationships often lead to more favorable terms and secure a stable supply of components. These established partnerships give Microchip leverage when negotiating. In 2024, Microchip's supply chain management efforts helped mitigate some of the industry-wide component shortages, a testament to the strength of its supplier relationships.
- Secured supply: Long-term contracts provide supply assurance.
- Cost advantages: Negotiated pricing can lower input costs.
- Collaboration: Joint efforts improve product development.
- Reduced risk: Diversified suppliers limit dependency.
Global sourcing options
Microchip Technology benefits from global sourcing, increasing its bargaining power. This approach broadens the supplier base, fostering competition. The company can negotiate favorable terms due to this competitive environment. In 2024, Microchip expanded its global presence, which further strengthened its supplier relationships.
- Wider Supplier Base: Global sourcing provides access to a larger pool of potential suppliers.
- Competitive Pricing: Competition among suppliers drives down prices and improves terms.
- Negotiating Leverage: Microchip can use multiple supplier options to negotiate favorable deals.
- Enhanced Terms: Better payment terms, delivery schedules, and service agreements are possible.
Microchip Technology's supplier power is moderate due to a diversified supplier base and standardized components. The company leverages design expertise and global sourcing to enhance its bargaining position. Long-term supplier relationships and strong supply chain management further strengthen its ability to negotiate favorable terms.
| Factor | Impact | Data |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Diversity | Reduces supplier power | Numerous component vendors. |
| Standardization | Facilitates supplier switching | Industry trend in 2024 |
| Design Expertise | Enhances negotiating power | Revenue of ~$8.7B in 2024. |
Customers Bargaining Power
Microchip Technology benefits from a diverse customer base. This includes various industries and applications, reducing reliance on any single customer. This diversification helps to lessen the impact of losing a major client. The broad customer base provides stability for Microchip. In 2024, Microchip's revenue reached approximately $8.4 billion, reflecting its wide market reach.
Microchip Technology's customer base is diverse, with varying order sizes. While some customers place substantial orders, many applications involve smaller volumes. This fragmentation reduces the bargaining power of individual buyers. For example, in 2024, Microchip reported a diversified customer base, with no single customer accounting for a significant portion of their revenue, limiting individual customer influence over pricing.
Switching costs for Microchip's customers can be substantial due to the integration of its products into their systems. This integration requires considerable design and development efforts, making it costly for customers to switch to alternatives. Microchip benefits from this, as these embedded products create a barrier to exit. In 2024, Microchip reported a gross margin of approximately 67.6%, reflecting the value customers place on their integrated solutions.
Importance of performance
The bargaining power of customers is moderate due to the importance of microchip performance. The reliability and performance of microchips are crucial in various applications, reducing customer price sensitivity. Customers often prioritize quality and dependability over cost. Microchip Technology can therefore charge higher prices for its superior products, boosting profitability. For the fiscal year 2024, Microchip's gross margin was approximately 66.5%.
- Performance Importance: Microchips are essential in critical applications.
- Customer Priorities: Quality and reliability are valued over price.
- Pricing Power: Microchip can command premium prices.
- Financial Impact: Boosts Microchip's profitability.
Value-added services
Microchip Technology's robust technical support and design assistance significantly enhance customer reliance, which in turn, reduces price sensitivity. These value-added services set Microchip apart from its competitors, fostering stronger customer relationships. For example, in 2024, Microchip invested approximately $400 million in R&D, including customer support, which underlines its commitment. This strategy boosts customer loyalty and retention rates.
- Microchip invested $400 million in R&D in 2024.
- Customer support is a key element of Microchip's strategy.
- Loyalty and retention rates are improved.
Microchip's customer bargaining power is moderate due to the importance of microchips and value-added services. Customers prioritize quality and reliability, allowing Microchip to set premium prices. In 2024, Microchip reported a gross margin of approximately 66.5%.
| Factor | Impact | Financial Metric (2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Performance Importance | High, critical applications | Gross Margin: ~66.5% |
| Customer Priorities | Quality & Reliability | R&D Investment: ~$400M |
| Pricing Power | Microchip sets premiums | Revenue: ~$8.4B |
Rivalry Among Competitors
The microchip industry is fiercely competitive, featuring both seasoned and new entrants. This environment fuels aggressive price wars and rapid innovation cycles. Microchip Technology faces continuous pressure to innovate, as rivals introduce advanced products. In 2024, the semiconductor market saw major shifts, with companies like TSMC and Intel vying for dominance. Microchip must adapt swiftly to stay competitive.
Companies fiercely compete based on product features, performance, and reliability, fostering ongoing innovation. Microchip Technology must differentiate its offerings through superior design and functionality to stay ahead. This differentiation is essential for retaining and growing market share. For example, in 2024, Microchip's net sales were approximately $8.5 billion, highlighting the importance of product competitiveness.
Price wars can significantly impact Microchip Technology, particularly in the commodity microchip segment, potentially squeezing profit margins. Microchip must carefully balance its pricing strategies with the value-added services it provides. In 2024, the semiconductor industry saw fluctuating prices, emphasizing the need for Microchip to avoid solely competing on price. For example, in Q3 2024, the gross margin stood at 61.7%.
Rapid technological change
The semiconductor industry, including Microchip Technology, experiences intense competitive rivalry due to rapid technological change. Companies must continually invest in research and development (R&D) to innovate and stay competitive. For example, Microchip's R&D expenses were approximately $794.7 million in fiscal year 2024. This investment is crucial for developing cutting-edge products and maintaining market share.
- R&D spending is critical for new product development.
- Constant innovation defines the industry landscape.
- Microchip must keep up with technological advancements.
- Failure to innovate can result in loss of market share.
Global competition
Microchip Technology faces fierce competition on a global scale, requiring constant innovation and cost management. This rivalry includes established international firms and companies from emerging markets, intensifying market pressures. The semiconductor industry's global nature necessitates a broad strategic outlook. Focusing on operational efficiency and technological advancement is critical for maintaining a competitive edge.
- Global semiconductor sales reached $526.8 billion in 2023.
- Microchip's revenue for FY24 was $8.45 billion.
- Major competitors include Texas Instruments and Analog Devices.
- Competition drives down average selling prices (ASPs).
Competitive rivalry in the microchip sector is intense. Microchip Technology competes with global firms, driving innovation and cost pressure. The industry’s global sales reached $526.8 billion in 2023, highlighting this pressure. This environment demands continuous R&D, such as Microchip's $794.7 million in fiscal year 2024.
| Metric | Value (2024) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Microchip Revenue | $8.45 billion | FY24 |
| R&D Expenses | $794.7 million | FY24 |
| Gross Margin | 61.7% | Q3 |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Microchip Technology faces a limited threat from substitutes due to the core functionality of its products. Microchips are essential in electronics, making direct replacements scarce. Their complex functions are hard to replicate with alternative technologies. This solidifies Microchip's position, as evidenced by its consistent revenue growth in 2024. The company's revenue reached $6.14 billion in Q1 2024.
Alternative technologies like FPGAs or ASICs present a threat, especially in specialized applications, although they often come with increased costs or performance compromises. For instance, in 2024, the FPGA market was estimated at $8.7 billion. These may substitute Microchip's products. They are not direct replacements in many instances.
Software-based solutions pose a threat to Microchip Technology, though the impact is nuanced. These solutions can sometimes replace hardware components, but performance constraints limit this. Software is improving; however, dedicated microchips provide superior speed and efficiency. In 2024, the global software market reached approximately $750 billion, showcasing its growing influence, yet it's not a complete substitute.
Integration of functionality
The increasing integration of functions into single chips represents a significant threat of substitution for Microchip Technology. This trend towards system-on-a-chip (SoC) designs could consolidate functionality, potentially reducing the demand for individual microchips. For example, in 2024, the market for SoCs is estimated at $200 billion, reflecting the growing adoption of integrated solutions. This shift is particularly relevant in automotive and IoT sectors, where space and power efficiency are critical.
- SoC market valued at $200 billion in 2024.
- Growing adoption in automotive and IoT sectors.
- Potential for reduced demand for discrete components.
- Emphasis on space and power efficiency.
Material science advancements
Material science breakthroughs pose a long-term threat to Microchip Technology. Novel materials could create superior components that substitute traditional chips. These advancements might boost performance and efficiency, but they remain in their infancy. The global semiconductor market was valued at approximately $527 billion in 2023.
- Research and development in alternative materials is intensifying.
- New materials could offer advantages in speed, power consumption, and size.
- The transition to new materials will require significant investment and time.
- Microchip Technology must monitor these developments closely.
The threat of substitutes for Microchip Technology is moderate, influenced by the specialized nature of its products. Alternatives like SoCs and software solutions pose challenges, especially in sectors like automotive. The $200 billion SoC market in 2024 indicates a shift towards integrated solutions. The company must adapt to these market dynamics.
| Substitute | Impact | 2024 Data |
|---|---|---|
| SoCs | High, integration trends | $200B market |
| Software | Moderate, performance limits | $750B software market |
| FPGAs/ASICs | Moderate, specialized apps | $8.7B market |
Entrants Threaten
The microchip industry presents high capital requirements, particularly in research and development, manufacturing facilities, and specialized equipment. This necessitates substantial financial commitments, acting as a significant barrier. Establishing a fabrication plant, or "fab," demands immense capital investments, often exceeding billions of dollars. For instance, in 2024, the cost to build a new fab could range from $10 to $20 billion.
Microchip Technology benefits from a strong barrier against new entrants due to its proprietary technology and intellectual property. Patents and trade secrets are crucial in protecting Microchip's market position. These assets make it incredibly challenging for newcomers to replicate its existing technologies. For instance, Microchip's R&D spending in 2024 was $760 million, underscoring its commitment to innovation and keeping its technological edge. This investment further solidifies its defenses against potential rivals.
Existing players like Microchip Technology benefit from economies of scale in manufacturing and distribution, offering a cost advantage. New entrants struggle to match these economies, facing higher per-unit costs. In 2024, Microchip Technology's gross margin was around 65%, reflecting these efficiencies. Established companies produce at lower costs due to their size and established infrastructure.
Established relationships
Microchip Technology benefits from established relationships with customers and suppliers, presenting a significant barrier to new entrants. These relationships, built over time, foster trust and loyalty, offering a competitive edge in the market. New competitors face the daunting task of replicating these established networks, which is both time-consuming and resource-intensive. Microchip's strong relationships contribute to its market stability and influence.
- Microchip's net sales for fiscal year 2024 reached $8.48 billion.
- The company has a global customer base, enhancing its network effect.
- Building new relationships requires substantial investment in sales and marketing.
- Established relationships provide a buffer against market volatility.
Regulatory hurdles
The microchip industry faces stringent regulatory hurdles, increasing the barriers for new entrants. Compliance with diverse regulations and standards elevates operational costs and complexity. New companies must navigate a complex regulatory landscape to gain a foothold.
- Regulations and standards significantly impact the microchip sector, increasing complexity.
- Adhering to these regulations adds to the financial burden and operational challenges for new entrants.
- The intricate regulatory environment presents a substantial barrier to entry.
The microchip industry has high barriers to entry due to capital needs, technology, and established networks. New entrants face substantial challenges replicating existing infrastructure and relationships. Regulatory hurdles further complicate entry, impacting costs and operations.
| Barrier | Impact | Example (2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High Initial Investment | Fab construction: $10-20B |
| Technology/IP | Protects Market Position | R&D spend: $760M |
| Established Networks | Competitive Advantage | Microchip's net sales: $8.48B |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Microchip's analysis uses SEC filings, industry reports, market data, and competitor financials to gauge forces. This gives a rounded view.