Banco Santander Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Banco Santander Bundle
What is included in the product
Analyzes Santander's competitive forces, including suppliers and buyers, impacting pricing and profitability.
Instantly see Santander's competitive landscape with color-coded force impact levels.
Full Version Awaits
Banco Santander Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview details the complete Banco Santander Porter's Five Forces analysis. The document you see reflects the exact analysis you'll download post-purchase. It's a fully formatted, ready-to-use resource, professionally crafted. No changes or extras, just the document shown.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Template
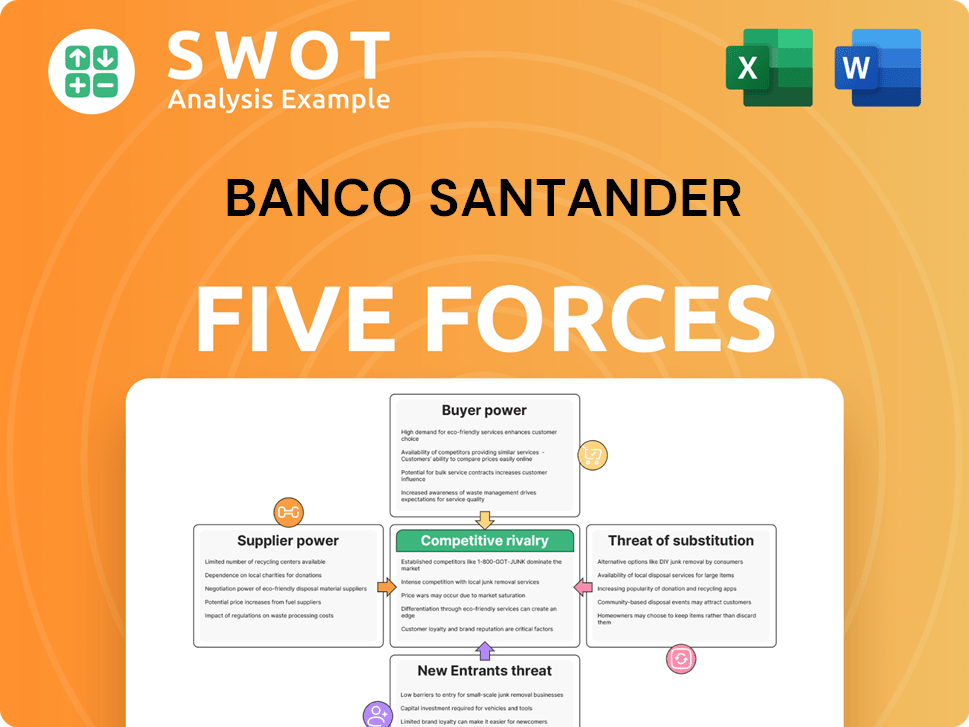
Banco Santander's competitive landscape is shaped by powerful forces. Bargaining power of buyers, especially corporate clients, is a key factor. The threat of new entrants is moderate, due to high capital requirements. Substitute products, like digital banking platforms, pose a growing challenge. Rivalry among existing competitors, including other global banks, is intense. Finally, supplier power is relatively low.
Ready to move beyond the basics? Get a full strategic breakdown of Banco Santander’s market position, competitive intensity, and external threats—all in one powerful analysis.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Banco Santander's bargaining power of suppliers is generally moderate. The bank sources inputs from various suppliers, like technology and consulting firms. If these suppliers are numerous and competitive, Santander has more leverage. However, if a few dominant suppliers exist, they could potentially increase costs. Consider that in 2024, the IT services market is highly competitive, offering Santander alternatives.
Banco Santander's ability to switch suppliers easily weakens supplier power. Low switching costs mean Santander can readily find alternative suppliers. Conversely, high switching costs, like those from specialized tech, boost supplier leverage. In 2024, Santander spent €2.5B on IT, highlighting potential supplier dependency if switching is costly.
If Santander's suppliers, like technology providers or data analytics firms, could offer financial services, their bargaining power grows. This could lead to direct competition, bypassing Santander. Consider if these suppliers possess the financial resources and expertise to enter the market. For example, in 2024, fintech investments surged, indicating supplier capacity.
Impact of Supplier Inputs on Quality
Banco Santander's reliance on supplier inputs directly impacts service quality. If these inputs are critical, suppliers gain leverage. For example, the technology supporting Santander's digital services gives providers substantial bargaining power. The importance of these inputs determines supplier power. Analyzing these dependencies is vital for risk assessment.
- Technology suppliers for online banking and mobile apps hold significant influence.
- Data providers supplying market analysis and customer insights also wield power.
- In 2024, Santander's IT spending reached €3.5 billion, highlighting this dependency.
- Quality issues in supplier inputs can lead to regulatory fines.
Availability of Substitute Inputs
The availability of substitute inputs significantly affects supplier power in Banco Santander's operations. If Santander can switch to alternative technologies, consultants, or services, suppliers' influence decreases. Assessing the presence of viable substitutes for critical products and services is crucial for Santander. For example, in 2024, Santander invested heavily in cloud services, reducing dependence on specific IT hardware suppliers.
- Cloud computing adoption reduces reliance on single hardware vendors.
- Diversification of consulting firms to avoid dependency.
- Competitive bidding processes ensure cost-effective alternatives.
- Strategic partnerships to secure substitute service providers.
Banco Santander's supplier power is moderate, influenced by the competitiveness of its suppliers. The ability to switch suppliers impacts this power; low switching costs weaken supplier leverage. In 2024, Santander's substantial IT spending (€3.5B) highlights its dependency on suppliers, such as tech providers.
| Supplier Factor | Impact | 2024 Data |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | High concentration increases power | Few dominant tech firms |
| Switching Costs | High costs increase power | €3.5B IT spend |
| Availability of Substitutes | More substitutes reduce power | Cloud adoption |
Customers Bargaining Power
High customer concentration boosts buyer power. If a few big clients drive Santander's revenue, they gain leverage for better deals. Santander's 2023 annual report showed a focus on diversifying its customer base. Data indicates a shift in customer segment distribution. This diversification helps reduce the risk of a few large clients dictating terms.
Low switching costs significantly amplify customer bargaining power. It's relatively easy for Santander's customers to move to other banks. This necessitates competitive offerings from Santander to retain clients. Factors like interest rates, fees, and service quality heavily influence customer loyalty. In 2024, the average cost to switch banks was around $50, a minor deterrent.
High customer price sensitivity boosts buyer power. If clients closely watch fees and rates, Santander may cut prices, affecting profits. Analyzing demand price elasticity for key services is vital. In 2024, Santander's net interest income faced pressure due to rate competition.
Availability of Information
Customers' access to information significantly boosts their bargaining power. This is particularly relevant in the digital age, where online tools and financial literacy resources are abundant. Evaluate how Santander's customer base leverages this information to compare financial offerings and negotiate better terms. In 2024, digital banking adoption rates continue to rise, with over 60% of Santander's customers actively using online services. This heightened digital engagement directly impacts customer ability to compare and contrast financial products.
- Digital Banking Usage: Over 60% of Santander customers utilize online services.
- Financial Literacy Resources: Availability of online tools and information.
- Customer Comparison: Ability to compare financial offerings and negotiate.
- Market Dynamics: Competitive landscape in the financial sector.
Customer Volume
Customers with significant transaction volumes or substantial deposit balances wield considerable bargaining power. These clients can negotiate for better interest rates, reduced fees, or bespoke services. In 2024, Santander's large-volume customers influenced pricing strategies, particularly in corporate and wealth management segments. This necessitates Santander to balance profitability with customer retention.
- Impact on Pricing: High-volume clients can secure better rates.
- Service Customization: Tailored services are often provided to retain these customers.
- Profit Margin: Balancing competitive rates with maintaining profit margins.
- Segment Focus: Corporate and wealth management are key areas.
Customer bargaining power at Banco Santander is influenced by concentration and diversification efforts. The ease with which customers can switch banks underscores the importance of competitive offerings. Price sensitivity and information access further enhance customer influence on pricing.
Santander's strategies must balance profitability with customer retention, especially in corporate and wealth management. Digital banking, with over 60% usage in 2024, amplifies customer ability to compare and negotiate.
Large transaction volumes and substantial deposit balances give clients significant leverage for better terms. In 2024, Santander faced pressure to balance competitive rates with profit margins.
| Factor | Impact | 2024 Data |
|---|---|---|
| Switching Costs | Low costs increase bargaining power | Avg. switch cost: ~$50 |
| Digital Banking | Enhances comparison ability | Over 60% online usage |
| Price Sensitivity | High sensitivity impacts profitability | NII pressure from rate competition |
Rivalry Among Competitors
A high number of competitors significantly increases rivalry. Banco Santander faces intense competition from a multitude of players. Key rivals include global banks and fintech firms. In 2024, Santander's market share fluctuates against competitors. Competitors employ diverse strategies to gain market share.
Slower industry growth intensifies competition. Banco Santander faces this in mature markets. For example, in 2024, the Eurozone's financial sector grew modestly. This limited growth heightens the fight for customers and assets. Santander's strategic moves must reflect these market dynamics.
Low product differentiation intensifies competitive rivalry. If offerings are similar, competition centers on price and service. Santander's ability to innovate and brand is key. In 2024, Santander invested heavily in digital banking. This aims to enhance customer experience.
Switching Costs for Competitors
The similarity among Banco Santander's competitors and the ease with which customers can switch banks significantly affects the competitive landscape. Lower switching costs intensify rivalry, as customers can readily move to better offers. Analyzing switching costs for Santander's rivals reveals insights into market dynamics.
- Digital banking adoption has increased, with over 60% of customers using mobile banking in 2024.
- Switching banks can be relatively easy, with some banks offering incentives to attract new customers.
- Competition is fierce, with banks battling for market share through attractive interest rates and services.
- Santander's competitors include BBVA, which reported a 2024 net profit increase of 26%.
Exit Barriers
High exit barriers, such as regulatory hurdles and asset illiquidity, intensify competitive rivalry in banking. If it’s tough to leave a market, banks like Santander might keep fighting, even if it hurts profits. Santander operates in markets with varying exit barriers, from the more regulated EU to the more volatile Latin America. These barriers shape the intensity of competition.
- Regulatory requirements in the EU and the US can be significant exit barriers.
- Asset illiquidity, particularly in certain loan portfolios, makes exiting more difficult.
- Santander's presence in Latin America presents higher exit risks due to market volatility.
- In 2024, Santander reported a CET1 ratio of 12.3%, showing financial strength to weather competitive pressures.
Competitive rivalry at Banco Santander is shaped by multiple factors, including the number of competitors, industry growth rate, and product differentiation. High rivalry is evident given the numerous banks and fintech companies in the market. Switching costs and exit barriers also intensify competition.
| Factor | Impact | Data Point (2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Competitors | High rivalry | BBVA's 26% profit increase. |
| Industry Growth | Intensified rivalry | Eurozone financial sector growth: modest. |
| Differentiation | Focus on price/service | Digital banking adoption: 60%+ |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The availability of substitute financial products and services presents a threat to Banco Santander. Fintech firms provide alternative payment solutions and lending platforms, potentially impacting Santander's market share. Key substitutes include digital wallets and peer-to-peer lending. For example, in 2024, the digital payments market grew significantly, with companies like PayPal and Stripe gaining traction. This shift highlights the need for Santander to innovate.
Low switching costs heighten the threat of substitutes for Banco Santander. Customers can readily shift to alternative financial services. This includes digital banking platforms and fintech solutions. In 2024, the rise of digital banking showed a 15% increase in user adoption. This poses significant competitive pressure for Santander.
The attractiveness of substitutes is significantly influenced by their relative price and performance compared to Banco Santander's services. If substitutes provide superior value or greater convenience, customers are likely to switch. For example, digital payment platforms like PayPal and Revolut offer alternatives to traditional banking services. In 2024, these platforms saw increased adoption, impacting Santander's market share.
Customer Propensity to Substitute
Customer propensity to substitute is crucial for Banco Santander. Younger customers might readily switch to fintech alternatives like digital wallets or peer-to-peer payment apps, especially if these offer more convenience or lower fees. Older customers may stick with traditional banking, valuing in-person services and established trust. Analyzing customer preferences and adoption rates is essential to understand the threat.
- Fintech adoption has surged, with digital banking users globally expected to reach 2.5 billion by 2024.
- In 2023, approximately 60% of adults in developed countries used fintech.
- Santander's digital customer base grew by 18% in 2023, showing a shift.
Substitute Innovation
Substitute innovation poses a significant threat to Banco Santander. Ongoing innovation in financial technology (fintech) increases this threat. Fintech companies constantly develop new solutions, potentially disrupting traditional banking models. Monitoring the pace of fintech innovation is crucial for Santander's strategic planning. The bank needs to adapt to stay competitive.
- Fintech investment reached $113.7 billion globally in 2023.
- Santander's digital transformation investments were over €12 billion between 2019-2022.
- Neobanks like Revolut and N26 gained millions of customers, offering services similar to Santander's.
- The rise of blockchain technology and decentralized finance (DeFi) offers alternative financial services.
Substitute financial products, like fintech, pose a threat to Banco Santander. Digital payments and lending platforms gain traction, impacting market share. Low switching costs and superior value drive customers to alternatives. For example, fintech investment globally reached $113.7 billion in 2023.
| Factor | Impact on Santander | 2024 Data/Example |
|---|---|---|
| Fintech Adoption | Increased Competition | Digital banking users: ~2.5B globally |
| Switching Costs | High Sensitivity | Rise of digital banking: 15% user growth |
| Innovation | Disruption | Fintech investment: $113.7B in 2023 |
Entrants Threaten
High barriers to entry significantly protect Banco Santander from new competitors. Strict regulatory requirements and substantial capital needs pose major challenges. In 2024, the European Central Bank (ECB) maintained stringent capital adequacy ratios. Brand reputation also acts as a barrier; Santander's established presence in key markets like Spain and the UK, with billions in assets, makes it difficult for new players to compete.
Substantial capital requirements significantly deter new entrants into the banking sector. The banking industry is inherently capital-intensive, demanding huge investments in infrastructure, technology, and regulatory compliance. In 2024, establishing a competitive bank in Santander's markets could require billions, considering the need for physical branches, digital platforms, and meeting stringent capital adequacy ratios set by regulators. For example, in 2023, the average capital adequacy ratio for Santander was around 12.2%, indicating a substantial capital base needed to operate.
Stringent regulatory hurdles significantly deter new entrants in the banking sector. Banks must comply with extensive regulations on capital, risk, and consumer protection. The complexity and cost of regulatory compliance, including meeting requirements set by agencies like the European Central Bank (ECB), can be substantial. For instance, in 2024, the ECB continued to enforce strict capital requirements, with banks needing to maintain specific capital ratios to ensure financial stability, making entry challenging.
Brand Loyalty
Brand loyalty significantly impacts the threat of new entrants. Banco Santander, a well-established bank, benefits from strong customer trust and brand recognition, creating a substantial barrier for newcomers. Measuring Santander's brand equity and customer loyalty is crucial to understand this advantage. This loyalty stems from years of consistent service and a trusted reputation. New banks struggle to immediately replicate this.
- Santander's Brand Value: Estimated at $14.8 billion in 2024.
- Customer Loyalty: High retention rates, with an average customer relationship lasting over 10 years.
- Impact: Reduces the likelihood of customers switching to new banks.
- Challenge for New Entrants: Requires significant investment in marketing and customer acquisition.
Access to Distribution Channels
A significant barrier for new entrants is accessing distribution channels. Established banks like Banco Santander benefit from extensive networks, including physical branches, online platforms, and partnerships, allowing them to reach a broad customer base. New banks face challenges in replicating this reach, which impacts their ability to attract customers and compete effectively. Building a distribution network requires substantial investment and time, hindering new entrants' ability to gain market share quickly. This advantage helps established banks maintain their competitive edge.
- Banco Santander had over 12,000 branches globally in 2024.
- Digital banking adoption is rapidly growing, with over 60% of adults using online banking in many countries.
- New banks often partner with fintech firms to access distribution channels.
- Regulatory compliance adds to the distribution challenges for new entrants.
The threat of new entrants to Banco Santander is low due to considerable barriers. High capital requirements and stringent regulations, like the ECB's capital adequacy ratios, protect its market position. Santander's strong brand and extensive distribution networks add to these protections.
| Factor | Details | Impact on New Entrants |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Needs | Billions required; 12.2% capital adequacy ratio (2023). | High barrier to entry; limits potential competitors. |
| Regulations | Compliance with ECB, capital, and risk rules. | High compliance costs; complex entry process. |
| Brand Value | Estimated at $14.8 billion (2024). | Requires significant marketing investment. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Banco Santander's analysis uses financial statements, market reports, and regulatory filings. These sources provide insights for competitor assessment.