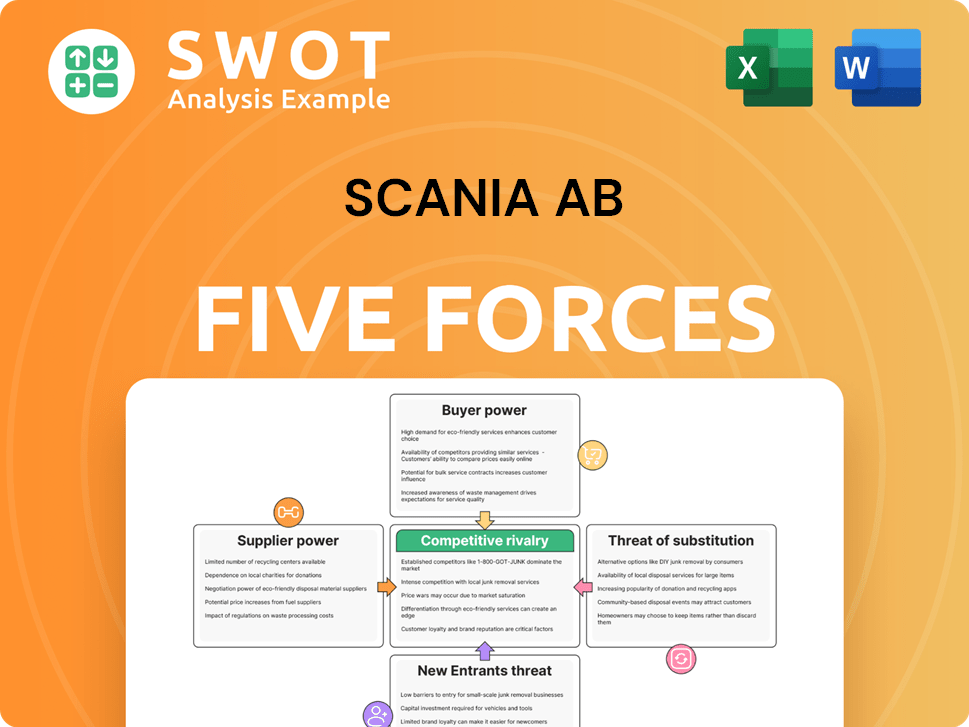
Scania AB Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Scania AB Bundle
What is included in the product
Analyzes Scania AB's competitive landscape through the lens of Porter's Five Forces, assessing threats and opportunities.
Customize pressure levels based on new data or evolving market trends.
Same Document Delivered
Scania AB Porter's Five Forces Analysis
You're previewing the final version—precisely the same document that will be available to you instantly after buying. This Scania AB Porter's Five Forces analysis examines the competitive intensity within the truck and bus industry, assessing the bargaining power of suppliers and buyers. It also explores the threat of new entrants, the rivalry among existing competitors, and the availability of substitute products. This comprehensive analysis is fully formatted and ready to use.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Template
Scania AB operates in a competitive heavy truck market, facing pressure from established rivals and potentially new entrants. Buyer power is moderate due to large fleet operators. Supplier bargaining power is influenced by engine and component technology. The threat of substitutes, particularly alternative fuels, is growing. Competitive rivalry is intense, shaped by global players.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Scania AB’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Scania faces supplier power challenges because it depends on a few specialized suppliers for essential parts. Switching suppliers is difficult, increasing costs and time due to industry-specific needs. This situation allows suppliers to negotiate better prices. For example, in 2024, the cost of raw materials for heavy vehicles rose by about 7%.
Scania faces high supplier concentration in tech, particularly for autonomous driving and EV components. These are crucial for its competitive edge. Key suppliers have pricing power due to limited alternatives. In 2024, the global autonomous vehicle market was valued at $68.09 billion.
Raw material price volatility significantly influences supplier power. Steel, aluminum, and rubber price fluctuations directly affect Scania's costs. Suppliers' ability to pass these costs impacts Scania's profitability; for instance, steel prices rose 15% in 2024. Hedging and contracts can mitigate this, but risks persist.
Impact of regulatory compliance
Suppliers capable of meeting rigorous environmental and safety standards gain significant bargaining power, especially in industries like automotive. Scania's focus on sustainability further strengthens this dynamic, as it seeks suppliers aligned with its eco-friendly goals. This emphasis on compliance can narrow Scania's supplier choices, increasing its dependence on these compliant providers. This, in turn, can affect procurement costs.
- In 2024, Scania's sustainability report highlighted an increased emphasis on supplier environmental performance.
- Regulatory compliance costs for suppliers can range from 5% to 15% of total production costs, influencing pricing.
- Scania's supply chain includes approximately 1,500 direct suppliers.
Integration of suppliers
Scania's integration with key suppliers shapes its bargaining power. This strategy fosters strong relationships and mutual dependence, potentially enhancing efficiency and innovation. However, it elevates the risk of supply chain disruptions if suppliers encounter difficulties. In 2024, Scania's supply chain disruptions impacted production, with an estimated 5% decrease in output. This integration strategy is a double-edged sword.
- Increased Dependency: Scania relies heavily on integrated suppliers for critical components.
- Efficiency Gains: Collaboration can streamline production and reduce costs.
- Disruption Risk: Supplier financial or operational issues can halt production.
- 2024 Impact: Supply chain issues caused a 5% production decrease.
Scania's supplier power is significant due to specialized components and industry standards. High supplier concentration, especially in tech, strengthens their pricing leverage. Raw material volatility and regulatory compliance also amplify supplier influence, impacting Scania's costs. In 2024, steel prices rose by 15% affecting Scania's procurement expenses.
| Factor | Impact | 2024 Data |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | High | Autonomous vehicle market valued at $68.09 billion |
| Raw Material Volatility | Significant cost impact | Steel prices rose 15% |
| Regulatory Compliance | Increased costs | Compliance costs can be 5-15% of production costs |
Customers Bargaining Power
Large fleet operators, like major logistics firms, wield considerable bargaining power. They can demand volume discounts, custom vehicle features, and attractive financing. In 2024, Scania's ability to offer competitive pricing, which directly impacts profit margins, is crucial. These customers' choices significantly affect Scania's revenue, with fleet sales accounting for a substantial portion of their total sales, approximately 60%.
Customers, particularly in competitive sectors, are price-conscious. During economic slowdowns, this intensifies, pushing them towards cheaper options. In 2024, the global truck market saw heightened price sensitivity due to inflation. Scania, aiming for premium pricing, must emphasize its quality and reliability to justify costs. For instance, Scania's focus on fuel efficiency, a key lifecycle cost factor, helps retain customers.
Switching costs for Scania's customers are moderate, requiring retraining and platform adaptation. The longevity of heavy vehicles, often exceeding a decade, locks customers into their initial decisions. This extended commitment limits their immediate ability to negotiate prices or terms. In 2024, Scania delivered 86,669 vehicles globally, indicating a substantial customer base bound by these switching dynamics.
Demand for customized solutions
Customers' growing demand for tailored solutions impacts Scania's operations. Scania's ability to offer customized vehicles and services strengthens its market position, decreasing customer bargaining power. This customization necessitates close customer collaboration and adaptable manufacturing processes. For instance, in 2024, Scania saw a 15% increase in orders for customized transport solutions, reflecting this trend.
- Customization reduces customer bargaining power.
- Increased demand for tailored solutions.
- Requires customer collaboration and flexible manufacturing.
- Scania's market position is strengthened.
Access to financing
Customers' access to financing significantly shapes their purchasing choices. Scania offers financial services, potentially boosting loyalty and mitigating interest rate impacts. Yet, alternative financing avenues empower customers in negotiating terms. In 2024, Scania Financial Services supported over 30% of global vehicle sales, showcasing its importance.
- Scania Financial Services supports over 30% of global vehicle sales in 2024.
- Customers can also seek financing from other sources, increasing their bargaining power regarding financing terms.
- Access to financing options influences customers' purchasing decisions.
Large fleet operators, like major logistics firms, have significant bargaining power, seeking discounts and custom features. In 2024, Scania's competitive pricing, crucial for margins, was impacted by these demands. Customers' price sensitivity, intensified by inflation, necessitates Scania's emphasis on quality.
| Aspect | Impact | 2024 Data |
|---|---|---|
| Fleet Sales | Influence on Revenue | Approx. 60% of sales |
| Price Sensitivity | Customer behavior | Heightened due to inflation |
| Customized Solutions | Market Position | 15% increase in orders |
Rivalry Among Competitors
The heavy truck and bus market is fiercely competitive, featuring giants such as Volvo and Daimler. These firms battle on price, tech, and brand image. Scania must continually innovate to stand out. In 2024, the global truck market saw intense price wars, with margins under pressure.
The commercial vehicle industry has seen notable consolidation. Volvo Group acquired the heavy-duty truck business of Renault in 2001, and Daimler AG acquired Chrysler in 1998, creating powerful competitors. This heightens rivalry, giving larger firms more resources. Scania needs strategic alliances to compete. In 2024, the global heavy-duty truck market was valued at $180 billion.
Scania faces fierce rivalry, with companies investing heavily in electric vehicles, autonomous driving, and connected services. This tech race intensifies competition, pushing firms to innovate for an edge. In 2024, Scania allocated a significant portion of its budget to R&D. Scania needs to maintain R&D investments, as in 2023, R&D expenses were 7.4% of net sales, to stay competitive.
Regional differences
Competitive dynamics for Scania AB differ significantly across regions. In Europe, Scania competes with Volvo and MAN, while in Latin America, it faces challenges from local players. Tailoring products and marketing is vital; for example, in 2024, Scania increased its focus on electric trucks in urban areas, particularly in Europe. Understanding regional nuances helps Scania maintain a competitive edge and boost sales.
- European sales account for a significant portion of Scania's revenue, about 40% in 2024.
- In Latin America, Scania's market share is around 15%, with strong competition from local brands.
- Adapting to local regulations, like emissions standards, is crucial for success in each region.
- Scania's global sales in 2023 reached approximately SEK 190 billion, showcasing its worldwide presence.
Aftermarket services
Competition in the commercial vehicle market goes beyond the initial sale, extending into aftermarket services like maintenance, repairs, and spare parts. These services are crucial revenue streams, fostering customer loyalty and repeat business for Scania. To stay competitive, Scania must offer robust, cost-effective aftermarket solutions. This includes ensuring parts availability and skilled service technicians to retain customers and boost profitability. In 2024, Scania's service revenue accounted for a significant portion of its total revenue, highlighting its importance.
- Service revenue is a major contributor to overall revenue.
- Customer loyalty is strongly linked to the quality of aftermarket services.
- Competition in aftermarket services drives the need for cost-effective solutions.
Scania faces intense rivalry in the truck market. Key competitors are Volvo and Daimler, engaging in price wars and tech battles. The competition extends to aftermarket services, crucial for revenue. Scania's R&D spending in 2023 was 7.4% of net sales.
| Metric | Data | Year |
|---|---|---|
| Global Truck Market Value | $180 billion | 2024 |
| R&D Expenses (% of Sales) | 7.4% | 2023 |
| European Sales (% of Revenue) | 40% | 2024 |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Rail transport and coastal shipping present a threat to Scania's trucking business, especially for long-haul routes. These modes can be cheaper and greener, potentially impacting Scania's market share. In 2024, the global rail freight market reached approximately $450 billion, and coastal shipping continues to grow, highlighting the need for Scania to innovate. Scania must watch these trends closely to stay competitive.
The used vehicles market presents a notable threat to Scania. During economic downturns, customers often choose used trucks and buses. In 2024, the used commercial vehicle market grew, reflecting this trend. Scania addresses this by offering certified pre-owned programs and financing for used vehicles. This strategy helps retain customers and compete effectively.
Technological advancements pose a threat to Scania. Innovations in logistics and supply chain, like optimized routing and load consolidation, cut demand for heavy vehicles. For example, in 2024, companies using advanced route optimization saw a 15% reduction in fuel costs. Scania must integrate these advancements to stay competitive.
Rental and leasing options
Rental and leasing services pose a threat to Scania, offering alternatives to direct purchases. These services provide flexibility, catering to short-term or fluctuating transportation needs. Scania must compete by providing attractive leasing options to retain customers. In 2024, the global vehicle rental market was valued at approximately $60 billion, showcasing the scale of this substitution threat.
- Market competition from rental services can significantly impact Scania's sales.
- Rental services offer financial flexibility, which can be appealing to businesses.
- Scania needs to offer competitive leasing deals to remain relevant.
- The rental market is substantial, representing a considerable portion of the transport sector.
Impact of remote work
The rise of remote work and e-commerce significantly impacts transportation needs, acting as a threat of substitute for Scania. E-commerce boosts demand for last-mile delivery trucks, while remote work potentially decreases the need for passenger transport. Scania must adapt its offerings to these shifts in demand, including electric vehicle options. This strategic pivot is crucial for sustained market relevance.
- In 2024, the e-commerce market grew by approximately 10%, indicating a rising need for delivery vehicles.
- Remote work adoption has stabilized, with around 30% of the workforce still working remotely at least part-time.
- Scania's 2024 investments in electric vehicles totaled €1.2 billion, reflecting its adaptation strategy.
- The shift to remote work presents a 5-10% decrease in public transport usage.
Scania faces threats from substitutes like rail and coastal shipping, which offer cheaper transport. Used vehicle markets also provide alternatives, especially during economic downturns. Technological advancements and rental services further compete with Scania's direct sales. E-commerce and remote work impact transportation needs.
| Substitute | Impact | 2024 Data |
|---|---|---|
| Rail Freight | Cheaper long-haul transport | $450 billion market |
| Used Vehicles | Cost-effective option | Market growth observed |
| Rental/Leasing | Flexibility for customers | $60 billion vehicle rental |
Entrants Threaten
The heavy truck and bus industry demands substantial capital for manufacturing, research, and distribution. This high barrier restricts new competitors, benefiting established firms like Scania. For instance, Scania's capital expenditure in 2023 was approximately SEK 8.9 billion. This investment underlines the financial hurdle for newcomers, reinforcing Scania's market position.
Scania faces the threat of new entrants, especially due to stringent regulations. These regulations, focusing on safety and the environment, demand substantial investment and expertise, acting as a barrier. For example, in 2024, the EU's Euro 7 emission standards are set to further increase compliance costs. New entrants struggle to match the established players' resources. This situation protects Scania.
Scania's strong brand reputation and customer loyalty pose a significant barrier to new entrants. Scania's brand is valued at approximately $10 billion as of late 2024. New competitors need substantial marketing investments. This is because established brands like Scania have a built-in advantage.
Access to distribution channels
Scania faces a moderate threat from new entrants due to the high barriers to entry in the heavy vehicle market. Building a global distribution network is crucial, demanding massive capital and expertise. Newcomers find it challenging to match Scania's extensive and established channels. This advantage limits the ability of new firms to effectively reach customers.
- Scania's global service network includes over 1,600 service points.
- Establishing a similar network could cost billions of dollars.
- New entrants often lack brand recognition, which Scania has built over decades.
Technological expertise
The commercial vehicle industry is rapidly evolving, with technology playing a crucial role. New entrants face a significant barrier due to the need for sophisticated technological expertise. This includes electric vehicle (EV) development, autonomous driving systems, and connected services. Scania's robust research and development (R&D) capabilities offer a substantial competitive edge in this landscape.
- Investments in R&D are crucial; Scania's parent company, TRATON, invested €1.4 billion in R&D in 2023.
- The shift to EVs requires expertise in battery technology, which is a high-cost area.
- Autonomous driving necessitates advanced software and sensor technology.
- Connected services involve data analytics and cybersecurity.
New entrants face high barriers. Scania's brand and global network pose challenges. Regulations and tech demands limit competition.
| Barrier | Details | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Needs | R&D, distribution, and manufacturing. | Limits new firms. |
| Regulations | Emission standards (Euro 7). | Increases compliance costs. |
| Brand & Network | Strong brand, global service network. | Customer loyalty. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Scania analysis is built on annual reports, market research, industry news, and financial data for robust Porter's Five Forces evaluations.