SunPower Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
SunPower Bundle
What is included in the product
Evaluates control held by suppliers and buyers, and their influence on pricing and profitability.
SunPower's analysis helps visualize market dynamics with a clear, concise five-force summary.
Preview the Actual Deliverable
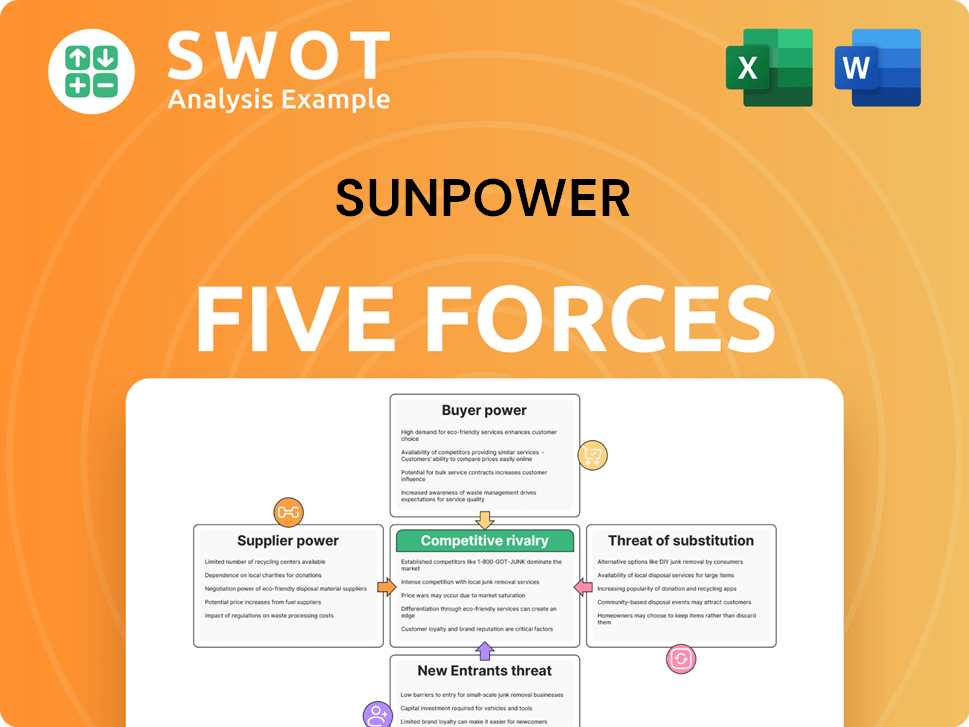
SunPower Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview presents SunPower's Porter's Five Forces analysis exactly as you'll receive it post-purchase.
It details the competitive landscape, threat of new entrants, and supplier/buyer power.
You'll gain immediate access to this comprehensive, professionally formatted analysis.
Understand industry rivalry, substitutes, and overall competitive dynamics instantly.
No revisions needed; this is the final, ready-to-use report.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Template
SunPower operates in a dynamic solar energy market, facing intense competition. Buyer power, largely driven by price sensitivity, significantly impacts profitability. The threat of new entrants, fueled by technological advancements, constantly looms. Supplier bargaining power, particularly for raw materials, presents a challenge. The availability of substitute energy sources adds further pressure.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore SunPower’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Supplier concentration in the solar panel component market affects SunPower's bargaining power. SunPower depends on suppliers for crucial parts like solar cells and inverters. This dependency can be a risk. However, alternative suppliers and vertical integration offer SunPower ways to diversify and reduce supplier power. In 2024, the solar panel market saw increased price competition among suppliers, impacting SunPower's costs.
Suppliers of raw materials, like polysilicon and glass, hold some sway, particularly during shortages. SunPower must manage these supplier relationships to secure its supply chain and pricing. For example, in 2024, polysilicon prices fluctuated significantly. Diversifying sources and using long-term contracts help reduce this risk.
Switching suppliers involves costs like qualifying new vendors and design changes. SunPower's supplier relationships create some stickiness. However, standardized components and flexible manufacturing can cut these costs. In 2024, SunPower's gross margin was negatively impacted by supply chain disruptions, highlighting the importance of managing supplier relationships efficiently. The company's ability to streamline its supply chain is crucial.
Supplier Forward Integration
Supplier forward integration poses a threat to SunPower, especially if suppliers of commoditized inputs decide to enter the solar panel manufacturing space. This move could increase their bargaining power significantly. However, highly specialized component suppliers are less likely to integrate forward, lessening the risk. SunPower must actively monitor supplier strategies to mitigate this risk effectively. Building strong, collaborative relationships with key suppliers is crucial for anticipating and responding to potential forward integration threats.
- Forward integration risk is moderate for SunPower.
- Commodity input suppliers pose a greater threat than specialized ones.
- SunPower should focus on relationship management.
- Monitoring supplier strategy is essential.
Impact of Tariffs
Trade policies and tariffs heavily influence supplier power by altering the costs of imported components. The imposition of tariffs on solar imports has spurred growth in domestic manufacturing. SunPower must strategically manage these trade dynamics to control costs and secure a consistent supply chain.
- In 2024, the U.S. solar industry faced tariffs on imported solar panels, affecting supply costs.
- These tariffs have encouraged domestic panel production, altering supplier dynamics.
- SunPower's ability to negotiate with suppliers is affected by these market changes.
- The company must adapt its procurement strategies to mitigate tariff-related risks.
SunPower's supplier bargaining power is influenced by market concentration and component specialization. In 2024, raw material price volatility, like polysilicon, affected costs. Trade policies and tariffs, such as those on imported panels, also shape supplier dynamics.
| Factor | Impact on SunPower | 2024 Data/Example |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | High concentration increases supplier power. | Polysilicon price fluctuations. |
| Raw Material Prices | Influences input costs. | Significant price changes in raw materials like polysilicon. |
| Trade Policies | Affects import costs and supply. | Tariffs on imported solar panels. |
Customers Bargaining Power
The bargaining power of customers for SunPower is moderate. This is due to the fragmented residential and commercial solar markets. SunPower's diverse customer base helps, but large utility-scale projects can concentrate buying power. In 2024, SunPower's revenue was approximately $3 billion, reflecting its broad customer reach. A balanced customer portfolio helps mitigate the risk of excessive influence.
Customers in the solar market show strong price sensitivity, particularly in residential sales. Government incentives, like the federal tax credit, significantly affect buying decisions. SunPower must provide competitive pricing and highlight long-term savings to justify its premium products. For example, in 2024, the federal tax credit remains at 30%, influencing customer purchasing power.
Customers can easily switch solar providers due to low switching costs. SunPower combats this by offering premium panels and a strong brand, aiming for customer loyalty. In 2024, the solar industry saw over 20,000 installers, highlighting the competition. High-efficiency panels and excellent service are key to retaining customers, as reported by Wood Mackenzie.
Availability of Information
Customers wield considerable power due to readily available information on solar products. Online resources and reviews enable informed choices, increasing their bargaining leverage. SunPower must maintain transparency and manage its online reputation proactively. This impacts pricing and sales strategies significantly. In 2024, the solar industry saw a 20% rise in online comparison usage.
- Online reviews significantly influence purchasing decisions.
- Comparison websites offer competitive pricing data.
- Consultant services provide expert advice.
- SunPower's reputation directly affects customer decisions.
Government Incentives
Government incentives heavily influence customer decisions in the solar market. Policies like net metering and tax credits directly affect the financial attractiveness of solar investments. For instance, in 2024, the federal Investment Tax Credit (ITC) remained at 30% for solar installations, significantly reducing upfront costs for customers. SunPower must adapt to policy changes to maintain its competitive edge.
- Federal ITC: 30% tax credit for solar installations.
- Net Metering: Policies vary by state, affecting solar savings.
- Rebate Programs: State and local incentives further reduce costs.
- Policy Impact: Changes can rapidly shift customer demand.
Customer bargaining power for SunPower is moderate. Price sensitivity and switching costs are notable factors. Government incentives, like the 30% federal tax credit in 2024, impact decisions.
| Factor | Impact | 2024 Data |
|---|---|---|
| Price Sensitivity | High | Influenced by federal tax credit (30%) |
| Switching Costs | Low | Over 20,000 solar installers |
| Government Incentives | Significant | ITC at 30%, net metering varies |
Rivalry Among Competitors
The solar panel manufacturing industry is fiercely competitive, featuring many global competitors. Market saturation and overcapacity can trigger price wars, squeezing profitability. SunPower combats this with high-efficiency panels and comprehensive energy solutions. In 2024, the global solar panel market is projected to reach $180 billion.
Intense price competition significantly impacts profit margins, particularly in the commoditized solar panel market. Chinese manufacturers, backed by substantial economies of scale and government subsidies, have aggressively lowered prices. SunPower, to stay competitive, must prioritize cost reduction strategies. The average solar panel price in 2024 was around $0.20 per watt.
Rapid technological advancements significantly intensify competition in the solar industry. Companies aggressively pursue more efficient and affordable solar panel technologies. Breakthroughs like perovskite cells and bifacial panels can quickly reshape the market. SunPower needs substantial R&D investments to maintain its competitive edge. In 2024, solar panel efficiency increased, with some panels exceeding 23% efficiency.
Brand Differentiation
SunPower leverages brand differentiation to compete effectively. Its reputation for premium, high-efficiency panels attracts customers willing to pay more. Strong brand loyalty, fostered by superior product performance, is essential for SunPower. This differentiation allows SunPower to navigate the competitive solar market. SunPower's focus on quality helps it stand out.
- SunPower's Maxeon panels achieve higher efficiencies than competitors.
- Customer satisfaction scores are consistently high, boosting loyalty.
- The premium market segment offers better margins.
- SunPower's brand recognition supports its market position.
Geographic Focus
Competitive rivalry for SunPower is significantly influenced by geographic focus. Different solar companies have strongholds in various regions, creating diverse competitive landscapes. SunPower primarily targets the U.S. residential and commercial solar markets, which places it in direct competition with companies like Tesla and Enphase. Adapting strategies to local market conditions is crucial for SunPower to maintain its competitive edge and increase market share.
- U.S. solar market growth in 2024 is projected at 25% by the Solar Energy Industries Association (SEIA).
- Tesla's residential solar installations in Q3 2023 were approximately 60 MW.
- Enphase reported $711 million in revenue for Q3 2023.
- SunPower's Q3 2023 revenue was $834.9 million.
Competitive rivalry in solar is intense. Market saturation and technological shifts drive price competition, affecting profitability. SunPower competes by focusing on high-efficiency panels and brand differentiation. The U.S. solar market is growing, with 25% growth projected in 2024.
| Metric | SunPower | Competitors |
|---|---|---|
| Q3 2023 Revenue | $834.9M | Tesla (~$300M), Enphase ($711M) |
| Panel Efficiency | Maxeon panels, high efficiency | Varies (e.g., Tesla, average) |
| U.S. Market Growth (2024) | Target market | Key market for all |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Energy storage solutions, like batteries, are substituting solar panels by letting users store excess energy for later use, decreasing grid reliance. This shift poses a threat to SunPower's standalone solar panel sales. The global energy storage market, valued at $16.4 billion in 2023, is projected to reach $34.5 billion by 2028. SunPower's move into storage helps offset this risk, offering a complete energy package.
Other renewable energy sources, like wind and hydro, compete with solar. The cost of these alternatives differs by location. In 2024, wind energy's levelized cost of electricity (LCOE) was about $0.04/kWh, while solar was around $0.06/kWh. SunPower should emphasize solar's scalability for homes and businesses.
Energy efficiency measures, like better insulation, threaten solar panel demand by cutting overall energy use. Promoting energy efficiency alongside solar can be a strong value proposition. For instance, the U.S. saw a 1.8% decrease in energy consumption in 2023 due to efficiency efforts. This impacts solar adoption rates.
Traditional Energy Sources
Traditional energy sources, including natural gas and coal, present a substantial competitive threat to SunPower, particularly in areas where fossil fuels are readily available and economically priced. Government policies and environmental regulations significantly influence the cost-effectiveness of solar energy compared to these established alternatives. For instance, in 2024, natural gas prices fluctuated, affecting the competitiveness of solar in different regions. SunPower must actively support policies that promote renewable energy and account for the environmental expenses associated with fossil fuels.
- In 2024, natural gas prices varied significantly across the US, impacting solar's competitiveness.
- Government incentives and regulations play a key role in solar adoption.
- SunPower's advocacy for renewable energy policies is crucial.
- The environmental costs of fossil fuels affect solar's value proposition.
Net Metering Policies
Changes in net metering policies pose a threat to SunPower. These policies affect how solar owners are compensated for excess energy sent to the grid, impacting the financial appeal of solar. SunPower must adjust its strategies to thrive amidst evolving net metering regulations. For example, in 2024, some states reduced net metering credits, requiring SunPower to offer competitive value.
- Policy Shifts: Changes in net metering can diminish solar's financial benefits.
- Compensation Impact: Reduced credits for excess energy lower solar investment returns.
- Business Adaptation: SunPower must modify its offerings to stay competitive.
- 2024 Example: States cut credits, influencing solar project economics.
Energy storage reduces grid reliance, threatening standalone solar panel sales. Wind and hydro compete; in 2024, solar's LCOE was ~$0.06/kWh. Energy efficiency cuts demand; the U.S. saw a 1.8% drop in energy use in 2023.
| Substitute | Description | Impact on SunPower |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Storage | Batteries store energy for later use. | Reduces demand for standalone panels. |
| Other Renewables | Wind, hydro offer alternatives. | Creates price competition. |
| Energy Efficiency | Better insulation, reducing energy use. | Lowers demand for solar. |
Entrants Threaten
The solar panel manufacturing industry faces high capital requirements, posing a significant barrier for new entrants. New companies need substantial funding for facilities, equipment, and R&D. Securing capital is crucial to compete with established firms. SunPower leverages its existing infrastructure and economies of scale to its advantage. In 2024, the cost to build a new solar panel factory can range from $500 million to over $1 billion.
Manufacturing high-efficiency solar panels requires specialized technical expertise, posing a barrier to new entrants. SunPower's long-standing experience and proprietary tech give it an edge. Continuous innovation and IP protection are essential. SunPower's R&D spending in 2024 was about $60 million, enhancing its technological moat.
SunPower's established brand recognition and strong customer relationships make it challenging for new solar companies to compete. SunPower benefits from a well-regarded brand and an extensive dealer network. Developing brand awareness and customer trust requires considerable time and financial investment. In 2024, SunPower's brand value was estimated at $1.5 billion, reflecting its strong market position.
Government Regulations
Government regulations pose a significant threat to new entrants in the solar industry. Complex permitting processes and interconnection standards demand specialized knowledge and resources, acting as barriers. SunPower's established expertise in navigating these regulatory landscapes offers a distinct advantage. This experience helps SunPower streamline operations and reduce compliance costs, unlike new players.
- Regulatory compliance costs can range from 5% to 15% of total project costs.
- Permitting timelines can vary from a few weeks to several months, impacting project schedules.
- Interconnection standards often require significant upfront investment in grid upgrades.
- SunPower's familiarity with state and federal incentives provides a competitive edge.
Supply Chain Access
The threat of new entrants in the solar panel market is influenced by supply chain access. Establishing a dependable supply chain for raw materials and components is crucial for solar panel production. New businesses might struggle to obtain favorable supply agreements and compete with established companies. SunPower's established relationships with suppliers offer a degree of security and cost competitiveness.
- Supply chain disruptions, such as those experienced in 2022, can significantly impact new entrants.
- SunPower's existing supplier relationships could offer it a competitive advantage in terms of pricing and availability, according to sources [1, 2].
- The cost of raw materials, like polysilicon, can fluctuate wildly, affecting the profitability of new entrants.
- Securing long-term supply contracts can be a barrier to entry, as established companies often have these in place [3].
New solar companies face steep entry barriers, including high capital needs and technical expertise. SunPower's established brand and supplier relationships give it an edge. Government regulations and supply chain access further complicate market entry.
| Factor | Impact on New Entrants | SunPower's Advantage |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High initial investment in facilities ($500M-$1B) | Leverages existing infrastructure and economies of scale |
| Technology | Requires specialized expertise and R&D ($60M in 2024) | Long-standing experience and proprietary tech |
| Brand & Customer Relationships | Difficult to build brand recognition and trust | Established brand value ($1.5B in 2024) and dealer network |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
The SunPower analysis utilizes financial reports, market research, and competitor analysis. This includes industry databases and government publications.