Turning Point Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Turning Point Bundle
What is included in the product
Analyzes competitive forces, including threats, bargaining power, and rivalry, for Turning Point.
Instantly visualize competitive threats with a powerful radar chart to make smarter decisions.
Same Document Delivered
Turning Point Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Turning Point Porter's Five Forces Analysis. You're seeing the exact document you'll receive instantly after your purchase, ready to download. It's professionally crafted and fully formatted for immediate use. There are no hidden sections or alterations; what you see is what you get. Consider this your ready-to-go resource.
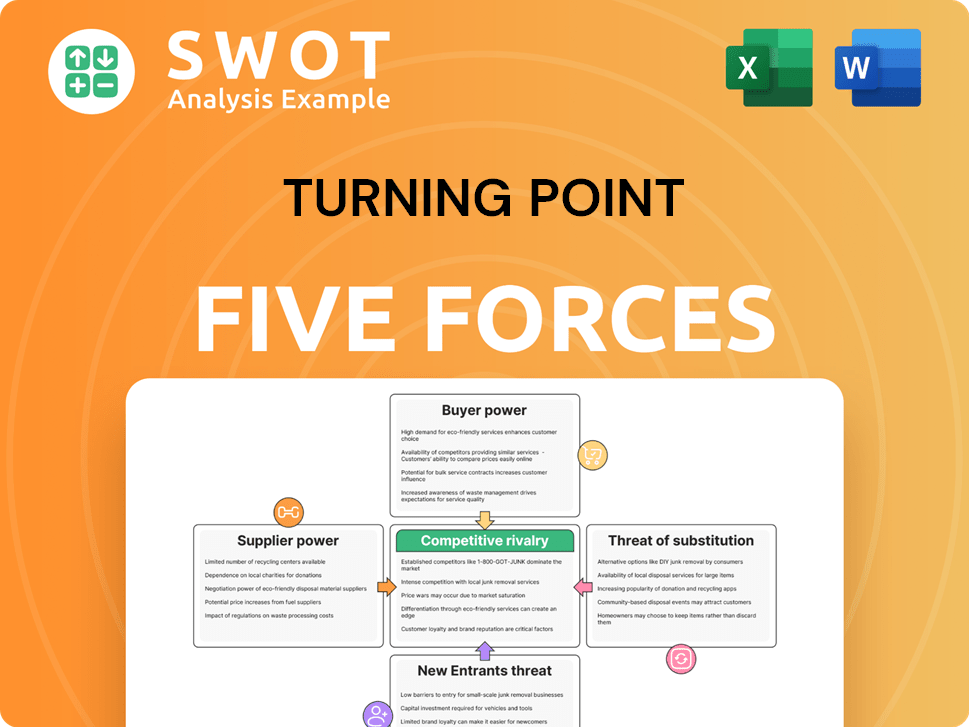
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Template
Turning Point faces intense rivalry, with numerous competitors vying for market share, especially in the ever-changing software industry. Buyer power is moderate, though customers have choices. Supplier power is relatively low, but key partnerships are vital. The threat of new entrants is high, with low barriers to entry. Substitutes pose a significant risk, given alternative software solutions.
Ready to move beyond the basics? Get a full strategic breakdown of Turning Point’s market position, competitive intensity, and external threats—all in one powerful analysis.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Turning Point Brands sources from various suppliers for its products. High supplier concentration could give these suppliers leverage. This may affect costs and supply stability for the company.
Turning Point Brands' supplier power hinges on switching costs. If changing suppliers is hard due to specialized materials or contracts, suppliers gain power. In 2024, long-term supply contracts can significantly impact this dynamic. Consider how the cost of switching affects Turning Point Brands' profitability.
Suppliers' power decreases with substitute inputs. Turning Point Brands benefits from readily available alternatives to their components. Market analysis of substitutes is crucial. For instance, the tobacco market offers various leaf sources. In 2024, the global tobacco market was valued at approximately $800 billion, indicating a wide array of potential suppliers and substitute options.
Supplier's Ability to Integrate Forward
If Turning Point Brands' suppliers integrate forward, their bargaining power increases. This means they could start producing and selling products that compete with Turning Point Brands. Monitoring this is crucial to assess the risk.
For instance, a supplier of flavored paper might launch its own rolling paper brand, directly competing with Turning Point Brands' Zig-Zag. This move could significantly impact Turning Point Brands' market share and profit margins.
In 2024, the tobacco industry saw shifts as suppliers explored direct-to-consumer models, heightening the need to analyze supplier integration. This strategic move by suppliers can change the competitive landscape.
The potential for suppliers to control both supply and retail channels creates a significant threat. Turning Point Brands must actively manage supplier relationships to mitigate this risk.
- Supplier integration increases bargaining power.
- Direct competition from suppliers impacts market share.
- Monitor supplier moves to manage risk.
- 2024 saw suppliers exploring new channels.
Impact of Inputs on Differentiation
If suppliers' inputs greatly affect Turning Point's product quality, their bargaining power increases. Unique ingredients can lead to premium prices, giving suppliers leverage. For example, if a key flavor component is scarce, its supplier gains power. Analyzing input impact is key for Turning Point. In 2024, raw material costs have impacted profitability, highlighting supplier influence.
- Supplier concentration and switching costs are vital.
- High-quality inputs can create differentiation.
- Scarcity of key ingredients boosts supplier power.
- Input cost increases directly affect profitability.
Supplier power for Turning Point Brands depends on their concentration and switching costs, impacting costs. Forward integration by suppliers poses a risk to market share. In 2024, the global tobacco market's size (approx. $800B) influences supplier dynamics, and raw material costs affect profitability.
| Factor | Impact on TPB | 2024 Data/Example |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | High concentration increases supplier power. | Tobacco market is vast but certain flavor components are scarce. |
| Switching Costs | High costs give suppliers leverage. | Long-term contracts can affect profitability. |
| Supplier Integration | Direct competition from suppliers. | Suppliers launching their own rolling paper brands. |
Customers Bargaining Power
Buyer volume significantly impacts bargaining power. Large-scale purchases, like those from major retailers, enable buyers to negotiate better terms. Turning Point Brands must assess buyer concentration to understand this dynamic. In 2024, approximately 60% of Turning Point's revenue came from its top 10 customers, highlighting this.
Switching costs significantly influence customer bargaining power. If customers can easily switch, their power rises, allowing them to seek better deals. High switching costs, maybe due to brand loyalty or exclusive offerings, reduce buyer power. For instance, a 2024 study shows that 60% of consumers prioritize brand loyalty when switching is difficult.
Price-sensitive customers can strongly influence Turning Point Brands to reduce prices. This is more likely when many similar products exist. In 2024, the price elasticity of demand will be important. For example, if a price increases by 10%, demand might drop. Analyze Turning Point Brands' pricing strategies considering customer price sensitivity.
Customer's Ability to Integrate Backward
If customers can make products themselves, they gain power. A big retailer might create its own brand to rival Turning Point Brands. This move directly impacts Turning Point Brands' market share and pricing control. Assessing this threat is crucial for strategic planning. For example, consider the shift towards private-label e-cigarettes. This illustrates customers' power to integrate backward and impact industry dynamics.
- Private-label brands in the e-cigarette market have grown by 15% in 2024.
- Retailers' control over shelf space and promotions affects Turning Point Brands' sales.
- Backward integration reduces Turning Point Brands' pricing power.
- Customer ability to switch to alternatives is a key factor.
Availability of Information
When customers have access to comprehensive product information, their ability to negotiate improves. Online platforms and price comparison tools enable informed decisions, increasing customer bargaining power. This transparency shifts the balance, empowering buyers to seek better terms. According to recent data, 75% of consumers research products online before purchasing, highlighting information's impact. This trend underscores the importance of understanding how readily available data shapes market dynamics.
- Online reviews significantly influence purchasing decisions.
- Price comparison websites provide instant pricing data.
- Product specifications are easily accessible.
- Transparency enhances buyer power.
Customer bargaining power significantly affects Turning Point Brands' market position. Large buyers, accounting for a significant portion of revenue, can negotiate favorable terms. Switching costs, brand loyalty, and price sensitivity also shape customer power. In 2024, factors like private-label growth and online information access further influence these dynamics.
| Factor | Impact | 2024 Data |
|---|---|---|
| Buyer Concentration | High concentration increases buyer power | Top 10 customers account for 60% of revenue |
| Switching Costs | High costs reduce buyer power | 60% of consumers prioritize brand loyalty |
| Price Sensitivity | High sensitivity boosts buyer power | Price elasticity of demand is critical |
Rivalry Among Competitors
Many competitors in active ingredients and smoking accessories increase rivalry. This boosts price wars, marketing, and innovation to capture market share. For instance, the global e-cigarette market was valued at $27.53 billion in 2023. Assessing the competition is key for success.
Slower industry growth intensifies competition. For instance, the global smartphone market's growth slowed to 2.5% in 2023, leading to increased rivalry among manufacturers. Conversely, fast growth, like the AI sector's projected 20% annual increase, can reduce direct competition. Tracking growth trends is crucial; consider the 2024 forecast for the renewable energy market.
Low product differentiation intensifies competitive rivalry. If products resemble commodities, price becomes the primary battleground, squeezing profit margins. In 2024, companies in the tobacco industry, like Turning Point Brands, face this challenge. To combat this, Turning Point should focus on differentiating its offerings. This could involve unique branding, enhanced features, or superior quality to stand out in the market.
Switching Costs
Low switching costs fuel fierce competition. Customers readily change brands if alternatives offer better value. Companies invest in customer retention through loyalty programs and superior service. These strategies aim to raise switching costs, increasing customer stickiness. For example, in 2024, the average customer churn rate in the telecom industry was around 25%.
- High churn rates indicate low switching costs.
- Loyalty programs can reduce churn by 10-15%.
- Excellent customer service is crucial for retention.
- Exclusive offerings provide a competitive edge.
Exit Barriers
High exit barriers can make competitive rivalry more intense because companies may persist in the market even when they aren't profitable. These barriers, like specialized assets or long-term contracts, keep firms locked in. For example, in the airline industry, high costs of selling planes and leased assets can exacerbate competition. Analyzing exit barriers reveals industry stability. In 2024, the airline industry faced intense competition, with many airlines operating near break-even or at a loss due to these factors.
- Specialized Assets: Unique equipment hard to sell.
- Long-Term Contracts: Commitments that lock companies in.
- High Exit Costs: The price of leaving the market.
- Impact: Intense rivalry even with losses.
Competitive rivalry intensifies with many competitors. Slow industry growth and low product differentiation fuel price wars. High exit barriers keep firms competing, even when unprofitable.
| Factor | Impact | Example (2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Many Competitors | Increased price wars | E-cigarette market: $28.8B |
| Slow Growth | Intensifies competition | Smartphone growth: ~2.0% |
| Low Differentiation | Focus on price | Tobacco industry: Price battles |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The availability of substitutes significantly impacts Turning Point Brands' pricing power. Consumers can switch to alternatives like vaping, nicotine patches, or even abstain. In 2024, the e-cigarette market, a direct substitute, was valued at approximately $19.5 billion globally, indicating a strong competitive landscape. Identifying and monitoring these alternatives is key.
If substitutes offer similar performance at a lower price, the threat of substitution rises. For example, in 2024, the market share of plant-based meat alternatives grew, pressuring traditional meat producers. Customers often choose alternatives offering similar benefits at a better value. Therefore, assessing the price-performance ratio of substitutes is crucial for businesses.
Low switching costs empower customers to readily embrace substitutes. For instance, in 2024, the e-cigarette market saw considerable shifts due to evolving consumer preferences and product innovations. Factors like brand loyalty and ease of access influence switching costs; however, if a rival offers similar products at a lower price point, customers may switch. Turning Point Brands must analyze these dynamics to protect their market share.
Brand Loyalty
Strong brand loyalty can protect Turning Point Brands from substitute threats. Loyal customers are less likely to switch, even with cheaper or similar alternatives. Maintaining this loyalty is key for sustained market position. Consider the 2024 revenue data for brands with high loyalty. Effective marketing and product innovation are vital to build and maintain loyalty.
- Loyal customers resist substitutes.
- Brand reputation is a key factor.
- Marketing and innovation build loyalty.
- High loyalty impacts revenue positively.
Perceived Differentiation
If Turning Point Brands' products are seen as unique, the threat of substitutes goes down. Strong branding and special features make their products stand out. This perceived differentiation makes it harder for other products to compete. Focusing on what makes Turning Point Brands different is super important.
- Turning Point Brands' net sales in Q3 2024 increased to $106.3 million, which is up 7.8% compared to Q3 2023.
- The company's focus is on its portfolio of differentiated products.
- This helps to create a strong brand image.
The threat of substitutes affects Turning Point Brands' pricing power. Alternatives like vaping and nicotine patches compete. E-cigarette market was $19.5B in 2024, showing competition. Brand loyalty and differentiation reduce this threat.
| Factor | Impact | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Substitute Availability | Increases Competition | E-cigarettes, nicotine patches |
| Switching Costs | Influences Customer Choice | Low costs encourage shifts |
| Brand Loyalty | Reduces Threat | High loyalty, stable revenue |
Entrants Threaten
High barriers to entry significantly decrease the threat of new competitors. These barriers often involve substantial capital needs, like the $1 billion cost to build a semiconductor plant. Regulatory obstacles, such as FDA approvals, also act as deterrents. Strong brand recognition, exemplified by Coca-Cola's market dominance, further protects incumbents. Finally, access to distribution channels, like Walmart's extensive network, is crucial.
Significant capital needs to enter the active ingredients or accessories market can deter new entrants. Manufacturing facilities and R&D are expensive. Marketing creates substantial financial hurdles. For example, building a pharmaceutical plant costs billions. This is a significant barrier.
Stringent regulations, like those from the FDA, act as a significant barrier. Compliance costs and approval processes can be high. The pharmaceutical industry, for example, faces substantial regulatory hurdles. In 2024, the FDA approved approximately 40 new drugs. Regulatory changes must be constantly monitored.
Brand Loyalty and Established Brands
Strong brand loyalty is a significant barrier for new entrants, especially in the tobacco industry. Established brands like Zig-Zag and Stoker's benefit from decades of customer recognition and trust, making it challenging for newcomers to compete. New entrants face the need for substantial marketing investments to build brand awareness and capture market share from these established players. This can involve spending millions on advertising and promotional activities to overcome the existing brand loyalty.
- Market leaders hold a significant portion of the market share.
- New brands struggle to get shelf space in retail stores.
- Established brands have large advertising budgets.
- Loyal customers are less likely to switch brands.
Access to Distribution Channels
Access to distribution channels significantly impacts new entrants. Established firms often possess strong relationships with retailers, making it challenging for newcomers to secure shelf space. These distribution barriers are a major hurdle for new companies. Overcoming these obstacles requires significant investment in marketing and sales. Limited access can delay market entry and reduce competitive viability.
- In 2024, the cost of establishing a new distribution network can range from $50,000 to several million dollars, depending on the industry and scale.
- Companies like Amazon have revolutionized distribution, but smaller entrants still face challenges in competing with established networks.
- Successful new entrants often leverage digital channels, which offer lower barriers to entry compared to traditional retail.
- The beverage industry, for example, sees about 20% of new product launches failing due to distribution issues.
The threat of new entrants varies by industry, influenced by barriers. High initial capital needs, like a semiconductor plant's $1B cost, deter entry. Regulations, such as FDA approvals (around 40 in 2024), also pose challenges. Brand loyalty and distribution access further complicate new entry.
| Barrier | Impact | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Needs | High | Pharma plant ($B) |
| Regulations | Significant | FDA approvals |
| Brand Loyalty | Protective | Coca-Cola |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
This analysis leverages company filings, market reports, competitor intelligence, and industry publications for a comprehensive overview.