Union Pacific Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Union Pacific Bundle
What is included in the product
Tailored exclusively for Union Pacific, analyzing its position within its competitive landscape.
Customize competitive pressure levels based on new Union Pacific market insights.
Preview the Actual Deliverable
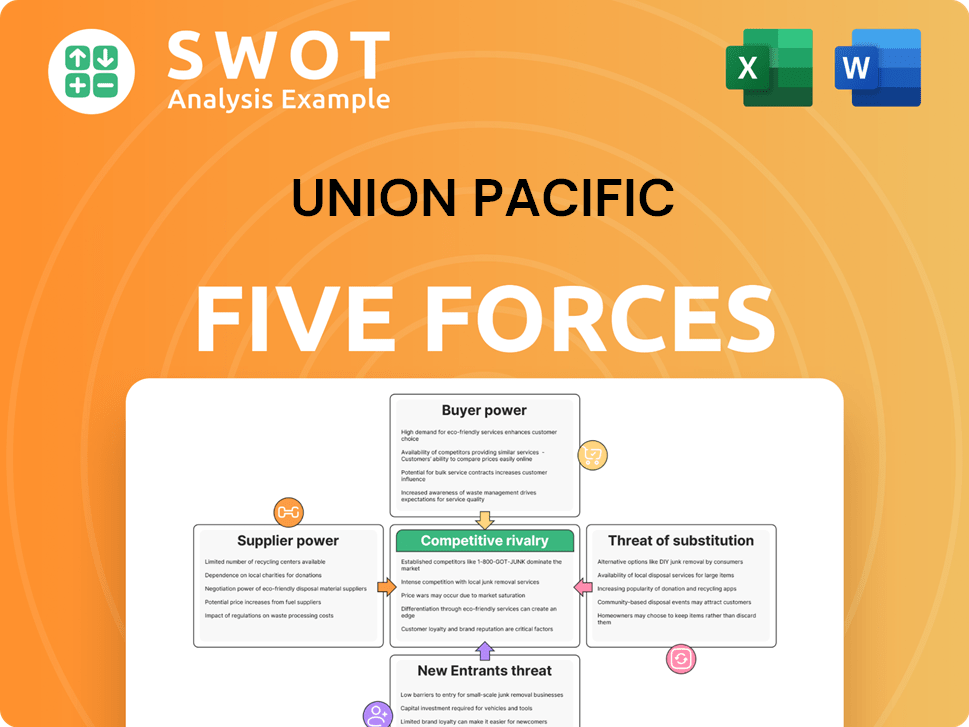
Union Pacific Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact document you'll receive immediately after purchase—no surprises, no placeholders. The Union Pacific Porter's Five Forces analysis examines industry rivalry, supplier power, buyer power, threat of substitution, and the threat of new entrants. It assesses competitive forces impacting UP's profitability and strategic positioning. This analysis provides crucial insights for understanding the company's strengths and weaknesses within the railway industry. This is the complete, ready-to-use analysis file.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Template
Union Pacific (UNP) navigates a complex railway industry. Bargaining power of buyers, mainly large shippers, is moderate, influencing pricing. Supplier power, particularly for fuel & equipment, poses a risk. The threat of new entrants is low due to high barriers. Competitive rivalry with BNSF is intense. Substitute threats, such as trucking, require constant adaptation.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Union Pacific’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The railroad industry's reliance on specialized equipment, like locomotives, concentrates supplier power. Limited suppliers can dictate prices and terms, particularly during fleet upgrades or expansions. Union Pacific, a major railroad, faces dependence on these suppliers for operations. In 2024, locomotive costs significantly impacted operating expenses.
Steel is essential for Union Pacific's tracks and rolling stock. The steel industry's concentration gives suppliers considerable power. Union Pacific's extensive network needs constant steel. In 2024, global steel prices fluctuated, impacting railroad maintenance costs. This dynamic underscores supplier influence on profitability.
Fuel is a significant operational cost for Union Pacific. The bargaining power of fuel suppliers is directly impacted by global oil prices and regional market dynamics. Union Pacific combats this by hedging and long-term contracts. Despite these measures, they are still vulnerable to market changes. In 2024, fuel costs for Union Pacific were substantial, reflecting the volatility in oil prices.
Labor Unions
Labor unions wield substantial bargaining power over Union Pacific, significantly impacting operational costs. These unions, representing crucial railroad workers, negotiate wages, benefits, and working conditions. In 2024, around 80% of Union Pacific's workforce was unionized, a key factor in labor negotiations. Disputes can disrupt operations, as seen in past contract impasses.
- Unionized workforce constitutes a significant portion of Union Pacific's employees.
- Negotiations with unions directly affect the company's financial performance.
- Labor disputes pose a risk of operational disruptions.
- Union influence impacts wage and benefit structures.
Specialized Railcar Manufacturers
Specialized railcar manufacturers hold considerable bargaining power, especially when producing unique railcars for specific commodities. Limited competition in manufacturing specialized railcars allows suppliers to set higher prices. Union Pacific's operational costs are directly impacted by these supplier dynamics, influencing profitability.
- High demand for specialized railcars, such as those for transporting chemicals and automobiles, gives suppliers pricing leverage.
- In 2024, the cost of specialized railcars increased by approximately 7% due to supply chain constraints and rising material costs.
- Union Pacific's capital expenditures for railcars in 2024 were $1.5 billion, reflecting the importance of this supplier relationship.
Union Pacific faces supplier power challenges across several areas. The high cost of steel and specialized railcars impacts operations and maintenance. Fuel costs and labor negotiations also exert financial pressure. These factors influenced operating expenses significantly in 2024.
| Supplier | Impact | 2024 Example |
|---|---|---|
| Locomotive | High Equipment Costs | Locomotive costs affected OpEx |
| Steel | Track & Rolling Stock | Fluctuating global steel prices |
| Fuel | Operational Costs | Significant fuel costs |
Customers Bargaining Power
Large volume shippers wield considerable influence, enabling them to negotiate favorable terms. These entities, like agricultural giants and chemical manufacturers, leverage their substantial shipping needs to secure lower rates. In 2024, Union Pacific's revenue from these key segments reflects the impact of these negotiations. For example, the agricultural sector accounts for a significant portion of UP's freight revenue, indicating the scale of these customer relationships.
Intermodal customers, utilizing rail and other transport modes, operate in a competitive landscape. These customers have options, boosting their bargaining power. In 2024, Union Pacific's intermodal revenue was significantly impacted by market dynamics. To stay competitive, Union Pacific must provide compelling pricing and top-notch service to retain this customer segment.
The bargaining power of commodity shippers, such as those transporting coal, varies with market dynamics. When demand for commodities like coal is low, shippers often gain more leverage. Union Pacific's pricing is influenced by these demand shifts across the diverse commodities it hauls. In 2024, coal's share of U.S. freight revenue was about 10%, reflecting its importance.
Geographic Constraints
In areas where Union Pacific is the main rail option, customers face reduced bargaining power. Without other rail choices, negotiating favorable rates becomes harder for them. But, customers can still turn to trucking, which serves as a substitute. Union Pacific's 2024 revenue hit $24.1 billion, showing its dominance. The company's network covers 23 states in the western U.S., influencing customer choices.
- Union Pacific's market share in exclusive service areas.
- Impact of trucking costs on customer negotiations.
- Customer concentration levels in key geographic regions.
- Rail vs. truck transportation cost comparisons.
Service Reliability
Customers prioritize dependable and prompt delivery; this is essential. Union Pacific's bargaining power increases if it offers better service than rivals. Superior service allows for maintaining customer loyalty and pricing flexibility. Operational efficiency is critical for retaining customers and supporting pricing strategies.
- In 2023, Union Pacific's on-time performance was approximately 78%, showing room for improvement.
- Improved service reliability can lead to increased customer satisfaction and contract renewals.
- Efficient operations reduce costs, which can be passed on to customers or retained as profit.
Customer bargaining power significantly shapes Union Pacific's profitability. Large shippers negotiate lower rates due to volume, affecting revenue. Intermodal and commodity shippers also wield power due to competition and market dynamics, respectively. Customers' options, from trucking to service quality, impact pricing.
| Factor | Impact | 2024 Data Point |
|---|---|---|
| Large Shippers | Volume discounts | Ag. revenue share - ~20% |
| Intermodal | Competitive pricing | Revenue influenced by market |
| Commodities | Demand-driven pricing | Coal share of freight - ~10% |
Rivalry Among Competitors
Union Pacific contends with major rivals like BNSF, CSX, and Norfolk Southern for freight business. This leads to price wars and service improvements to gain clients. The industry's consolidation boosts this competition. In 2024, these railroads collectively moved billions of tons of goods.
Trucking companies present significant competition for Union Pacific, particularly in short-haul and time-sensitive deliveries. Trucks' flexibility and speed challenge Union Pacific's market share. The American Trucking Associations reported over 733,000 trucking companies operating in 2024. The trucking sector's ability to adapt to fluctuating demands intensifies the rivalry, pressuring Union Pacific to optimize costs and services. The road sector's competitive dominance remains a key challenge for rail.
Intermodal transport, which combines rail with trucks and ships, is a competitive space for Union Pacific. They compete with other intermodal providers and various transportation solutions to win customers. This competition pushes Union Pacific to innovate and improve efficiency. In 2024, the intermodal segment faced challenges, with volumes down due to economic conditions.
Operational Efficiency
Railroads aggressively pursue operational efficiency to cut expenses and boost service quality, intensifying competition. Union Pacific, for instance, is keen on refining train schedules and leveraging tech for a competitive advantage. Precision Scheduled Railroading (PSR) is a key strategy to improve efficiency and boost profitability. These efficiency gains directly affect the ability to offer competitive pricing and service levels.
- Union Pacific's operating ratio was 60.8% in 2023, showcasing efficiency.
- PSR implementation has been a major focus for cost reduction in the industry.
- Technological investments in tracking and automation are ongoing.
- Efficient operations drive better resource allocation and asset utilization.
Regulatory Environment
The railroad industry faces regulatory scrutiny, influencing competitive dynamics. Changes in regulations can significantly impact competition, potentially increasing costs or creating new barriers. Compliance with safety and environmental standards is a continuous operational requirement, affecting profitability. The Surface Transportation Board (STB) oversees aspects of the industry, impacting competitive behavior.
- 2024: Union Pacific spent ~$3.3B on capital expenditures, including regulatory compliance.
- STB decisions can affect pricing and service, influencing competitive strategies.
- Environmental regulations, like those on emissions, increase operational expenses.
- Safety regulations necessitate ongoing investment in technology and training.
Union Pacific faces intense rivalry from railroads and trucking companies. Price wars and service enhancements are common strategies for attracting customers. Trucking, with over 733,000 companies in 2024, offers flexibility. Efficient operations and tech investments are crucial for staying competitive.
| Competitive Factor | Impact | Data |
|---|---|---|
| Rail vs. Trucking | Market Share Pressure | Trucking revenue: $800B+ (2024 est.) |
| Operational Efficiency | Cost & Service Optimization | UP's Op. Ratio (2023): 60.8% |
| Regulatory Influence | Cost & Compliance | UP's CapEx (2024): ~$3.3B |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Trucking represents a major substitute for Union Pacific's rail services, particularly for urgent and shorter hauls. Its broad highway network offers unparalleled accessibility and flexibility. However, trucking faces higher fuel expenses and greater emissions per ton-mile compared to rail. In 2024, the trucking industry's revenue was approximately $800 billion, reflecting its significant market presence.
Pipelines pose a direct threat as substitutes for transporting liquids and gases, like petroleum and natural gas. They offer a cost-effective option for high-volume transport, though limited to specific commodities and routes. Union Pacific competes with pipelines in certain markets, impacting its revenue. In 2024, the U.S. pipeline network transported approximately 1.7 billion tons of crude oil and petroleum products.
Barge transport presents a substitute for Union Pacific, especially for bulk goods. Waterways offer cheaper transport but are slower and geographically limited. In 2023, barge transport accounted for roughly 15% of U.S. freight. Union Pacific competes with barges in areas with navigable rivers, affecting freight pricing. For example, the cost of moving a ton of coal by barge is $7.6, while rail is $14.7.
Air Freight
Air freight serves as a substitute for Union Pacific, particularly for high-value, urgent goods. Although air transport is considerably pricier than rail, it ensures swift delivery over extensive distances. Union Pacific doesn't directly compete with air freight in most cases; however, it's a consideration for specific cargo types. The air cargo market's revenue in 2024 is projected to be around $150 billion globally.
- Air freight is quicker but more costly than rail.
- Union Pacific mainly transports bulk goods, not time-sensitive items.
- Air freight's global market is substantial.
Alternative Supply Chains
Changes in supply chain strategies pose a threat to Union Pacific. Onshoring and nearshoring trends, where companies bring manufacturing closer to their markets, can decrease the need for long-distance freight transport. If companies reduce their reliance on long-haul transportation, Union Pacific's volume and revenue may be negatively impacted. To mitigate this, Union Pacific needs to offer competitive and value-added services.
- Nearshoring has increased, with Mexico's exports to the U.S. rising.
- Union Pacific's revenue in 2023 was $24.1 billion.
- Adapting to changing supply chains is crucial for sustained profitability.
Substitutes like trucking, pipelines, and barges offer alternatives to Union Pacific's rail services. Trucking competes with rail for short hauls, while pipelines transport liquids and gases. Barges provide cost-effective transport for bulk goods, affecting pricing in navigable areas. The U.S. freight market is highly competitive.
| Substitute | Description | Impact on Union Pacific |
|---|---|---|
| Trucking | Offers flexibility for short hauls | Competes on speed and accessibility |
| Pipelines | Transports liquids and gases | Direct competition in specific markets |
| Barge transport | Cheaper for bulk goods | Price competition in navigable regions |
Entrants Threaten
The railroad industry's high capital needs, like billions for tracks and terminals, are a huge hurdle. Building a rail network is incredibly expensive; this favors existing firms. For example, Union Pacific's assets totaled over $60 billion in 2024. Newcomers face immense challenges competing against such established giants. This financial barrier strongly limits new entrants in this sector.
Union Pacific faces significant regulatory hurdles, including stringent safety and environmental standards. Compliance requires substantial investment in technology and infrastructure. The Surface Transportation Board (STB) oversees the industry, adding another layer of complexity. These regulations, coupled with the need for substantial capital, significantly deter new entrants. In 2024, regulatory compliance costs continue to be a major expense for established railroads, like Union Pacific.
Union Pacific, as an established railroad, enjoys significant economies of scale. They spread fixed costs across substantial freight volumes, reducing per-unit expenses. New entrants face a tough battle, needing immense capital to match these efficiencies. In 2024, Union Pacific's operating ratio, a measure of efficiency, was around 60%, demonstrating their cost advantage. This makes it difficult for any new railroad company to compete.
Land Acquisition Challenges
New rail lines and terminals face significant land acquisition hurdles. Securing land is tough and costly, as existing railroads hold established rights-of-way. Environmental regulations further complicate land development, increasing expenses and timelines. These factors create substantial barriers for new companies. In 2024, land acquisition costs rose by approximately 7%, impacting infrastructure projects.
- High land acquisition costs can deter new entrants.
- Established rights-of-way favor existing railroads.
- Environmental regulations add complexity and expense.
- These challenges limit the threat of new entrants.
Technological Expertise
Technological expertise poses a significant barrier for new entrants in the railroad industry. Union Pacific, for instance, has invested heavily in advanced signaling systems and train control technologies. These systems are crucial for operational efficiency and safety, requiring substantial upfront investment and specialized knowledge. New companies would struggle to replicate the technological infrastructure and expertise that established players like Union Pacific have built over decades. This disparity in technological capability gives existing railroads a competitive edge.
- Advanced signaling systems and train control technologies are key.
- Union Pacific has a long-standing advantage in this area.
- New entrants face high barriers to entry due to technology.
- Replicating existing infrastructure is costly and complex.
The railroad industry's high barriers, including enormous capital needs, regulatory hurdles, and established economies of scale, limit the threat of new entrants. These challenges include substantial land acquisition costs and the need for advanced technology, favoring existing players like Union Pacific. In 2024, these factors continue to protect the industry from new competition.
| Barrier | Impact | 2024 Data (Approx.) |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Costs | High initial investment | Union Pacific assets: $60B+ |
| Regulations | Compliance costs | Increased by 5% |
| Economies of Scale | Cost advantage | Union Pacific operating ratio: ~60% |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
The Porter's Five Forces analysis draws from SEC filings, industry reports, competitor data, and market research. These sources are cross-referenced for accurate and comprehensive insights.