Anheuser-Busch InBev Bundle
How Did Anheuser-Busch InBev Conquer the Global Beer Market?
Journey back in time to explore the fascinating Anheuser-Busch InBev SWOT Analysis and its rise to prominence. From a small brewery in 1852 to a global behemoth, the story of AB InBev is a testament to strategic vision and relentless innovation. Discover how this brewing giant navigated the complexities of the beer industry to become a household name worldwide.
The AB InBev company's history is a compelling narrative of strategic acquisitions and market dominance. Understanding the brief history of Anheuser-Busch InBev provides invaluable insights into the dynamics of the global beer market. Explore the key milestones and mergers and acquisitions that shaped AB InBev's remarkable journey, from its humble beginnings to its current status as a leader in the brewing history.
What is the Anheuser-Busch InBev Founding Story?
The AB InBev history is a story of strategic vision, innovation, and global expansion. It began with humble roots in the mid-19th century and evolved into the world's largest brewing company through a series of mergers and acquisitions. This journey showcases how a focus on quality, distribution, and brand building can transform a local brewery into a global powerhouse.
The founding of Anheuser-Busch InBev is a compelling narrative of entrepreneurial spirit and strategic foresight. From its inception, the company demonstrated a commitment to quality and a forward-thinking approach to the beer industry. This laid the groundwork for its future success and set the stage for its evolution into a global leader.
The story of Anheuser-Busch InBev starts on November 13, 1852, when Eberhard Anheuser, a German immigrant and soap manufacturer, acquired the Bavarian Brewery in St. Louis, Missouri. Anheuser aimed to revitalize the struggling brewery, which was facing financial difficulties. The pivotal moment came in 1864 when Adolphus Busch, Anheuser's son-in-law, joined the company. Busch, also a German immigrant with experience in brewing supply sales, brought a sharp business acumen and an innovative mindset that would be crucial to the brewery's future success.
The initial challenge Anheuser and Busch identified was the fragmented and localized nature of the American brewing industry. Most breweries served only their immediate communities due to limitations in transportation and refrigeration. Their original business model centered on producing high-quality lager beer, a popular style among the growing German immigrant population, and expanding its reach beyond St. Louis. The first significant product was Budweiser, introduced in 1876, designed to be a nationally distributed, consistent-quality beer. The company was renamed Anheuser-Busch in 1879, recognizing Adolphus Busch's significant contributions. Early funding primarily came from Anheuser's existing wealth and re-invested profits from the brewery. A key challenge overcome during establishment was the development of innovative transportation and refrigeration methods to allow for the widespread distribution of their beer, a crucial factor in their early growth.
- 1852: Eberhard Anheuser purchases the Bavarian Brewery.
- 1864: Adolphus Busch joins the company.
- 1876: Budweiser is introduced.
- 1879: The company is renamed Anheuser-Busch.
The company's focus on quality and innovation, particularly in distribution, set the stage for its future success. The development of efficient transportation and refrigeration was critical, allowing Anheuser-Busch to reach a wider market and establish its brands nationally. To learn more about the company's target market, you can read about the Target Market of Anheuser-Busch InBev.
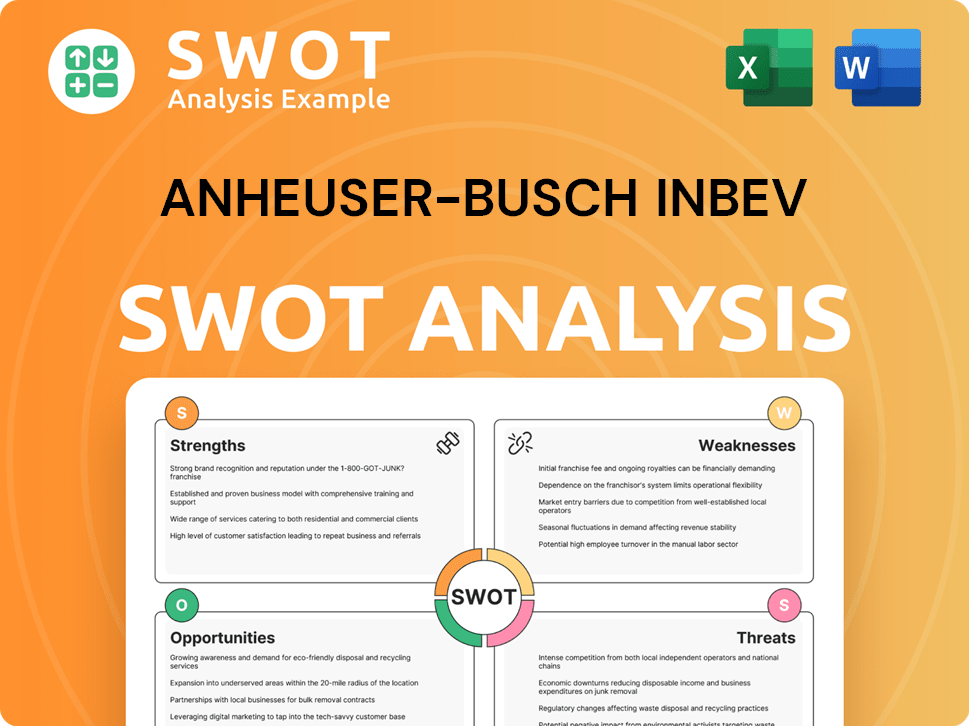
Anheuser-Busch InBev SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
What Drove the Early Growth of Anheuser-Busch InBev?
The early growth of Anheuser-Busch, now known as AB InBev, was marked by significant innovations in brewing and distribution, setting the stage for its future dominance in the global beer market. Following the introduction of Budweiser in 1876, the company strategically focused on establishing a strong national presence. This involved pioneering methods to transport beer across the country. By the late 19th and early 20th centuries, Anheuser-Busch expanded its product line, introducing beers like Michelob in 1896.
Anheuser-Busch was among the first to utilize refrigerated railcars, a key innovation that allowed for the efficient and widespread distribution of beer, preventing spoilage and giving them a competitive edge. This technological advancement was crucial for establishing a national footprint and expanding beyond local markets. The company's focus on quality and distribution helped it to grow rapidly.
During Prohibition (1920-1933), Anheuser-Busch adapted by diversifying into non-alcoholic products. They produced Bevo, a non-alcoholic cereal beverage, and even ventured into ice cream. This strategic shift allowed the company to survive the challenging period. The company's ability to adapt ensured its survival and set the stage for its post-Prohibition resurgence.
After Prohibition ended, Anheuser-Busch quickly re-established its dominance in the beer industry. The company focused on expanding its brewing capacity and distribution network across the United States. Leadership changes, such as August A. Busch Jr. taking over in 1946, further solidified its position. The market's positive reception to their consistent quality beers helped them to outcompete smaller breweries.
While significant consolidation efforts came later, early acquisitions and mergers began to shape the company's trajectory. Throughout the mid-20th century, Anheuser-Busch focused on expanding its brewing capacity and distribution across the U.S. These early strategic moves set the foundation for the future growth of Owners & Shareholders of Anheuser-Busch InBev.
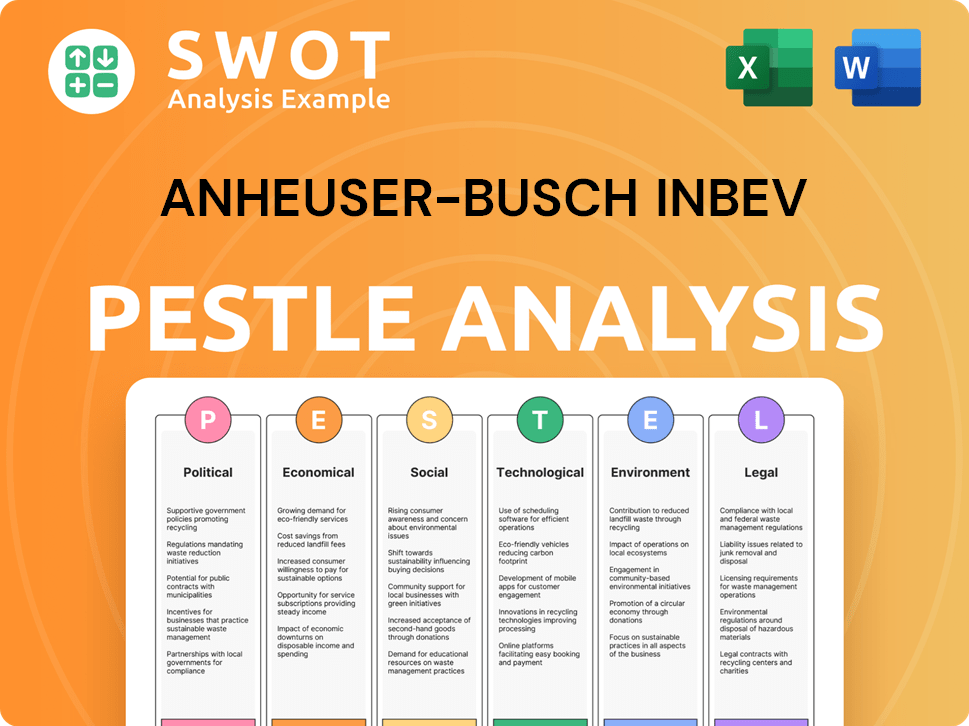
Anheuser-Busch InBev PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
What are the key Milestones in Anheuser-Busch InBev history?
The AB InBev history is marked by significant milestones that have shaped its trajectory in the global beer market. From its origins to its current status, the company has navigated through various phases of growth, innovation, and strategic realignments. These key moments have been crucial in defining its position in the beer industry.
| Year | Milestone |
|---|---|
| Late 19th Century | Adolphus Busch developed pasteurization for beer, extending shelf life and enabling national distribution. |
| 1933 | Introduction of the Budweiser Clydesdales as a marketing strategy following the repeal of Prohibition. |
| 2008 | InBev acquired Anheuser-Busch for approximately $52 billion, forming the world's largest brewer. |
| 2016 | Acquisition of SABMiller for around $100 billion, further consolidating the global beer market. |
AB InBev has consistently pursued innovations to maintain its competitive edge. One notable innovation was the development of pasteurization, which revolutionized beer preservation and distribution. The company continues to focus on brewing technology and marketing strategies.
The development of pasteurization by Adolphus Busch in the late 19th century significantly extended the shelf life of beer, enabling wider distribution.
The introduction of the Budweiser Clydesdales in 1933 became an iconic marketing strategy, symbolizing the brand's heritage and quality.
Continuous innovation in brewing processes and technology has helped maintain efficiency and quality in production.
Establishing robust global distribution networks has been key to AB InBev's expansion and market presence.
Focusing on premium and high-end beer brands to cater to evolving consumer preferences and increase profit margins.
Expanding the portfolio to include non-alcoholic beers to meet the growing demand for healthier beverage options.
AB InBev company has faced various challenges throughout its history. Market shifts, consumer preference changes, and intense competition have tested the company. The mergers, while expanding its global reach, also brought integration complexities.
Economic recessions and fluctuations in consumer spending have impacted sales and profitability.
The rise of craft beers and changing tastes have required AB InBev to adapt its product offerings and marketing strategies.
Intense competition from other global brewers and regional players has put pressure on market share and pricing.
Integrating acquired companies, such as Anheuser-Busch and SABMiller, presented challenges in terms of cultural alignment and operational efficiency.
Global economic conditions, including inflation and supply chain disruptions, have affected production costs and consumer demand.
Changes in alcohol regulations and tax policies in various markets have required AB InBev to adjust its business practices.
For a deeper dive into the competitive landscape, consider exploring the Competitors Landscape of Anheuser-Busch InBev.
Anheuser-Busch InBev Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout

What is the Timeline of Key Events for Anheuser-Busch InBev?
The AB InBev history is marked by significant milestones, from its origins in the 19th century to its current position as a global leader in the beer industry. The company's journey includes strategic mergers, acquisitions, and a constant focus on innovation and market expansion. AB InBev has navigated various economic cycles and consumer trends, solidifying its presence in the global beer market. The company's commitment to quality, sustainability, and digital transformation will likely shape its future trajectory.
| Year | Key Event |
|---|---|
| 1852 | Eberhard Anheuser acquires the Bavarian Brewery in St. Louis, Missouri. |
| 1864 | Adolphus Busch joins the company, marking a pivotal partnership. |
| 1876 | Budweiser beer is introduced, becoming a flagship brand. |
| 1879 | The company is renamed Anheuser-Busch, reflecting its growing influence. |
| 1933 | Prohibition ends, and the Budweiser Clydesdales debut, becoming iconic. |
| 2004 | Interbrew and AmBev merge to form InBev, expanding its global footprint. |
| 2008 | InBev acquires Anheuser-Busch, creating Anheuser-Busch InBev (AB InBev). |
| 2016 | AB InBev acquires SABMiller, significantly increasing its market share. |
| 2023 | AB InBev reports strong financial performance, with global revenue increasing. |
| 2024-2025 | Continued focus on premiumization, no-alcohol beer, and digital transformation. |
AB InBev is heavily investing in premium and super-premium beer segments. This strategic shift is in response to evolving consumer preferences for higher-quality products. The company aims to capitalize on the increased demand for specialized and craft beers, driving revenue growth. This focus includes expanding its portfolio with high-end brands and innovative brewing techniques.
The no-alcohol beer category is a significant growth area for AB InBev. They are actively expanding their offerings to cater to health-conscious consumers and changing social trends. This includes launching new non-alcoholic versions of popular brands and investing in marketing campaigns. The company recognizes the growing demand for alternatives to traditional alcoholic beverages.
Digital transformation is a key focus for AB InBev, involving e-commerce and direct-to-consumer models. This strategy enhances distribution channels and improves consumer engagement. The company is investing in technology to streamline operations and gather consumer insights. This includes utilizing data analytics for more effective marketing and sales strategies.
AB InBev is committed to sustainable brewing practices and environmental responsibility. This includes reducing carbon emissions, conserving water, and promoting sustainable agriculture. The company is leveraging technology to enhance efficiency and reduce its environmental impact. This commitment aligns with growing consumer demand for eco-friendly products and practices.
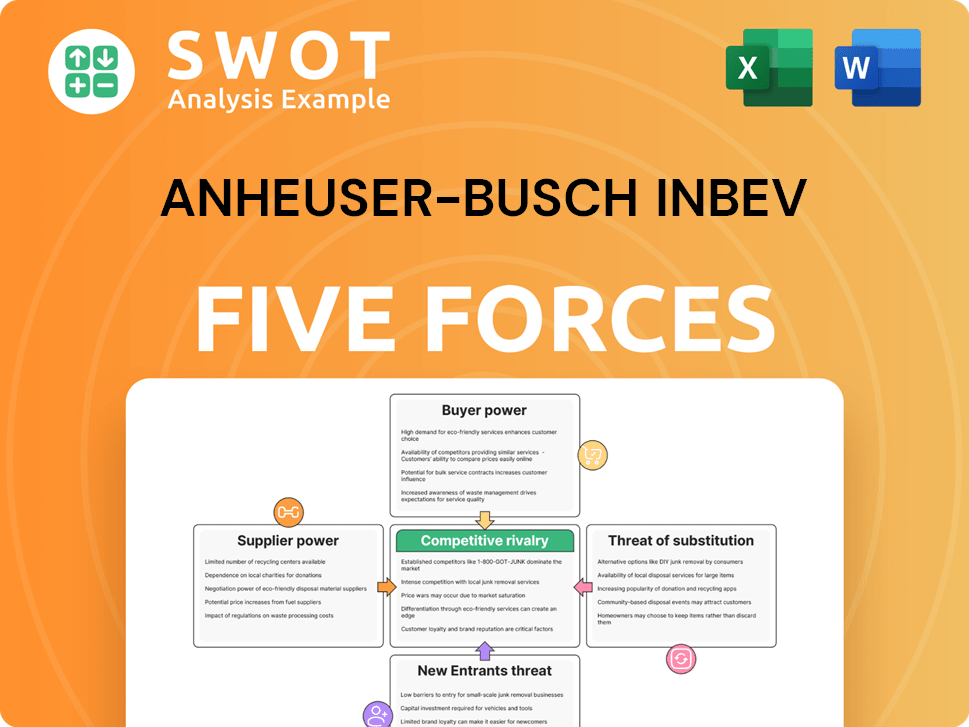
Anheuser-Busch InBev Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What is Competitive Landscape of Anheuser-Busch InBev Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of Anheuser-Busch InBev Company?
- How Does Anheuser-Busch InBev Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of Anheuser-Busch InBev Company?
- What is Brief History of Anheuser-Busch InBev Company?
- Who Owns Anheuser-Busch InBev Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of Anheuser-Busch InBev Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.