BlackBerry Bundle
How did BlackBerry, once a titan of tech, transform?
BlackBerry's story is a compelling narrative of innovation, dominance, and reinvention within the ever-evolving landscape of mobile technology. From its humble beginnings in 1984 as Research In Motion (RIM), the company revolutionized communication with its groundbreaking BlackBerry devices. These iconic smartphones, famous for their BlackBerry SWOT Analysis, became indispensable tools for professionals worldwide, setting the standard for secure mobile communication.
This article delves into the brief history of BlackBerry company, exploring its rise to prominence and subsequent transition. We'll examine the early BlackBerry models, the impact of BlackBerry smartphones on business, and the reasons behind its decline. Furthermore, we'll analyze where BlackBerry is now, and its enduring legacy in the world of mobile technology and cybersecurity.
What is the BlackBerry Founding Story?
The story of the [Company Name] begins with Research In Motion (RIM), a company that would revolutionize mobile communication. Founded in 1984, RIM set out to solve the challenges of wireless data transmission, a problem that would define its early success. This commitment to innovation laid the groundwork for the [Company Name]'s future.
Mike Lazaridis, an engineering student from the University of Waterloo, and Jim Balsillie, formed a partnership that would shape the company's trajectory. Their combined skills in technology and business were crucial. RIM's early focus on wireless data solutions marked the beginning of the [Company Name]'s journey.
RIM was founded on March 7, 1984. Mike Lazaridis, the co-founder, and Jim Balsillie, co-CEO from 1992 to 2012, were key figures. The company's initial focus was on two-way paging systems and local area network (LAN) solutions. RIM identified the need for efficient and secure wireless data transmission for business professionals.
RIM's early business model involved consulting services and custom hardware and software solutions for wireless data communication. Their initial funding came from bootstrapping and early investments.
- The RIM 950 Inter@ctive Pager, launched in 1998, was a key product.
- This pager allowed users to send and receive emails wirelessly.
- Lazaridis's engineering background and Balsillie's business expertise were complementary.
- The name 'Research In Motion' reflected their focus on wireless technology.
The RIM 950 Inter@ctive Pager, launched in 1998, was a precursor to the [Company Name] smartphone. This device showcased the company's commitment to secure, mobile communication, a key feature that would later define the brand. RIM's early success was built on solving the needs of business professionals, providing them with the ability to stay connected on the go. If you want to know more about the [Company Name] then read Owners & Shareholders of BlackBerry.
BlackBerry SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
What Drove the Early Growth of BlackBerry?
The early growth of the company, formerly known as RIM (Research In Motion), was characterized by a strategic focus on enterprise clients and the development of secure, reliable wireless communication devices. This approach led to the creation of the first true smartphone, the BlackBerry 5810, in 2002. This device quickly became a must-have for business professionals.
Following the success of the Inter@ctive Pager, the company launched the BlackBerry 5810 in 2002. This model integrated phone capabilities with email, web browsing, and organizer functions. Its robust security and push email capabilities made it essential for business users.
Early major clients included government agencies and large corporations. These organizations were attracted to the reputation of the company for secure and efficient mobile communication. The company's focus on security and reliability quickly gained traction in the enterprise market, driving early adoption of their BlackBerry devices.
The company experienced significant team expansion, growing from a small group of engineers to hundreds of employees. Initial office locations were in Waterloo, Ontario, which became the hub of its research and development. RIM expanded its market reach by partnering with mobile carriers globally, facilitating the widespread adoption of BlackBerry devices.
Major capital raises, including its IPO in 1997, provided funding for aggressive product development and market penetration. Leadership remained stable with Lazaridis and Balsillie at the helm. By the mid-2000s, the company had become a dominant force in the mobile industry, with its devices being adopted by millions worldwide.
BlackBerry PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
What are the key Milestones in BlackBerry history?
The BlackBerry company, formerly known as Research In Motion (RIM), experienced a dynamic journey marked by significant milestones. From its early days as a pager manufacturer to its evolution into a global leader in mobile technology, the company's story is one of innovation, market dominance, and eventual transformation. The BlackBerry history is a testament to the rapid changes in the tech industry.
| Year | Milestone |
|---|---|
| 1999 | RIM releases the first BlackBerry device, the 850, a two-way pager that offered email capabilities. |
| 2002 | The BlackBerry 5810, one of the first smartphones with phone functionality, is introduced. |
| 2003 | The BlackBerry 7210, one of the first color-screen BlackBerry devices, is launched. |
| 2006 | BlackBerry reaches a market share peak, dominating the enterprise market with its secure email and messaging services. |
| 2007 | Apple launches the iPhone, marking the beginning of a significant shift in the smartphone market. |
| 2013 | BlackBerry transitions to the BlackBerry 10 operating system and releases new devices, including the Z10 and Q10. |
| 2016 | BlackBerry ceases in-house hardware manufacturing, shifting its focus to software and services. |
BlackBerry smartphones were pioneers in integrating email, messaging, and mobile computing. The company introduced groundbreaking features such as the BlackBerry Messenger (BBM), a popular instant messaging service, and advanced security protocols that set a new standard for secure communication in the mobile space.
BlackBerry was a pioneer in providing push email, allowing users to receive emails instantly on their devices, revolutionizing mobile communication for businesses. This feature was a key differentiator, attracting corporate clients seeking real-time communication.
BBM was one of the first mobile instant messaging services, enabling secure and private communication among BlackBerry users. It helped to build a strong community around BlackBerry devices, fostering loyalty and contributing to its market dominance.
The physical QWERTY keyboard on BlackBerry phones became iconic, offering a superior typing experience compared to early touchscreen devices. This feature was highly valued by business users who needed to write emails and documents on the go. The BlackBerry QWERTY keyboard was a key feature.
BlackBerry Enterprise Server (BES) provided robust security and management features for corporate clients, making it a preferred choice for businesses. BES allowed IT departments to manage BlackBerry devices securely, ensuring data protection and compliance.
BlackBerry was known for its strong security features, including end-to-end encryption and secure boot processes, which were critical for protecting sensitive corporate data. These security features helped BlackBerry gain a strong foothold in the enterprise market.
BlackBerry held numerous patents related to mobile technology, particularly in secure communication and keyboard design, which provided a competitive advantage. These patents protected its innovations and allowed it to maintain its market position for a time.
The BlackBerry company faced significant challenges, including the rise of touchscreen smartphones and the shift in consumer preferences. The company struggled to adapt to the changing market dynamics, leading to a decline in market share and financial difficulties. The BlackBerry's decline reasons are well documented.
The launch of the iPhone in 2007 and the subsequent rise of Android created intense competition, with these platforms offering more user-friendly interfaces and a wider range of apps. BlackBerry found it difficult to compete with the innovative features and user experience of these new platforms.
The BlackBerry Storm, a touchscreen device released in 2008, was poorly received due to its clunky interface and lack of a physical keyboard. This failure highlighted BlackBerry's difficulty in adapting to the changing consumer preferences for full touchscreen devices.
BlackBerry faced delays in launching new products, such as the BlackBerry 10 operating system, which hindered its ability to compete effectively. These delays allowed competitors to gain further market share.
Internal issues, including management changes and strategic missteps, further exacerbated BlackBerry's decline. These issues diverted focus from innovation and market adaptation.
BlackBerry struggled to adapt to the shift towards touchscreen devices and the demand for a robust app ecosystem. The company's reluctance to fully embrace these changes contributed to its declining market share.
BlackBerry's market share plummeted as consumers and businesses shifted to competing platforms like iOS and Android. The company's once-dominant position in the enterprise market was significantly eroded.
For a deeper dive into BlackBerry's strategic moves and future prospects, consider reading about the Growth Strategy of BlackBerry. Today, BlackBerry has pivoted to focus on software and services, particularly in cybersecurity and endpoint management, leveraging its expertise in secure communication.
BlackBerry Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
What is the Timeline of Key Events for BlackBerry?
The story of the BlackBerry company is a journey through the evolution of mobile technology, from its early days as RIM (Research In Motion) to its current focus on software and services. The
BlackBerry history
is marked by innovation, market dominance, and a pivotal shift in the smartphone landscape.| Year | Key Event |
|---|---|
| 1984 | Mike Lazaridis founded Research In Motion (RIM). |
| 1997 | RIM went public on the Toronto Stock Exchange. |
| 1998 | The RIM 950 Inter@ctive Pager, a precursor to the BlackBerry devices , was launched. |
| 1999 | The first BlackBerry device, the BlackBerry 850, was introduced, focusing on secure wireless email. |
| 2002 | The BlackBerry 5810, the first with integrated phone capabilities, was launched. |
| 2003 | The BlackBerry 7210, one of the first color-screen devices, was introduced. |
| 2007 | Apple introduced the iPhone, changing the smartphone market. |
| 2008 | The BlackBerry Storm, the company's first touchscreen device, was launched. |
| 2013 | RIM officially rebranded as BlackBerry Limited; the BlackBerry 10 operating system was launched. |
| 2016 | BlackBerry announced it would cease all internal hardware development, shifting focus to software and services. |
| 2020 | BlackBerry sold its patent portfolio for $600 million, solidifying its software-centric strategy. |
BlackBerry is expanding its intelligent security software and services, particularly in cybersecurity (BlackBerry Cylance) and IoT (BlackBerry QNX). The company is actively growing in enterprise and government markets. Innovation includes AI-driven cybersecurity solutions and advanced embedded systems.
The company is focusing on further penetration into automotive, healthcare, and critical infrastructure industries. The proliferation of IoT devices, increasing cyber threats, and the demand for secure software-defined vehicles are likely to positively impact BlackBerry's future. As of early 2024, QNX software is in over 235 million vehicles globally.
BlackBerry reported revenue of $696 million for fiscal year 2024. The company's strategic initiatives are centered on expanding its intelligent security software and services. Analyst predictions suggest continued growth in the cybersecurity and IoT markets.
BlackBerry aims to evolve from a hardware pioneer to a leading provider of intelligent security software and services. The company's vision is to ensure a secure and trusted connected future. Leadership emphasizes the company's commitment to innovation.
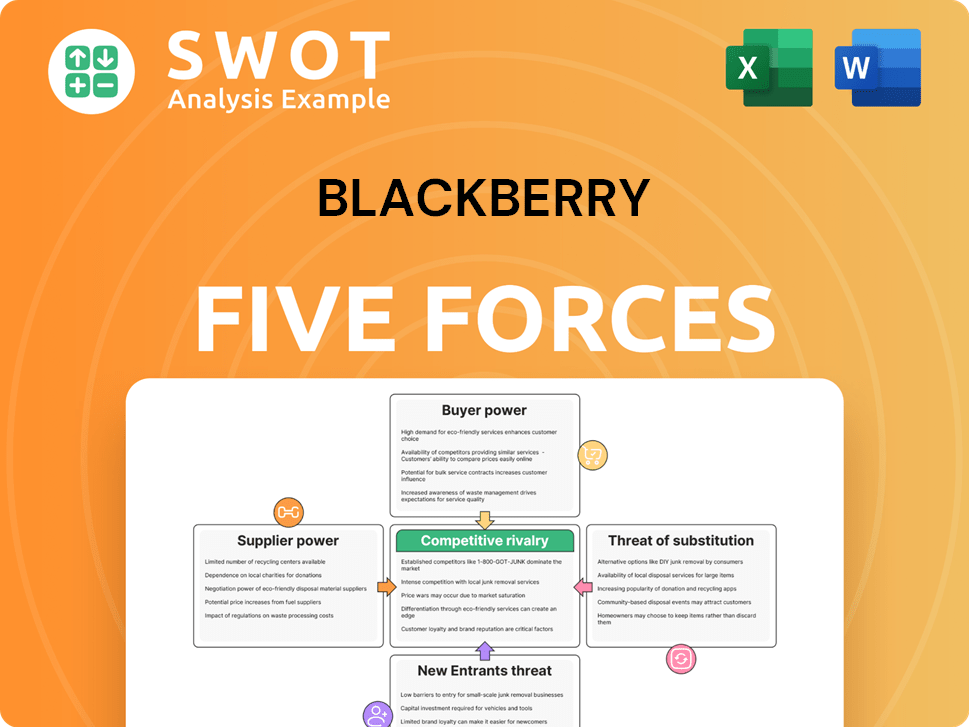
BlackBerry Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What is Competitive Landscape of BlackBerry Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of BlackBerry Company?
- How Does BlackBerry Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of BlackBerry Company?
- What is Brief History of BlackBerry Company?
- Who Owns BlackBerry Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of BlackBerry Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.