Bank Negara Indonesia Bundle
Unveiling the Legacy: What is the Story of Bank Negara Indonesia?
Ever wondered how a single bank could shape a nation's financial destiny? Bank Negara Indonesia (BNI), a pivotal player in Indonesia's economic narrative, boasts a history as compelling as the nation's own struggle for independence. From its inception in 1946, BNI's journey reflects the resilience and evolution of Indonesian banking.

Delving into the Bank Negara Indonesia SWOT Analysis reveals the intricacies of its past. Understanding the brief history of Bank Negara Indonesia, or Sejarah BNI, is crucial for grasping its current market position. This article explores the significant events in BNI's history, from its BNI establishment date to its transformation journey, highlighting its role in the Indonesian economy and its impact on Indonesian banking.
What is the Bank Negara Indonesia Founding Story?
The story of Bank Negara Indonesia (BNI) begins on July 5, 1946. This pivotal moment marked the formal establishment of the Indonesian bank, a crucial step for the newly independent Republic of Indonesia. The creation of BNI was a direct response to the need for a national financial institution, a necessity following the declaration of independence from Dutch colonial rule on August 17, 1945.
The primary goal was to establish a financial infrastructure independent of the Dutch-controlled banking system. Initially named 'Bank Negara Indonesia 1946,' the bank was designed to serve as the central bank, responsible for issuing the first Indonesian currency, the 'Oeang Republik Indonesia' (ORI). This move was essential for asserting the nation's economic sovereignty.
The initial challenge was the absence of a national bank capable of managing the country's finances and supporting its economic independence. BNI's early business model focused on meeting the government's financial needs, providing credit for national development, and facilitating trade. The establishment was a collective effort led by the new republic's leaders, including Margono Djojohadikusumo, who played a key role as the first president. The initial funding came directly from the state, reflecting its crucial role in the nation-building process. The name 'Bank Negara Indonesia' (BNI) directly reflected its status as the state bank, embodying the aspirations for national economic independence. The cultural and economic context of a newly independent nation striving for self-sufficiency profoundly influenced BNI's creation and its initial mandate.
BNI's founding was a critical step in Indonesia's post-colonial development, aimed at creating a national financial system.
- BNI establishment date: July 5, 1946.
- Initial Role: Serving as the central bank and issuing the first Indonesian currency.
- Primary Objective: To support the financial needs of the newly independent nation.
- Funding Source: Direct funding from the Indonesian state.
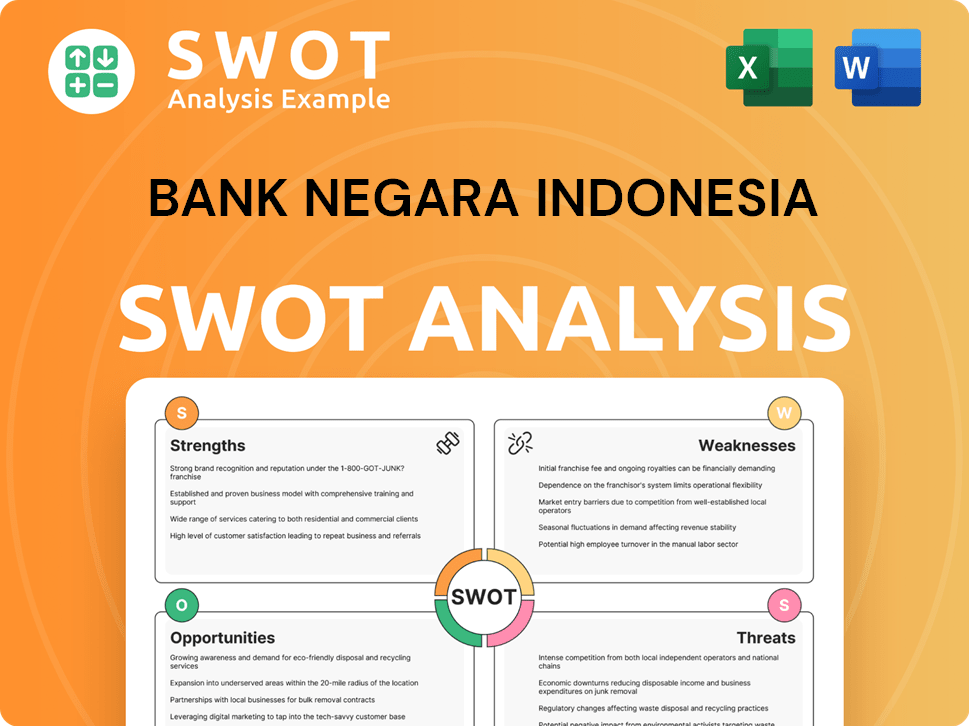
Bank Negara Indonesia SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
What Drove the Early Growth of Bank Negara Indonesia?
The early growth and expansion of Bank Negara Indonesia (BNI) were closely tied to Indonesia's economic and political evolution. Following its establishment, BNI transitioned into a commercial bank in 1949, marking a significant shift. This change allowed BNI to broaden its banking services, supporting the emerging Indonesian economy. This period was crucial for the Growth Strategy of Bank Negara Indonesia.
After becoming a commercial bank, BNI began offering deposit and loan services. These services were essential for supporting the developing Indonesian economy. The bank's focus was on providing basic financial products to the public and businesses. This early phase laid the foundation for its future growth and role in the Indonesian banking sector.
BNI expanded its physical presence by opening branches in key Indonesian cities. This expansion increased its accessibility to a growing customer base. By extending its reach, BNI aimed to serve more customers and support economic activities across the country. This strategy was crucial for building a strong presence in the Indonesian banking market.
During the 1950s and 1960s, BNI played a key role in funding national development projects. The bank supported vital sectors like agriculture, industry, and trade. This support aligned with the government's economic policies, helping drive growth in these critical areas. This period highlighted BNI's commitment to national development.
BNI's client base expanded to include both state-owned enterprises and private businesses. The growth in operations required more personnel to manage the branches and serve customers. This expansion reflected BNI's increasing importance in the Indonesian economy and its ability to support a diverse range of clients.
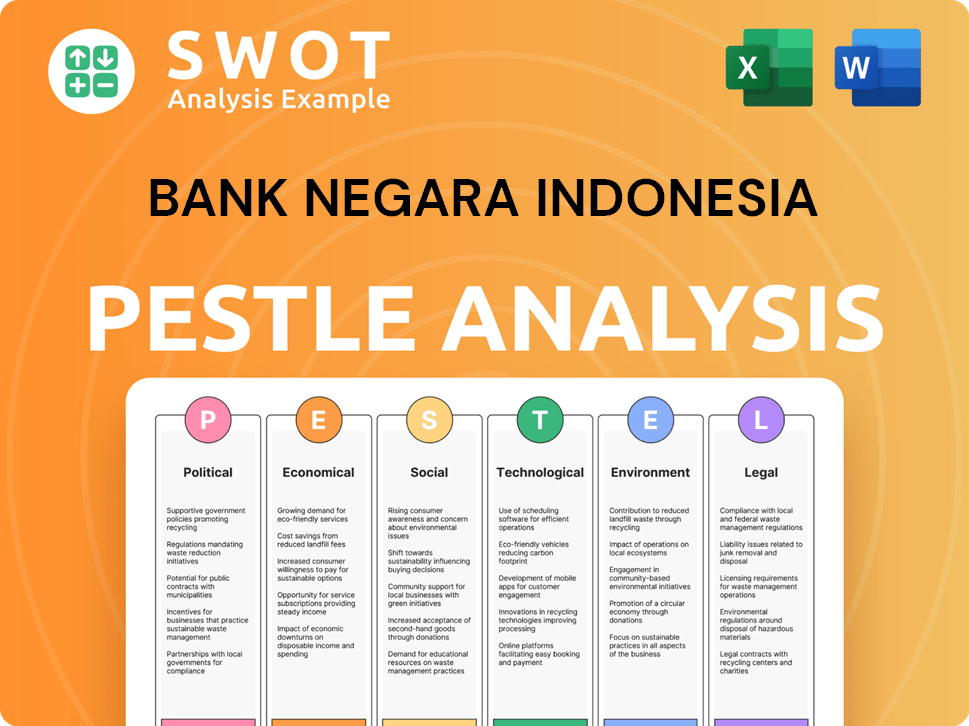
Bank Negara Indonesia PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
What are the key Milestones in Bank Negara Indonesia history?
The BNI history is marked by significant milestones that have shaped its evolution into a leading Indonesian bank. From its inception to its current status, BNI has played a crucial role in the Indonesian economy, adapting and innovating to meet the changing needs of its customers and the market.
| Year | Milestone |
|---|---|
| 1946 | Bank Negara Indonesia (BNI) was established, marking a pivotal moment in Indonesian banking. |
| Late 20th Century | BNI introduced electronic banking services, including ATMs and debit cards, enhancing customer convenience. |
| 1997-1998 | BNI navigated the Asian financial crisis, undertaking restructuring efforts to strengthen its capital base. |
| 2023 | BNI Mobile Banking transactions reached 787 million, a 28.5% increase year-on-year, with transaction value growing by 21% to Rp 1,170 trillion. |
BNI has consistently embraced innovations to stay at the forefront of the Indonesian banking sector. The bank has focused on digital transformation to cater to the evolving needs of its customers.
BNI introduced ATMs and debit cards, significantly improving customer access to financial services in the late 20th century.
The launch of BNI Mobile Banking has seen substantial growth, with continuous updates and feature enhancements to improve user experience.
BNI has developed various digital payment solutions to meet the needs of its customers, particularly the younger demographic.
BNI has integrated with various fintech platforms, expanding its reach and providing diverse financial services.
Focus on providing a seamless and user-friendly experience through its digital channels, aiming for a 'one-stop solution'.
Collaborations with other companies to enhance service offerings and expand market reach.
Despite its successes, BNI has faced several challenges throughout its history. These challenges have tested the bank's resilience and adaptability.
The Asian financial crisis of 1997-1998 severely impacted the Indonesian economy and banking sector, requiring significant restructuring.
Competition from both traditional banks and emerging fintech companies necessitates continuous innovation and strategic adjustments.
Product failures, while not always publicly detailed, are inherent to the banking sector, requiring constant refinement and adaptation.
Managing non-performing loans has been addressed through robust risk management frameworks to maintain financial stability.
Adapting to increased digital adoption and emphasizing digital channels to meet evolving customer expectations.
Navigating and complying with evolving banking regulations to ensure operational compliance and financial stability.
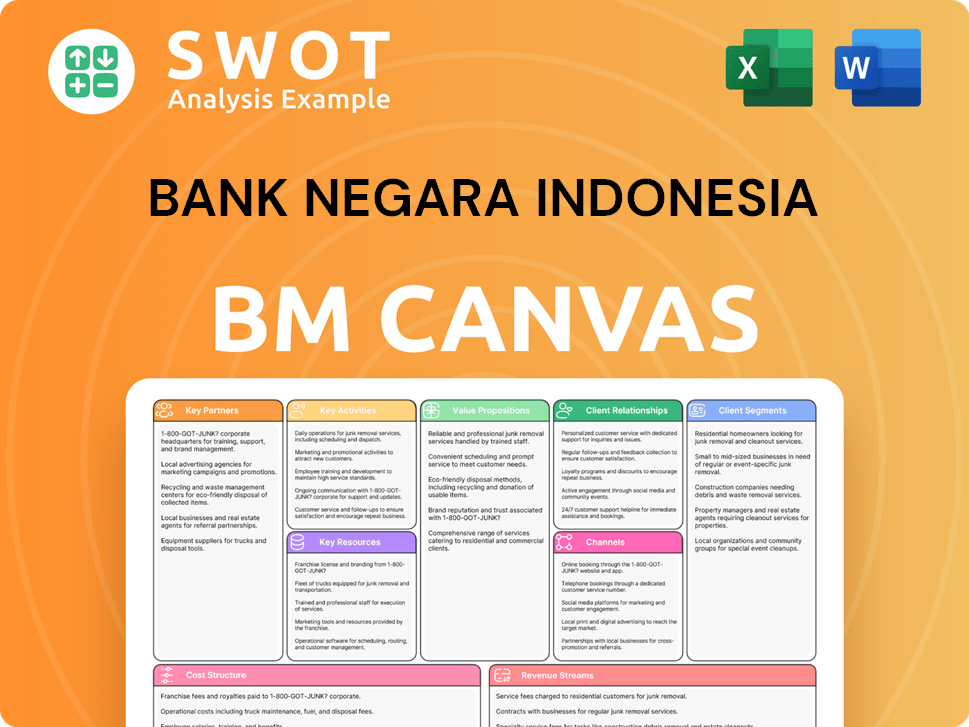
Bank Negara Indonesia Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
What is the Timeline of Key Events for Bank Negara Indonesia?
The Marketing Strategy of Bank Negara Indonesia has a rich history, evolving alongside Indonesia's economic development. From its inception as the first state-owned bank, it has navigated significant milestones, including transitioning from a central bank to a commercial bank, embracing technological advancements, and adapting to financial crises. The bank's journey reflects its commitment to supporting national economic development, making it a key player in the Indonesian banking sector.
| Year | Key Event |
|---|---|
| July 5, 1946 | Bank Negara Indonesia (BNI) is established, initially functioning as a central bank for the newly independent Republic of Indonesia. |
| 1949 | BNI transitions to a commercial bank, broadening its services. |
| 1968 | BNI becomes a state-owned enterprise (Persero), solidifying its commercial banking role. |
| 1988 | BNI introduces its first ATM, marking a significant step in banking automation. |
| 1996 | BNI goes public and is listed on the Jakarta Stock Exchange. |
| 1997-1998 | BNI navigates the Asian financial crisis, undergoing restructuring and recapitalization. |
| 2000s | BNI actively expands its digital banking services, including internet banking. |
| 2010s | BNI launches and significantly develops its mobile banking application, BNI Mobile Banking. |
| 2023 | BNI Mobile Banking records 787 million transactions, a 28.5% increase year-on-year, with transaction value reaching Rp 1,170 trillion, up 21% year-on-year. |
| 2024 | BNI focuses on strengthening its digital ecosystem and expanding its international reach. |
| 2025 | BNI aims to continue its digital transformation, focusing on personalized services and enhanced customer experience. |
BNI is heavily investing in its digital capabilities. The goal is to create a comprehensive 'one-stop solution' through its BNI Mobile Banking platform. This includes integrating more financial services and improving the user experience. Data analytics will also be used to provide personalized offerings to customers.
BNI plans to expand its global presence, especially in important economic centers. This expansion aims to support Indonesian businesses involved in international trade and investment. This strategy aligns with the increasing demand for seamless cross-border financial services.
The bank is focused on sustainable growth, using technology to improve efficiency and reach new customers. BNI is looking to capitalize on Indonesia's growing digital economy and expanding middle class. This includes enhancing its corporate banking segment and supporting SMEs.
BNI's future direction is tied to its original vision of supporting national economic development. This is being adapted for the digital age and a globally connected economy. The bank aims to remain a vital part of Indonesia's financial system, ensuring its continued contribution to the country's growth.
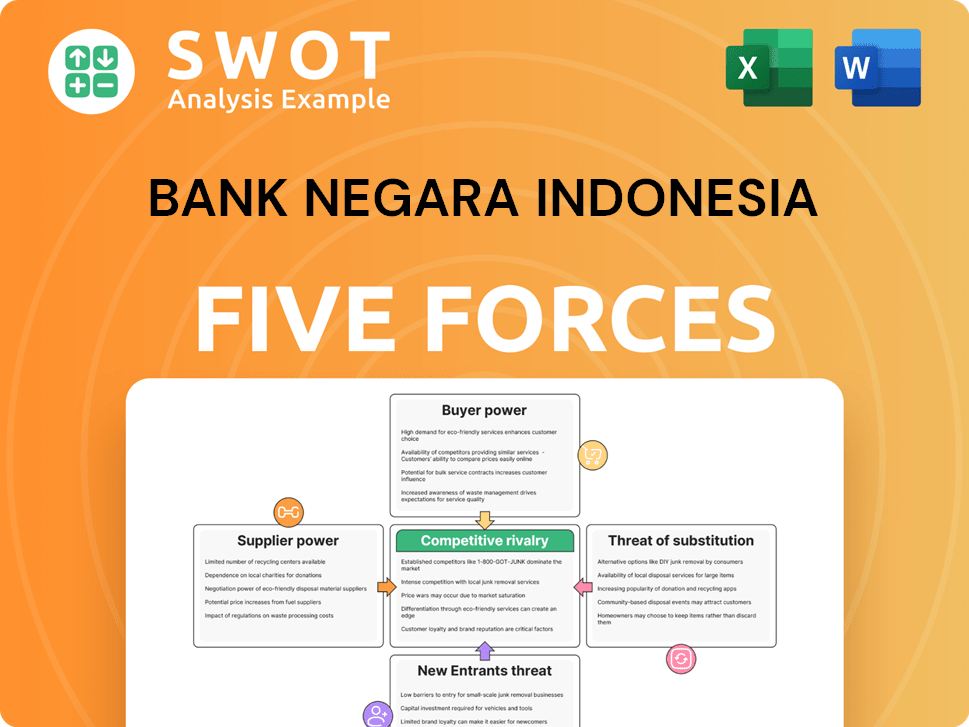
Bank Negara Indonesia Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What is Competitive Landscape of Bank Negara Indonesia Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of Bank Negara Indonesia Company?
- How Does Bank Negara Indonesia Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of Bank Negara Indonesia Company?
- What is Brief History of Bank Negara Indonesia Company?
- Who Owns Bank Negara Indonesia Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of Bank Negara Indonesia Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.