H.B. Fuller Bundle
How Did H.B. Fuller Become a Global Adhesive Powerhouse?
Dive into the fascinating H.B. Fuller SWOT Analysis and discover the remarkable story of H.B. Fuller Company, a global leader in adhesives and sealants. From its inception in 1887, this adhesive manufacturer has consistently innovated, transforming from a small operation into a multinational corporation. Explore the key milestones and strategic decisions that have propelled H.B. Fuller's growth and cemented its place in the industrial adhesives market.

The early history of H.B. Fuller, beginning with Harvey Benjamin Fuller's innovative liquid fish glue, laid the foundation for decades of success. Understanding the H.B. Fuller history is crucial for grasping its current market position and future potential. This company timeline reveals how strategic acquisitions, technological advancements, and a commitment to customer needs have shaped H.B. Fuller's trajectory, making it a key player in the adhesive industry.
What is the H.B. Fuller Founding Story?
The story of H.B. Fuller Company, a prominent adhesive manufacturer, began in 1887. Harvey Benjamin Fuller, Sr., established the company in St. Paul, Minnesota, with a clear vision: to create and market innovative glue solutions. This marked the genesis of what would become a global leader in the adhesives industry.
Fuller's background included experimenting with glue mixtures in Chicago, where he repackaged and sold an existing adhesive. This experience provided him with the foundation to identify a market need. He saw an opportunity to develop a versatile, cost-effective, and strong adhesive suitable for both household and industrial applications. This early focus on innovation laid the groundwork for the company's future success.
The initial business model centered on formulating and selling a wet, flour-based paste. The first product, Fuller's Premium Liquid Fish Glue, gained recognition for its ability to bond various materials. An interesting aspect of the company's early days was Harvey Fuller's invention of adjustable scaffolding to aid customers in hanging wallpaper more safely. This demonstrates the company's early commitment to providing comprehensive solutions.
The company was initially named Fuller Manufacturing Company and operated as a one-man show by Harvey Benjamin Fuller.
- In 1888, Albert, Harvey's son, became the first employee.
- The company's early growth was likely fueled by the success of its initial product sales.
- The late 19th-century context of industrial expansion and rising demand for adhesives provided a favorable environment for Fuller's venture.
- The early focus on customer solutions set a precedent for innovation.
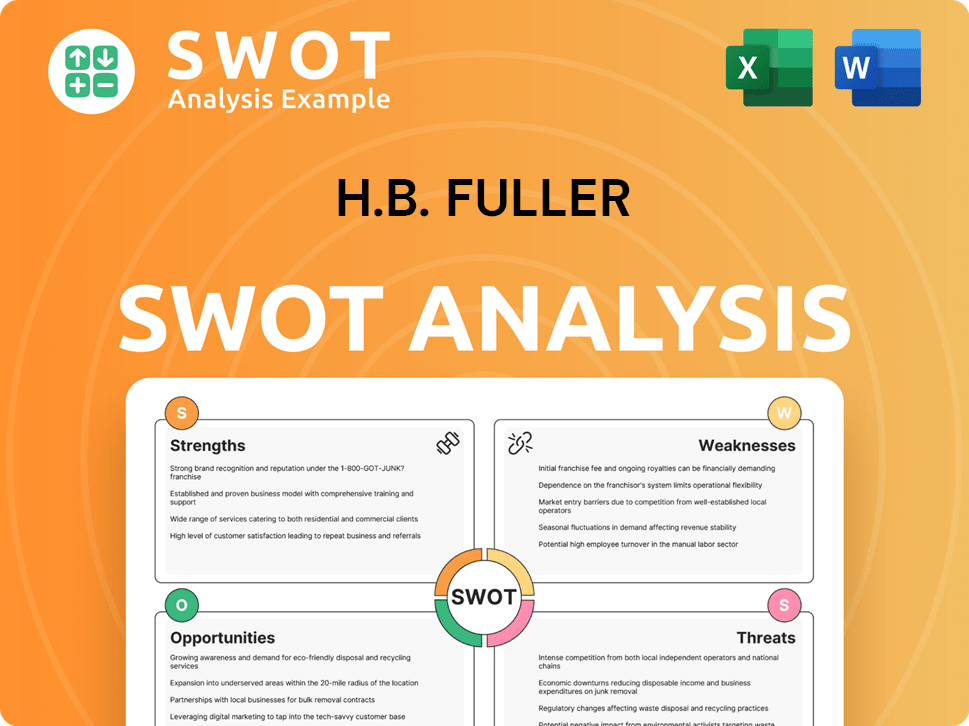
H.B. Fuller SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
What Drove the Early Growth of H.B. Fuller?
The early years of the H.B. Fuller Company, a prominent adhesive manufacturer, were marked by significant product diversification, geographical expansion, and strategic leadership changes. Following the initial success with fish glue, the company broadened its offerings to include specialized adhesives. This period saw the company grow from a local business to a national player, laying the groundwork for its future global presence.
H.B. Fuller's early expansion included the development of various adhesive products. In 1892, the company made its first acquisition by purchasing The Minnesota Paste Company for $200. By 1893, the company secured a patent for Fuller's Cold Water Dry Wall Cleaner, demonstrating early innovation in its product line. This diversification helped the company serve different markets and applications, crucial for its growth.
The company was initially incorporated as Fuller Manufacturing Company in 1887. Later, it reincorporated as H.B. Fuller Company in 1915, issuing stock valued at $75,000. This shift to a public structure provided access to capital for further expansion. H.B. Fuller went public in 1968, listing on the New York Stock Exchange, which increased its visibility and access to capital.
A pivotal moment occurred in 1941 when Elmer L. Andersen acquired a majority stake, shifting from family ownership to professional management. At the time of Andersen's purchase, annual sales were approximately $200,000. Andersen implemented a 'double it in five' strategy, targeting a 14% annual sales increase and decentralized growth.
International expansion began in 1958 with the launch of H.B. Fuller Company (Canada) Ltd. in Winnipeg, followed by Fuller Adhesives International of Panama. By 1962, H.B. Fuller was among the top three adhesive manufacturers in the U.S., with 20 manufacturing facilities across the U.S., South America, and Canada. The acquisition of Kativo Chemical Industries in Costa Rica in 1967 marked its entry into new markets, such as paints and inks.
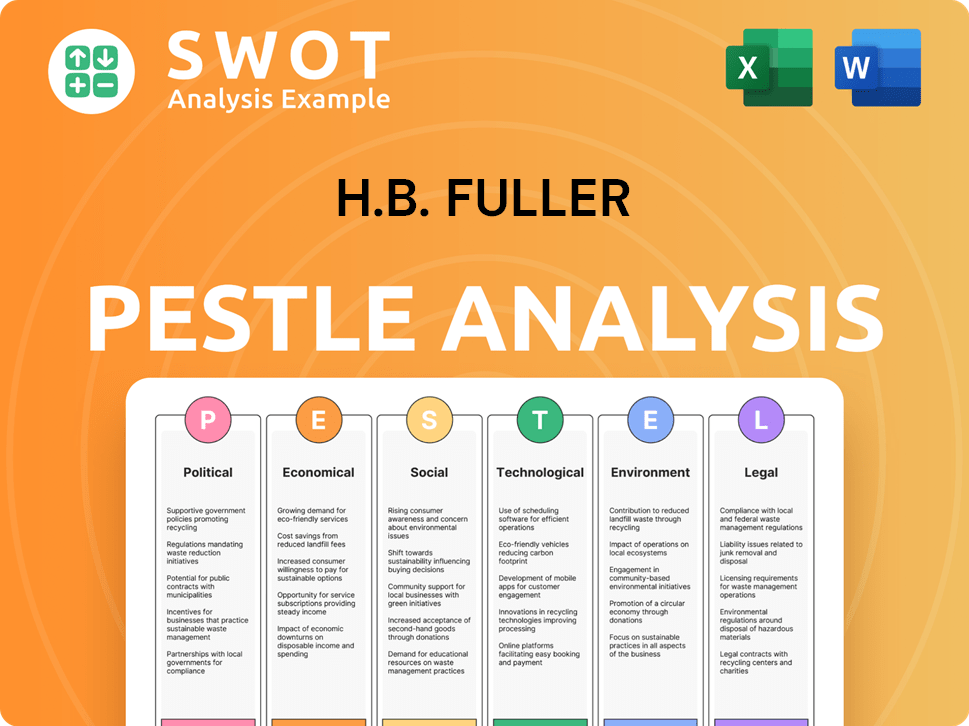
H.B. Fuller PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
What are the key Milestones in H.B. Fuller history?
The H.B. Fuller history is marked by significant milestones in the adhesive industry, showcasing its evolution and impact. From its early days to its current global presence, the company has consistently adapted and innovated to meet market demands and overcome challenges.
| Year | Milestone |
|---|---|
| 1887 | Introduction of Fuller's Premium Liquid Fish Glue, marking an early innovation in adhesives. |
| 1974 | The company's sales exceeded $100 million despite a recession, demonstrating resilience. |
| 1990s | Diversification into engineering adhesives, reducing reliance on traditional markets. |
| 1998 | Major restructuring initiated by new CEO Albert Stroucken. |
| 2022 | Held 500 active patents and operated on 17 technology platforms. |
| 2023-2024 | Announced restructuring actions to optimize operations and integrate acquired businesses. |
| December 2024 | Divested its flooring business to realign building and construction units. |
Innovations have been a cornerstone of the H.B. Fuller Company. The company has consistently developed new products and technologies to meet evolving market needs. This commitment is evident in its numerous patents and awards for innovative adhesive solutions.
Introduced in 1887, this was a key early innovation for the adhesive manufacturer. It set the stage for future product developments and the company's growth in the industrial adhesives market.
Another early product that helped establish the company's presence. This adhesive was designed for various applications and helped expand the company's product line.
Awarded in 2024, this innovation for photovoltaic solar modules lowers LCOE and enhances stability. This demonstrates the company's focus on sustainable and high-performance solutions.
Recognized in 2023, this lightweight encapsulant for lithium-ion batteries reduces thermal propagation in EVs. This innovation highlights the company's commitment to improving safety in the automotive industry.
This patented adhesive offers a safer and non-hazardous alternative for various industries, recognized in 2022. It reflects the company's dedication to safer and more environmentally friendly products.
The company's investment in sustainable adhesives demonstrates its commitment to reducing environmental impact. These products aim to provide eco-friendly alternatives for various applications.
H.B. Fuller has faced several challenges throughout its history. These challenges have ranged from market downturns to volatile raw material costs and currency fluctuations.
The company has navigated economic downturns, including a recession in 1974, and more recently, faced increased competition. These economic pressures have required strategic adjustments to maintain profitability.
Volatile raw material costs have impacted gross profit margins. Fluctuations in these costs require careful management and strategic sourcing to mitigate financial impacts.
Currency fluctuations have negatively affected net revenue, particularly in 2024. Managing currency risk is crucial for maintaining financial stability and global competitiveness.
Increased competition in the adhesive industry poses an ongoing threat. The company must continuously innovate and improve its offerings to stay ahead of competitors.
The company has faced the need to optimize operations and integrate acquired businesses. Restructuring efforts aim to streamline processes and improve efficiency.
In the 1990s, the company addressed concerns about its solvent-based adhesives. Proactive measures were taken to reformulate products and ensure safety.
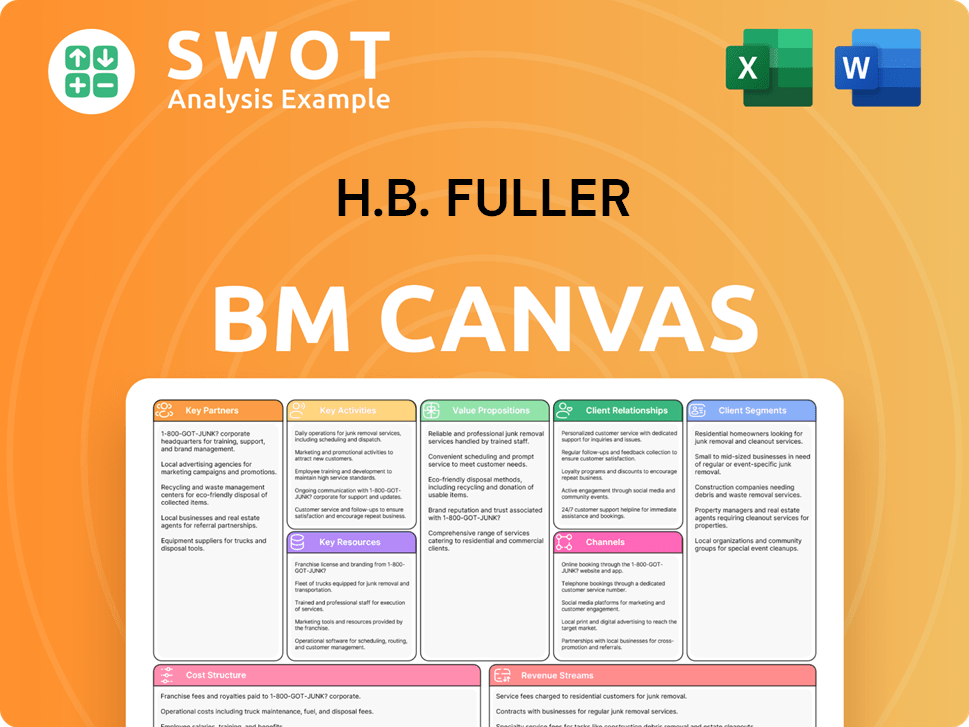
H.B. Fuller Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
What is the Timeline of Key Events for H.B. Fuller?
The Owners & Shareholders of H.B. Fuller, a leading adhesive manufacturer, has a rich history marked by significant milestones. Founded in 1887 by Harvey Benjamin Fuller, the company began with the introduction of Fuller's Premium Liquid Fish Glue. Over the years, it has evolved through strategic acquisitions, international expansion, and technological advancements, solidifying its position in the industrial adhesives market. The company's commitment to innovation and customer collaboration has driven its growth and adaptation to changing market demands.
| Year | Key Event |
|---|---|
| 1887 | Harvey Benjamin Fuller founded Fuller Manufacturing Company in St. Paul, Minnesota, introducing Fuller's Premium Liquid Fish Glue. |
| 1915 | The firm reincorporated as H.B. Fuller Company. |
| 1941 | Elmer L. Andersen acquired a majority stake and assumed leadership, initiating a period of modernization and expansion. |
| 1946 | Sales reached $1 million. |
| 1958 | H.B. Fuller Company (Canada) Ltd. was launched, marking the beginning of international expansion. |
| 1968 | H.B. Fuller went public and was listed on the New York Stock Exchange. |
| 1971 | Tony Andersen, Elmer's son, became company president. |
| 1974 | Sales surpassed $100 million. |
| 1983 | H.B. Fuller became a member of the Fortune 500. |
| 1994 | Sales exceeded $1 billion. |
| 2017 | Acquisition of Royal Adhesives & Sealants for approximately $1.575 billion, significantly broadening its portfolio. |
| 2022 | Celeste Mastin was appointed President and CEO, succeeding Jim Owens. |
| 2023 | Mergers and Acquisitions included Adhezion Biomedical (US), XCHEM International (UAE), Beardow Adams (UK), and Aspen Research (US). |
| 2024 | Mergers and Acquisitions included ND Industries (US), HS Butyl, Medfill, and GEM S.r.l. The company reported net revenue of $3.57 billion. |
| 2025 | H.B. Fuller expects to sell or close 16 facilities by the end of the year as part of its manufacturing footprint consolidation. |
H.B. Fuller is strategically focused on enhancing its EBITDA margin to consistently greater than 20%. The company is also working to significantly reduce its global manufacturing footprint and North American warehouse count.
The company anticipates approximately $75 million in annualized cost savings by 2030. H.B. Fuller expects to invest around $150 million in incremental capital over the next five years for its expanded plan.
H.B. Fuller aims to expand into high-growth markets like electronics and electric vehicles. They are investing in research and development for sustainable adhesive technologies, including bio-based and compostable options.
While facing a challenging volume growth environment in 2025, H.B. Fuller anticipates organic revenue growth to be flat to up 2% in fiscal 2025. Adjusted EBITDA is expected to be in the range of $600 million to $625 million.
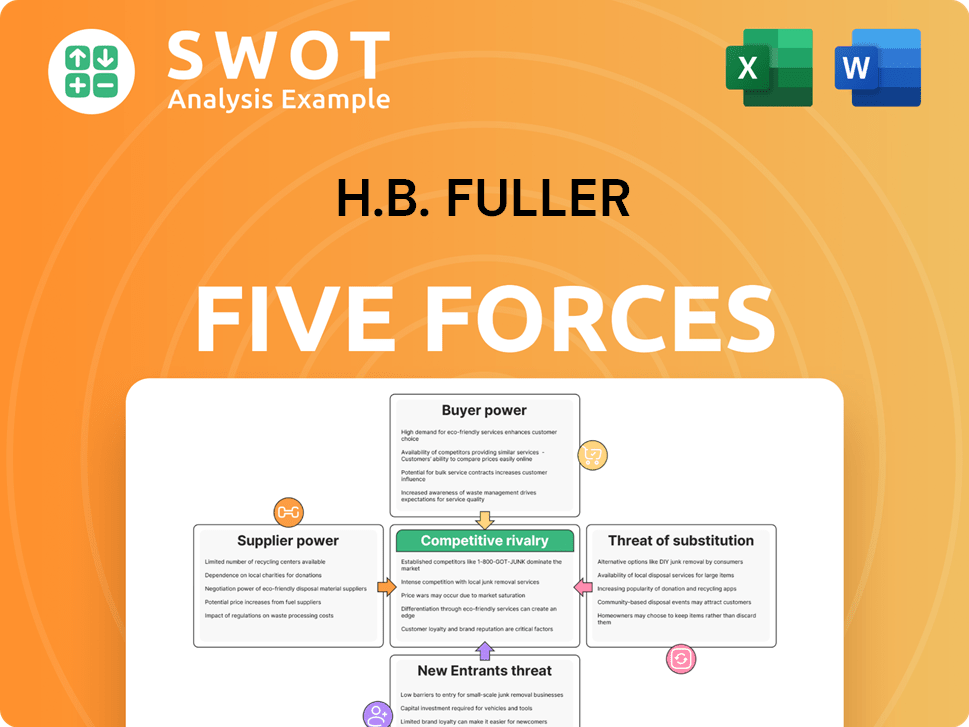
H.B. Fuller Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What is Competitive Landscape of H.B. Fuller Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of H.B. Fuller Company?
- How Does H.B. Fuller Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of H.B. Fuller Company?
- What is Brief History of H.B. Fuller Company?
- Who Owns H.B. Fuller Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of H.B. Fuller Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.