H.B. Fuller Bundle
Who Really Owns H.B. Fuller?
Uncover the intricate web of ownership behind H.B. Fuller, a global leader in adhesives and sealants. Understanding the company's ownership structure is key to grasping its strategic moves and future potential. From its humble beginnings to its current status as a publicly traded entity, the evolution of H.B. Fuller's ownership tells a compelling story.

Founded in 1887, H.B. Fuller has grown from a one-man glue operation to a multinational corporation with a market capitalization of $2.94 billion as of June 13, 2025. This analysis explores the H.B. Fuller SWOT Analysis, its major shareholders, and the impact of key investors like Elmer L. Andersen, who significantly shaped its trajectory. Discover who controls H.B. Fuller and the dynamics of its ownership, including the H.B. Fuller ownership percentage breakdown and how to buy H.B. Fuller stock, providing valuable insights for investors and business strategists alike. Learn about H.B. Fuller's company profile and the H.B. Fuller shareholders.
Who Founded H.B. Fuller?
The story of H.B. Fuller begins in 1887, with Harvey Benjamin Fuller, Sr. as the founder. He started the business as a one-man operation in St. Paul, Minnesota, focusing on inventing and selling glue. The company's early years were marked by innovation, with Fuller expanding his product line to include wall cleaners by the 1890s, and establishing a presence across the United States.
The firm was officially reincorporated as H.B. Fuller Company in 1915, a move that involved issuing stock valued at $75,000. This marked a significant step in its evolution, setting the stage for future growth and changes in ownership. The company's history is a testament to its adaptability and its ability to evolve with the times.
Following Harvey B. Fuller, Sr.'s death in 1921, Harvey B. Fuller, Jr. took over the presidency. However, a major shift in the company's ownership occurred in 1941. Elmer L. Andersen acquired a majority stake and assumed leadership. At the time of Andersen's purchase, the company's annual sales were approximately US$200,000. This transition was a pivotal moment in the company's history, setting the stage for the international expansion that would follow under Andersen's guidance.
H.B. Fuller was founded in 1887 by Harvey Benjamin Fuller, Sr.
The company was reincorporated in 1915, issuing stock valued at $75,000.
Harvey B. Fuller, Jr. became president in 1921 after his father's death.
Elmer L. Andersen acquired a majority stake in 1941.
At the time of Andersen's purchase, annual sales were around US$200,000.
Under Andersen's leadership, the company began its international expansion.
Understanding the early ownership structure of H.B. Fuller provides insight into its foundational years. The transition from a family-run business to a company with broader ownership, particularly with Elmer L. Andersen's involvement, highlights the evolution of the company. For more on the company's strategic direction, consider reading about the Growth Strategy of H.B. Fuller.
- Harvey B. Fuller, Sr. founded the company in 1887.
- The company reincorporated in 1915, issuing stock.
- Elmer L. Andersen became a major shareholder in 1941.
- The early focus was on glue and adhesives, expanding over time.
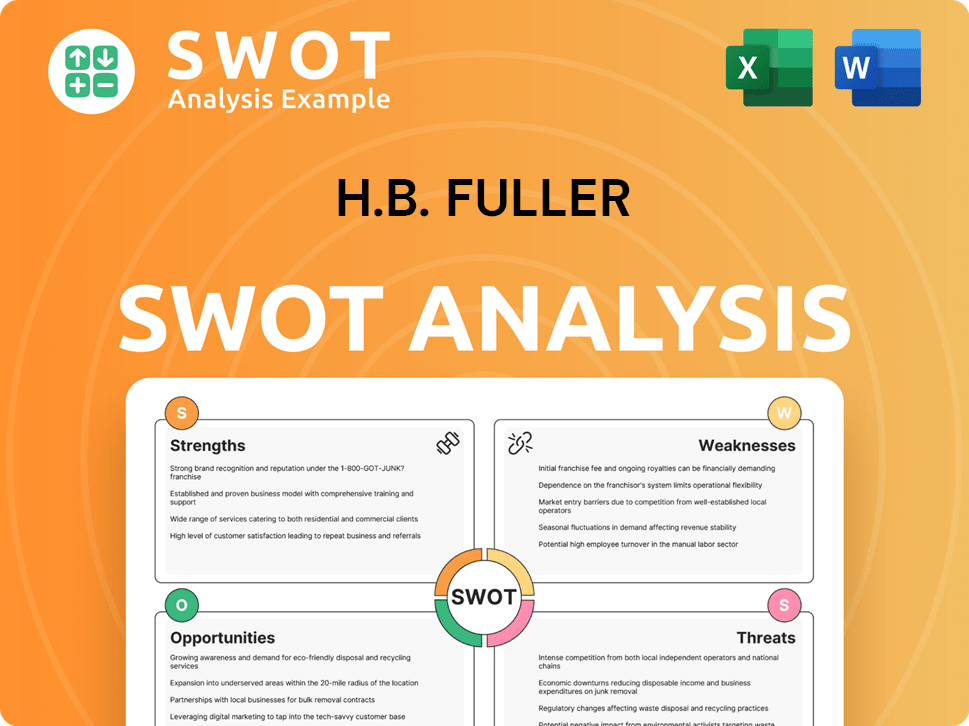
H.B. Fuller SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
How Has H.B. Fuller’s Ownership Changed Over Time?
The journey of H.B. Fuller's ownership began on April 25, 1968, when the company went public with an initial public offering (IPO) at $23 per share on the National Over-the-Counter market. This marked a significant shift, opening the door for external investors to participate in the company's growth. Later, on December 2, 2002, the company transitioned to the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE), further solidifying its presence in the financial markets. As of June 13, 2025, the market capitalization of H.B. Fuller stands at a robust $2.94 billion, reflecting its continued relevance and performance.
The ownership structure of H.B. Fuller, a publicly traded company, is primarily composed of institutional investors, retail investors, and insiders. Institutional investors hold a substantial portion of the shares, ranging from approximately 97.75% to 99.51% as of May and June 2025. Insiders, including company executives and board members, hold a smaller percentage, between 0.36% and 2.27%. Public companies and individual investors collectively own approximately 3.40% to 29.78% of the company's stock. Understanding the dynamics of H.B. Fuller ownership provides insights into its financial health and strategic direction.
| Shareholder Category | Approximate Ownership (May/June 2025) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Institutional Investors | 97.75% - 99.51% | Includes BlackRock, Vanguard, State Street, and others. |
| Insiders | 0.36% - 2.27% | Company executives and board members. |
| Retail/Individual Investors | 3.40% - 29.78% | Public companies and individual investors. |
Major institutional shareholders such as BlackRock, Inc., Vanguard Group Inc, iShares Core S&P Small-Cap ETF, State Street Corp, and Capital World Investors significantly influence the company's direction. A key event impacting the company's strategy was the acquisition of Royal Adhesives & Sealants in 2017 for approximately $1.575 billion. This acquisition broadened its product portfolio and market reach, shaping its competitive landscape. If you're interested in how the company approaches its market, you might find insights in this Marketing Strategy of H.B. Fuller article.
H.B. Fuller's ownership is primarily held by institutional investors, with a significant portion controlled by major firms.
- Institutional investors hold the majority of shares, influencing company decisions.
- Insiders own a smaller percentage, aligning their interests with the company's success.
- The IPO in 1968 and NYSE listing in 2002 were pivotal moments in its ownership journey.
- Acquisitions, such as Royal Adhesives & Sealants, have reshaped its market position.
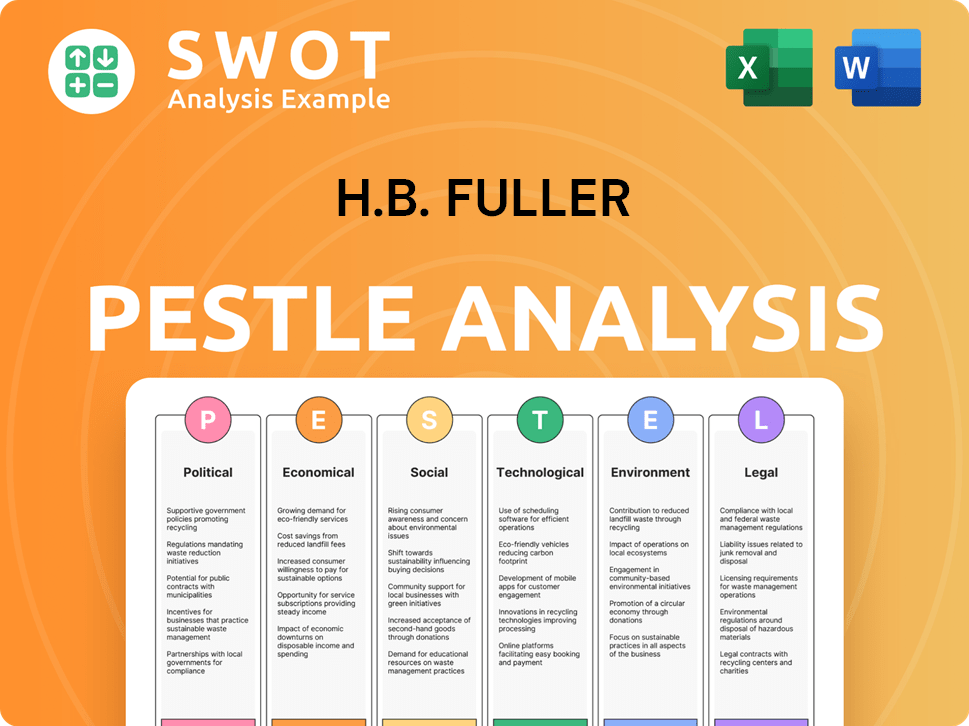
H.B. Fuller PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
Who Sits on H.B. Fuller’s Board?
The Board of Directors of H.B. Fuller plays a vital role in the company's governance and strategic direction. As of January 22, 2025, Teresa (Terry) J. Rasmussen serves as the Chair of the Board of Directors, succeeding Lee R. Mitau. Rasmussen, who joined the board in 2020, is also the president and CEO of Thrivent, a Fortune 500 financial services organization. Understanding the composition and influence of the board is key to assessing the overall H.B. Fuller ownership structure and the interests of H.B. Fuller shareholders.
Celeste Mastin is currently the President and Chief Executive Officer of H.B. Fuller. The company regularly solicits proxies for its annual meetings, detailing proposals for shareholder votes. These proposals include the election of directors and advisory votes on executive compensation. The voting structure generally follows a one-share-one-vote principle, a common practice for publicly traded companies like H.B. Fuller. The H.B. Fuller company profile and its governance structure are important for H.B. Fuller investors.
| Board Member | Position | Other Affiliations |
|---|---|---|
| Teresa (Terry) J. Rasmussen | Chair of the Board | President and CEO of Thrivent |
| Celeste Mastin | President and CEO | H.B. Fuller |
| Lee R. Mitau | Former Chair of the Board | (Retired) |
In fiscal year 2024, shareholders expressed strong support for the executive compensation program, with 97% of votes cast for approval. This highlights the alignment between the company's leadership and its shareholders. For those interested in the company's strategic direction and financial performance, further details can be found in the H.B. Fuller annual report and proxy statements, offering insights into the H.B. Fuller stock and the company's operational strategies. For more information on the customers of H.B. Fuller, consider reading this article about Target Market of H.B. Fuller.
Shareholders vote on key decisions, including director elections and executive compensation. The voting structure generally follows a one-share-one-vote principle. Understanding the board's composition and shareholder voting results provides insights into the company's governance.
- Board of Directors oversees the company's strategic direction.
- Shareholders vote on important matters.
- Executive compensation receives shareholder scrutiny.
- The company's governance structure is transparent.
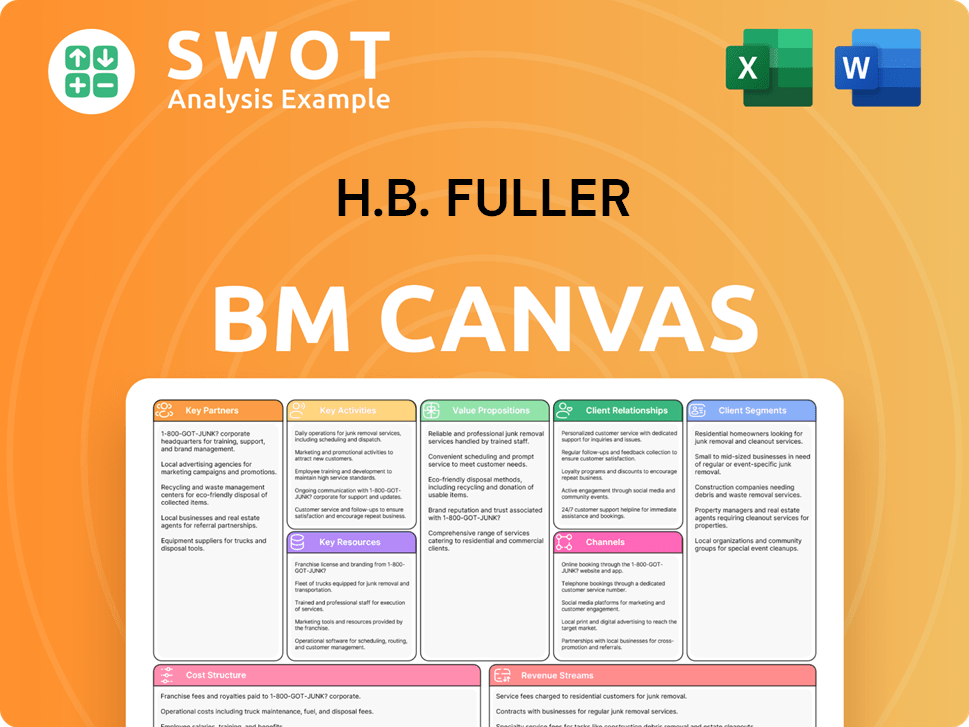
H.B. Fuller Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
What Recent Changes Have Shaped H.B. Fuller’s Ownership Landscape?
In recent years, the strategic direction of H.B. Fuller has been marked by significant leadership changes and financial performance. In October 2024, the company announced that Teresa (Terry) J. Rasmussen would become the new Chair of the Board of Directors, effective January 22, 2025. This transition follows Lee R. Mitau's retirement and aims to guide the company towards growth in new markets, focusing on achieving a 20% EBITDA margin.
Financially, H.B. Fuller reported a net revenue of $3.57 billion for fiscal year 2024, marking a 1.6% year-on-year increase. The adjusted EBITDA reached $594 million, with an adjusted EBITDA margin of 16.6%. For fiscal year 2025, the company anticipates a net revenue decrease of 2% to 4% compared to 2024, though it expects a 1% to 2% increase when adjusting for the divestiture of its Flooring business. Adjusted EBITDA for fiscal 2025 is projected to be between $600 million and $625 million, representing a 1% to 5% year-on-year increase. This indicates the company's continued efforts to maintain and improve profitability despite market challenges. For further insights into the company's financial strategy, you can explore Revenue Streams & Business Model of H.B. Fuller.
| Metric | Fiscal Year 2024 | Fiscal Year 2025 (Projected) |
|---|---|---|
| Net Revenue | $3.57 billion | Down 2% to 4% (excluding Flooring divestiture: Up 1% to 2%) |
| Adjusted EBITDA | $594 million | $600 million to $625 million (Up 1% to 5%) |
| Adjusted EBITDA Margin | 16.6% | Not explicitly stated, but implied to be stable or improved |
Ownership trends in H.B. Fuller reveal a strong presence of institutional investors. Data from May and June 2025 shows that institutional investors held approximately 97.75% to 99.51% of shares. Insider holdings remained relatively stable, ranging from 0.36% to 2.27%. There has been some insider trading activity, including both purchases and sales. The company has a consistent history of returning value to shareholders, as demonstrated by its 56th consecutive year of increasing its quarterly dividend in May 2025. This consistent dividend growth reflects the company's financial stability and commitment to its shareholders.
Institutional investors hold the majority of shares, indicating strong market confidence. Insider ownership is relatively small but present, with instances of trading activity. Understanding the ownership structure is key for investors.
The company's financial performance shows revenue growth and expanding EBITDA margins. Projected figures for 2025 indicate continued profitability. Investors should monitor these trends.
The company's consistent dividend payouts demonstrate a commitment to shareholders. The shareholder base is primarily institutional. This indicates investor confidence.
The majority of H.B. Fuller is owned by institutional investors, with a smaller percentage held by insiders. Understanding the ownership breakdown helps in assessing the company's stability and direction.
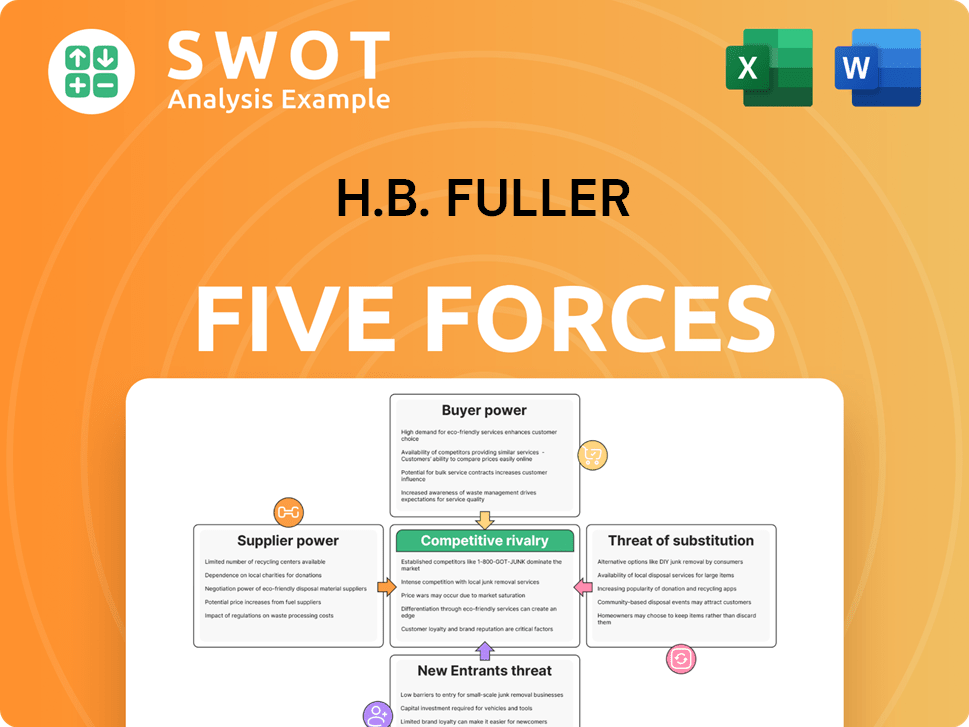
H.B. Fuller Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What are Mission Vision & Core Values of H.B. Fuller Company?
- What is Competitive Landscape of H.B. Fuller Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of H.B. Fuller Company?
- How Does H.B. Fuller Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of H.B. Fuller Company?
- What is Brief History of H.B. Fuller Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of H.B. Fuller Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.