Lloyds Banking Group Bundle
How did Lloyds Banking Group become a UK financial giant?
Journey back in time to uncover the Lloyds Banking Group SWOT Analysis and the fascinating story of Lloyds Bank history, a financial institution that has shaped the UK's economic narrative. From its humble beginnings in 1765, this financial powerhouse has weathered economic storms and emerged as a cornerstone of the British financial landscape. Discover the pivotal moments that defined its evolution and its lasting impact on the nation.
Tracing the brief history of Lloyds reveals a story of remarkable adaptability and strategic foresight. Understanding the Early history Lloyds Bank is crucial to grasping its current stature. This exploration will delve into key milestones, from its founding date to its present-day structure, highlighting the innovations and challenges that have shaped its trajectory. Explore the impact of Lloyds Banking Group on the UK economy, and understand the strategic decisions that have defined its identity within the financial institutions UK.
What is the Lloyds Banking Group Founding Story?
The story of Lloyds Banking Group begins on June 3, 1765, when Sampson Lloyd II and John Taylor established Taylors and Lloyds in Birmingham. This marked the genesis of what would become one of the UK's largest financial institutions. Their vision was to address the critical need for dependable banking services in the swiftly industrializing Midlands region of England.
In an era where formal banking was limited outside London, Taylors and Lloyds provided a safe haven for merchants and manufacturers to deposit funds and secure credit. This initiative was crucial for fostering trade and economic advancement. The bank's early operations were significantly influenced by the Industrial Revolution, as the demand for capital and efficient financial transactions increased with the expansion of manufacturing.
Taylors and Lloyds was founded in Birmingham in 1765 by Sampson Lloyd II and John Taylor. The bank's initial focus was on providing credit and secure money management for the growing industrial class.
- The original business model involved accepting deposits, issuing notes, and providing loans.
- The company's name reflected the partnership between its founders.
- Initial funding came from the partners' capital, a common practice at the time.
- The Quaker background of Sampson Lloyd II instilled a strong ethical foundation.
The early business model was straightforward: accepting deposits, issuing notes, and providing loans to local businesses. Their first 'product' was essentially credit and secure money management for the burgeoning industrial class. The company's name, Taylors and Lloyds, directly reflected the partnership of its two founders. Initial funding was primarily sourced from the partners' own capital. One interesting aspect from its early days is the emphasis on trust and personal relationships, which were paramount in an unregulated banking environment. The Quaker background of Sampson Lloyd II instilled a strong ethical foundation in the bank's early operations, contributing to its reputation for integrity. The cultural and economic context of the Industrial Revolution significantly influenced the company's creation, as the demand for capital and efficient financial transactions surged in line with rapid manufacturing expansion.
The bank's early focus was on serving the needs of the rapidly expanding industrial sector in the Midlands. This strategic positioning allowed it to capitalize on the economic growth of the region. The ethical principles of the founders, particularly Sampson Lloyd II's Quaker background, played a pivotal role in shaping the bank's culture and reputation for trustworthiness. This commitment to ethical practices was crucial in an era with limited regulatory oversight. The company's evolution reflects a deep understanding of the financial needs of its customers and a commitment to adapting to the changing economic landscape.
For more insights into the core values that guide the institution today, explore Mission, Vision & Core Values of Lloyds Banking Group.
Lloyds Banking Group SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
What Drove the Early Growth of Lloyds Banking Group?
The early growth of Lloyds Banking Group, initially known as Taylors and Lloyds, was driven by the industrial boom of the 18th and 19th centuries. It began by serving the local merchant and manufacturing community in Birmingham, establishing itself as a reliable financial partner. As the Industrial Revolution progressed, the bank expanded its operations, launching products like credit and deposit accounts tailored for businesses. This period set the stage for its future as a major player in the UK's banking sector.
A key phase of expansion involved strategic mergers and acquisitions in the 19th century. The merger with Barnetts Hoares & Co. in 1864, forming Lloyds Banking Company Limited, was a major step. This period saw the opening of new branches across England, extending its reach beyond the Midlands. These moves helped Lloyds adapt to market reception and meet the growing financial demands of a modernizing economy.
Leadership transitions were also crucial to its early growth. The bank evolved from a family-run partnership to a more structured corporate entity, allowing for increased capitalization and operational scope. By the turn of the 20th century, Lloyds had established a significant presence across the UK. The 1918 merger with the London & Brazilian Bank further expanded its international reach.
The bank's early clients included large industrial enterprises and wealthy individuals, reflecting its role in financing economic development. Lloyds offered a comprehensive range of services to adapt to market changes. By the early 1900s, the bank had a substantial footprint across the UK, setting the foundation for its future growth and influence in the banking industry.
Key milestones for Lloyds Banking Group include the merger with Barnetts Hoares & Co. in 1864, which was pivotal in its expansion. The merger with the London & Brazilian Bank in 1918 was also significant for its international reach. These strategic moves allowed Lloyds to navigate the competitive landscape and meet the increasing financial demands of a modernizing economy.
Lloyds Banking Group PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
What are the key Milestones in Lloyds Banking Group history?
The Lloyds Banking Group has a rich history, marked by significant milestones that have shaped its evolution within the UK's banking landscape. From its origins to its current status, the Group's journey reflects broader trends in banking history UK and the development of financial institutions UK.
| Year | Milestone |
|---|---|
| 1765 | Sampson Lloyd and John Taylor establish Taylors and Lloyds, marking the early history Lloyds Bank. |
| 1865 | Lloyds & Co. becomes a limited company, expanding its operations and influence. |
| 1918 | The bank acquires the Capital and Counties Bank, significantly increasing its branch network. |
| 1995 | The merger of Lloyds Bank and TSB Group creates Lloyds TSB, a major player in the market. |
| 2009 | Lloyds TSB acquires HBOS during the financial crisis, leading to the formation of Lloyds Banking Group. |
| 2013 | The UK government sells its stake in Lloyds Banking Group, marking the end of the state bailout. |
| 2017 | The Group reports a pre-tax profit of £5.3 billion, demonstrating its recovery post-crisis. |
| 2024 | Lloyds Banking Group continues to invest in digital capabilities, with a focus on enhancing customer experience and operational resilience. |
Innovations at Lloyds Banking Group have often centered on leveraging technology to improve customer service and operational efficiency. The bank’s early adoption of automated tellers and electronic banking systems reflects its commitment to modernization.
Early investment in automated teller machines (ATMs) and electronic banking systems enhanced customer access and operational efficiency. These initiatives were part of a broader strategy to modernize banking processes and improve service delivery.
Significant investment in digital banking platforms and mobile applications has improved customer experience. The Group continues to enhance its digital offerings to meet evolving customer expectations and maintain a competitive edge.
Enhanced cybersecurity measures have been implemented to protect customer data and ensure operational resilience. These measures are crucial in the face of increasing cyber threats and the growing reliance on digital banking.
Strategic partnerships with other financial institutions have facilitated the expansion and diversification of services. These collaborations have enabled the Group to offer a broader range of products and services to its customers.
The use of data analytics to personalize customer experiences and improve risk management is a key innovation. Data-driven insights help the Group make informed decisions and enhance customer satisfaction.
The Group is increasingly focused on sustainable finance initiatives, including green lending and investments. This reflects a broader trend in the financial industry towards environmental, social, and governance (ESG) considerations.
The challenges faced by Lloyds Banking Group include navigating market downturns and regulatory changes. The 2008-2009 financial crisis, the acquisition of HBOS, and the subsequent government bailout presented significant hurdles.
The global financial crisis of 2008-2009 led to substantial government intervention and restructuring. This period highlighted critical issues in risk management and product failures, particularly in lending practices.
Stricter capital requirements and conduct rules have necessitated significant internal adjustments. These changes have impacted operational strategies and required ongoing compliance efforts.
Economic downturns and market volatility have posed challenges to profitability and asset quality. The Group must adapt to changing economic conditions to maintain financial stability.
Intense competition from both traditional banks and fintech companies has required continuous innovation and customer-centric strategies. The Group must stay ahead of market trends to maintain its competitive edge.
Operational risks, including cybersecurity threats and fraud, require constant vigilance and investment in robust security measures. These risks can impact customer trust and financial performance.
Evolving customer expectations and the rise of digital banking have necessitated significant investments in technology and customer service. Adapting to these changes is crucial for long-term success.
Lloyds Banking Group Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
What is the Timeline of Key Events for Lloyds Banking Group?
The brief history of Lloyds Banking Group reflects a journey of mergers, acquisitions, and strategic shifts. From its humble beginnings in Birmingham to its current status as a major financial institution, the company has navigated significant economic and regulatory changes. This timeline highlights key events in the evolution of Lloyds Banking Group, showcasing its adaptability and growth over the years.
| Year | Key Event |
|---|---|
| 1765 | Sampson Lloyd II and John Taylor establish Taylors and Lloyds in Birmingham, marking the beginning of the bank's history. |
| 1864 | Merger with Barnetts, Hoares & Co. leads to the formation of Lloyds Banking Company Limited, expanding its reach. |
| 1918 | Merger with the London & Brazilian Bank broadens its international presence. |
| 1971 | The company officially becomes Lloyds Bank Limited, solidifying its identity. |
| 1986 | Acquisition of the remaining shares of the Bank of London and South America (BOLSA) further strengthens its international portfolio. |
| 1995 | Merger with TSB Group results in Lloyds TSB Group, creating a larger financial entity. |
| 2000 | Acquisition of Scottish Widows allows entry into the life, pensions, and insurance market. |
| 2009 | Acquisition of HBOS leads to the formation of Lloyds Banking Group and a government bailout during the financial crisis. |
| 2014 | The government begins divesting its stake in Lloyds Banking Group, signaling a return to private ownership. |
| 2017 | The UK government sells its final shares in Lloyds Banking Group, returning it to full private ownership. |
| 2024 | Lloyds Banking Group announces a new strategic plan focused on digital transformation, sustainability, and targeted growth. |
| 2025 | Lloyds Banking Group continues to invest in AI and data analytics to personalize customer experiences and enhance operational efficiency. |
The Group's strategic plan for 2024-2026 focuses on 'Accelerating Digital,' 'Deepening Customer Relationships,' and 'Building a Sustainable Future.' This plan emphasizes digital capabilities, aiming to improve customer experiences and operational efficiency. The company plans to invest approximately £3 billion over three years in technology and data to achieve these goals. The aim is to become a leading digital bank.
Lloyds Banking Group is heavily investing in digital transformation, including AI and data analytics. This investment is designed to personalize customer experiences and boost operational efficiency. The strategic focus on AI aims to streamline processes and offer tailored financial solutions, which is critical in a competitive market. The company is aiming for higher customer satisfaction through these innovations.
The company is committed to sustainability and is aligning its lending and investment strategies with sustainability goals. Lloyds aims to play a leading role in the UK's transition to a low-carbon economy. This includes supporting green initiatives and integrating environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors into its business model. The focus is on long-term value creation.
The increasing adoption of digital banking and the growing importance of ESG factors are key industry trends. Analysts predict continued pressure on traditional banking models, necessitating innovation and diversification. Lloyds Banking Group is positioning itself to adapt to these changes, focusing on digital leadership and customer-centric strategies. The bank is also expanding its wealth management and commercial banking sectors.
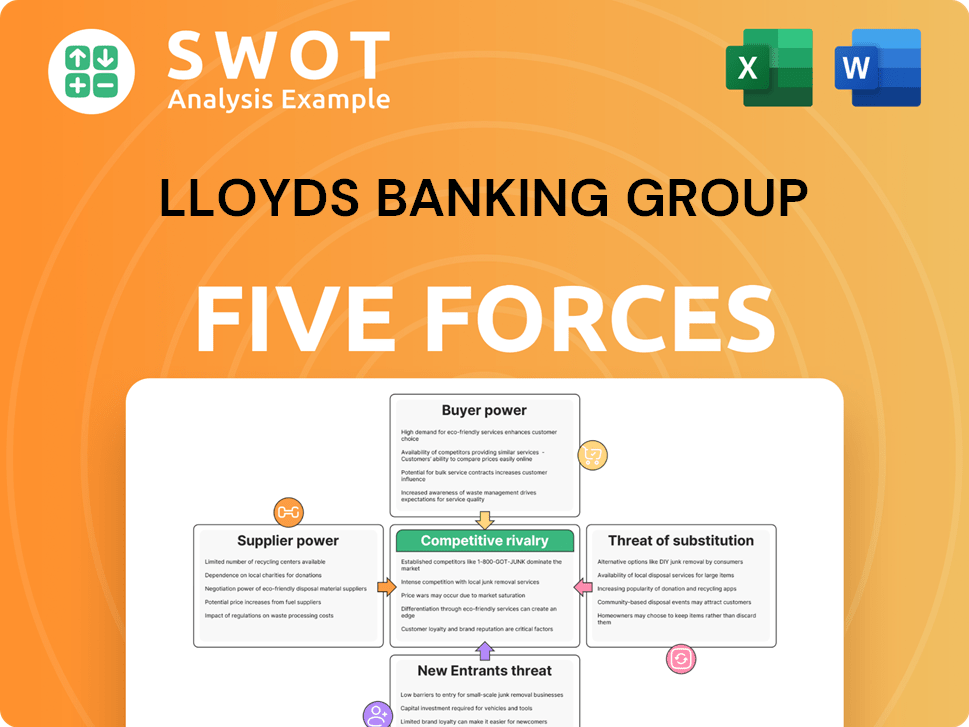
Lloyds Banking Group Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What is Competitive Landscape of Lloyds Banking Group Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of Lloyds Banking Group Company?
- How Does Lloyds Banking Group Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of Lloyds Banking Group Company?
- What is Brief History of Lloyds Banking Group Company?
- Who Owns Lloyds Banking Group Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of Lloyds Banking Group Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.