Nokia Bundle
How did Nokia transform from a paper mill to a tech giant?
Nokia's story is a captivating saga of reinvention, spanning over a century of technological evolution. From its roots in 1865 Finland, this company has consistently adapted to industrial shifts, leaving an indelible mark on the world. Its journey showcases remarkable resilience and innovation in a landscape of constant change. Today, understanding the Nokia SWOT Analysis is key to grasping its current strategic position.

Delving into the Nokia company history reveals a fascinating Nokia timeline of early business ventures and key milestones. The Nokia evolution from rubber and cable manufacturing to becoming a global leader in mobile phones is a testament to its adaptability. This brief history of Nokia mobile phones explores the rise to mobile phone dominance, the impact of early Nokia phone models, and its eventual comeback in the smartphone market, all rooted in Nokia's origins in Finland.
What is the Nokia Founding Story?
The Nokia history begins in Finland with a simple paper mill. This mill, established in the mid-1800s, marked the initial steps of a company that would later become a global leader in telecommunications. The story of the
The
The roots of Nokia trace back to May 12, 1865, when Fredrik Idestam, a mining engineer, established a groundwood pulp mill in Tampere, Finland. The company's initial focus was on paper production, capitalizing on Finland's abundant forest resources.
- The name 'Nokia' was adopted in 1871, inspired by the Nokianvirta River, which flowed past Idestam's second mill.
- This strategic location provided the necessary water power for his operations.
- While Idestam was the sole founder of the paper mill, the broader Nokia Corporation as we know it today was formed through a series of mergers.
- The company's early success was driven by the growing demand for paper products in an industrializing Europe, laying the groundwork for its future diversification.
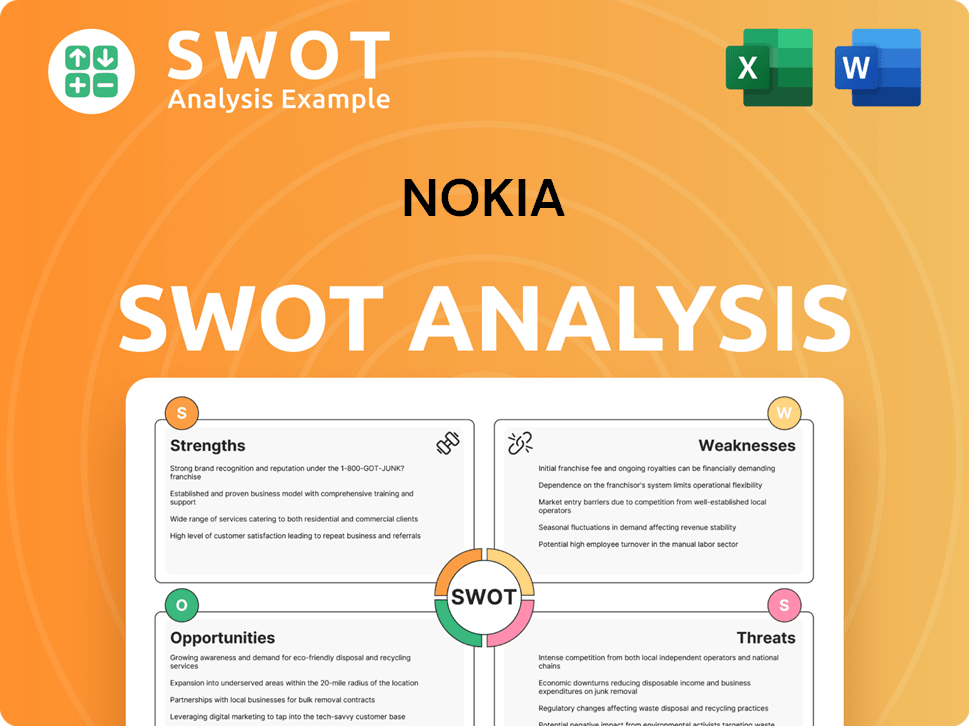
Nokia SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
What Drove the Early Growth of Nokia?
The early growth of the company, now known as Nokia, marked a significant shift beyond its initial focus on paper production. This expansion involved strategic acquisitions and diversification into new sectors, laying the groundwork for its future as a global technology leader. These moves were crucial in shaping the company's trajectory and its eventual dominance in the telecommunications industry. Understanding the Competitors Landscape of Nokia helps to contextualize its historical journey.
In 1922, the company expanded beyond paper, acquiring Finnish Rubber Works, which manufactured rubber products like tires and footwear. This strategic move was followed by the acquisition of Finnish Cable Works, a producer of telephone and electricity cables. These acquisitions were pivotal in broadening the company's scope and reducing its reliance on a single industry.
The three companies formally merged in 1967 to create Nokia Corporation. This conglomerate structure allowed for the sharing of resources and expertise across various sectors. The merger was a strategic move to consolidate operations and enhance efficiency, setting the stage for future growth.
During this period, Nokia began its foray into electronics, a strategic shift that proved crucial for its future. Early electronic products included industrial automation systems and military equipment. This move into electronics marked the beginning of the company's transformation into a technology-driven entity.
The company's expansion into new markets, both geographically and in terms of product categories, highlighted its adaptability and foresight. This ability to identify and capitalize on emerging opportunities was a key factor in its early success. The company's focus on innovation and diversification helped it navigate changing market dynamics.
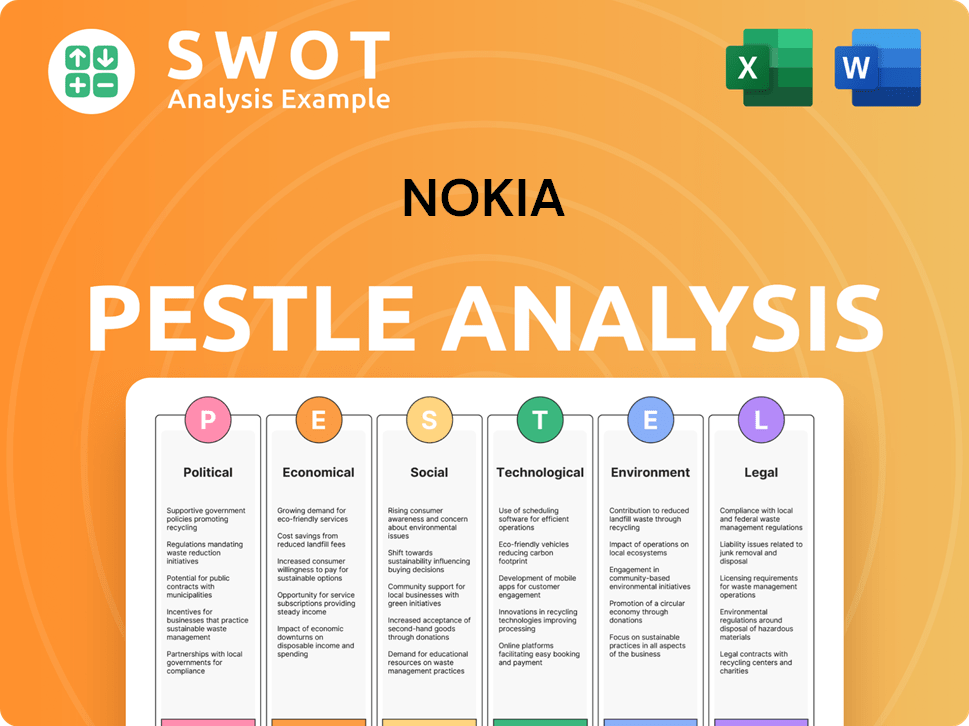
Nokia PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
What are the key Milestones in Nokia history?
The Nokia history is marked by significant milestones, from its early days in Finland to its global impact on the telecommunications industry. The company's journey includes pioneering mobile technology and navigating the turbulent shifts in the tech market.
| Year | Milestone |
|---|---|
| 1984 | Developed the Mobira Talkman, one of the world's first handheld mobile phones. |
| 1992 | Launched the Nokia 1011, the first mass-produced GSM phone. |
| 1998 | Became the world's best-selling mobile phone brand. |
| 2000 | Released the iconic Nokia 3310, a globally recognized model. |
| 2014 | Sold its devices and services division to Microsoft. |
| 2016 | Acquired Alcatel-Lucent to strengthen its network infrastructure business. |
Nokia's innovation played a crucial role in shaping the mobile phone industry. The company was at the forefront of introducing features like mobile gaming, camera phones, and early internet browsing on mobile devices, significantly impacting the
Nokia was an early adopter of mobile gaming, introducing games like Snake, which became incredibly popular. This early move helped establish the company as a leader in mobile entertainment, influencing how people interacted with their phones.
Nokia was among the first to integrate cameras into mobile phones, revolutionizing how people captured and shared photos. This innovation transformed mobile phones from communication devices into versatile multimedia tools.
Nokia enabled early internet browsing on mobile devices, allowing users to access the web on the go. This innovation was crucial in the early days of mobile internet, paving the way for future developments in mobile connectivity.
Nokia played a key role in the adoption of GSM technology, which became the global standard for mobile communications. This helped establish the company as a leader in the telecommunications industry, influencing how people communicated worldwide.
Nokia phones were known for their robust designs and durability, making them popular among consumers. Models like the Nokia 3310 were celebrated for their resilience, contributing to the brand's strong reputation.
Nokia developed and used the Symbian operating system, which was a key platform for smartphones before the rise of iOS and Android. This operating system supported a wide range of applications and features, helping Nokia compete in the early smartphone market.
Despite its early success, Nokia faced significant challenges, especially with the rise of smartphones. The company struggled to adapt to the new market dynamics, leading to a decline in market share and strategic shifts.
Nokia struggled to transition from feature phones to smartphones, losing ground to competitors like Apple and Samsung. This shift in consumer preference and technological advancement was a major challenge for the company.
The decision to stick with Symbian OS, rather than adopting Android earlier, proved to be a significant strategic misstep. This delayed Nokia's ability to compete effectively in the rapidly evolving smartphone market.
Nokia experienced a substantial decline in market share as competitors gained dominance in the smartphone sector. This decline forced the company to re-evaluate its strategy and seek new opportunities.
The sale of Nokia's devices and services division to Microsoft in 2014 marked a significant turning point. This acquisition allowed Microsoft to enter the mobile phone market, but it also meant Nokia had to redefine its business focus.
Nokia strategically refocused on network infrastructure, acquiring Alcatel-Lucent in 2016 to strengthen its position in the telecommunications equipment market. This pivot allowed Nokia to leverage its core strengths in network technology and intellectual property.
Intense competition from companies like Apple, Samsung, and Huawei put significant pressure on Nokia's market position. These competitors introduced innovative products and aggressive marketing strategies, challenging Nokia's dominance.
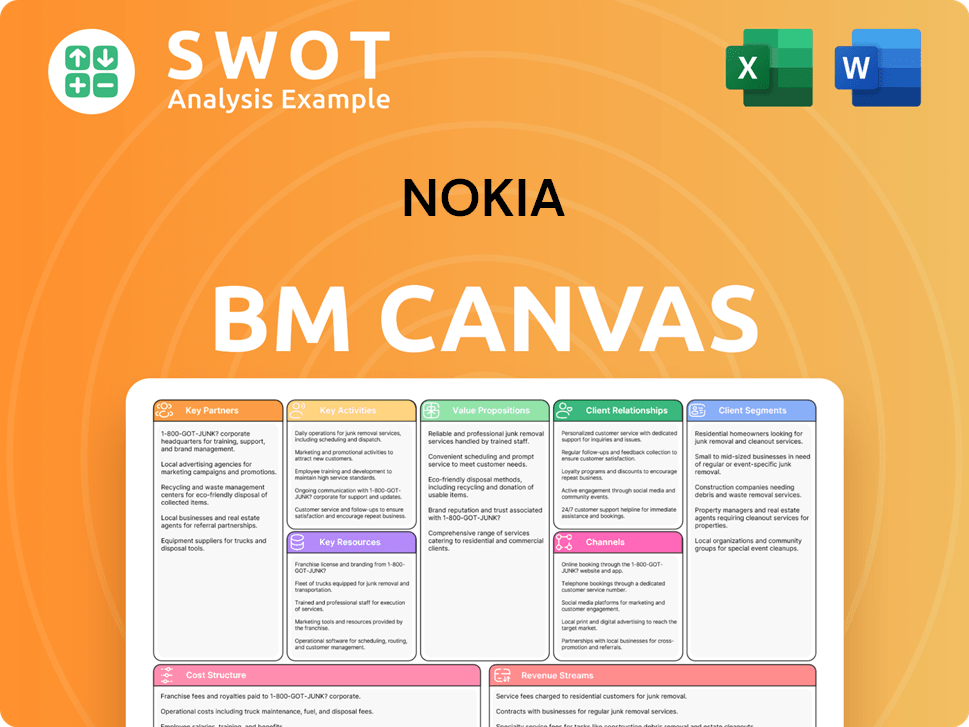
Nokia Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
What is the Timeline of Key Events for Nokia?
The Nokia history is a story of innovation and adaptation. From its origins in Finland to its global impact, the company has navigated significant shifts in technology and market dynamics. The
| Year | Key Event |
|---|---|
| 1865 | Fredrik Idestam establishes a pulp mill in Tampere, Finland. |
| 1871 | The company officially becomes the Nokia Company. |
| 1922 | Acquisition of Finnish Rubber Works and Finnish Cable Works. |
| 1967 | Formation of Nokia Corporation through the merger of the three companies. |
| 1982 | Introduction of the world's first car phone, the Mobira Talkman. |
| 1984 | Launch of the first portable phone, the Mobira Talkman. |
| 1992 | Introduction of the first GSM digital handheld phone, the Nokia 1011. |
| 1998 | Nokia becomes the world's largest mobile phone manufacturer. |
| 2007 | Apple introduces the iPhone, marking a turning point in the mobile industry. |
| 2014 | Sale of Nokia's Devices & Services division to Microsoft. |
| 2016 | Acquisition of Alcatel-Lucent, strengthening Nokia's network infrastructure business. |
| 2020s | Focus on 5G, enterprise solutions, and network as a service. |
Nokia is heavily invested in the global rollout of 5G networks. The company is working with numerous telecom operators worldwide to expand 5G infrastructure. In 2024, the 5G market is expected to continue growing, with further deployments and upgrades.
Nokia is focusing on providing private wireless networks and other solutions for enterprises. This includes services for various industries, such as manufacturing, logistics, and mining. The enterprise market represents a significant growth opportunity for Nokia.
Nokia is actively involved in research and development for 6G technologies. The company is exploring new advancements in wireless communication to maintain its technological leadership. This involves investments in areas such as new spectrum bands and advanced network architectures.
Nokia is exploring new business models, including 'Network as a Service.' This approach aims to provide flexible and scalable network solutions. The company is adapting to the evolving needs of its customers in the cloud computing era.
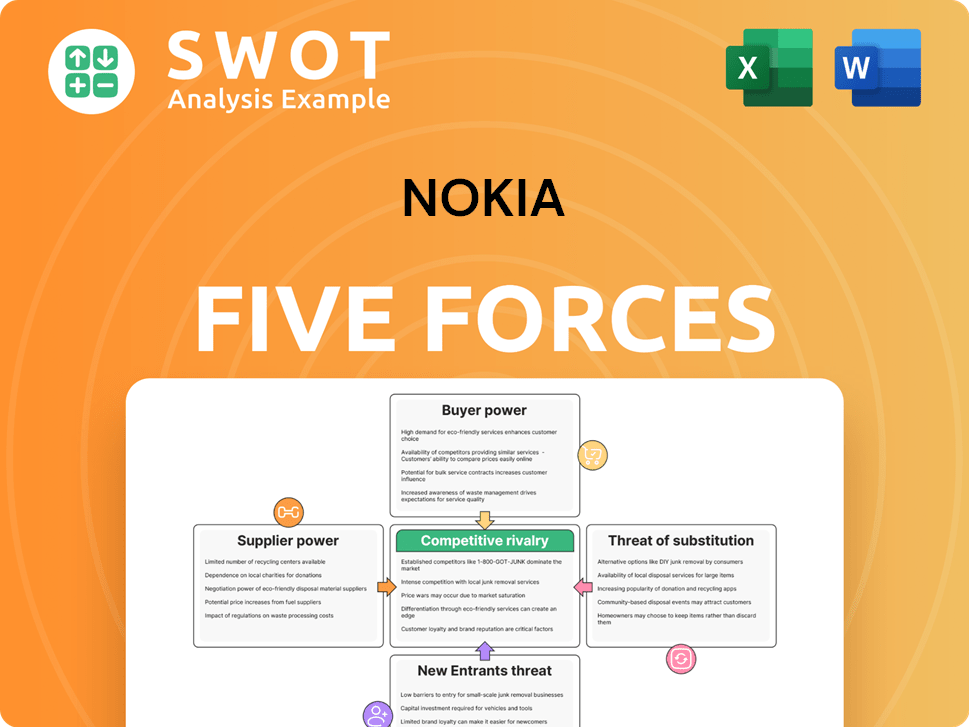
Nokia Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What is Competitive Landscape of Nokia Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of Nokia Company?
- How Does Nokia Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of Nokia Company?
- What is Brief History of Nokia Company?
- Who Owns Nokia Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of Nokia Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.