Rakuten Bundle
How Did Rakuten Conquer the Digital World?
Ever wondered how a company could rise from a small Tokyo startup to a global internet powerhouse? Rakuten's journey is a testament to strategic vision and relentless innovation. Founded in 1997 by Mickey Mikitani, this Japanese e-commerce giant has reshaped the digital landscape. Discover the fascinating Rakuten SWOT Analysis to understand its strengths and weaknesses.
This brief history of Rakuten company explores its transformation from a Japanese e-commerce platform to a diversified global conglomerate. From its early business model to its current business ventures, Rakuten's evolution showcases its impact on Japanese e-commerce and beyond. Explore Rakuten's key milestones, expansion timeline, and the strategic decisions that have shaped its remarkable journey.
What is the Rakuten Founding Story?
The story of Rakuten begins on February 7, 1997, when Hiroshi Mikitani launched the company. Mikitani, with experience in banking, saw a chance to capitalize on the growing e-commerce market in Japan. He noticed that while big companies were going online, smaller businesses needed help to compete digitally, which led to the creation of Rakuten.
Rakuten's initial goal was to provide an online marketplace, Rakuten Ichiba, where merchants could sell products directly to consumers. This approach differed from other e-commerce platforms by focusing on building a community where merchants could interact with customers and build their brands. Mikitani funded Rakuten with his savings and investments from friends and family. The name 'Rakuten,' meaning 'optimism' in Japanese, reflected the founders' positive outlook on the internet industry.
Hiroshi Mikitani founded Rakuten in 1997, aiming to support small and medium-sized businesses in Japan's emerging e-commerce market. The company's original business model centered on an online marketplace, Rakuten Ichiba, which allowed merchants to create their storefronts and sell directly to consumers.
- Rakuten's founding date: February 7, 1997.
- Founder: Hiroshi Mikitani, who had a background in banking.
- Initial focus: Providing an e-commerce platform for small and medium-sized businesses.
- Initial funding: Mikitani's personal savings and investments from friends and family.
- Rakuten's name: Derived from the Japanese word for 'optimism'.
Mikitani's entrepreneurial drive and his team's dedication to supporting small businesses were crucial in establishing an online business in the late 1990s. Rakuten's early success set the stage for its future growth and expansion. Today, Rakuten is a global leader in e-commerce and various other services. You can learn more about the company's core values by reading Mission, Vision & Core Values of Rakuten.
Rakuten SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
What Drove the Early Growth of Rakuten?
The early growth of the Rakuten company was marked by a rapid expansion of its merchant base and product offerings on Rakuten Ichiba. This Japanese e-commerce platform's unique business model, which prioritized merchant independence and direct customer engagement, resonated well with Japanese businesses. By the year 2000, Rakuten had already established itself as a leading e-commerce platform in Japan, demonstrating its early success. The company strategically diversified its portfolio, venturing into new product categories and services.
Rakuten's initial strategy focused on empowering merchants with an independent platform, allowing them to manage their stores and directly engage with customers. This approach contrasted with other e-commerce models, fostering a diverse marketplace. The emphasis on merchant independence was a key factor in attracting a wide range of businesses to the platform. This model enabled Rakuten to quickly expand its product offerings and merchant base.
In 2001, Rakuten launched Rakuten Travel, entering the online travel sector. The acquisition of Infoseek Japan in 2003 bolstered its internet portal services. Rakuten Card was launched in 2005 and quickly became a popular credit card in Japan. These strategic moves were crucial to its sustained growth during this period.
Rakuten's global ambitions were demonstrated through key acquisitions. In 2010, the company acquired Buy.com (later Rakuten.com) in the United States. Play.com was acquired in the UK in 2011. These moves significantly expanded Rakuten's international footprint, establishing a significant presence in the global internet economy.
By 2014, Rakuten reported a total transaction volume of 2.9 trillion yen. This financial performance underscored Rakuten's market leadership in Japan. The company's ability to adapt to evolving market demands and its continuous pursuit of new opportunities were crucial to its sustained growth during this period.
Rakuten PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
What are the key Milestones in Rakuten history?
The Rakuten history is marked by significant achievements. The Rakuten company has evolved significantly since its inception, establishing itself as a major player in the global market.
| Year | Milestone |
|---|---|
| 1997 | Founded by Mickey Mikitani as a Japanese e-commerce platform. |
| 2000 | Launched the 'Rakuten Ichiba' marketplace, becoming a key player in Japanese e-commerce. |
| 2005 | Expanded internationally through acquisitions and partnerships. |
| 2010 | Entered the e-reader market with the acquisition of Kobo. |
| 2014 | Launched Rakuten Mobile, entering the telecommunications sector. |
| 2019 | Officially launched its mobile carrier services in Japan, challenging established telecommunication giants. |
Rakuten has consistently introduced innovative strategies to enhance its offerings. A central innovation is the 'Rakuten Ecosystem,' a comprehensive loyalty program integrating various services.
The Rakuten Ecosystem integrates e-commerce, financial services, and telecommunications, rewarding users with points across platforms. This integrated approach boosts customer loyalty and encourages cross-service usage, setting it apart in the e-commerce platform landscape.
Rakuten Mobile's launch challenged the dominance of established telecom companies in Japan. This move expanded Rakuten's service portfolio and enhanced its presence in the digital market, driving competition and innovation in the industry.
Rakuten invests in AI and data analytics to enhance user experience and merchant capabilities. These technologies help personalize recommendations, improve customer service, and optimize operational efficiency, leading to better user engagement.
Integration of fintech services, including payment solutions and financial products, within the Rakuten Ecosystem. This integration simplifies transactions, enhances user experience, and fosters financial inclusion, creating a seamless user journey.
Rakuten's global expansion strategy involved acquisitions and partnerships to enter new markets. This strategy aimed to extend its reach and diversify revenue streams, although it faced challenges in adapting to local market dynamics.
Rakuten's loyalty program, which rewards users with Rakuten Points across various services. This program boosts customer retention and encourages users to engage with multiple services within the Rakuten ecosystem, fostering a loyal customer base.
Despite its successes, Rakuten has faced several challenges. The company's international expansion has sometimes struggled to gain traction.
The e-commerce landscape is highly competitive, with giants like Amazon and Alibaba dominating the market. This intense competition puts pressure on Rakuten to innovate and differentiate itself to maintain market share and profitability.
Rakuten Mobile has faced financial challenges, reporting significant operating losses. In 2023, the mobile segment reported an operating loss of 337.2 billion yen, though this was an improvement from the 492.8 billion yen loss in 2022, requiring strategic adjustments.
Expansion into international markets has presented difficulties in adapting to diverse consumer preferences and market conditions. Some ventures have not achieved the desired success, leading to strategic divestments and a need for localized strategies.
Rakuten has demonstrated a strong ability to adapt and pivot its strategies in response to challenges. This includes focusing on profitability in its mobile segment and leveraging its fintech services, which saw a 38.3% increase in non-GAAP operating income in 2023, reaching 182.4 billion yen.
Navigating complex regulatory environments and ensuring compliance across multiple markets presents ongoing challenges. These issues can impact operational costs and require continuous monitoring and adaptation to maintain legal and ethical standards.
Successfully integrating acquired companies and their technologies into the existing Rakuten ecosystem can be complex. This requires careful planning and execution to realize synergies and avoid operational disruptions, which can impact overall performance.
Rakuten Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
What is the Timeline of Key Events for Rakuten?
The story of the Rakuten company is one of rapid expansion and diversification, beginning in Japan and growing into a global force. Founded by Mickey Mikitani, the company has evolved from a simple e-commerce platform to a multifaceted business encompassing e-commerce, financial services, digital content, and mobile communications. Its history is marked by strategic acquisitions and innovative service launches, establishing its presence in key markets worldwide and significantly impacting Japanese e-commerce.
| Year | Key Event |
|---|---|
| February 7, 1997 | Founded as MDM, launching Rakuten Ichiba, marking the beginning of its e-commerce journey. |
| 1999 | The company officially changed its name to Rakuten, Inc., solidifying its brand identity. |
| 2001 | Launched Rakuten Travel, entering the online travel market and expanding its service offerings. |
| 2003 | Acquired Infoseek Japan, enhancing its internet portal services and user reach. |
| 2005 | Launched Rakuten Card, a significant move into financial services, diversifying its revenue streams. |
| 2010 | Acquired Buy.com (USA), boosting its global e-commerce footprint. |
| 2011 | Acquired Play.com (UK), further expanding its international presence. |
| 2014 | Reported a total transaction volume of 2.9 trillion yen, reflecting substantial growth. |
| 2015 | Partnered with Lyft, investing in the ride-sharing service, showcasing its diversification efforts. |
| 2016 | Launched Rakuten Kobo Aura ONE, expanding its digital content offerings. |
| 2019 | Launched Rakuten Mobile as a full-fledged mobile network operator, entering the telecommunications sector. |
| 2023 | Reported a non-GAAP operating income of 182.4 billion yen for its FinTech segment, highlighting financial services' strong performance. |
| 2024 | Continues to focus on improving profitability for Rakuten Mobile and expanding its global presence through strategic partnerships. |
Rakuten is focused on enhancing the profitability of Rakuten Mobile. This involves optimizing operational efficiencies and expanding its subscriber base. The company is also looking at innovative ways to leverage its mobile infrastructure to offer new services and improve customer experience.
The FinTech segment, which includes Rakuten Card, is a key area for future growth. Rakuten aims to integrate its financial services more deeply within the Rakuten Ecosystem. This will create a more seamless experience for users and drive further engagement across its services.
Rakuten is working to further integrate its diverse services within the 'Rakuten Ecosystem'. This integration is designed to boost user engagement and increase cross-service utilization. By creating a cohesive digital environment, Rakuten aims to increase customer loyalty and drive overall platform growth.
Technological innovation, particularly in AI and data analytics, will be crucial. Rakuten is investing in these technologies to personalize user experiences and optimize merchant operations. This will help the company stay competitive and meet the evolving demands of the digital market.
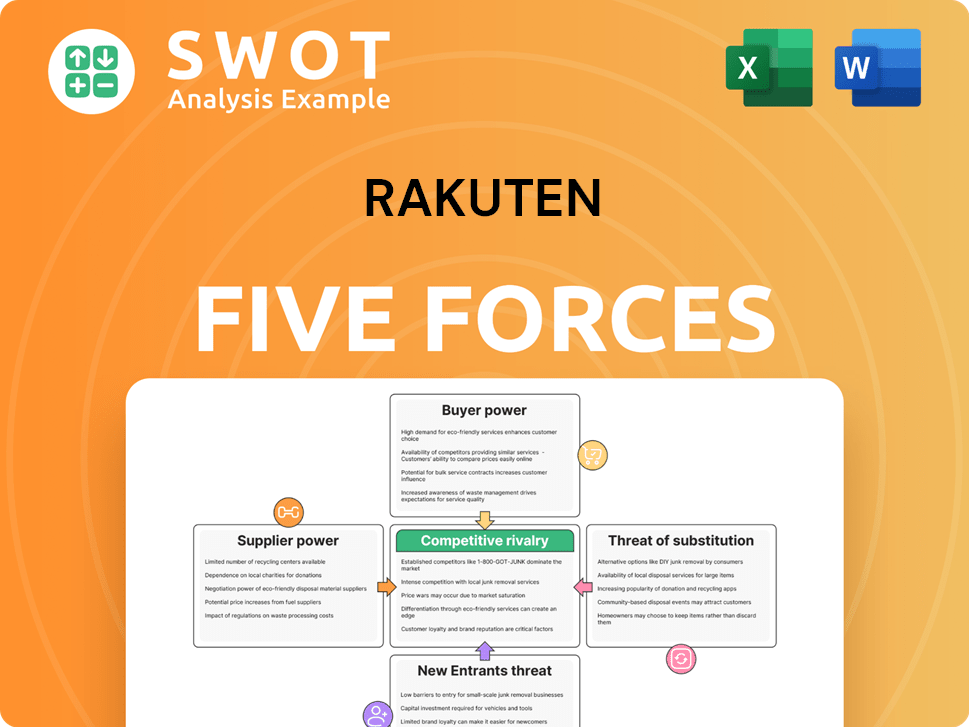
Rakuten Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What is Competitive Landscape of Rakuten Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of Rakuten Company?
- How Does Rakuten Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of Rakuten Company?
- What is Brief History of Rakuten Company?
- Who Owns Rakuten Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of Rakuten Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.