Salesforce Bundle
How Did Salesforce Revolutionize the Business World?
Salesforce, a name synonymous with innovation, has fundamentally altered the enterprise software landscape. Its journey from a disruptive startup to a global leader is a testament to its groundbreaking vision. Founded in 1999, Salesforce pioneered the cloud-based Customer Relationship Management (CRM) model, changing how businesses interact with their customers.
This Salesforce SWOT Analysis offers a glimpse into the company's strategic positioning. From its early days challenging the status quo to its current dominance, understanding the Salesforce company timeline reveals a story of relentless innovation. Salesforce's evolution, driven by the vision of Marc Benioff, has redefined CRM software and its impact on businesses worldwide. The company's key milestones and acquisitions over time further highlight its remarkable growth.
What is the Salesforce Founding Story?
The story of Salesforce, a leading cloud-based software company, began on March 8, 1999. The company was founded by Marc Benioff, Parker Harris, Dave Moellenhoff, and Frank Dominguez. This marked the start of what would become a significant player in the tech industry, revolutionizing how businesses manage customer relationships.
Marc Benioff, with his background at Oracle, envisioned a new approach to enterprise software. He saw the potential of delivering software as a service, a concept that would transform the industry. The other co-founders, software developers, brought the technical skills needed to build the platform.
The founders aimed to solve the problems associated with traditional, on-premise CRM systems. They saw an opportunity to use the internet to offer a more accessible and efficient alternative. Their initial focus was on sales force automation, providing a web-based application as their first product.
Salesforce's founding was driven by a vision to transform enterprise software. The company's initial product was a web-based sales automation application. Early funding came from angel investors and venture capital.
- The name 'Salesforce' was chosen to reflect its focus on sales automation and cloud-based delivery.
- The founders faced the challenge of convincing businesses to trust a new software delivery model.
- The team's combined expertise in software development and enterprise sales was key to early success.
- The company's mission is to connect with customers in a whole new way. Learn more about the Mission, Vision & Core Values of Salesforce.
The company's early success was fueled by its innovative subscription-based model. This approach eliminated the need for businesses to manage their own IT infrastructure, a significant advantage. Salesforce quickly gained traction by offering a more user-friendly and cost-effective solution compared to traditional CRM systems.
In its early years, Salesforce focused on building its core product and establishing a strong customer base. The company's growth was steady, with early adopters recognizing the benefits of cloud-based CRM. The founders' vision and the team's dedication were critical in overcoming initial skepticism and establishing Salesforce as a leader in the industry. By 2024, Salesforce's revenue reached approximately $34.86 billion, a testament to its enduring impact.
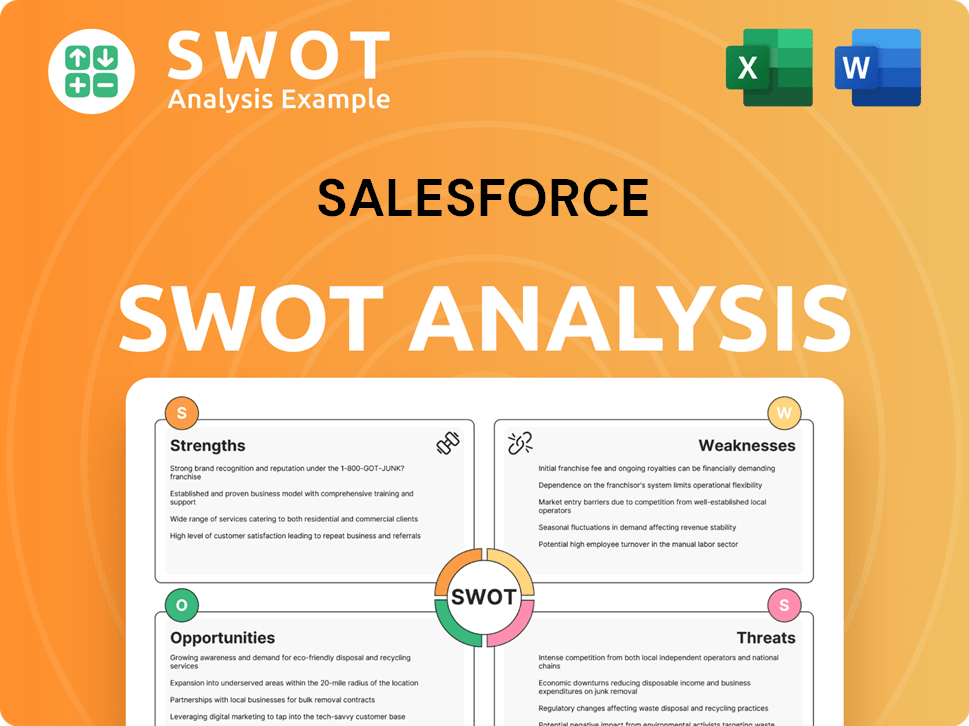
Salesforce SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
What Drove the Early Growth of Salesforce?
The early growth of the company, now known as Salesforce, was marked by a strong focus on proving the viability of its Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) model and expanding its core Customer Relationship Management (CRM) offerings. Founded in 1999, the company quickly launched its initial web-based sales automation product. This early phase was crucial for establishing its value proposition and gaining traction against traditional software providers.
The company's initial web-based sales automation product was a key step in its early days. This product was designed to provide a compelling alternative to traditional software solutions. The early success of this product helped the company gain a foothold in the CRM market.
The company rapidly expanded its team, attracting talent from established technology firms. This rapid expansion was crucial for the company's growth and innovation. The early team's focus on innovation helped the company differentiate itself in the market.
The company expanded beyond its core sales offerings by introducing Service Cloud and Marketing Cloud. Acquisitions, such as Sendia in 2006, enhanced its mobile capabilities. Major capital raises, including its IPO in 2004, provided funding for expansion and product development. The company's early focus on customer needs and agile development helped it gain significant market share against established players. The Target Market of Salesforce has evolved over time.
Initial market reception was mixed, but early adopters quickly recognized the benefits of the cloud. The company emphasized its 'No Software' mantra and built a strong developer ecosystem. This ecosystem approach, exemplified by the AppExchange launched in 2006, became a significant growth driver.
By 2008, the company had achieved $1 billion in annual revenue, demonstrating the rapid validation of its cloud-first strategy. This milestone underscored the company's successful transition from a startup to a major player in the tech industry. The IPO in 2004 was a critical step in securing the necessary funding for further expansion and product development.
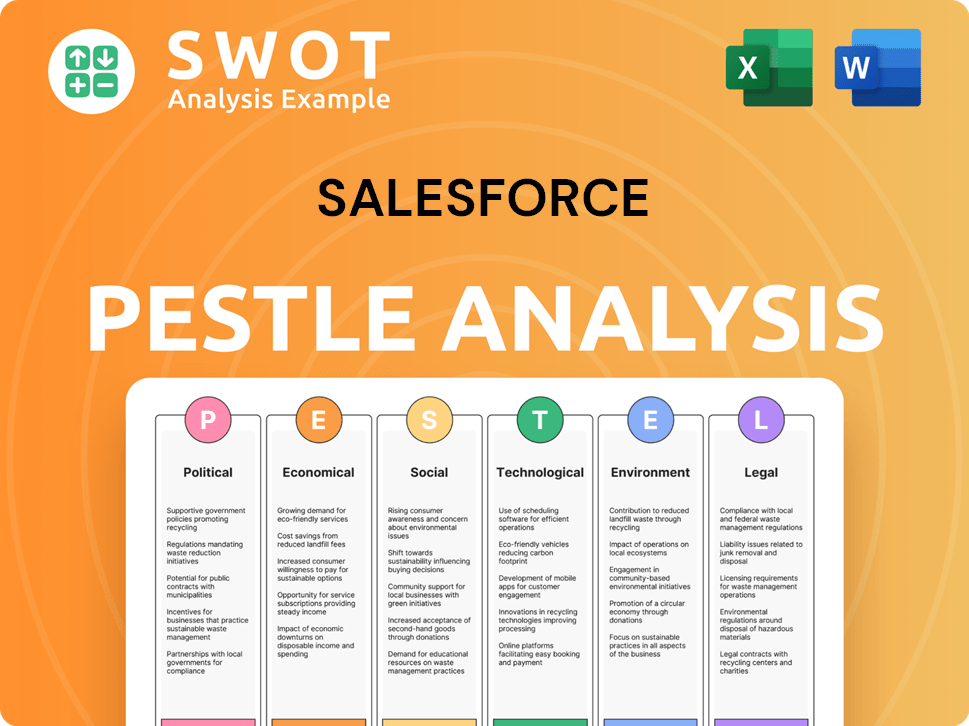
Salesforce PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
What are the key Milestones in Salesforce history?
The Salesforce journey, a story of innovation and growth, began with a vision to revolutionize customer relationship management (CRM). Founded in 1999, the Salesforce company quickly became a pioneer in cloud computing, transforming how businesses manage their customer interactions. The Salesforce evolution is marked by strategic decisions and technological advancements that have shaped the CRM software landscape.
| Year | Milestone |
|---|---|
| 1999 | Salesforce is founded by Marc Benioff, Parker Harris, Dave Moellenhoff, and Frank Dominguez, launching its initial CRM software. |
| 2000 | Salesforce releases its first version of the CRM platform, introducing a new model of software delivery. |
| 2004 | Salesforce goes public, marking a significant step in its growth and expansion. |
| 2006 | The AppExchange is launched, creating a marketplace for third-party applications and expanding the Salesforce ecosystem. |
| 2018 | Salesforce acquires MuleSoft for $6.5 billion, enhancing its integration capabilities. |
| 2019 | Salesforce acquires Tableau for $15.7 billion, strengthening its data analytics offerings. |
| 2021 | Salesforce acquires Slack for $27.7 billion, expanding its collaboration tools. |
Salesforce has consistently introduced industry-first innovations. These include its multi-tenant architecture, allowing all customers to share the same infrastructure, and its early focus on social and mobile CRM capabilities. These innovations have set new standards in the CRM software market, influencing the direction of the entire industry.
Salesforce pioneered multi-tenancy, where multiple customers share the same infrastructure, improving efficiency and reducing costs. This approach allowed for rapid updates and scalability, which was crucial for its early success.
The launch of the AppExchange in 2006 transformed Salesforce into a platform. This marketplace allowed third-party developers to build and sell applications, expanding the functionality of the Salesforce platform.
Salesforce integrated social media features into its CRM platform early on, enabling businesses to engage with customers on social networks. This was a forward-thinking move that anticipated the importance of social media in customer interactions.
Salesforce was among the first to offer robust mobile CRM capabilities, allowing sales teams to access and update customer data on the go. This enhanced productivity and responsiveness for field teams.
Salesforce introduced Einstein AI, integrating artificial intelligence into its CRM platform to provide predictive insights and automate tasks. This enhanced the capabilities of sales, service, and marketing teams.
Through strategic acquisitions like MuleSoft, Tableau, and Slack, Salesforce expanded its platform beyond core CRM. This allowed it to offer comprehensive solutions for integration, data analytics, and collaboration.
The Salesforce company has faced several challenges throughout its history. The dot-com bust in the early 2000s created a difficult environment, and competition from established companies like Microsoft and Oracle required continuous innovation. The company has also had to overcome the technical challenges of scaling its cloud infrastructure to meet rapid growth. For more details, read the Marketing Strategy of Salesforce.
The dot-com bust in the early 2000s created financial instability for many tech companies, including Salesforce. Navigating this period required careful financial management and strategic decision-making.
Competition from established software giants like Microsoft and Oracle, who developed their cloud offerings, put pressure on Salesforce. This required continuous innovation and differentiation to maintain market leadership.
While not always publicly highlighted, Salesforce has experienced product failures, requiring agile responses and rapid iterations. This is a common challenge in the fast-paced tech industry.
Scaling its cloud infrastructure to meet exponential growth has been a persistent technical challenge for Salesforce. This required significant investment in data centers and network infrastructure.
Salesforce, like all tech companies, is subject to market fluctuations and economic downturns. These factors can impact revenue growth and require strategic adjustments.
Integrating acquired companies like MuleSoft and Slack into the Salesforce platform presented challenges. This required careful planning and execution to ensure seamless functionality.
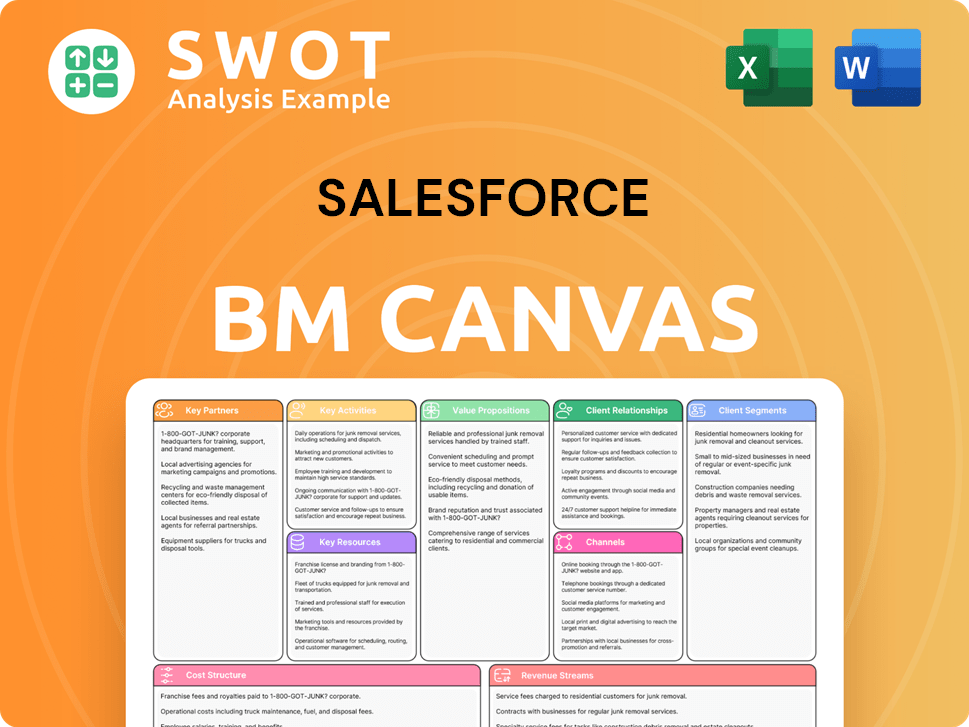
Salesforce Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
What is the Timeline of Key Events for Salesforce?
The Salesforce company journey, a story of innovation and expansion, began on March 8, 1999, when Marc Benioff, Parker Harris, Dave Moellenhoff, and Frank Dominguez founded the company. Since its inception, it has grown from a pioneering CRM software provider to a global leader in cloud computing, marked by strategic acquisitions and technological advancements. This evolution reflects its commitment to adapting and leading in the ever-changing tech landscape, with a strong focus on customer success and technological innovation.
| Year | Key Event |
|---|---|
| March 8, 1999 | Salesforce is founded by Marc Benioff, Parker Harris, Dave Moellenhoff, and Frank Dominguez. |
| February 2000 | Launches its first customer relationship management (CRM) product. |
| June 2004 | Salesforce goes public on the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) under the ticker symbol CRM. |
| September 2006 | Launches AppExchange, an online marketplace for third-party applications. |
| January 2009 | Introduces Force.com, a platform-as-a-service (PaaS) offering, allowing developers to build and deploy applications. |
| December 2012 | Achieves $3 billion in annual revenue, demonstrating significant growth. |
| June 2013 | Unveils Salesforce1 Platform, a mobile-first platform for building enterprise apps. |
| July 2018 | Acquires MuleSoft for $6.5 billion, enhancing its integration capabilities. |
| August 2019 | Acquires Tableau for $15.7 billion, significantly boosting its data analytics offerings. |
| December 2020 | Announces the acquisition of Slack for $27.7 billion, marking a major push into enterprise communication. |
| March 2022 | Reaches $26.49 billion in annual revenue for its fiscal year 2022. |
| February 2024 | Reports revenue of $34.86 billion for its fiscal year 2024, ending January 31, 2024. |
| May 2024 | Salesforce announces enhanced AI capabilities across its platform, including new Einstein Copilot actions and generative AI innovations for developers. |
| June 2024 | Salesforce continues to integrate AI into its core offerings, with a focus on delivering personalized customer experiences and boosting productivity. |
The future of Salesforce is heavily reliant on artificial intelligence. The company is actively integrating AI, particularly through its Einstein AI platform, to improve customer interactions and automate workflows. Recent announcements highlight new AI capabilities, including Einstein Copilot actions and generative AI innovations for developers, showing a strong commitment to AI-driven solutions.
The acquisitions of Slack and Tableau have significantly strengthened Salesforce's platform. These integrations enhance the company's capabilities in data analysis and enterprise communication. These tools are crucial for businesses to thrive in the current digital environment, making Salesforce a comprehensive platform for collaboration and data-driven decision-making.
Salesforce is expected to continue its strategy of targeted acquisitions to fill any gaps in its product portfolio. The company is also focused on areas such as hyper-personalization and seamless data flow. These strategic moves are designed to ensure that Salesforce remains at the forefront of technological advancements and market demands.
Analysts predict continued revenue growth for Salesforce, with a strong emphasis on profitability and operational efficiency. The company's leadership is committed to empowering businesses with trusted AI to enhance productivity and drive customer success. This commitment to innovation and customer satisfaction is expected to drive future growth.
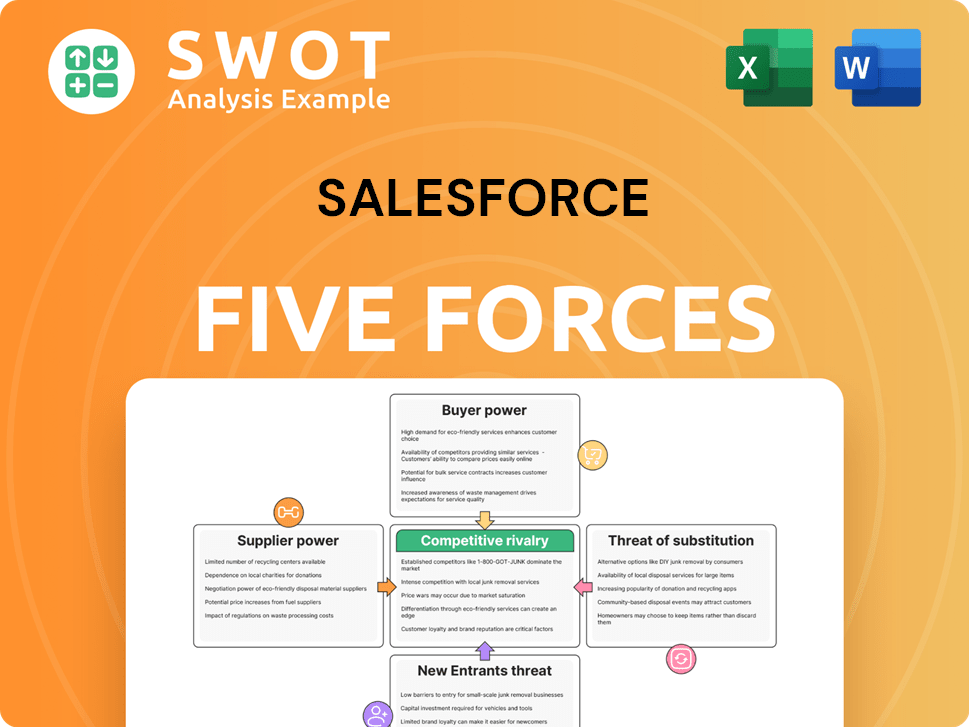
Salesforce Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What is Competitive Landscape of Salesforce Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of Salesforce Company?
- How Does Salesforce Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of Salesforce Company?
- What is Brief History of Salesforce Company?
- Who Owns Salesforce Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of Salesforce Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.