Telesat Bundle
How has the Telesat SWOT Analysis shaped the trajectory of the Telesat Company?
Embark on a journey through the Telesat SWOT Analysis, a story of innovation and global impact. From its humble beginnings in Canada to its current status as a leader in space technology, Telesat's evolution is a testament to its pioneering spirit. Discover how this Telesat SWOT Analysis has shaped the landscape of satellite communications.
Founded in 1969 as a Canadian satellite operator, the Telesat SWOT Analysis has played a pivotal role in global communication. The company's early satellite launches and its involvement in the Anik satellites were critical milestones. Today, Telesat's current satellite fleet and its plans for future innovations, including Telesat Lightspeed, continue to redefine the industry, making it a key player in the space technology sector.
What is the Telesat Founding Story?
The Telesat story began on September 1, 1969. It was established as a Crown corporation by an act of the Canadian Parliament. This move was driven by the need for reliable telecommunications across Canada, especially in remote areas.
The primary goal was to provide comprehensive telecommunications services. The absence of widespread, high-quality communication in remote and northern communities was the initial problem identified. The company's initial focus was on operating a domestic satellite communications system.
Telesat wasn't founded by individuals but was a government initiative. The aim was to address a critical national need for communication infrastructure. The government provided all the initial funding, highlighting its strategic importance as a national project.
Telesat was created to improve telecommunications across Canada, especially in remote areas.
- The company's first service was providing satellite capacity for television broadcasting and telephone services.
- A major early achievement was the launch of Anik A1 in 1972.
- Initial funding came entirely from the Canadian government.
- The cultural and economic context of the late 1960s in Canada emphasized national development and technological self-sufficiency.
The original business model centered on operating a domestic satellite communications system. Telesat's first service was offering satellite capacity for television broadcasting and telephone services. A significant milestone was the 1972 launch of Anik A1, the world's first domestic geostationary communications satellite. This launch cemented Canada's position as a leader in space technology. The establishment of Telesat reflected the Canadian emphasis on national development and technological self-sufficiency during the late 1960s.
In 2024, the satellite industry is highly competitive. To understand the competitive environment, you can explore the Competitors Landscape of Telesat. The company continues to play a crucial role in global communication.
Telesat SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
What Drove the Early Growth of Telesat?
The early growth of the Telesat company was significantly shaped by its pioneering work in satellite communications. Following the launch of Anik A1 in 1972, the company quickly expanded its services across Canada. These early launches were crucial for connecting remote areas and establishing a national broadcast network. This period laid the foundation for Telesat history as a key player in the space technology sector.
The Anik series was central to Telesat's early success. Anik A2 and A3 were launched in 1973 and 1975, respectively, increasing the company's capacity for television and telephone services. These satellites were essential for providing services to the Canadian Broadcasting Corporation (CBC) and various telephone companies, extending their reach across the country.
In the 1980s and 1990s, Telesat expanded beyond domestic services, entering new markets and offering data communications and internet services. While acquisitions were not a primary driver of growth, the company's expansion was fueled by technological advancements and the growing demand for satellite communications. The company also grew its team and established ground facilities across Canada.
A significant turning point occurred in 1998 when Telesat was privatized, transforming it from a government entity into a commercial enterprise. This shift allowed the company to pursue more aggressive commercial strategies and expand into international markets. Post-privatization, Telesat focused on broadening its global reach, providing services to international broadcasters and telecommunications companies.
Market reception during this period was generally positive, as satellite technology proved reliable for connectivity in many areas. The competitive landscape evolved with the emergence of other satellite operators, but Telesat maintained a strong position due to its early mover advantage and established infrastructure. The company's early successes solidified its position as a leading Canadian satellite operator.
Telesat PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
What are the key Milestones in Telesat history?
The Telesat company has a rich Telesat history, marked by numerous milestones that have shaped the landscape of satellite communications. From its inception, Telesat has been at the forefront of technological advancements in the space industry, significantly impacting global communication networks.
| Year | Milestone |
|---|---|
| 1969 | Telesat was established by an Act of Parliament, marking its official founding date. |
| 1972 | Launched Anik A1, making Canada the first country to have a domestic geostationary communications satellite system. |
| 2004 | Introduced high-throughput satellites (HTS) like Anik F2, significantly increasing broadband capacity. |
| 2023 | Secured a C$2.1 billion financing commitment from the Canadian government for the Lightspeed project. |
Telesat has consistently pushed the boundaries of space technology through various innovations. These advancements have not only improved communication capabilities but also expanded the reach of satellite services globally.
The Anik series of satellites has been a cornerstone of Telesat history, continuously evolving to meet the growing demands for communication services. Each generation of Anik satellites brought advancements in capacity and coverage, solidifying Telesat's position as a leading Canadian satellite operator.
Telesat pioneered the use of HTS, significantly increasing broadband capacity. This innovation enabled more robust internet services, catering to the rising demand for high-speed data transmission across various sectors.
The development of Lightspeed, a LEO satellite constellation, represents a major strategic pivot. This project addresses the growing demand for low-latency, high-speed broadband, positioning Telesat to compete in the evolving satellite internet market.
Telesat has secured numerous patents related to satellite design and ground systems. These innovations have enhanced the efficiency and reliability of Telesat's satellite operations, contributing to its strong engineering capabilities.
Telesat has developed advanced communication protocols to optimize data transmission. These protocols have improved the efficiency of satellite communications, ensuring reliable connectivity for its global customer base.
Telesat has formed major partnerships with global telecommunications providers. These collaborations have extended its service reach worldwide, enhancing its ability to provide comprehensive communication solutions.
Despite its successes, Telesat has faced several challenges throughout its history. Market dynamics, technological advancements, and competitive pressures have required Telesat to continuously adapt and innovate.
Market downturns, such as the dot-com bust in the early 2000s, impacted demand for satellite capacity. These economic fluctuations required Telesat to adjust its strategies and adapt to changing market conditions.
Competitive threats from new satellite operators and the emergence of fiber optic networks required continuous innovation. Telesat has responded by diversifying its service offerings and embracing next-generation technologies to maintain its leadership position.
Technical challenges, including satellite anomalies, have required constant technological upgrades. Telesat has leveraged its extensive experience in satellite operations to overcome these hurdles and maintain service reliability.
The development of the Lightspeed project involves significant capital expenditure. Telesat has secured financing and strategic partnerships to support this ambitious project, ensuring its continued growth and innovation.
The Lightspeed project involves complex technological development. Telesat's strong engineering capabilities and strategic partnerships have enabled it to advance this project, positioning it at the forefront of space technology.
Securing launch capabilities is crucial for the success of the Lightspeed project. Telesat is working with various launch providers to ensure timely deployment of its LEO constellation, supporting its strategic goals.
For more insights into Telesat's strategic approach, you can explore the Growth Strategy of Telesat.
Telesat Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
What is the Timeline of Key Events for Telesat?
The Telesat company has a rich history, evolving from a Canadian Crown corporation to a global satellite communications provider. Over the decades, Telesat has played a significant role in advancing space technology and satellite communications. This evolution has been marked by significant milestones, from pioneering satellite launches to strategic expansions and innovations.
| Year | Key Event |
|---|---|
| 1969 | Telesat Canada was established as a Crown corporation, marking the beginning of its journey. |
| 1972 | Launch of Anik A1, the world's first domestic geostationary communications satellite, was a groundbreaking achievement. |
| 1973-1975 | Anik A2 and A3 were launched, increasing satellite capacity and expanding services. |
| 1980s | Telesat diversified its services beyond television and telephone, incorporating data communications. |
| 1998 | Telesat was privatized, transforming into a commercial enterprise. |
| 2004 | The launch of Anik F2, a high-throughput satellite (HTS), showcased technological advancement. |
| 2007 | The merger with Loral Skynet significantly expanded Telesat's global reach. |
| 2010s | Advanced geostationary satellites were developed and launched, with a focus on broadband and video services. |
| 2019 | The Telesat Lightspeed LEO constellation project was announced, signaling a new strategic direction. |
| 2023 | Securing C$2.1 billion financing from the Canadian government for Telesat Lightspeed was a major financial milestone. |
| 2024-2025 | Continued progress on manufacturing and deployment of Telesat Lightspeed, with initial launches anticipated. |
Telesat's future is largely defined by the Lightspeed LEO constellation. This project aims to deliver ultra-low latency, high-capacity broadband globally. The company plans to capture a substantial share of the growing demand for connectivity across various sectors, including underserved regions and enterprise markets. The total cost of the Lightspeed program is estimated to be approximately $5 billion USD.
Securing additional funding is a key strategic initiative. Telesat is finalizing manufacturing contracts with companies like MDA and Thales Alenia Space. In 2024, Telesat's capital expenditures reflect continued investment in the Lightspeed program. The company is also actively pursuing partnerships to integrate Lightspeed services into existing telecommunications networks.
Telesat aims to be a key player in the next generation of satellite broadband. The company is positioned to compete with other satellite operators in the industry. The success of Lightspeed is critical for Telesat's long-term growth and market share. The global satellite internet market is projected to reach $20.3 billion USD by 2027.
Telesat's focus is on delivering the promises of Lightspeed. The company's financial reports show continued investment. The strategic focus is on delivering on the promise of Lightspeed, which ties back to the founding vision of providing essential and advanced connectivity solutions, but now on a global, high-performance scale. The company's revenue for Q1 2024 was $159 million USD.
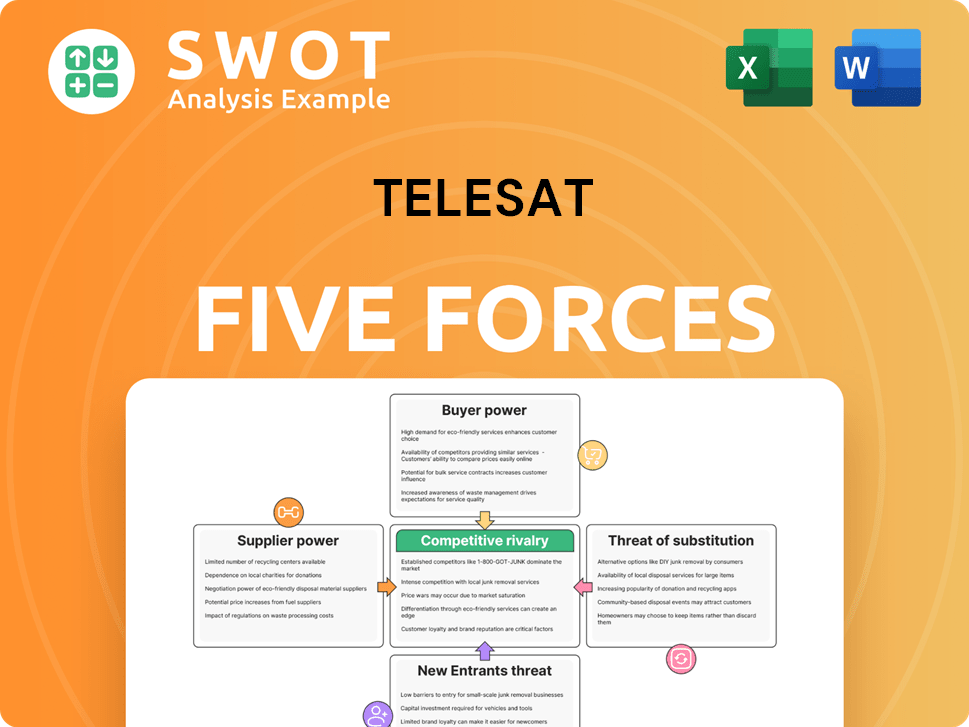
Telesat Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What is Competitive Landscape of Telesat Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of Telesat Company?
- How Does Telesat Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of Telesat Company?
- What is Brief History of Telesat Company?
- Who Owns Telesat Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of Telesat Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.