Taiwan Semiconductor Bundle
How Did Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company Conquer the Chip World?
Ever wondered how a company could become the world's largest semiconductor foundry, powering nearly every piece of modern technology? The story of Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company (TSMC) is one of innovation, strategic foresight, and relentless technological advancement. From its humble beginnings in Taiwan, TSMC revolutionized the Taiwan Semiconductor SWOT Analysis and the entire semiconductor industry.

This deep dive into TSMC history will explore the key milestones that shaped this chipmaker's journey, from its groundbreaking business model to its current dominance. We'll examine the early days of Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company, its technological leaps, and its profound impact on the global chip market. Discover how TSMC's commitment to innovation has transformed the landscape of semiconductor manufacturing.
What is the Taiwan Semiconductor Founding Story?
The story of Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company (TSMC) begins in 1987, a pivotal year for the global semiconductor industry. Founded by Dr. Morris Chang, often hailed as the 'father of semiconductors,' TSMC emerged as a groundbreaking force in chip manufacturing. This marked the beginning of a new era in the Marketing Strategy of Taiwan Semiconductor.
Dr. Chang's vision was to revolutionize the semiconductor industry by creating the world's first pure-play foundry. This innovative business model allowed companies to focus on chip design while TSMC handled the complex and capital-intensive manufacturing process. This unbundling of the semiconductor value chain would prove to be a game-changer.
The early days of TSMC were marked by strategic partnerships and significant investments. The Taiwanese government, through its National Development Fund (NDF), provided substantial financial backing, while the Dutch electronics giant Philips contributed both capital and crucial technology transfer. This combination of resources laid the foundation for TSMC's rapid growth and its eventual dominance in the Taiwan semiconductor industry.
TSMC was founded in 1987 by Dr. Morris Chang. His vision was to create a pure-play foundry, a business model dedicated solely to manufacturing chips for other companies.
- Dr. Morris Chang, born in 1931, spent 25 years at Texas Instruments.
- The Taiwanese government, through its National Development Fund (NDF), supplied a significant portion of the initial capital, holding a 48% stake.
- Philips invested approximately $58 million, acquiring just under a 28% stake and transferring its production technology.
- TSMC's first CEO was James E. Dykes, provided by Philips, before Morris Chang took over.
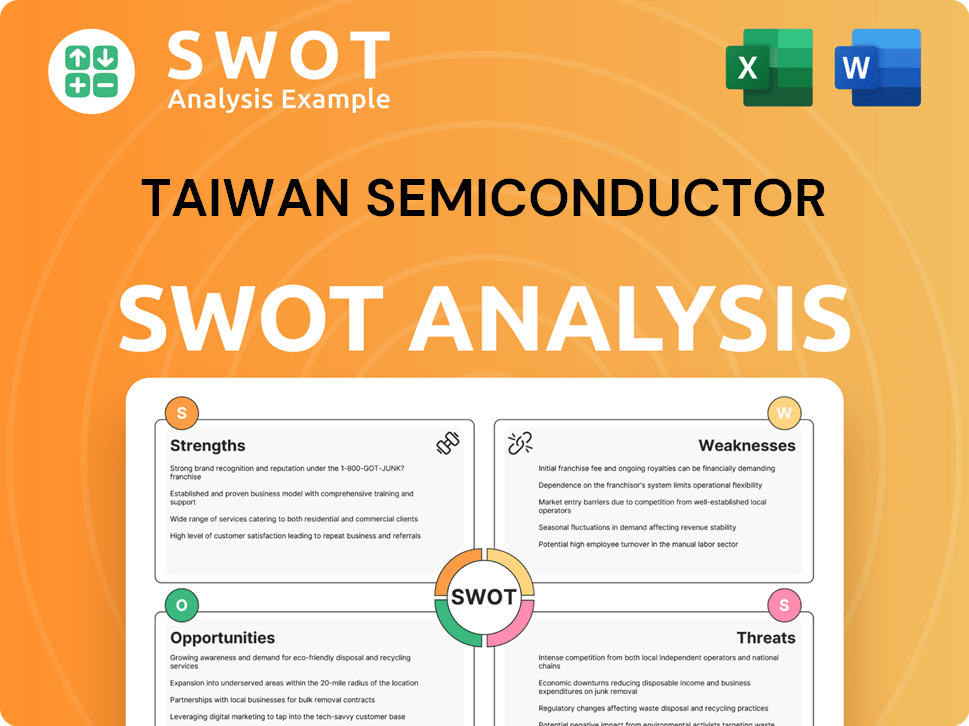
Taiwan Semiconductor SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
What Drove the Early Growth of Taiwan Semiconductor?
The early years of the Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company (TSMC) were crucial for establishing its pure-play foundry model. During this period, TSMC focused on proving its viability in a competitive market. This commitment to innovation and quality laid the groundwork for its future success. The company's initial focus was on serving Taiwanese semiconductor companies, but it quickly expanded its reach.
A significant milestone occurred in late 1987 when Intel became TSMC's first American customer. This pivotal moment pushed TSMC to establish rigorous production control systems. These systems included quality control, preventative maintenance, and statistical process control. TSMC's ability to meet Intel's stringent yield requirements was a key factor in securing this partnership. This early success helped to solidify TSMC's reputation in the Owners & Shareholders of Taiwan Semiconductor industry.
TSMC continued to expand its technological capabilities, introducing its first 0.5-micron process technology in 1991. The company achieved profitability in 1994 and unveiled its 0.35-micron process technology in the same year. By 1999, TSMC had become the world's largest dedicated semiconductor foundry. TSMC's growth was fueled by consistent investment in new silicon nodes and expansion of its manufacturing capacity.
TSMC prioritized the development of a large number of IP blocks available for each process node. This strategy attracted numerous IP vendors to commit to its roadmap, making TSMC a preferred foundry. TSMC has been listed on the Taiwan Stock Exchange since 1993. It became the first Taiwanese company to be listed on the New York Stock Exchange in 1997. From 1994, TSMC has shown a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 17.4 percent in revenue and 16.1 percent in earnings.
TSMC's early success significantly impacted the Taiwan semiconductor industry. The company's focus on quality and technological advancements helped to establish Taiwan as a major player in the global chip market. TSMC's ability to attract major clients and consistently deliver high-quality products solidified its position as a leader in semiconductor manufacturing. The company's growth has been a key driver of Taiwan's economic development.
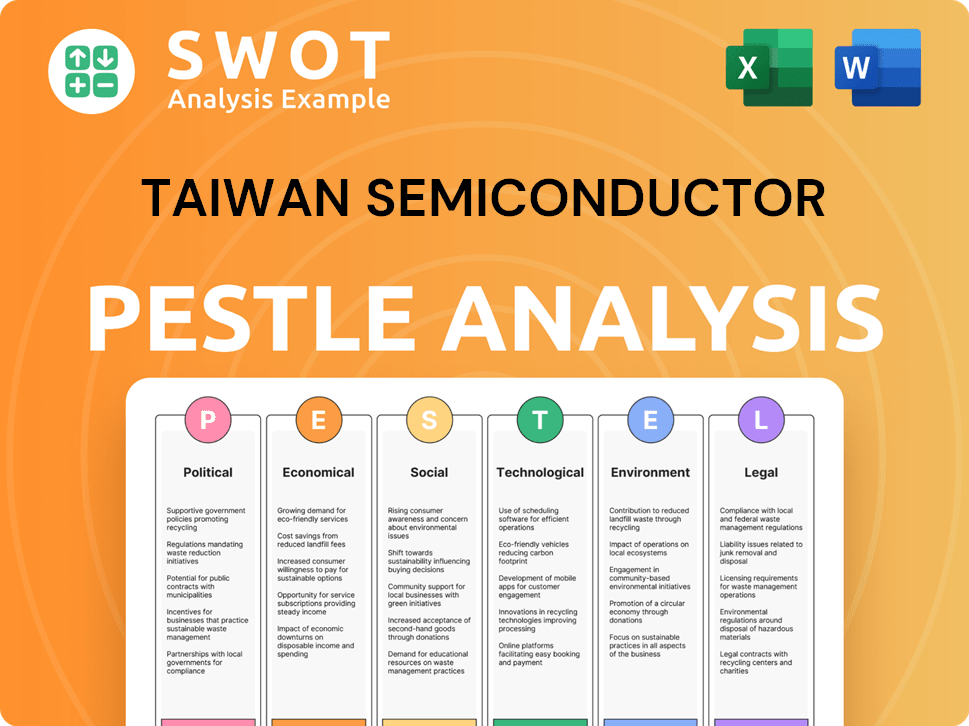
Taiwan Semiconductor PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
What are the key Milestones in Taiwan Semiconductor history?
The TSMC history is marked by significant achievements and strategic adaptations. From its inception, Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company (TSMC) has consistently pushed the boundaries of semiconductor manufacturing, establishing itself as a global leader in the industry. The company's journey reflects a blend of technological innovation, market responsiveness, and strategic foresight, solidifying its pivotal role in the tech sector.
| Year | Milestone |
|---|---|
| 1987 | Founded in Taiwan, marking the beginning of the pure-play foundry model. |
| 1991 | Introduced 0.5-micron technology, a significant advancement in chip manufacturing. |
| 1994 | Launched 0.35-micron technology, further enhancing its manufacturing capabilities. |
| 2009 | Navigated the global financial crisis by implementing workforce adjustments. |
| 2020-2023 | Managed the global semiconductor shortage, adjusting prices for mature processors. |
| 2024 | N3P (3-nanometer) process entered volume production in Q4. |
| 2025 | Began shipping 3nm chips for automotive battery applications. |
TSMC revolutionized the semiconductor manufacturing landscape with its pure-play foundry model, enabling fabless companies to thrive. The company has consistently invested in cutting-edge process technologies, such as the N3 (3-nanometer) process, to maintain its competitive edge in the Taiwan semiconductor industry.
TSMC pioneered the pure-play foundry model, allowing fabless companies to design chips without investing in manufacturing. This model significantly lowered the entry barrier for chip design and fostered widespread innovation across the tech industry.
TSMC consistently invested in advanced process technologies, including 3-nanometer (N3) and its variants, to meet the diverse needs of its customers. The company's focus on innovation has kept it at the forefront of the chipmaker industry.
TSMC expanded its global footprint with new fabs in Arizona, USA, and Kumamoto, Japan, to diversify its manufacturing base. These strategic moves have allowed TSMC to maintain leadership in dynamic market conditions.
TSMC's N3 (3-nanometer) process has been in high volume production for mobile and high-performance computing (HPC)/AI products with excellent yield. The company offers multiple 3nm variants, including N3E, N3P, and N3X, to cater to diverse customer needs.
TSMC has begun shipping 3nm chips for automotive battery applications in 2025. This expansion into the automotive sector shows TSMC's commitment to meeting the increasing demand for advanced semiconductors in various industries.
To overcome challenges and maintain its edge, TSMC has consistently invested heavily in research and development, allocating approximately 70% of its capital expenditure to advanced process technologies. This commitment ensures that TSMC remains at the forefront of innovation.
TSMC has faced challenges such as market downturns and geopolitical tensions, including the US-China trade conflicts. The company also navigated the global semiconductor shortage between 2020 and 2023, which led to price adjustments for its mature processors.
The global financial crisis in 2009 led to workforce adjustments, although the company quickly recovered as business conditions improved. TSMC has demonstrated resilience in managing economic fluctuations.
Geopolitical pressures, particularly from US-China trade tensions and shifts in global trade alignments, continue to pose challenges. TSMC must balance innovation with navigating these external factors.
TSMC managed the global semiconductor shortage from 2020 to 2023, which saw price increases for its mature processors by approximately 20%. This demonstrates TSMC's ability to adapt to market dynamics.
TSMC must balance innovation with navigating external factors to maintain its leadership. This involves strategic investments and continuous technological advancements.
TSMC has consistently invested heavily in research and development, allocating approximately 70% of its capital expenditure to advanced process technologies. This investment ensures the company's competitive edge.
The company is also expanding its global footprint with new fabs in Arizona, USA, and Kumamoto, Japan, diversifying its manufacturing base. These strategic moves, including significant capital investments and continuous technological advancements, have allowed TSMC to maintain its leadership and resilience in the face of dynamic market conditions.
For more details on TSMC's mission, vision, and core values, you can read this article.
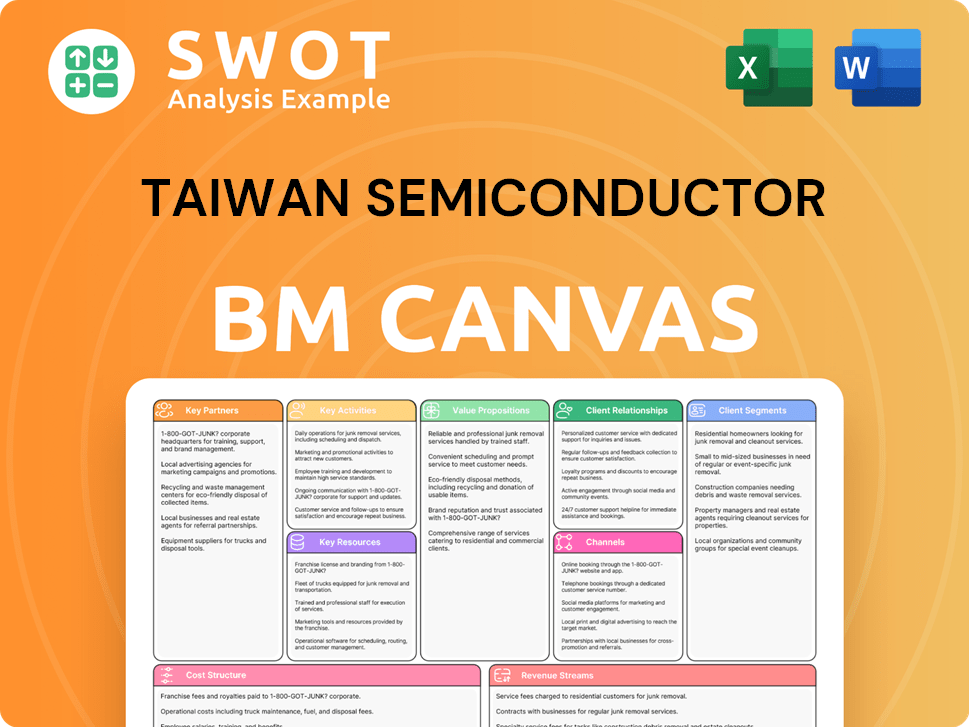
Taiwan Semiconductor Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
What is the Timeline of Key Events for Taiwan Semiconductor?
The story of Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company (TSMC) is one of remarkable growth and technological prowess. Founded in 1987 by Morris Chang, the company began as the world's first dedicated semiconductor foundry in Taiwan. Over the years, TSMC has consistently pushed the boundaries of semiconductor manufacturing, becoming a global leader in the industry. From early advancements in process technology to strategic expansions worldwide, TSMC's journey reflects its commitment to innovation and its impact on the global chip market. The company's evolution has been a key driver in the Competitors Landscape of Taiwan Semiconductor.
| Year | Key Event |
|---|---|
| 1987 | Founded by Morris Chang in Hsinchu Science Park, Taiwan, as the world's first dedicated semiconductor foundry. |
| 1991 | Introduced its first 0.5-micron process technology, marking an early technological milestone. |
| 1993 | Listed on the Taiwan Stock Exchange, signaling its growth and market presence. |
| 1994 | Achieved profitability and unveiled 0.35-micron process technology, demonstrating its success. |
| 1997 | Became the first Taiwanese company listed on the New York Stock Exchange, expanding its investor base. |
| 1999 | Ascended to become the world's largest dedicated semiconductor foundry, solidifying its industry leadership. |
| 2020 | Approved plans to build a $12 billion chip plant in Phoenix, Arizona, USA, expanding its global footprint. |
| 2022 | Launched Fab 20 in Hsinchu and Fab 22 in Kaohsiung, key 2nm production sites, enhancing its manufacturing capacity. |
| 2024 | Consolidated revenue reached NT$2,894.31 billion, a 33.9% increase over 2023, reflecting strong financial performance. |
| Q4 2024 | Held approximately 67.1% of the global semiconductor foundry market, highlighting its dominant market share. |
| Q1 2025 | Revenue reached NT$839.25 billion, a year-on-year increase of 41.6%, showing continued growth. |
| April 2025 | Monthly revenue was approximately NT$349.57 billion. |
TSMC is actively expanding its manufacturing capacity globally, with significant investments in the United States and Japan. These expansions are designed to meet the increasing demand for advanced semiconductors. The company is also investing heavily in research and development to maintain its technological edge. This includes exploring new materials and manufacturing processes.
TSMC is at the forefront of developing advanced chip manufacturing technologies. The company is focusing on 3nm and 2nm processes, which will enable smaller, faster, and more energy-efficient chips. Continued advancements in chip design and manufacturing are crucial for the company. TSMC is also exploring new packaging technologies to improve chip performance.
The demand for semiconductors continues to grow, driven by applications like AI, 5G, and electric vehicles. TSMC faces challenges such as geopolitical tensions and supply chain disruptions. The company is also working to address environmental concerns. TSMC's ability to navigate these challenges will be critical to its continued success.
TSMC's financial performance remains strong, with robust revenue growth and profitability. The company is expected to maintain its market leadership. The continued demand for advanced chips supports a positive financial outlook. The company's investments in innovation and expansion are expected to drive future growth.
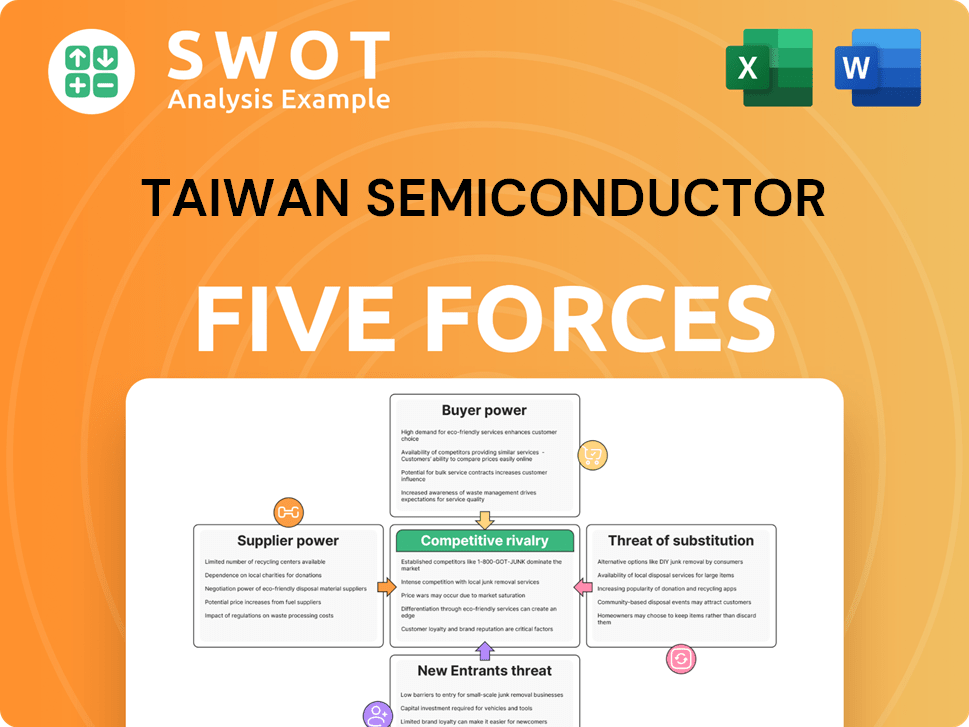
Taiwan Semiconductor Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What is Competitive Landscape of Taiwan Semiconductor Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of Taiwan Semiconductor Company?
- How Does Taiwan Semiconductor Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of Taiwan Semiconductor Company?
- What is Brief History of Taiwan Semiconductor Company?
- Who Owns Taiwan Semiconductor Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of Taiwan Semiconductor Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.