Taiwan Semiconductor Bundle
How Does Taiwan Semiconductor Actually Work?
Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company (TSMC) is the unseen force driving the technology we rely on daily, from our phones to advanced AI systems. Its massive scale and technological leadership are evident in its record-breaking financial performance, solidifying its status as the world's largest dedicated independent semiconductor foundry. TSMC's influence is far-reaching, enabling countless companies to bring their innovative chip designs to life.

This deep dive into Taiwan Semiconductor SWOT Analysis will explore the intricacies of TSMC's operations, revenue generation, and strategic advantages within the competitive semiconductor industry. We'll uncover how TSMC's foundry model and advanced chip fabrication processes contribute to its success, providing insights for investors, customers, and industry observers alike. Understanding TSMC's role is key to grasping the future of technology and the global economy, examining everything from its manufacturing facilities to its relationship with key partners like Apple and its impact on the global supply chain.
What Are the Key Operations Driving Taiwan Semiconductor’s Success?
The core operation of Taiwan Semiconductor (TSMC) centers on its pure-play foundry model. This means TSMC exclusively manufactures integrated circuits based on designs provided by its clients. These clients include fabless semiconductor companies, integrated device manufacturers (IDMs), and system companies, forming a diverse customer base.
TSMC's value proposition lies in offering a wide range of advanced process technologies. These technologies span from mature nodes to cutting-edge advancements like 3nm and upcoming 2nm technologies. This broad spectrum supports various applications, including mobile devices, high-performance computing (HPC), automotive electronics, and the Internet of Things (IoT).
The operational process begins with receiving customer designs. These designs are then translated into silicon wafers through a complex, proprietary manufacturing process. This process involves photolithography, etching, deposition, and doping, all conducted in state-of-the-art fabrication facilities (fabs). TSMC's operational excellence is supported by its massive scale, enabling economies of scale, and continuous investment in research and development (R&D).
TSMC operates as a pure-play foundry, focusing solely on manufacturing chips designed by others. This model avoids competition with its customers. Its neutrality fosters trust and collaboration, allowing customers to leverage TSMC’s expertise.
TSMC offers a wide array of advanced process technologies, including 3nm and upcoming 2nm nodes. These advanced nodes provide significant competitive advantages. This enables faster time-to-market and access to power-efficient chips for customers.
TSMC's supply chain is globally managed, sourcing raw materials like silicon wafers from various suppliers. It utilizes advanced equipment from companies like ASML for EUV lithography. The company's robust intellectual property (IP) ecosystem and comprehensive design services enhance its value proposition.
TSMC invests heavily in research and development to push the boundaries of semiconductor technology. This commitment to innovation is critical for maintaining its technological leadership. Continuous investment in R&D is key to its long-term success.
TSMC's commitment to being a dedicated foundry sets it apart from competitors. This neutrality builds deep trust and collaboration, which allows customers to fully leverage TSMC’s manufacturing expertise. Furthermore, its continuous technological leadership, particularly in advanced nodes, provides a significant competitive edge. This translates into customer benefits such as faster time-to-market and reduced capital expenditure. Its robust intellectual property (IP) ecosystem and comprehensive design services further enhance its value proposition, enabling seamless integration from design to production. For example, in 2024, TSMC is expected to invest between $28 billion and $32 billion in capital expenditures, underscoring its commitment to expanding capacity and advancing technology. The company's revenue for 2024 is projected to reach approximately $70 billion, reflecting its strong market position and the increasing demand for advanced chips. The company's net income for 2024 is estimated to be around $30 billion, demonstrating its profitability and efficiency. The company's market capitalization as of late 2024 is around $700 billion, making it one of the most valuable companies in the world.
TSMC's operational model provides several key advantages, including technological leadership and economies of scale. This allows the company to maintain a competitive edge in the semiconductor industry. The company's focus on advanced nodes, such as 3nm and 2nm, enables it to meet the evolving needs of its customers.
- Technological Leadership: Continuous advancements in process technology, including 3nm and 2nm nodes.
- Economies of Scale: Massive production capacity leading to cost efficiencies.
- Neutrality: Focus on being a dedicated foundry, avoiding competition with customers.
- Customer Benefits: Faster time-to-market and access to advanced chips.
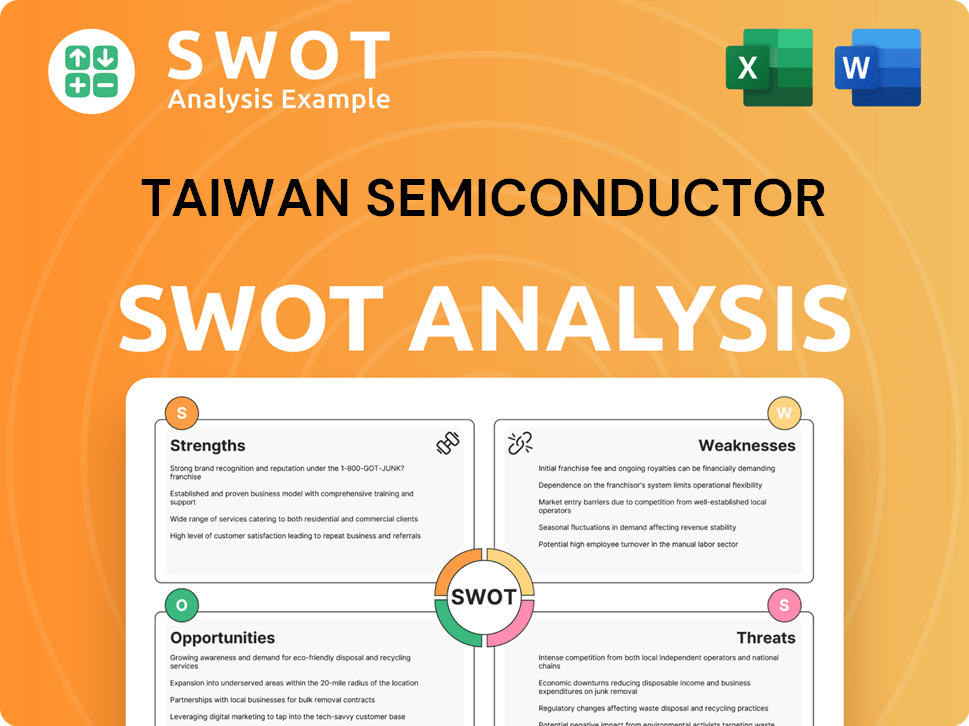
Taiwan Semiconductor SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
How Does Taiwan Semiconductor Make Money?
TSMC, a leading player in the semiconductor manufacturing sector, primarily generates revenue through the fabrication of integrated circuits for its diverse customer base. The company's financial performance is heavily influenced by its technological advancements and the demand for its chip fabrication services. The company's revenue streams are categorized by technology node and application, reflecting the varied needs of its clients.
In the first quarter of 2024, TSMC reported consolidated revenue of NT$592.64 billion, which is approximately US$18.87 billion. This figure underscores the significant scale of its operations and its crucial role in the global semiconductor industry. The company's ability to maintain its technological edge and meet the evolving demands of the market is critical to its financial success.
The company's revenue streams are primarily categorized by technology node and application. This reflects the diverse needs of its client base and the importance of advanced technologies in driving revenue growth. TSMC's business model is centered around providing cutting-edge chip fabrication services to a global clientele.
Advanced technologies (7-nanometer and more advanced) accounted for 65% of total wafer revenue in Q1 2024. This highlights the importance of leading-edge technologies.
3-nanometer technology contributed 9% to total wafer revenue in Q1 2024. This indicates growing adoption of the most advanced nodes.
5-nanometer technology contributed 37% to total wafer revenue in Q1 2024, showcasing its significant market presence.
7-nanometer technology contributed 19% to total wafer revenue in Q1 2024, demonstrating its continued relevance.
HPC was the largest revenue contributor in Q1 2024, accounting for 46% of net revenue. This reflects the growing demand for high-performance computing.
Smartphones followed, contributing 38% to net revenue in Q1 2024. This underscores the importance of mobile devices.
TSMC's monetization strategy is primarily based on a per-wafer pricing model. The price varies based on the complexity of the process technology, production volume, and customer requirements. The more advanced the technology node, the higher the price per wafer. The company also generates revenue from mask production, design services, and intellectual property (IP) licensing. For more insights, consider reading about the Marketing Strategy of Taiwan Semiconductor.
TSMC's revenue is driven by advanced technology nodes and diverse applications. The company's monetization strategy focuses on per-wafer pricing and value-added services.
- Advanced Technology Nodes: Higher prices for advanced nodes like 3nm and 5nm.
- Application-Based Revenue: HPC and smartphones are significant revenue contributors.
- Per-Wafer Pricing: Pricing varies based on technology and customer needs.
- Additional Revenue Streams: Mask production, design services, and IP licensing.
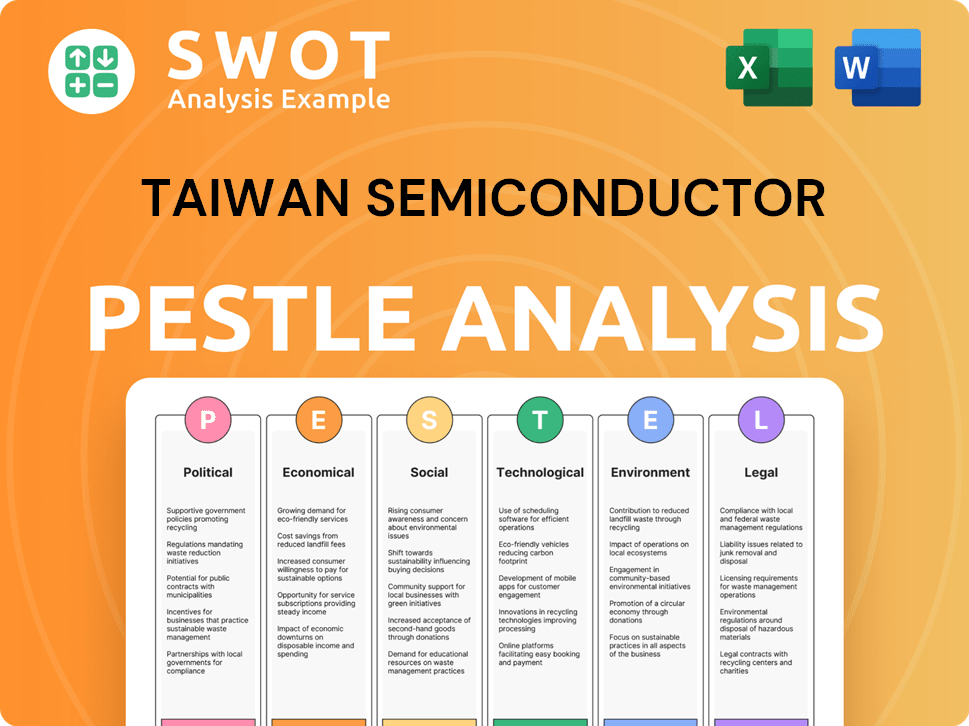
Taiwan Semiconductor PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
Which Strategic Decisions Have Shaped Taiwan Semiconductor’s Business Model?
The journey of Taiwan Semiconductor (TSMC) is marked by significant milestones and strategic shifts that have solidified its leadership in the semiconductor industry. A key decision was the early adoption of the pure-play foundry model in 1987, which allowed TSMC to focus solely on manufacturing, avoiding competition with its customers. This model was revolutionary, enabling the growth of fabless semiconductor companies. More recently, TSMC has achieved a critical milestone with the rapid ramp-up and mass production of its 3-nanometer process technology, which began volume production in late 2022 and has become a significant revenue generator.
The ongoing development of 2-nanometer technology, expected to enter mass production in 2025, is another crucial strategic move to maintain its technological lead. TSMC's strategic moves also include adapting to operational challenges, such as global supply chain disruptions and geopolitical tensions. In response, TSMC has diversified its manufacturing footprint with substantial investments in new fabs outside Taiwan, including Arizona, USA, and Kumamoto, Japan. The Arizona fab, with its first phase expected to begin production in the first half of 2025, and the second fab planned for 2028, are vital steps to enhance supply chain resilience and serve key international customers.
TSMC's competitive advantages are multifaceted, stemming from its technological leadership in advanced process nodes, massive R&D investments, and economies of scale. The company's pure-play foundry model fosters trust and deep partnerships, and it continues to adapt to new trends by heavily investing in technologies for artificial intelligence and high-performance computing. TSMC navigates competitive threats by pushing the boundaries of Moore's Law and expanding its global presence to mitigate geopolitical risks. To understand the competitive environment, it's helpful to examine the Competitors Landscape of Taiwan Semiconductor.
TSMC's success is rooted in its technological prowess and strategic foresight. The company's ability to consistently deliver smaller, more powerful, and energy-efficient chips is a direct result of its significant R&D investments. TSMC's advanced packaging technologies, such as Chip on Wafer on Substrate (CoWoS), further enhance its competitive edge by enabling high-performance computing solutions.
- 3-Nanometer Production: Volume production since late 2022, significantly contributing to revenue.
- 2-Nanometer Technology: Expected mass production in 2025, maintaining its technological lead.
- Global Expansion: Investments in fabs in Arizona and Japan to enhance supply chain resilience.
- R&D Investment: Continuous investment in advanced process nodes and packaging technologies.
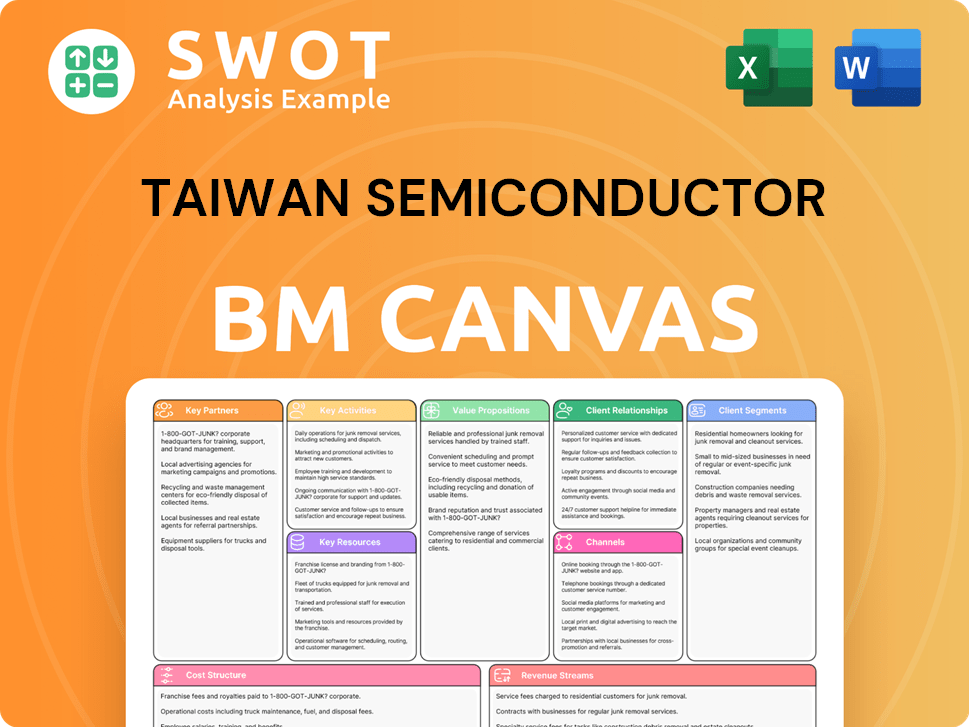
Taiwan Semiconductor Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
How Is Taiwan Semiconductor Positioning Itself for Continued Success?
As the world's largest dedicated independent semiconductor foundry, TSMC holds a commanding position in the semiconductor manufacturing industry. In the fourth quarter of 2023, the company controlled approximately 61% of the global foundry market, demonstrating its significant lead over competitors. This dominance is reinforced by strong customer loyalty, with leading tech companies depending on TSMC for their most advanced chip production.
TSMC's global reach is extensive, serving a diverse international customer base across various industries. Its technological superiority and reliable manufacturing processes have solidified its status as a critical partner for major technology companies. The company's ability to consistently deliver cutting-edge solutions has made it an indispensable part of the global technology ecosystem. For a deeper understanding of how TSMC achieves its market leadership, consider exploring the Growth Strategy of Taiwan Semiconductor.
Geopolitical tensions, particularly cross-strait relations, are a significant concern, given that a large portion of its manufacturing capacity is located in Taiwan. The company's expansion into the U.S. and Japan is an effort to diversify its manufacturing footprint. The increasing capital intensity of advanced process technology development also poses a risk due to colossal investments needed in R&D and new equipment.
TSMC is focused on sustaining its technological lead and expanding its global footprint. The company is investing heavily in the development and mass production of its 2-nanometer process technology, expected to be in volume production by 2025. TSMC plans to capitalize on the accelerating demand for AI-driven semiconductors, high-performance computing, and the broader digitalization trend.
Potential technological disruption from new materials or manufacturing processes could alter the competitive landscape. The cyclical nature of the semiconductor industry also presents a risk, as downturns in demand for electronics can directly impact wafer orders and revenue. TSMC's competitors include Samsung, Intel, and GlobalFoundries.
The company's expansion into Arizona and Japan underscores a commitment to supply chain resilience and serving key regional markets. Leadership consistently emphasizes innovation, customer collaboration, and operational excellence to navigate future challenges. TSMC is investing in advanced packaging technologies to meet the growing demand for high-performance computing.
TSMC's financial performance is closely tied to the overall health of the semiconductor industry. The company's revenue and profitability are influenced by factors such as global demand for electronic devices, technological advancements, and geopolitical events. In 2024, the semiconductor industry is projected to experience moderate growth, driven by demand in AI and high-performance computing.
- Market Share: TSMC holds approximately 61% of the global foundry market as of Q4 2023.
- Revenue: TSMC's revenue is significantly impacted by the demand for advanced chips used in smartphones, data centers, and automotive applications.
- Capital Expenditure: The company continues to invest heavily in R&D and new facilities to stay ahead of the competition.
- Customer Base: TSMC serves a diverse customer base, including Apple, Qualcomm, and AMD.
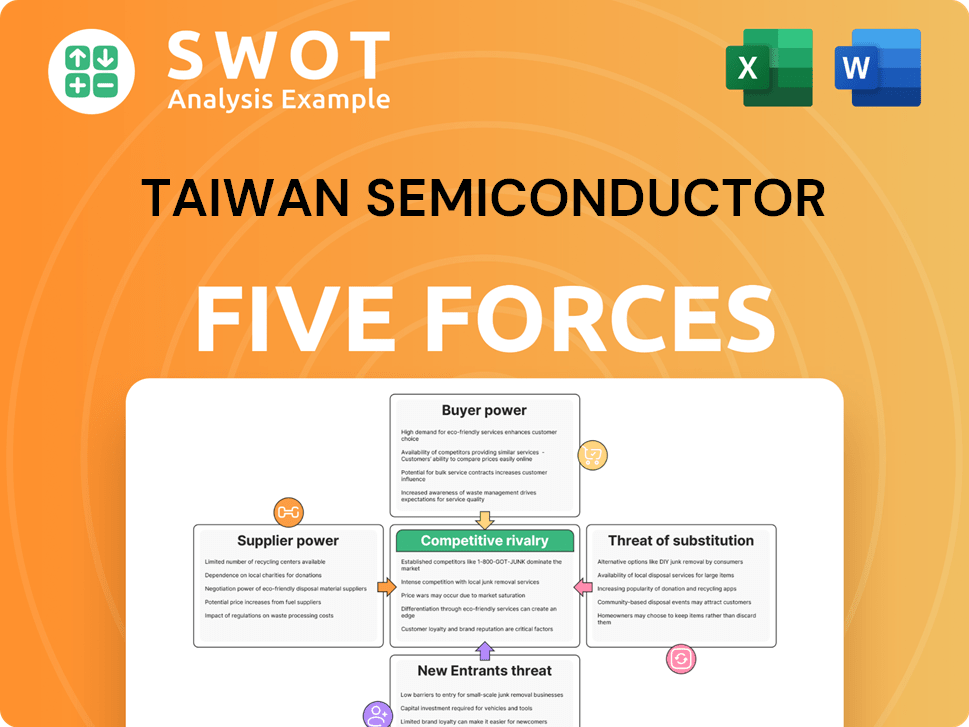
Taiwan Semiconductor Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What are Mission Vision & Core Values of Taiwan Semiconductor Company?
- What is Competitive Landscape of Taiwan Semiconductor Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of Taiwan Semiconductor Company?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of Taiwan Semiconductor Company?
- What is Brief History of Taiwan Semiconductor Company?
- Who Owns Taiwan Semiconductor Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of Taiwan Semiconductor Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.