GOL Bundle
How Did Gol Linhas Aéreas Revolutionize Air Travel in South America?
GOL Linhas Aéreas, a leading GOL SWOT Analysis, transformed air travel in South America by pioneering a low-cost model. Founded in 2001, the GOL Company history is a testament to its innovative approach and strategic vision. Its goal was to make air travel accessible to more people in Brazil, a country with vast distances and a growing middle class.
From its inception, GOL Airlines focused on competitive pricing and customer satisfaction, quickly gaining market share. Gol Linhas Aéreas expanded rapidly, becoming a major player in the region. This exploration will examine the GOL Company founding date and trajectory, from its early years to its current position, highlighting its impact on Brazilian aviation.
What is the GOL Founding Story?
The story of GOL Company, a prominent Brazilian airline, began on January 15, 2001. It was founded by the Constantino family, who brought extensive experience from their successful bus company, Cometa. Their vision was to introduce affordable air travel to Brazil, mirroring the low-cost carrier model seen in the United States.
The Constantino brothers, particularly Nenê Constantino, saw an opportunity to address the unmet demand for budget-friendly flights. This was in a market where existing airlines primarily served business travelers and higher-income individuals. GOL aimed to replicate the success of low-cost carriers like Southwest Airlines but tailored to the Brazilian market's specific needs.
GOL Airlines started with a clear goal: to make air travel accessible to more Brazilians. The initial strategy focused on efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
- The initial business model centered on a single aircraft type, the Boeing 737.
- High aircraft utilization and quick turnarounds were key to minimizing costs.
- Direct sales channels were used to streamline the booking process.
- The name 'GOL' was chosen for its simplicity and association with soccer, a beloved sport in Brazil.
The initial funding for GOL primarily came from the Constantino family's capital, accumulated through their bus operations. This self-funding approach allowed GOL to maintain control over its strategic direction. This financial foundation was crucial for navigating the challenges of establishing a new airline in a competitive environment. The family's expertise in transportation logistics and their entrepreneurial spirit were vital in overcoming hurdles, from regulatory approvals to infrastructure development.
The airline's early years were marked by strategic decisions aimed at growth and market penetration. GOL focused on domestic passenger air transportation, connecting major Brazilian cities. The company's expansion strategy involved increasing its fleet and route network to serve a wider range of destinations. The Marketing Strategy of GOL was also crucial in attracting customers and building brand recognition. By 2024, the GOL fleet included approximately 140 aircraft, serving a wide network of destinations.
Over time, GOL's financial performance has been influenced by various factors, including market conditions and operational efficiency. GOL's acquisition of Varig in 2007 significantly expanded its market presence and route network. Despite facing challenges, the company has remained a key player in the Brazilian aviation industry. As of late 2024, GOL's route network includes both domestic and international destinations, reflecting its growth and strategic adjustments over the years.
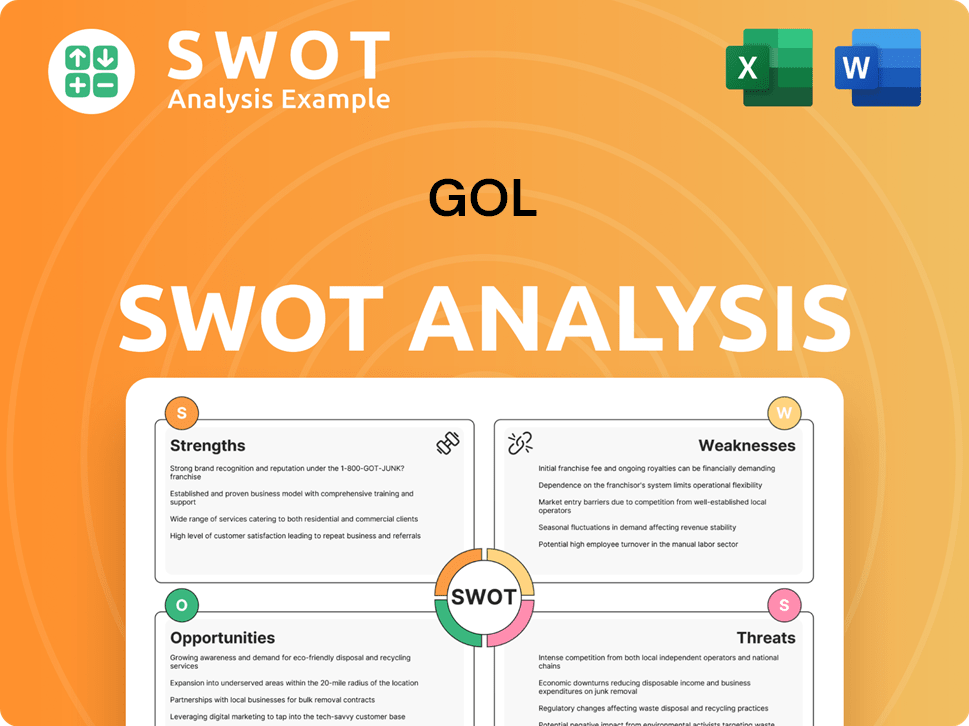
GOL SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
What Drove the Early Growth of GOL?
The early growth of Gol Linhas Aéreas, also known as GOL Airlines, was marked by rapid expansion and strategic market penetration. This approach leveraged its low-cost model to attract leisure and budget-conscious business travelers in Brazil. Following its launch, the Brazilian airline quickly expanded its domestic route network, adding new cities and increasing flight frequencies.
By 2004, GOL had captured a significant share of the Brazilian domestic market, challenging established carriers. The company's initial team expansion focused on operational efficiency, hiring experienced pilots, flight attendants, and ground staff while keeping administrative overhead lean. GOL's success can be seen as part of a broader trend in the aviation industry, with low-cost carriers reshaping the competitive landscape.
A pivotal moment in GOL's early growth was its initial public offering (IPO) in June 2004, listed on the São Paulo Stock Exchange (Bovespa) and the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE). This capital raise provided substantial funds for further fleet expansion and technological investments, solidifying its financial position and enabling more aggressive growth strategies. The IPO allowed GOL to raise capital to fuel its expansion plans.
GOL's fleet primarily consisted of Boeing 737 aircraft, allowing for streamlined maintenance and pilot training, further contributing to cost efficiency. This focus on a single aircraft type helped reduce operational complexities and costs. This standardization is a common strategy among low-cost carriers to improve efficiency and reduce expenses.
In 2007, GOL acquired Varig, once Brazil's largest airline, a strategic move that significantly expanded GOL's international reach and slot portfolio, despite Varig's financial difficulties. This acquisition allowed GOL to absorb Varig's international routes, particularly to destinations in South America and the Caribbean, and gain valuable brand recognition. This expansion significantly increased GOL's market share and route network.
This period also saw GOL introduce innovations such as web check-in and e-tickets, enhancing customer convenience and further reducing operational costs. By the end of the decade, GOL had firmly established itself as one of the leading airlines in Brazil, continuously adapting its strategies to the evolving competitive landscape and market demand. For more insights into the competitive environment, consider reading about the Competitors Landscape of GOL.
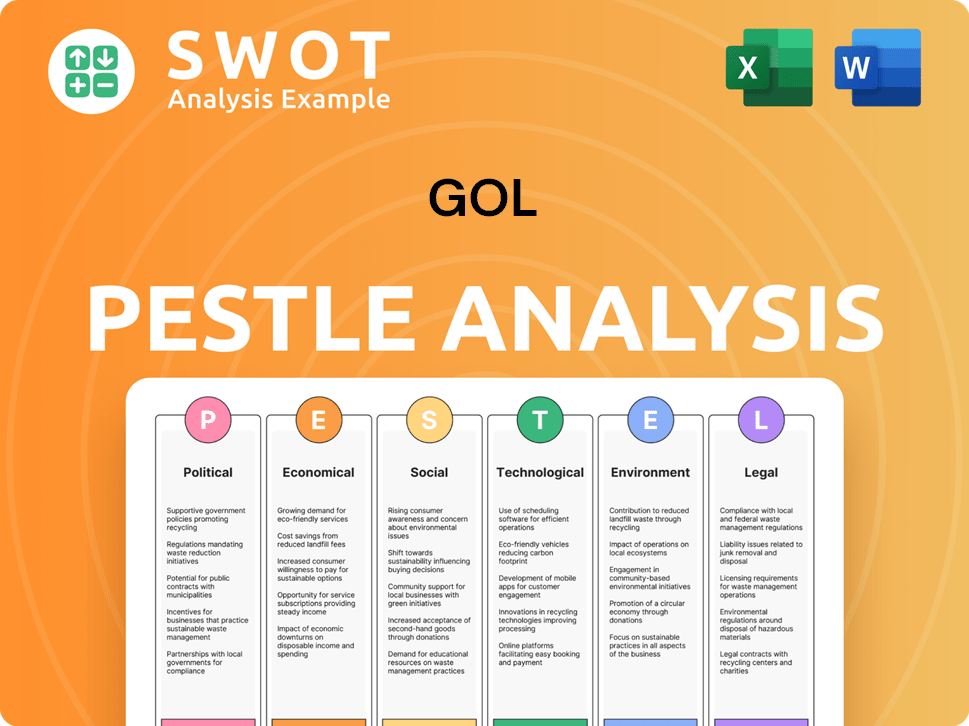
GOL PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
What are the key Milestones in GOL history?
The GOL Company history is marked by several key milestones, including its initial public offering and strategic acquisitions, which have shaped its growth and market position within the Brazilian airline industry. These events have been critical in defining Gol Linhas Aéreas' trajectory, influencing its operational strategies and financial outcomes over time.
| Year | Milestone |
|---|---|
| 2001 | GOL Airlines begins operations, starting its journey in the Brazilian aviation market. |
| 2004 | GOL successfully completes its Initial Public Offering (IPO), providing capital for expansion. |
| 2007 | GOL acquires Varig, expanding its network and market share. |
| 2020 | GOL faces significant challenges due to the COVID-19 pandemic, leading to operational adjustments. |
| 2023 | GOL initiates a financial restructuring process to address debt and operational challenges. |
GOL Airlines has been at the forefront of adopting digital solutions, enhancing both operational efficiency and the customer experience. Innovations such as online check-in and mobile services have streamlined processes and improved accessibility for passengers.
Introduction of online check-in services to streamline passenger processing and reduce airport congestion.
Development of mobile applications to provide passengers with convenient access to flight information, booking, and management tools.
Ongoing efforts to modernize the GOL fleet with fuel-efficient aircraft, contributing to cost savings and environmental sustainability.
Enhancement of the Smiles loyalty program to increase customer engagement and generate ancillary revenue through partnerships and rewards.
Expansion of cargo operations to diversify revenue streams and optimize aircraft utilization, especially during periods of reduced passenger demand.
Continuous investment in digital technologies to improve operational efficiency, enhance customer service, and support business growth.
GOL has faced considerable challenges, including economic volatility and intense competition within the Brazilian airline market. The airline has had to navigate fluctuating fuel prices and the impacts of global events like the COVID-19 pandemic. For more information on the airline's performance, you can read about the company's financial struggles in this article about GOL Company history.
The Brazilian economy's fluctuations have significantly impacted passenger demand and operational costs, requiring strategic financial planning.
Jet fuel price volatility has consistently posed a challenge, impacting operational expenses and profitability, necessitating hedging strategies.
Competition from other airlines has demanded continuous strategic adjustments and cost-cutting measures to maintain market share.
The 2008 financial crisis and the COVID-19 pandemic severely disrupted air travel, leading to revenue losses and operational adjustments.
High debt levels and financial restructuring processes have been necessary to address economic downturns and maintain financial stability.
Adaptation to changing market conditions, including fleet optimization and route network adjustments, to improve efficiency and profitability.
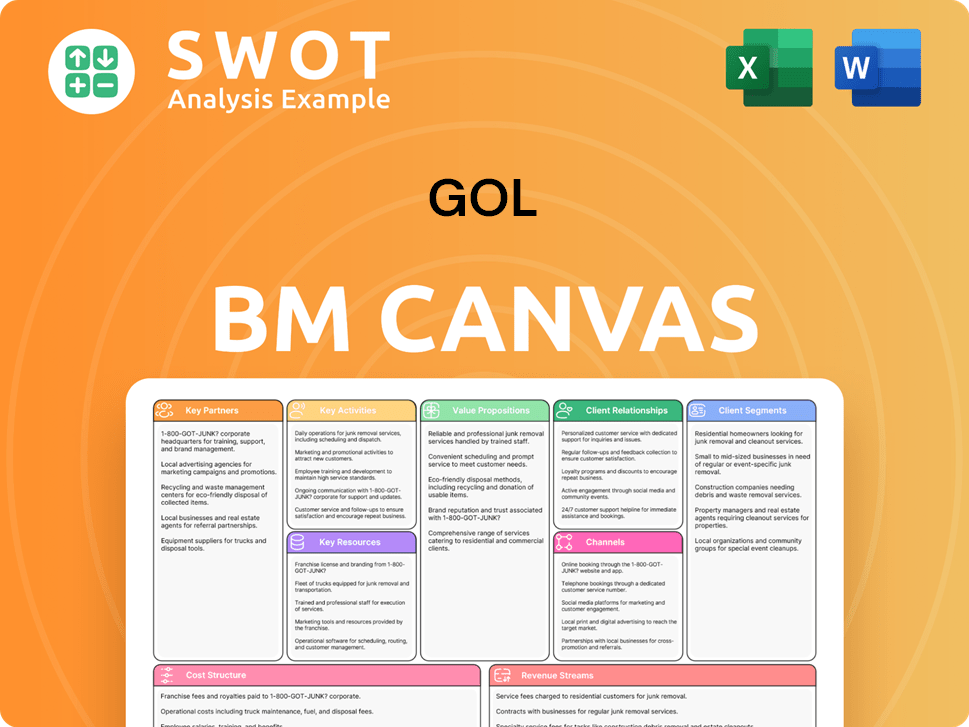
GOL Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
What is the Timeline of Key Events for GOL?
The GOL Company history is marked by strategic moves and adaptation. The Brazilian airline, Gol Linhas Aéreas, began operations on January 15, 2001, introducing the low-cost model to Brazil. The company expanded significantly through its IPO in June 2004 and the acquisition of Varig in March 2007. GOL Airlines has innovated with in-flight Wi-Fi in 2011 and partnerships like the one with Delta Air Lines in 2012. Financial restructuring and fleet adjustments have been key, including the phasing out of the Boeing 737-700 fleet in 2019. Recent challenges include the COVID-19 pandemic and the Chapter 11 bankruptcy filing in January 2024, with passenger traffic increasing in April 2024.
| Year | Key Event |
|---|---|
| January 15, 2001 | GOL Linhas Aéreas begins operations, introducing the low-cost model to Brazil. |
| June 2004 | GOL completes its Initial Public Offering (IPO) on Bovespa and NYSE, raising significant capital for expansion. |
| March 2007 | GOL acquires Varig, significantly expanding its international routes and market share. |
| 2011 | GOL becomes the first Brazilian airline to offer Wi-Fi on board its flights, enhancing passenger experience. |
| 2012 | GOL enters into a commercial cooperation agreement with Delta Air Lines, expanding its international network through codeshares. |
| 2015 | GOL undergoes a major restructuring, including fleet rationalization and network adjustments, to improve profitability amidst economic downturns. |
| 2019 | GOL phases out its Boeing 737-700 fleet, standardizing its operations around the more efficient Boeing 737-800 and MAX models. |
| 2020-2021 | GOL faces significant challenges due to the COVID-19 pandemic, implementing stringent cost-cutting measures and adapting its operations. |
| January 2024 | GOL files for Chapter 11 bankruptcy protection in the U.S. to restructure its finances, aiming to optimize its capital structure and continue operations. |
| May 2024 | GOL's passenger traffic (RPK) increased by 13.5% in April 2024 compared to the previous year, while domestic passenger traffic grew by 12.3%. |
GOL's future hinges on its fleet modernization, especially with the fuel-efficient Boeing 737 MAX aircraft. This strategy aims to reduce operational costs and enhance environmental sustainability, aligning with global trends in the aviation industry.
Strengthening its domestic and regional network is a key focus for GOL, leveraging its strong brand presence within Brazil. This expansion strategy will likely include optimizing GOL destinations and route networks to meet evolving market demands.
The company's ongoing financial restructuring under Chapter 11 is crucial for optimizing its capital structure and ensuring long-term sustainability. This process is designed to position the airline for future growth.
Prioritizing operational efficiency and customer satisfaction will be central to GOL's strategy. The airline is aiming to capitalize on the recovery of the Brazilian and South American air travel markets.
GOL Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What is Competitive Landscape of GOL Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of GOL Company?
- How Does GOL Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of GOL Company?
- What is Brief History of GOL Company?
- Who Owns GOL Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of GOL Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.