Zomato Bundle
How Did Zomato Conquer the Food Tech World?
From a simple office project to a global food tech giant, the Zomato company story is a compelling example of digital disruption. Initially conceived to solve a basic need, Zomato rapidly evolved into a multifaceted online food platform, changing how we interact with restaurants. This journey showcases the power of innovation in the food delivery service industry and the strategic vision behind its success.
Founded in 2008 as Foodiebay in Gurgaon, India, Zomato's initial focus on digitizing restaurant menus quickly expanded. The company's early success stemmed from identifying a gap in the market and providing a convenient solution for diners. Today, Zomato's Zomato SWOT Analysis reveals the key factors behind its rise as a leading Indian startup in the online food platform space, offering a comprehensive suite of services.
What is the Zomato Founding Story?
The Zomato company, a prominent player in the online food platform and food delivery service sector, has an intriguing founding story. It began with a simple observation that blossomed into a global enterprise. This brief history of Zomato details its inception and early development.
Zomato's journey to success started on July 10, 2008. Deepinder Goyal and Pankaj Chaddah, both working at Bain & Company in New Delhi, are the founders. Their initial idea, which later evolved into Zomato, was initially called Foodiebay.
The inspiration for Zomato arose from the founders' colleagues' difficulty in finding restaurant menus online. The founders noticed their colleagues relied on paper menus in the office. This led to the creation of a digital platform for restaurant information.
The initial solution involved digitizing paper menus for internal use, which quickly gained popularity. Recognizing the broader potential, they launched it as a public platform.
- The original business model focused on providing scanned restaurant menus online.
- The first product was a digital directory of restaurant menus.
- The venture was bootstrapped, with Goyal and Chaddah self-funding the project.
- The founders personally collected and digitized menus, demonstrating a hands-on approach.
In 2010, the name changed from Foodiebay to Zomato to avoid confusion with eBay and to reflect a broader vision. This rebranding aimed for a more unique and memorable brand identity, moving beyond just food listings.
Zomato SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
What Drove the Early Growth of Zomato?
The early growth and expansion of the Zomato company, formerly known as Foodiebay, was marked by a strategic focus on building a comprehensive restaurant database and expanding its geographical reach. Initially concentrated in India, the online food platform quickly grew beyond Delhi NCR. This expansion was fueled by meticulous data collection and the introduction of mobile applications, which improved user engagement.
After rebranding to Zomato in 2010, the Indian startup expanded rapidly. Key cities included Mumbai, Bangalore, Chennai, and Kolkata. This involved curating detailed restaurant information, including menus and contact details. The platform's growth was significantly aided by user reviews and ratings.
A major milestone was the launch of mobile apps in 2011, which boosted user accessibility. This aligned with India's increasing smartphone penetration. Early customer acquisition relied heavily on word-of-mouth and the platform's utility.
Between 2011 and 2013, Zomato entered international markets, starting with Dubai, UAE. Launches followed in Sri Lanka, the UK, and South Africa. Funding from Info Edge India Ltd. supported expansion and product development.
Zomato began monetizing through advertising services for restaurants. The platform evolved from menu listings to include user-generated content. The competitive landscape was emerging, but Zomato's early mover advantage and data focus positioned it strongly.
Zomato PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
What are the key Milestones in Zomato history?
The Zomato company has experienced a dynamic journey marked by significant milestones, innovations, and challenges, shaping its evolution from a restaurant discovery platform to a leading player in the online food platform space.
| Year | Milestone |
|---|---|
| 2008 | Founded as Foodiebay, a restaurant directory service. |
| 2010 | Rebranded as Zomato and expanded services to multiple cities in India. |
| 2015 | Launched online food ordering and delivery services, transforming its business model. |
| 2017 | Introduced Zomato Gold, a subscription-based loyalty program. |
| 2019 | Launched Zomato Hyperpure, a B2B platform for supplying ingredients to restaurants. |
| 2021 | Successfully completed its Initial Public Offering (IPO). |
Zomato's innovations have been pivotal in its growth, particularly the launch of its online food delivery service in 2015, which enabled it to compete directly with emerging food delivery service startups. Other key initiatives, such as Zomato Gold and Zomato Hyperpure, demonstrated its strategy to diversify revenue streams and integrate deeper within the restaurant ecosystem.
This service transformed Zomato from a restaurant discovery platform to a full-fledged food tech company.
A subscription-based loyalty program offering dining benefits to attract and retain customers.
A B2B platform supplying ingredients to restaurants, expanding the company's reach within the food industry.
Despite its successes, Zomato has faced challenges such as intense competition, particularly from Swiggy, which led to marketing and discounting wars. The COVID-19 pandemic presented both opportunities and difficulties, as online food delivery demand increased, but the dine-out segment suffered, demanding rapid adaptation.
Competition with Swiggy has led to significant marketing and discounting pressures, affecting profitability.
The company faced operational hurdles and criticism related to its Zomato Gold program, necessitating model adjustments.
The pandemic increased online food delivery demand but severely impacted the dine-out segment, requiring quick adaptation.
Zomato Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
What is the Timeline of Key Events for Zomato?
The Zomato company has evolved significantly since its inception, marked by key milestones that have shaped its trajectory in the food and quick commerce industries. From its initial days as Foodiebay to its current status as a publicly listed entity, Zomato's journey reflects strategic expansions, acquisitions, and innovations aimed at capturing a larger share of the market.
| Year | Key Event |
|---|---|
| 2008 | Founded as Foodiebay by Deepinder Goyal and Pankaj Chaddah, marking the beginning of Zomato's journey. |
| 2010 | Rebranded to Zomato, signaling a shift in branding and focus. |
| 2011 | Launched mobile applications, enhancing user accessibility. |
| 2012 | Began international expansion, starting with Dubai, extending its reach beyond India. |
| 2015 | Launched online food ordering and delivery services, entering the core food delivery market. |
| 2017 | Introduced the Zomato Gold subscription program, aiming to boost customer loyalty. |
| 2018 | Acquired Runnr, a B2B logistics company, to bolster delivery capabilities. |
| 2019 | Launched Hyperpure, a B2B platform for restaurant supplies, diversifying its offerings. |
| 2020 | Acquired Uber Eats' India operations, consolidating its position in the market. |
| 2021 | Successfully went public with its IPO on Indian stock exchanges, a significant milestone. |
| 2022 | Acquired Blinkit (formerly Grofers), venturing into quick commerce. |
| 2024 | Announced plans to launch a new 'everyday' value meal offering, expanding service offerings. |
Zomato is focused on deepening its presence in food delivery and quick commerce. The company aims to expand Blinkit into more cities, leveraging its existing logistics network. Zomato is also exploring new avenues to enhance customer value and restaurant partnerships.
Industry trends, such as the increasing adoption of online food ordering and demand for rapid delivery, will significantly impact Zomato. Analysts predict continued growth in the Indian food tech market, with Zomato well-positioned to capitalize on this expansion through its dual focus.
Leadership is committed to improving unit economics, expanding service offerings, and leveraging technology to create a more seamless experience for users and restaurants. The long-term vision remains aligned with being the go-to platform for all food-related needs.
In Q4 FY24, Zomato reported a consolidated revenue of ₹3,562 crore, a 59% increase year-over-year. The company's adjusted EBITDA improved to ₹194 crore. Blinkit's revenue grew by 97% year-over-year, indicating strong momentum in quick commerce.
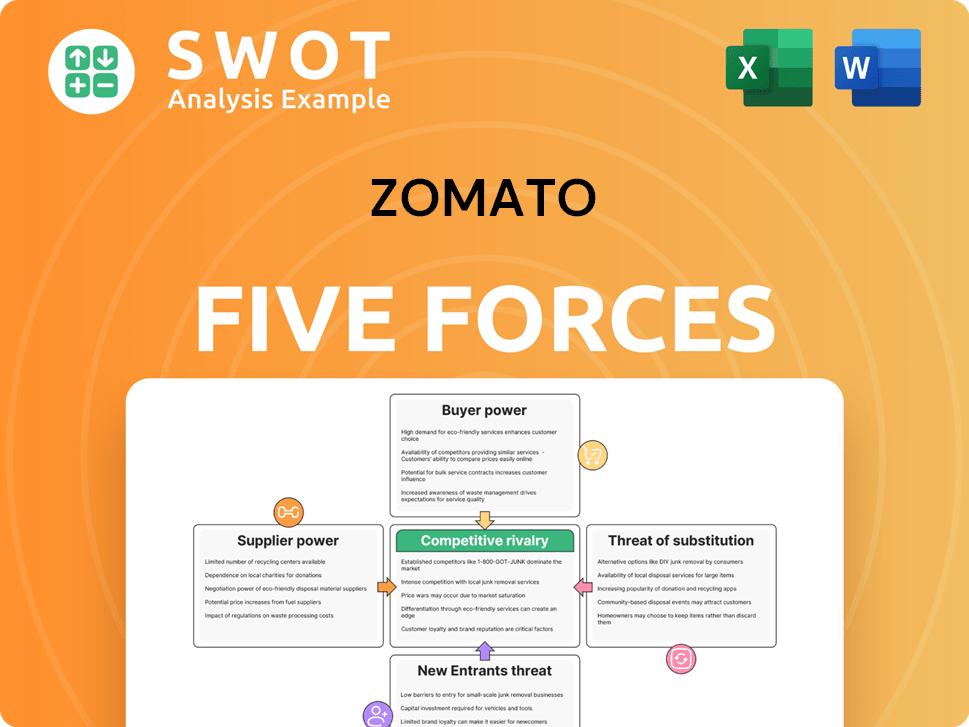
Zomato Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What is Competitive Landscape of Zomato Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of Zomato Company?
- How Does Zomato Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of Zomato Company?
- What is Brief History of Zomato Company?
- Who Owns Zomato Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of Zomato Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.