Global Brands Group Bundle
What Went Wrong at Global Brands Group?
Global Brands Group (GBG company) once dominated the fashion landscape, but its story took a dramatic turn. From managing a vast portfolio of brands to facing liquidation, understanding Global Brands Group SWOT Analysis is crucial. This analysis unveils the complexities of the apparel industry and the challenges of global brand management.
The rise and fall of the GBG company offers a compelling case study in the fashion industry. Exploring "How GBG works" reveals the intricate interplay of licensing, supply chain management, and brand partnerships that defined its operations. Examining its business model provides valuable insights into the factors that contributed to its success and eventual financial difficulties. This comprehensive overview delves into Global Brands Group's revenue streams, brand management strategies, and the impact of market dynamics on its performance.
What Are the Key Operations Driving Global Brands Group’s Success?
The core operations of the GBG company revolved around creating and delivering value through its diverse portfolio of apparel, footwear, and fashion accessories. Their business model focused on leveraging well-known licensed brands and developing private labels. This approach allowed them to offer varied product lines across kidswear, men's, and women's fashion, catering to a wide range of consumers.
The company's value proposition was centered on providing fashionable products across different market segments. This strategy enabled them to serve both value-conscious consumers and those seeking premium brand experiences. Operational processes included design and development, translating trends into marketable products, and global sourcing to optimize costs and production efficiency.
Their operational effectiveness was unique due to broad licensing agreements, providing access to numerous brands without direct ownership overhead. This agility, combined with a robust distribution network, translated into benefits for customers, such as access to a wide variety of fashionable products and consistent availability across retail touchpoints. To understand more about their journey, you can read a Brief History of Global Brands Group.
Key processes included design and development, global sourcing, and supply chain management. The supply chain encompassed raw material procurement to finished goods distribution, relying on manufacturing partners and a sophisticated logistics system for timely delivery.
- Brand management and licensing were central to their strategy, allowing them to offer diverse products.
- Supply chain management was critical, ensuring efficient production and distribution.
- Their ability to quickly adapt to fashion cycles and consumer demands was a key factor.
- They maintained a strong distribution network across department stores, specialty retailers, and e-commerce platforms.
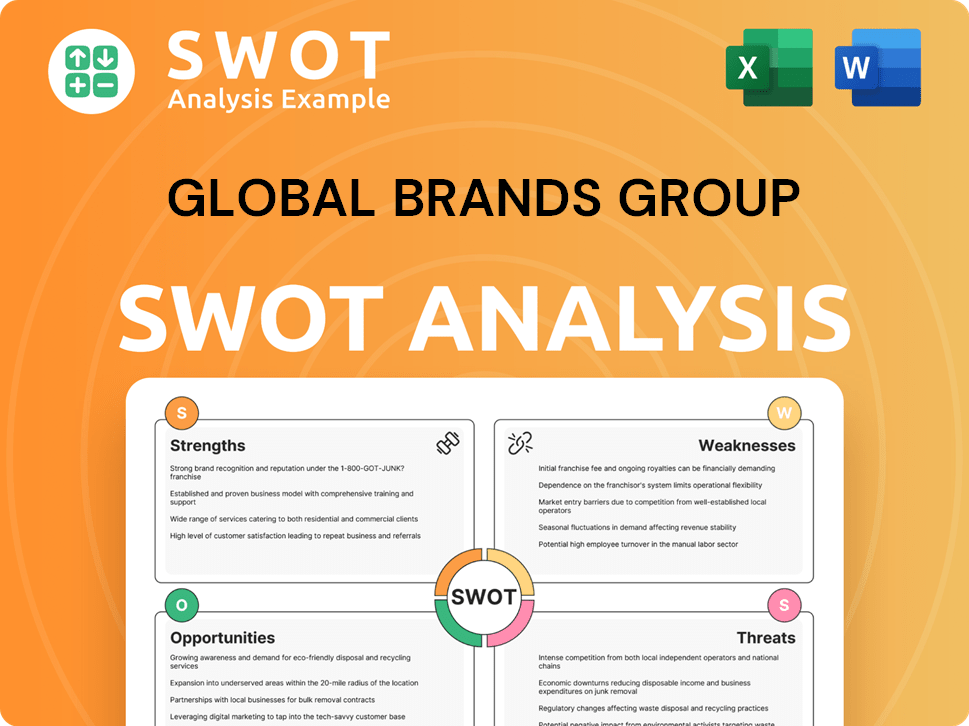
Global Brands Group SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
How Does Global Brands Group Make Money?
The core of how the GBG company operated revolved around generating revenue through the design, development, marketing, and sale of apparel, footwear, fashion accessories, and related products. Its business model was primarily driven by product sales across various segments, including kidswear, and men's and women's fashion. A key aspect of its strategy involved leveraging licensing agreements to use established brand names, which allowed it to tap into existing consumer recognition and loyalty.
A significant portion of the Global Brands Group's monetization strategy was centered on licensing. The company paid royalties to brand owners for the right to use their trademarks on its products. This approach enabled the company to capitalize on the brand recognition and consumer loyalty associated with these established names. Additionally, the company developed and sold private labels, providing an alternative revenue stream that offered greater control over design, production, and pricing. To understand more about their approach, you can read about the Growth Strategy of Global Brands Group.
While specific recent figures are unavailable due to the company's liquidation, product sales from both licensed brands and private labels historically constituted the majority of its income. The company's global distribution network also played a crucial role in maximizing sales volume across different markets. Any innovative strategies would have focused on optimizing inventory management, negotiating favorable licensing terms, and expanding into new product categories or geographical regions to drive sales growth, although financial challenges ultimately impacted their long-term sustainability.
The Global Brands Group employed a multi-faceted approach to generate revenue and maximize profitability. This included a strong focus on licensing and brand management, alongside other strategic initiatives.
- Licensing Agreements: Paying royalties to brand owners for the right to use their trademarks on products. This provided access to established brands and consumer loyalty.
- Product Sales: Generating revenue through the sale of apparel, footwear, fashion accessories, and related products across various segments.
- Private Labels: Developing and selling private label products, which offered greater control over design, production, and pricing, creating an alternative revenue stream.
- Global Distribution Network: Leveraging its global network to maximize sales volume across different markets, ensuring products reached a wide consumer base.
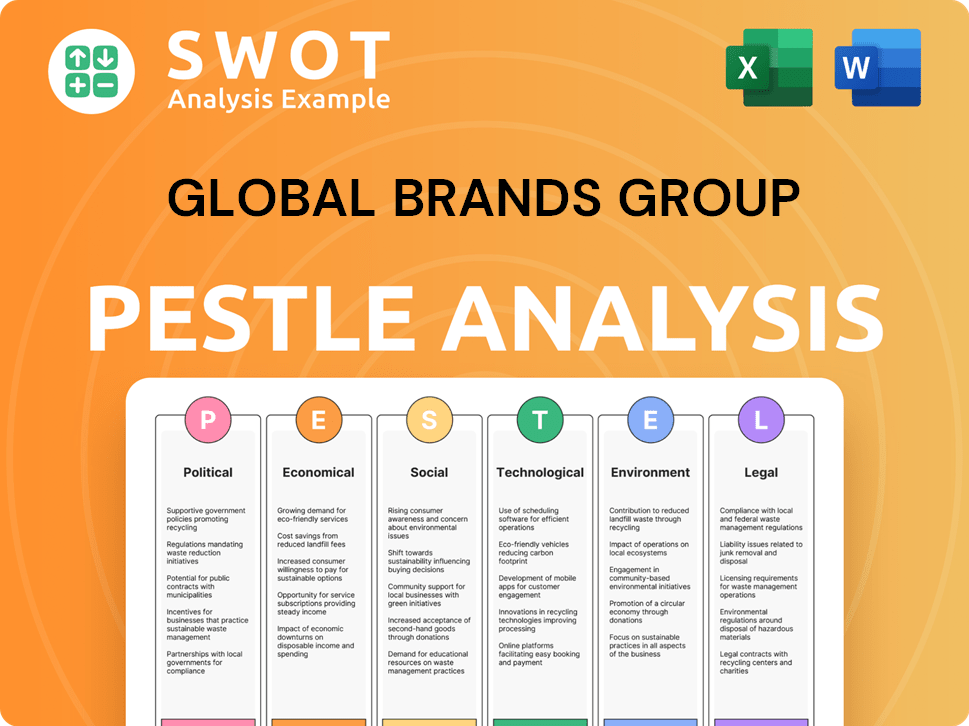
Global Brands Group PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
Which Strategic Decisions Have Shaped Global Brands Group’s Business Model?
The journey of Global Brands Group (GBG company) was marked by significant milestones, strategic shifts, and considerable operational hurdles. Historically, the company's growth was primarily fueled by aggressive expansion of its brand portfolio. This was achieved through numerous licensing agreements and strategic acquisitions within the apparel and accessories sectors. These moves allowed GBG to diversify its product offerings and broaden its consumer reach, establishing a strong presence across different market segments, from luxury to mass-market.
Strategic moves included a focus on brand management and licensing, which were core to How GBG works. This approach enabled the company to manage a diverse portfolio of brands without the direct costs of manufacturing and distribution. Acquisitions played a crucial role in expanding its brand portfolio. However, the company faced challenges related to supply chain disruptions and intense competition within the fashion industry.
GBG's competitive edge stemmed from its extensive network of licensed brands, offering a diverse product range. Its ability to manage complex global supply chains and distribution networks also provided a competitive advantage. Despite these strengths, the company struggled to adapt to rapidly changing consumer preferences and the financial pressures associated with managing a vast portfolio of licensed brands, ultimately leading to its liquidation. For more details on the company's ownership, you can read more about Owners & Shareholders of Global Brands Group.
Early growth was characterized by rapid expansion through licensing and acquisitions. GBG established a significant presence in the apparel and accessories market. The company's focus on brand management was a key strategic decision.
Strategic acquisitions and licensing agreements were central to GBG's business model. The company aimed to diversify its brand portfolio to cater to a wider consumer base. GBG managed complex global supply chains to support its extensive brand portfolio.
GBG's diverse brand portfolio offered a wide range of products. The company's ability to manage global supply chains was a key advantage. However, adapting to market changes proved challenging.
Supply chain disruptions, especially during economic downturns, significantly impacted operations. Intense competition within the fashion industry posed constant challenges. Adapting to changing consumer preferences was a major hurdle.
While specific recent financial data leading up to its liquidation is not publicly available, GBG's historical performance reflected the challenges of managing a large brand portfolio. The company's success was heavily dependent on its ability to secure and maintain licensing agreements.
- The company's revenue streams were primarily derived from royalties and fees from its licensing agreements.
- GBG's financial health was closely tied to the performance of its licensed brands and the overall market conditions in the fashion industry.
- Supply chain management and operational efficiency were critical factors influencing profitability.
- The company faced increasing pressure to adapt to changing consumer behavior and the rise of e-commerce.
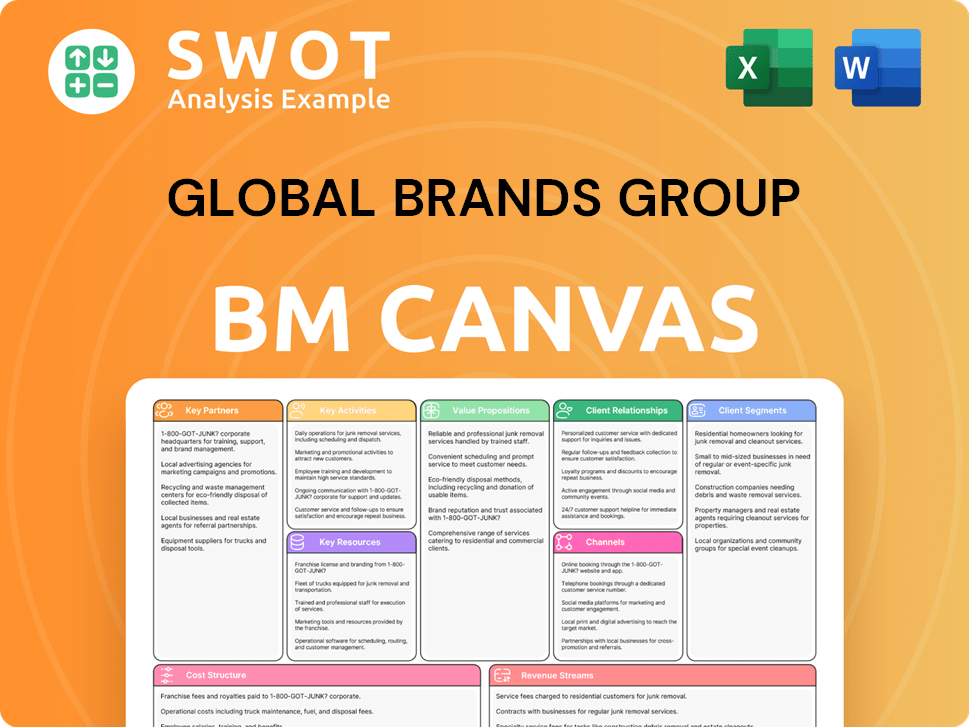
Global Brands Group Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
How Is Global Brands Group Positioning Itself for Continued Success?
Prior to its liquidation, the GBG company held a notable position in the global apparel and fashion accessories market. The company navigated a competitive environment alongside established brands and emerging direct-to-consumer businesses. Its market presence was built on a portfolio of licensed and private label brands, offering wide consumer reach. While customer loyalty was specific to individual brands, Global Brands Group had a substantial global footprint due to its extensive distribution networks.
The Global Brands Group business model involved managing a diverse array of brands, primarily through licensing agreements. This approach allowed the company to expand its portfolio without directly owning the manufacturing or retail operations. The company's revenue model depended on royalties and fees from these licensing agreements. The success of How GBG works was closely tied to its ability to secure and maintain these agreements, as well as effectively managing the brands within its portfolio.
The apparel and fashion accessories industry is highly competitive, with numerous established brands, fast-fashion retailers, and direct-to-consumer businesses. Global Brands Group aimed to differentiate itself through its brand portfolio and licensing model. The company's global reach was significant, but its success depended on its ability to adapt to changing consumer preferences and market dynamics.
Key risks included intense price competition, shifting consumer preferences, and the volatility of licensing agreements. Economic downturns and supply chain disruptions, especially during the COVID-19 pandemic, severely impacted operations. Inventory management and adapting to e-commerce trends also presented challenges. The Global Brands Group stock faced significant volatility due to these factors.
Given its liquidation status, the future of Global Brands Group as an operating entity is non-existent. Its assets and brands are being unwound. This marks the end of its operational presence in the industry. The company's trajectory highlights the risks of over-reliance on licensing and the importance of agile business strategies. You can read more about the Marketing Strategy of Global Brands Group.
The company faced financial difficulties, leading to its liquidation. Specific financial data, such as revenue figures, are difficult to ascertain post-liquidation, but the company's struggles are well-documented. The challenges were compounded by supply chain issues and changing consumer behavior. The company's financial performance was severely impacted by these factors.
Global Brands Group faced several critical challenges, including managing a complex supply chain and adapting to e-commerce. The company's licensing model required careful brand management and the ability to forecast market trends accurately. The licensing process itself was a key component of the company's operations.
- Supply Chain Management: The company had to navigate complex global supply chains.
- Brand Management: Effectively managing a diverse portfolio of brands.
- E-commerce Adaptation: Adapting to the shift towards online retail.
- Licensing Agreements: Securing and maintaining profitable licensing deals.
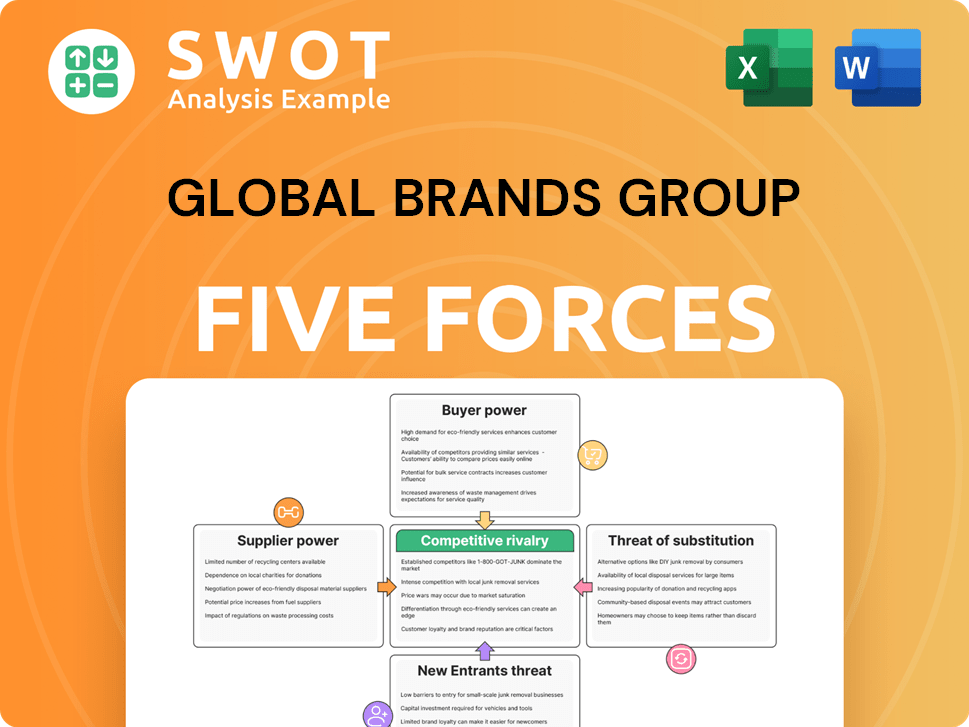
Global Brands Group Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What are Mission Vision & Core Values of Global Brands Group Company?
- What is Competitive Landscape of Global Brands Group Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of Global Brands Group Company?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of Global Brands Group Company?
- What is Brief History of Global Brands Group Company?
- Who Owns Global Brands Group Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of Global Brands Group Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.