Charles Schwab Bundle
How Does Charles Schwab Make Its Billions?
Charles Schwab, a financial services giant, has reshaped the investing landscape with its innovative approach. From commission-free trading to a vast array of financial products, Schwab has become a go-to platform for millions. But how does this financial titan actually operate and generate its massive revenue streams? Understanding the inner workings of Charles Schwab is key to making informed financial decisions.
This exploration will uncover the core strategies that have propelled Charles Schwab to the forefront of the Charles Schwab SWOT Analysis, examining its Schwab brokerage, Schwab accounts, and diverse financial services. Whether you're a seasoned investor or just starting out, gaining insights into Schwab's business model offers a valuable perspective on navigating the complexities of online trading and the broader investment world. We'll also touch on topics like Charles Schwab investment options and Charles Schwab retirement accounts.
What Are the Key Operations Driving Charles Schwab’s Success?
The core of Charles Schwab's operations centers on delivering value through an integrated model. This model combines wealth management, securities brokerage, banking, asset management, custody, and financial advisory services. It caters to two main customer segments: individual investors and independent registered investment advisors (RIAs).
Its primary offerings include brokerage accounts for stocks, options, and fixed income, along with mutual funds and ETFs. Schwab also provides banking products such as checking and savings accounts. Furthermore, it offers a range of advisory solutions, from automated investing (Schwab Intelligent Portfolios) to personalized financial planning with human advisors. This diverse approach allows it to serve a wide array of financial needs.
Schwab's operational processes are supported by a strong technological infrastructure. This infrastructure facilitates seamless digital experiences for clients. Clients can open accounts, execute trades, and access financial planning and customer support through its proprietary trading platforms, mobile applications, and online portals. The company also maintains physical branches across the United States, providing in-person support and advice. This blend of digital and physical services is a key aspect of the company's strategy, as discussed in Growth Strategy of Charles Schwab.
The company provides a wide array of services. These include brokerage accounts, banking products, and financial advisory services. It also offers asset management and custody solutions. Schwab's offerings are designed to meet the diverse needs of its clients.
Schwab primarily serves two key customer segments. These include individual investors and independent registered investment advisors (RIAs). The company tailors its services to meet the specific needs of each group. This dual approach allows for a broad market reach.
Schwab relies heavily on technology to deliver its services. Its proprietary trading platforms, mobile apps, and online portals are central to its operations. These tools provide clients with efficient ways to manage their investments. Technology is crucial for providing a seamless experience.
Schwab uses multiple distribution channels to reach its clients. These include direct-to-consumer digital channels and a network of independent RIAs. The RIAs custody client assets with Schwab. This multi-channel approach ensures broad market coverage.
Schwab's value proposition lies in its hybrid approach. It combines low-cost, high-volume digital brokerage services with comprehensive, personalized wealth management. This strategy differentiates it from competitors. The company aims to empower clients to achieve their financial goals.
- Competitive Pricing: Schwab offers competitive pricing on its services, including low trading fees.
- Broad Investment Choices: Clients have access to a wide range of investment options, including stocks, ETFs, and mutual funds.
- Advanced Trading Tools: The company provides advanced trading tools and platforms for both beginners and experienced traders.
- Accessible Financial Guidance: Schwab offers accessible financial guidance through various channels, including online resources and human advisors.
Charles Schwab SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format

How Does Charles Schwab Make Money?
The financial success of Charles Schwab hinges on a multifaceted revenue model designed to capture value from various financial services. This approach allows the company to generate income from multiple sources, providing resilience and stability in fluctuating market conditions. The primary revenue streams include interest income, asset management fees, and trading revenue, each contributing significantly to the company's overall financial performance.
Understanding the revenue streams of Charles Schwab is essential for grasping how it operates and generates profits. The company's ability to diversify its income sources and offer a wide array of financial services is a key factor in its success. This strategy not only strengthens its financial position but also enhances its appeal to a broad customer base, from individual investors to institutional clients.
Charles Schwab's primary revenue streams are diverse, reflecting its comprehensive financial services offerings. These include net interest revenue, asset management and administration fees, and trading revenue. Each stream contributes differently to the company's financial health, making it a well-rounded financial institution.
Net interest revenue is a significant part of Charles Schwab's earnings. It's the difference between what the company earns from client assets and what it pays on deposits. This revenue stream is often the largest contributor to the company's overall financial performance.
Asset management and administration fees are another substantial revenue source. These fees are generated from managing mutual funds, ETFs, and advisory solutions. They include fees from services like Schwab Intelligent Portfolios and 401(k) retirement plan services.
Trading revenue comes from options contract fees and other transaction-based charges. While a smaller percentage compared to interest and asset management fees, it still contributes to the overall revenue. Equity commissions are largely eliminated.
Charles Schwab also generates revenue from banking services, including lending activities. This diversification helps the company to maintain a steady income stream.
The company uses tiered pricing for certain advisory services, where fees vary based on asset levels. This strategy allows for customized pricing based on the client's needs.
Cross-selling opportunities are utilized across brokerage, banking, and advisory platforms. For instance, clients using Charles Schwab brokerage services might be encouraged to use Schwab Bank or Schwab Intelligent Portfolios.
In the first quarter of 2024, net interest revenue was a significant contributor to the company's overall financial performance. The company continuously evaluates and adjusts its revenue strategies in response to market conditions and competitive pressures. While specific regional or product line breakdowns of revenue mix are not always publicly detailed, the overall strategy emphasizes maximizing client relationships across the entire spectrum of financial needs. The company's innovative monetization strategies include tiered pricing for certain advisory services and cross-selling opportunities across its brokerage, banking, and advisory platforms.
Charles Schwab employs several strategies to maximize revenue and client engagement. These strategies are designed to ensure the company remains competitive and meets the evolving needs of its clients. The focus is on providing a comprehensive suite of financial services to a wide range of investors.
- Net Interest Margin: Managing the difference between interest earned on client assets and interest paid on deposits to maximize profitability.
- Fee-Based Advisory Services: Offering managed accounts and other advisory services that generate recurring revenue based on assets under management.
- Trading Commissions and Fees: Charging fees for options contracts and other transactions while eliminating equity commissions.
- Cross-Selling of Services: Encouraging clients to use multiple services, such as brokerage, banking, and advisory services, to increase revenue per client.
- Technological Innovation: Leveraging technology to provide efficient services, attract new clients, and reduce operational costs.
Charles Schwab PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable

Which Strategic Decisions Have Shaped Charles Schwab’s Business Model?
The journey of Charles Schwab has been marked by significant milestones and strategic moves that have shaped its operations and financial performance. A pivotal moment was its early adoption of discount brokerage, which challenged the traditional full-commission model. More recently, the elimination of commissions on online stock, ETF, and options trades in late 2019 was a strategic move that reshaped the brokerage industry.
The acquisition of TD Ameritrade, finalized in 2020, was another monumental strategic move, expanding Schwab's client base and advisor network. This integration presented operational challenges related to merging technology platforms and client accounts, which Schwab has been systematically addressing. The company has also navigated operational challenges such as fluctuating interest rate environments, impacting its net interest revenue, and increased regulatory scrutiny.
Schwab's competitive advantages are multifaceted, including strong brand recognition, significant economies of scale, and a robust technology platform. Schwab's comprehensive ecosystem, offering a wide array of products and services, also provides a significant competitive edge. The company continues to adapt to new trends, such as the increasing demand for digital wealth management solutions and personalized financial advice.
Early adoption of discount brokerage. Elimination of commissions on online stock, ETF, and options trades in late 2019. Acquisition of TD Ameritrade in 2020, expanding client base and advisor network.
Focus on low-cost brokerage services. Expansion through acquisitions. Investment in technology and digital capabilities. Diversification of revenue streams to mitigate interest rate impacts. Enhanced cybersecurity and compliance infrastructure.
Strong brand recognition built on trust and client focus. Significant economies of scale derived from vast client assets and operational efficiency. Robust technology platform supporting retail investors and independent financial advisors.
Fluctuating interest rate environments impacting net interest revenue. Increased regulatory scrutiny. Integration of acquired businesses, such as TD Ameritrade, which involves merging technology platforms and client accounts.
In 2024, the company reported strong financial results, with net revenues of approximately $18.8 billion. Client assets reached over $9 trillion. The company continues to hold a leading position in the brokerage industry, with a significant market share of retail clients and assets under management.
- The company's focus on low-cost services has attracted a large client base.
- Schwab's technology platform offers a wide range of services.
- The acquisition of TD Ameritrade has expanded its market reach.
- The company's commitment to innovation and client service has helped it maintain its competitive edge. For more details, you can explore the Competitors Landscape of Charles Schwab.
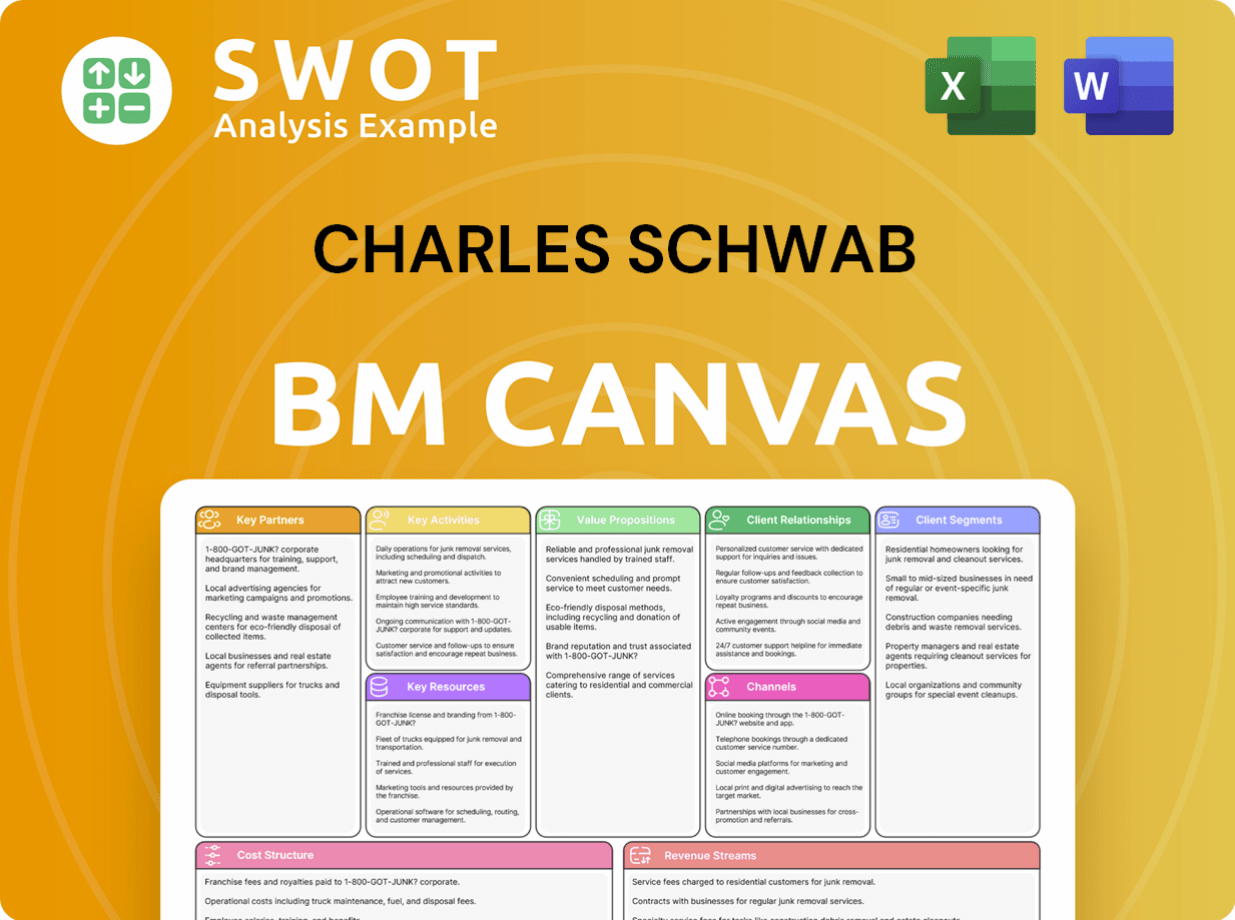
Charles Schwab Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
How Is Charles Schwab Positioning Itself for Continued Success?
Charles Schwab holds a prominent position within the financial services sector, particularly excelling in wealth management and brokerage services. It boasts a significant market share in both retail brokerage and as a custodian for independent registered investment advisors (RIAs). This strong standing is supported by a vast client base and substantial client assets, demonstrating considerable customer loyalty, often attributed to its client-focused approach and competitive pricing.
Despite its robust market position, Charles Schwab faces several risks. These include regulatory changes, the emergence of new competitors, technological disruptions, changing consumer preferences, and macroeconomic factors. These elements could impact its operations and profitability. The company's strategic initiatives focus on integrating the TD Ameritrade acquisition, investing in technology, and expanding advisory services.
Charles Schwab is a leading player in the financial services industry, especially in wealth management and brokerage. Its success is evident in its large client base and significant client assets. The company's client-centric approach and competitive pricing have helped it maintain strong customer loyalty.
Charles Schwab faces risks such as regulatory changes, new competitors, and technological disruptions. Changing consumer preferences and macroeconomic factors also pose challenges. These factors could affect the company's operations and profitability.
Charles Schwab plans to integrate TD Ameritrade, invest in technology, and expand its advisory services. The company aims to deepen client relationships and leverage its scale for competitive pricing. Its strategic focus on both retail and institutional clients positions it for future growth.
Key initiatives include integrating TD Ameritrade, enhancing digital platforms, and expanding advisory services. These strategies aim to improve client experience and meet evolving market demands. These efforts are designed to support long-term growth and client satisfaction.
Understanding Charles Schwab's position, risks, and outlook is crucial for investors. The company's strategic moves and market dynamics provide insights into its future. For a deeper understanding of who uses the services, consider the target market of Charles Schwab.
- Market Share: Charles Schwab holds a substantial market share in both retail brokerage and as a custodian for independent RIAs.
- Client Assets: The company manages trillions in client assets, demonstrating its significant influence.
- Strategic Focus: Key initiatives include integrating TD Ameritrade, investing in technology, and expanding advisory services.
- Future Growth: The company aims to deepen client relationships and leverage its scale for competitive pricing.
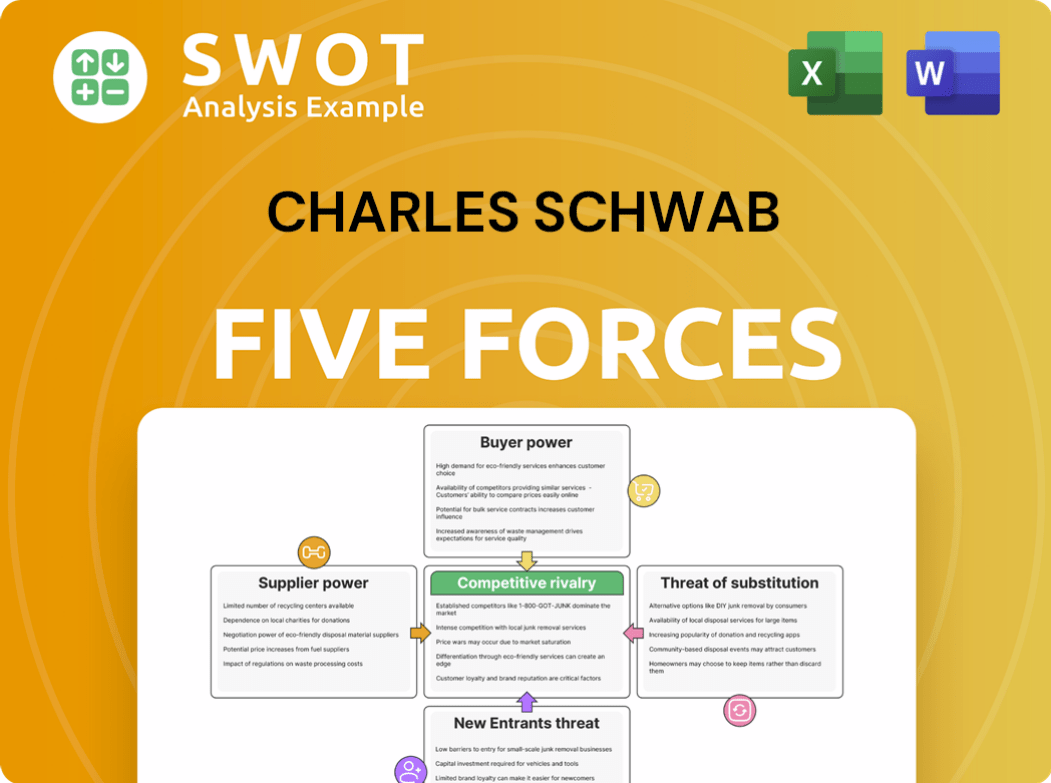
Charles Schwab Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What are Mission Vision & Core Values of Charles Schwab Company?
- What is Competitive Landscape of Charles Schwab Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of Charles Schwab Company?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of Charles Schwab Company?
- What is Brief History of Charles Schwab Company?
- Who Owns Charles Schwab Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of Charles Schwab Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.