Alphabet Bundle
Who Really Controls Alphabet?
In 2015, Google underwent a significant transformation, reorganizing under the parent company Alphabet Inc. This shift wasn't just a name change; it highlighted the crucial role of Alphabet SWOT Analysis in understanding a company's direction. Knowing who owns Alphabet Inc is key to deciphering its strategic moves and long-term vision. The ownership structure of this tech giant, from its founders to its public shareholders, is a fascinating case study in corporate control.
As the Google parent company, Alphabet's influence is undeniable, with a market capitalization exceeding $2 trillion as of early 2025. Understanding the dynamics of Alphabet company ownership, including the roles of Sundar Pichai and the board of directors, is essential for anyone invested in the future of technology. Delving into Alphabet Inc shareholders and their influence provides critical insights into this global powerhouse, its subsidiaries, and its enduring impact on the global technology landscape.
Who Founded Alphabet?
The story of Alphabet's ownership begins with Google Inc., established in September 1998. The founders, Larry Page and Sergey Brin, both Stanford University Ph.D. students, initially held significant equity in the company. Their vision shaped the company's direction from the start.
Early financial backing came from angel investors and venture capital firms. These investments provided crucial capital for Google's rapid expansion. The founders maintained substantial control, reflecting their desire to guide the company's strategic direction.
Early agreements likely included standard startup provisions like vesting schedules to ensure founder commitment. There were no widely reported initial ownership disputes, indicating a cohesive early leadership. Their continued control through special voting shares, even after the IPO, reflected their desire to maintain strategic direction against short-term market pressures.
The initial ownership of Alphabet, then Google, was primarily held by founders Larry Page and Sergey Brin.
Early investors, like Andy Bechtolsheim, provided crucial seed funding. Venture capital firms such as Sequoia Capital and Kleiner Perkins Caufield & Byers invested significantly in later rounds.
The founders' control was maintained through special voting shares, ensuring their long-term strategic vision for the company.
- In 1998, Andy Bechtolsheim provided a $100,000 check.
- In 1999, Sequoia Capital and Kleiner Perkins Caufield & Byers led a $25 million funding round.
- The founders' influence remained strong, even after the IPO.
- The early structure set the stage for Alphabet's future as a publicly traded company. For more information, read about the Target Market of Alphabet.
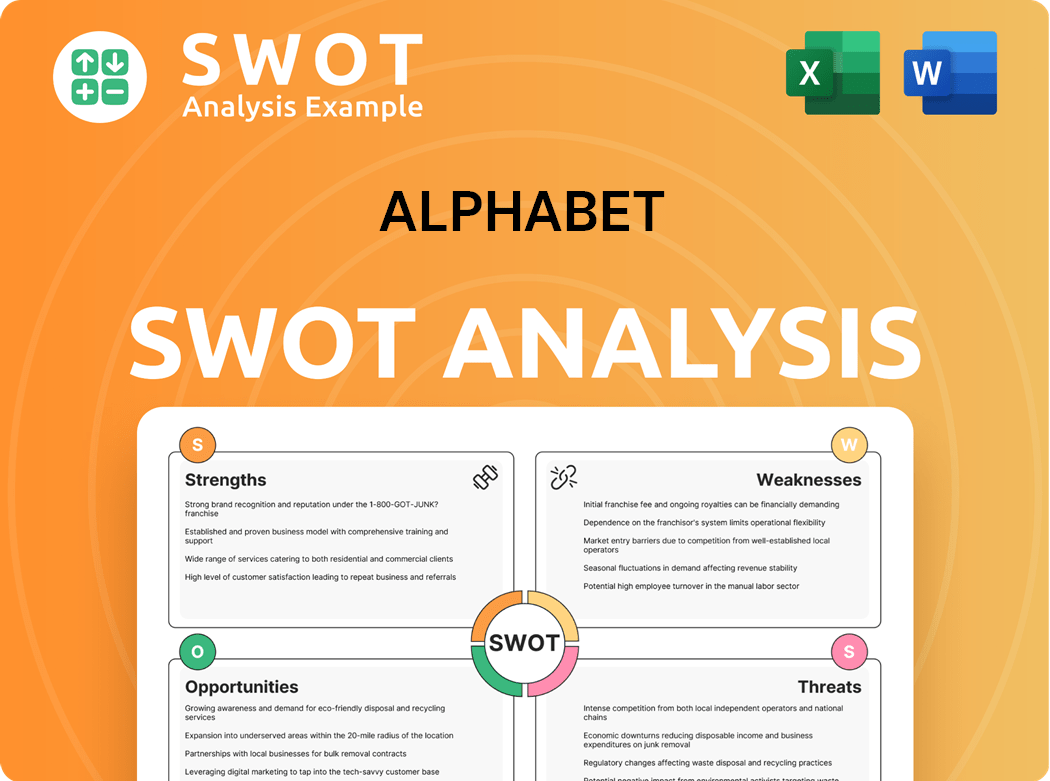
Alphabet SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
How Has Alphabet’s Ownership Changed Over Time?
The ownership structure of Alphabet has seen significant changes since its inception. The initial public offering (IPO) of Google in August 2004 was a key event, raising $1.67 billion and establishing an initial market capitalization exceeding $23 billion. The restructuring into Alphabet Inc. in 2015 was another pivotal moment, creating a holding company to encompass Google and its various ventures, although this didn't fundamentally alter the ultimate ownership.
The evolution of Alphabet's ownership reflects its growth and strategic shifts. Understanding who owns Alphabet Inc. is crucial for investors and anyone interested in the company's direction. The structure, including the dual-class share system, provides insights into the control dynamics and the influence of major shareholders on the company's long-term strategies. The Marketing Strategy of Alphabet has also been affected by these ownership dynamics.
| Key Event | Date | Impact on Ownership |
|---|---|---|
| Google IPO | August 2004 | Established initial public ownership and market capitalization. |
| Alphabet Inc. Restructuring | 2015 | Created a holding company structure, re-organized corporate entities. |
| Shareholder Meetings & Filings | Ongoing (Early 2025) | Regular updates on major stakeholders and voting power distribution. |
As of early 2025, the major shareholders of Alphabet Inc. include a mix of institutional investors, mutual funds, and the co-founders. The dual-class share structure is a critical aspect of Alphabet company ownership, with Class B shares held by the founders giving them significant voting power. Larry Page and Sergey Brin, through their Class B shares, control over 50% of the voting power, even though their economic ownership is around 11-12% each. Major institutional investors like Vanguard and BlackRock hold substantial portions of the Class A and Class C shares, primarily for index funds and managed portfolios.
Alphabet's ownership structure is complex, involving founders, institutional investors, and a dual-class share system. The founders retain significant control through their Class B shares, influencing long-term strategies. Knowing who owns Alphabet Inc. is essential for anyone interested in the company's direction.
- Dual-class shares give founders control.
- Institutional investors hold significant portions.
- Long-term strategic initiatives are prioritized.
- Understanding the ownership structure is key for investors.
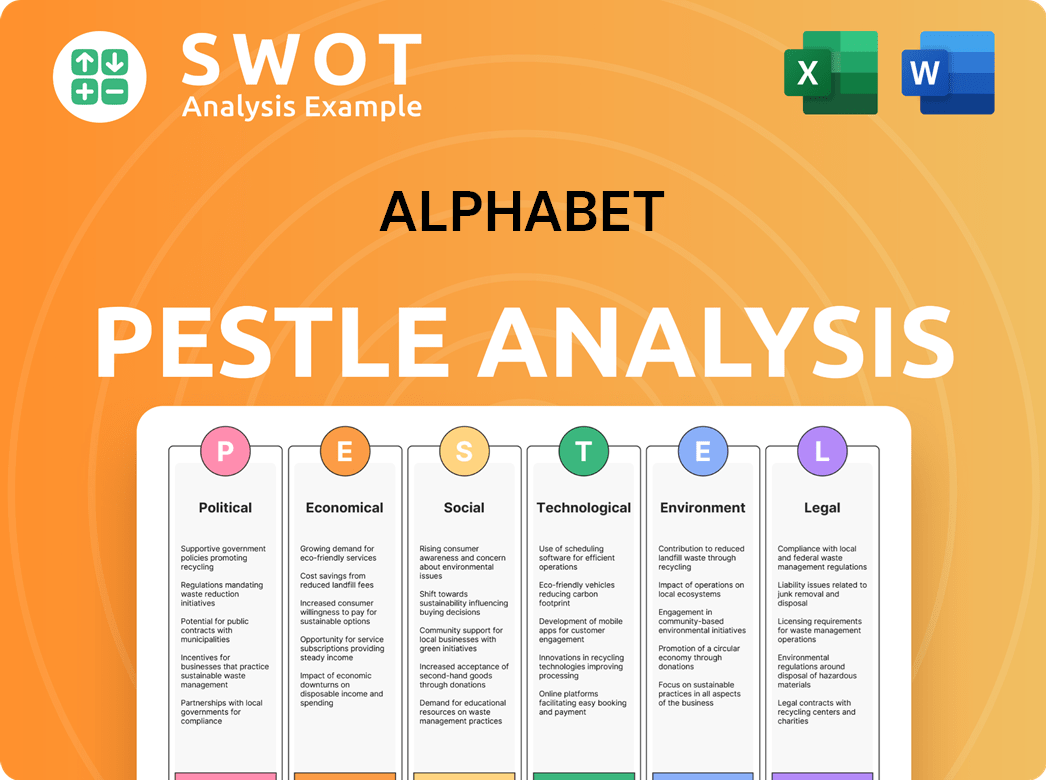
Alphabet PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
Who Sits on Alphabet’s Board?
As of early 2025, the board of directors for the Alphabet company includes a blend of individuals, featuring founders, executives, and independent members. This composition aims to balance the founders' control with external oversight. Larry Page and Sergey Brin, the co-founders, remain on the board. Sundar Pichai, the CEO of Google and Alphabet, also holds a key position. The board also includes independent directors, each bringing expertise from various industries.
The current board structure reflects the ongoing evolution of the Alphabet company ownership. The presence of both founders and independent directors is intended to ensure a balance between strategic direction and external perspectives. This structure is critical for navigating the complexities of the tech industry and maintaining a focus on long-term innovation. Understanding the Alphabet company shareholders is key to grasping the company's governance.
| Board Member | Title | Role |
|---|---|---|
| Larry Page | Board Member | Co-founder |
| Sergey Brin | Board Member | Co-founder |
| Sundar Pichai | CEO | Board Member |
| John L. Hennessy | Lead Independent Director | Independent Director |
The voting structure significantly impacts the Alphabet company ownership structure. The company uses a dual-class share system. Class B shares, largely held by Larry Page and Sergey Brin, have ten votes per share. Class A shares (GOOGL) have one vote per share, while Class C shares (GOOG) have no voting rights. This arrangement gives Page and Brin substantial control over strategic decisions and board appointments. Despite their economic ownership being a minority, their combined voting power remains well over 50%, ensuring their continued influence. For those wondering how to buy Alphabet stock, understanding this structure is essential.
The dual-class share system allows founders to maintain control. This structure has faced scrutiny, with some arguing it limits accountability. Others believe it supports long-term innovation. The long-term vision of the founders is a key aspect of the company. Learn more about Revenue Streams & Business Model of Alphabet.
- Dual-class shares give founders significant voting power.
- Class B shares have ten votes per share.
- Class A shares have one vote per share.
- Class C shares have no voting rights.
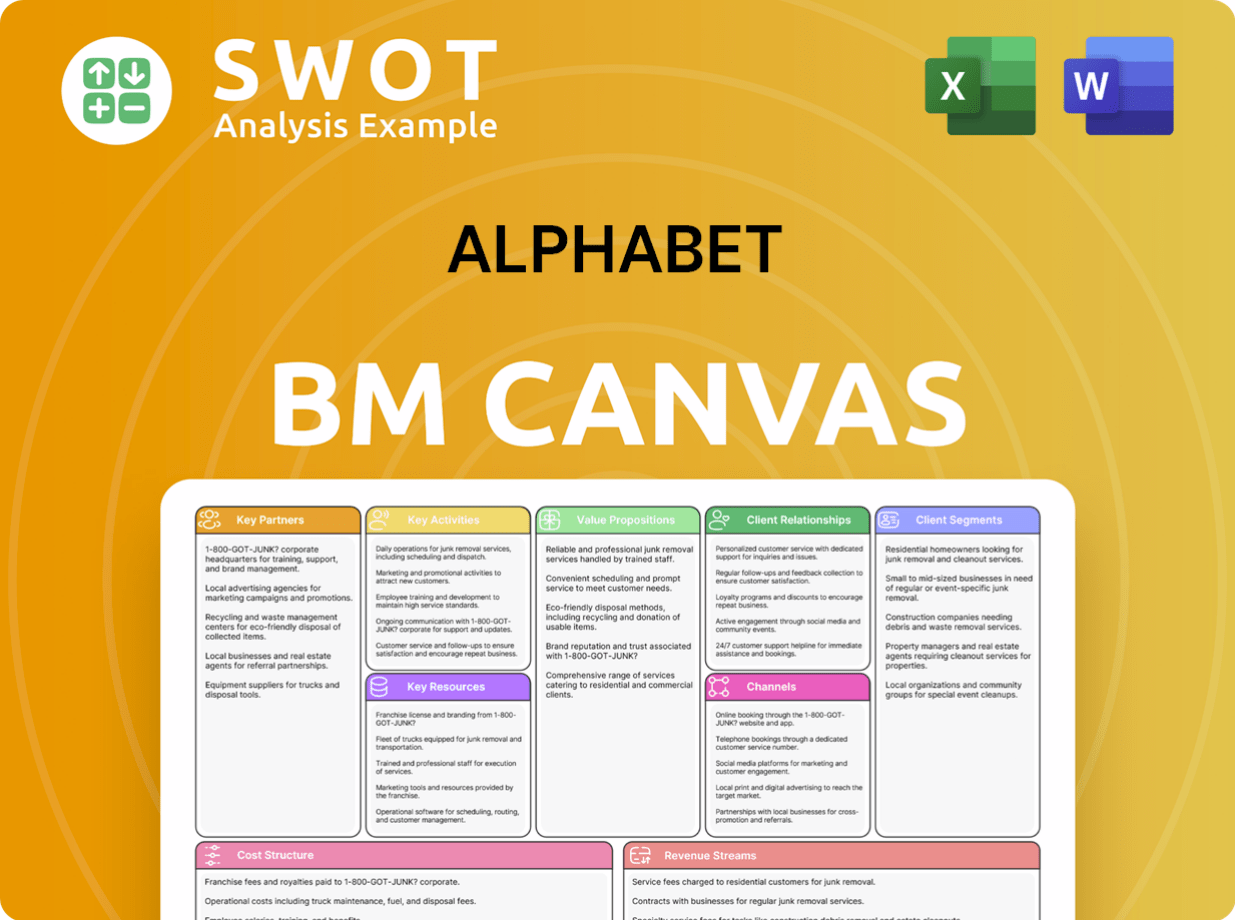
Alphabet Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
What Recent Changes Have Shaped Alphabet’s Ownership Landscape?
Over the past few years (2022-2025), the ownership of the Alphabet company has seen a rise in institutional investors, which is common for large public companies. However, the founders have maintained control. The company has been actively buying back its shares to give money back to shareholders and potentially offset the impact of stock-based compensation. For example, in the first quarter of 2024, Alphabet authorized an additional $70 billion for share repurchases.
Leadership has remained consistent, with Sundar Pichai as the CEO of Alphabet and Google. Even though founders Larry Page and Sergey Brin have stepped back from day-to-day management, their significant voting power through Class B shares ensures they still influence major decisions and the company's overall direction. There are no public indications from the company or analysts suggesting a change in the dual-class share structure or a move towards privatization.
Industry trends show that institutional investors are increasingly owning large technology companies. However, founder-led companies like Alphabet, with their dual-class structures, go against this trend. This allows Alphabet to invest heavily in long-term, high-risk ventures such as artificial intelligence and quantum computing without the immediate pressure of quarterly earnings. This is evident in Alphabet's shareholder base, with major index funds and passive investment vehicles increasing their stakes.
Alphabet's stock has shown significant growth. The stock price today reflects the company's strong financial performance. Investors interested in Alphabet stock can find it on major stock exchanges.
Major shareholders include institutional investors and the founders, Larry Page and Sergey Brin. The ownership structure provides stability and allows for long-term strategic planning. Understanding who owns Alphabet Inc is key for investors.
Sundar Pichai, as CEO, leads the company. His leadership is crucial for Alphabet's strategic direction and operational success. The CEO's role influences the company's performance and future.
The ownership structure includes a dual-class share system. This structure gives founders significant control. The dual-class structure impacts how major decisions are made.
Alphabet Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What are Mission Vision & Core Values of Alphabet Company?
- What is Competitive Landscape of Alphabet Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of Alphabet Company?
- How Does Alphabet Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of Alphabet Company?
- What is Brief History of Alphabet Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of Alphabet Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.