Acenta Steel Bundle
Who Really Owns Acenta Steel Company?
Corporate ownership is a powerful force, shaping a company's destiny and market presence. Unraveling the ownership structure of a major player like Acenta Steel Company offers critical insights into its strategic direction and future prospects. As a leading steel stockholder and distributor, understanding Acenta Steel SWOT Analysis is key to grasping its position within the evolving steel industry.
This exploration into Acenta Steel ownership will uncover its historical roots, tracing its evolution from its inception to its current form. The steel industry, with its complex web of mergers, acquisitions, and strategic alliances, makes understanding Acenta Steel ownership even more critical. This analysis will provide essential company information, shedding light on the key individuals and entities that have shaped Acenta Steel's journey, helping you understand the current Acenta Steel ownership structure and its future trajectory.
Who Founded Acenta Steel?
The history of Acenta Steel Company begins in the 19th century. Its roots trace back to George Gadd, which was established in Tipton in 1865. The bright bar business, a key part of Acenta Steel's operations, was formed in the 1940s through the consolidation of four businesses.
While specific details about the initial founders and their exact equity splits aren't readily available, the company's ownership has changed several times. This dynamic early landscape highlights the evolution of Acenta Steel. Understanding the shifts in ownership is crucial to grasping the company's trajectory within the steel industry.
Early on, Acenta Steel faced challenges when owned by US entities. They viewed the company as 'non-core', which led to difficulties due to the volatility in global steel demand. This period underscores the impact of ownership decisions on a company's performance. Discovering the current ownership structure is essential for anyone interested in the Marketing Strategy of Acenta Steel.
Acenta Steel's story began in 1865 with George Gadd in Tipton. The bright bar business was established in the 1940s.
The company has experienced multiple ownership changes. These shifts reflect the company's evolving strategic direction.
US owners initially considered Acenta Steel 'non-core'. This led to difficulties due to fluctuating global steel demand.
In January 2011, Endless, a private equity firm, acquired Acenta Steel. This marked a significant turning point.
Endless recognized the long-term potential of Acenta Steel. They saw the strength of its market position and workforce.
Ownership decisions greatly influence a company's performance. Understanding these shifts is crucial.
The early ownership structure of Acenta Steel reveals its evolution within the steel industry. Key events include the establishment of George Gadd and the consolidation of the bright bar business. The acquisition by Endless in January 2011 was a pivotal moment, recognizing the company's potential. Understanding the changes in Acenta Steel ownership provides insights into its strategic direction and its ability to navigate market challenges.
- Acenta Steel's origins date back to 1865.
- The bright bar business was formed in the 1940s.
- US ownership presented challenges.
- Endless acquired Acenta Steel in January 2011.
Acenta Steel SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
How Has Acenta Steel’s Ownership Changed Over Time?
The ownership of the Acenta Steel Company has seen several significant changes over the years. Initially acquired by the private equity firm Endless in January 2011, the company later underwent a management buyout (MBO) in March 2013, led by CEO Tarlok Singh and CFO Colin Mills. This MBO was supported by GE Commercial Finance, and it resulted in Endless receiving approximately six times its initial investment. This transition marked a shift towards private ownership, with the management team taking control of the business.
The ownership structure evolved further in 2018 when Aar Tee Industries Holdings Pte Limited, a Singaporean metals trading business, acquired Acenta Steel. This acquisition provided Aar Tee with a new presence in the UK manufacturing sector. At the time of the acquisition, Acenta Steel reported a turnover of £68.4 million and pre-tax profits of £2.6 million for the year ending December, operating across six UK sites with a workforce of 350 employees. The senior management team, including Colin Mills as CEO and Tarlok Singh as executive chairman, remained in place to lead the company. However, in a later development, Acenta Steel, now known as Aartee Bright Bar Limited (ABB), entered administration following a creditor dispute. In March 2023, Barrett Steel acquired Aartee Bright Bar.
| Timeline | Event | Stakeholders |
|---|---|---|
| January 2011 | Acquired by Endless | Endless |
| March 2013 | Management Buyout (MBO) | Tarlok Singh, Colin Mills, GE Commercial Finance |
| 2018 | Acquired by Aar Tee Industries Holdings Pte Limited | Aar Tee Industries Holdings Pte Limited |
| February 2023 | Aartee Group acquired by GFG Alliance | GFG Alliance |
| March 2023 | Aartee Bright Bar acquired by Barrett Steel | Barrett Steel |
It's worth noting that a separate entity, Acenta Group AB, was listed in January 2025 through a reverse acquisition, focusing on padel infrastructure. This company's activities are distinct from those of the steel stockholder and distributor, Acenta Steel Company. For more insights into the company's target market, you can review this article about the Target Market of Acenta Steel.
Acenta Steel Company's ownership has changed multiple times, reflecting strategic shifts and market dynamics.
- Endless acquired Acenta Steel in 2011.
- The management team led an MBO in 2013.
- Aar Tee Industries acquired the company in 2018.
- Barrett Steel acquired Aartee Bright Bar in 2023.
Acenta Steel PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
Who Sits on Acenta Steel’s Board?
Information regarding the current board of directors for the Acenta Steel Company (now operating as Aartee Bright Bar Limited under Barrett Steel ownership) is not readily available in public sources. As a privately-held entity, the specifics of the board's composition, including individual members and their affiliations, are not typically disclosed. The operational leadership, including the CEO and executive chairman, likely remained in place following the acquisition.
The ultimate control and voting power within Acenta Steel Company now rests with Barrett Steel, the acquiring entity. Detailed information on the board, specific voting arrangements, or shareholder affiliations is not generally released unless there are specific regulatory requirements or major governance issues. The focus remains on the operational aspects of the business under the new ownership structure.
| Aspect | Details | Status |
|---|---|---|
| Ownership | Barrett Steel | Current |
| Operational Leadership | Colin Mills (CEO), Tarlok Singh (Executive Chairman) | Confirmed in 2018, likely continues |
| Public Information | Limited; Private Company | Not readily available |
Understanding the Acenta Steel Company's journey involves tracing its ownership transitions. The company, now part of Barrett Steel, has seen significant changes since its acquisition by Aar Tee Industries in 2018. For further insights into the company's strategic direction, you can read about the Growth Strategy of Acenta Steel.
The ownership of Acenta Steel Company is currently held by Barrett Steel.
- The board of directors' details are not publicly available due to its private status.
- Key management figures likely remained in place after the acquisition.
- Barrett Steel controls the voting power.
- Acenta Steel Company's historical context is crucial for understanding its current operations.
Acenta Steel Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
What Recent Changes Have Shaped Acenta Steel’s Ownership Landscape?
In the past few years, the Acenta Steel Company, now operating as Aartee Bright Bar Limited, has undergone significant ownership changes. Initially, Aartee Group, a shareholder in Aartee Bright Bar (ABB), was part of this transformation. In February 2023, following a creditor dispute, ABB entered administration. GFG Alliance, which owns Liberty Steel Group, then sought to intervene, aiming to restart operations and preserve approximately 250 UK jobs. This period reflects the volatility and challenges within the steel industry.
Subsequently, in March 2023, Barrett Steel acquired Aartee Bright Bar. This acquisition is a prime example of the consolidation happening within the UK steel distribution sector. These shifts highlight the dynamic nature of Acenta Steel ownership and the broader steel industry, which has seen increasing merger and acquisition activity. If you want to learn more about the competitive environment, consider exploring the Competitors Landscape of Acenta Steel.
| Key Event | Date | Details |
|---|---|---|
| ABB Enters Administration | February 2023 | Due to a creditor dispute. |
| GFG Alliance Involvement | February 2023 | Sought to restart operations to save jobs. |
| Barrett Steel Acquisition | March 2023 | Acquired Aartee Bright Bar. |
The steel industry is evolving rapidly. In 2024, mergers and acquisitions in the steel sector increased by 15%, reflecting a trend toward market consolidation. The global steel market is projected to reach $1.4 trillion by 2025. However, the industry faces economic headwinds, with the World Bank forecasting global growth slowing to 2.4% in 2024, potentially impacting steel demand. Furthermore, the steel industry saw a 3% decrease in overall profitability in 2024 due to increased competition. These factors influence the operational landscape and Acenta Steel Company owner details.
70% of steel companies aim to cut carbon footprints by integrating low-emission processes by 2025. This involves investments in electric arc furnaces (EAFs) and hydrogen-based steel production.
Restructuring and increased automation and digital technology are key trends. Demand for precision metals is expected to grow, with a projected 4% increase in stainless steel requirements in 2025.
Fluctuating raw material and energy costs continue to pose challenges, with energy costs for steel manufacturers rising by an average of 15% in 2024.
Tata Steel is planning to begin construction of its low-carbon EAF at its Port Talbot mill in the UK in July 2025, indicating a focus on sustainable practices.
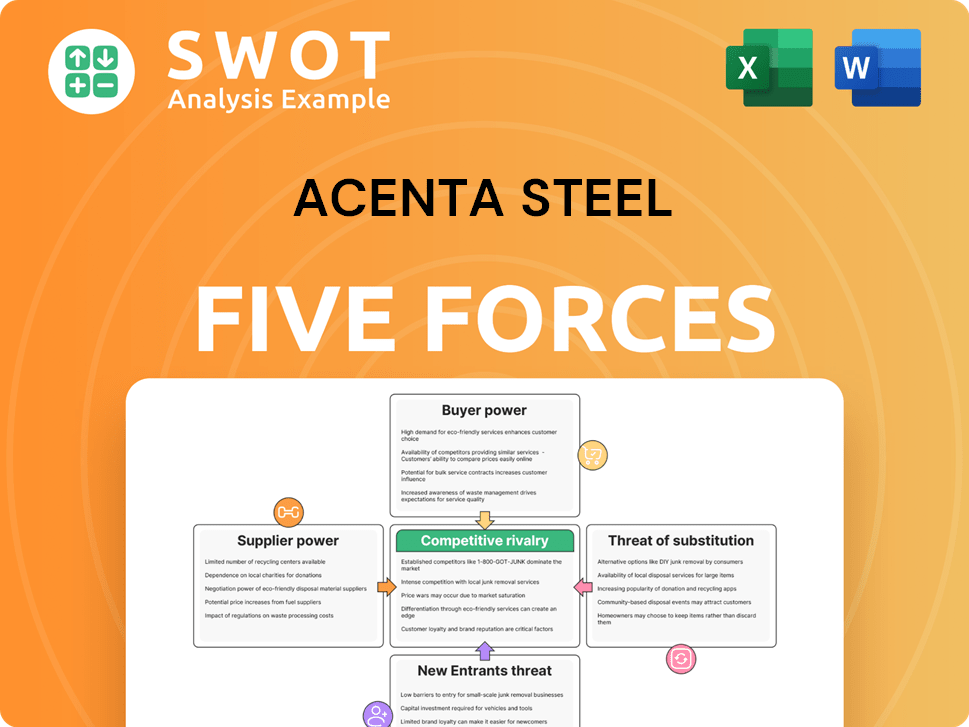
Acenta Steel Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What are Mission Vision & Core Values of Acenta Steel Company?
- What is Competitive Landscape of Acenta Steel Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of Acenta Steel Company?
- How Does Acenta Steel Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of Acenta Steel Company?
- What is Brief History of Acenta Steel Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of Acenta Steel Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.