Akamai Technologies Bundle
Who Really Controls Akamai Technologies?
Unraveling the Akamai Technologies SWOT Analysis is just the beginning; understanding its ownership structure is key to grasping its future. Akamai, a titan in content delivery and cybersecurity, has a fascinating ownership story shaped by its 1999 IPO. From its academic roots to its current status as a publicly traded entity, the evolution of Akamai's ownership reveals critical insights.
This deep dive into Akamai Technologies will explore who owns Akamai, from its initial founders to its current Akamai shareholders. Discover how the diverse ownership base impacts everything from strategic decisions to the company's ability to navigate the ever-changing digital landscape. Understanding the Akamai company profile through an ownership lens offers a unique perspective on its long-term prospects and market positioning.
Who Founded Akamai Technologies?
The story of Akamai Technologies begins with its founders, Professor Tom Leighton and Daniel Lewin. Their collaboration led to the creation of a company that would revolutionize content delivery on the internet. Their early work laid the groundwork for the distributed network that powers much of today's web traffic.
Tom Leighton, a professor of applied mathematics at MIT, developed the core algorithms. Daniel Lewin, an MIT graduate student, joined Leighton to co-found the company. The initial vision was a response to a challenge from the then-President of MIT, aimed at solving internet bottlenecks.
While specific equity details from the company's inception aren't always public, academic founders often retain significant stakes. This is typically in exchange for their intellectual property and leadership. Early backing likely came from venture capital firms and angel investors who saw the potential in their solution to internet congestion.
Tom Leighton, a professor at MIT, conceived the core algorithms for Akamai.
Daniel Lewin, an MIT graduate student, collaborated with Leighton.
Early investors likely included venture capital firms and angel investors.
The founding vision was to create a faster and more reliable internet.
Early agreements included vesting schedules to ensure founder commitment.
The founders' control was crucial to the company's early direction.
The early agreements would have included standard startup provisions. These included vesting schedules to ensure founder commitment over time. They also included buy-sell clauses to manage ownership transfers. The founding team’s vision of a faster, more reliable internet was intrinsically linked to their control over the company's early direction and technological development. As of 2024, Akamai Technologies has a market capitalization of approximately $13 billion, reflecting its significant presence in the content delivery network market. The company's revenue for 2023 was around $3.6 billion, demonstrating its continued growth and impact. The company's headquarters are located in Cambridge, Massachusetts.
Understanding the early ownership of Akamai Technologies provides insight into its foundational values and direction. The founders' initial vision and the backing they received were critical to the company's early success.
- Founded by Tom Leighton and Daniel Lewin.
- Early backing from venture capital and angel investors.
- Focus on solving internet congestion issues.
- Early agreements included vesting schedules.
- The founders' vision shaped the company's early direction.
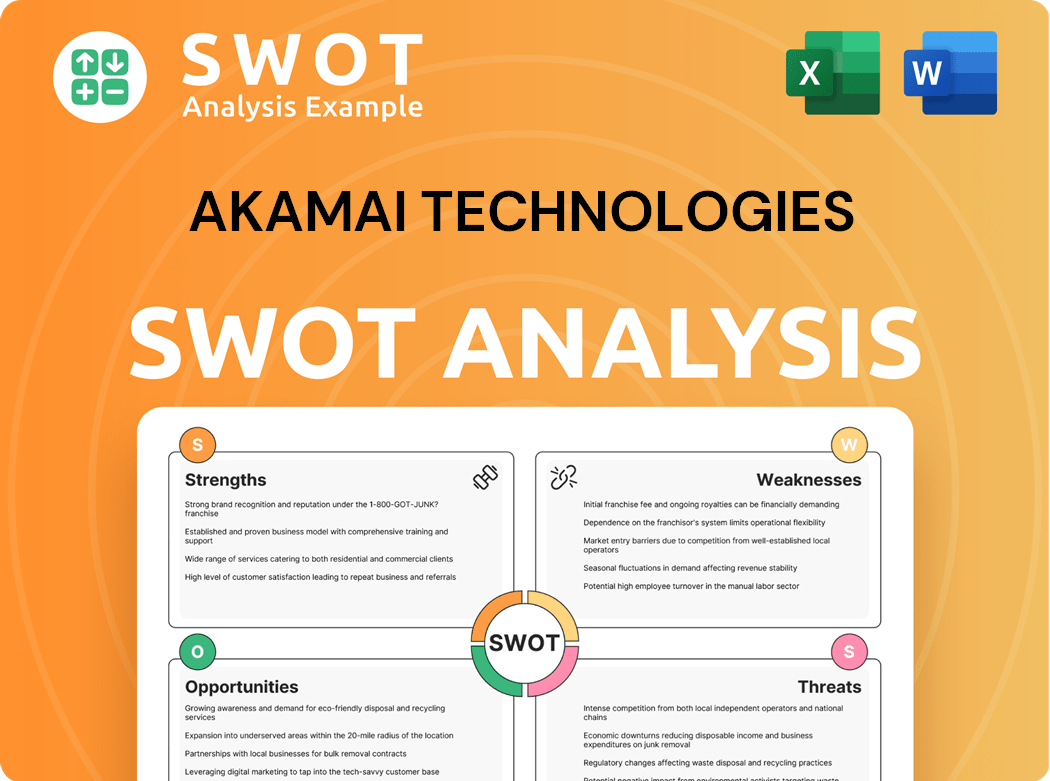
Akamai Technologies SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
How Has Akamai Technologies’s Ownership Changed Over Time?
The evolution of Akamai Technologies' ownership has been marked by significant shifts since its initial public offering (IPO) on October 29, 1999. The IPO, occurring during the dot-com boom, dramatically expanded the shareholder base beyond the original founders and early venture capitalists. This transition from private to public ownership introduced a diverse group of investors, fundamentally altering the company's financial dynamics and strategic direction. The shift towards institutional ownership has been a defining characteristic of Akamai's shareholder structure.
As of early 2025, the ownership structure of Akamai is primarily composed of institutional investors. These investors include a broad range of entities such as mutual funds, index funds, and hedge funds. These institutional holders collectively manage substantial assets, and their investment decisions significantly influence Akamai's strategic direction and financial performance. The concentration of ownership among these institutions gives them considerable influence over corporate governance and key strategic decisions.
| Shareholder | Approximate Ownership (as of December 31, 2024) | Type |
|---|---|---|
| Vanguard Group Inc. | 11.5% | Institutional |
| BlackRock Inc. | 9.8% | Institutional |
| State Street Corp. | 4.5% | Institutional |
The major shareholders, such as Vanguard Group Inc., BlackRock Inc., and State Street Corp., play a crucial role in shaping Akamai's strategic decisions. Their substantial holdings provide them with significant voting power, influencing capital allocation, executive appointments, and long-term growth initiatives. Changes in these ownership percentages often reflect shifts in investor confidence and market trends. For more information on Akamai's target market, you can read this article: Target Market of Akamai Technologies.
Akamai's ownership has evolved significantly since its IPO in 1999, now dominated by institutional investors.
- Vanguard, BlackRock, and State Street are among the largest institutional shareholders.
- These major shareholders influence key strategic decisions due to their significant voting power.
- Ownership changes reflect investor confidence and market trends.
- Understanding Akamai's ownership structure is vital for assessing its strategic direction.
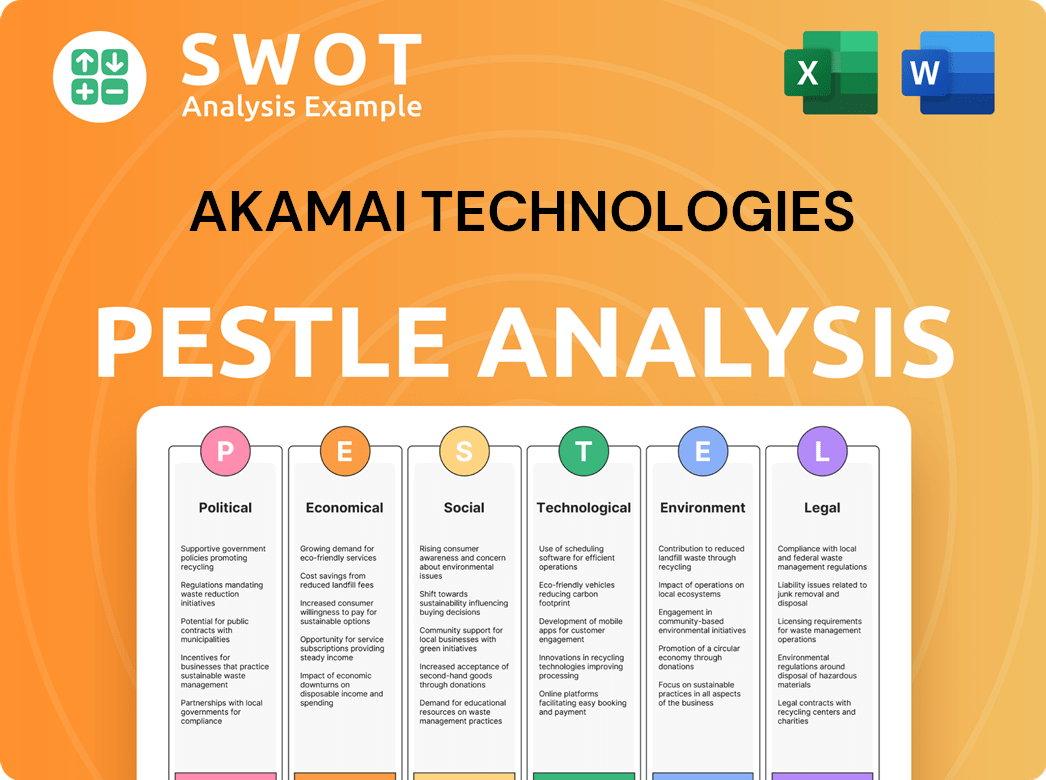
Akamai Technologies PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
Who Sits on Akamai Technologies’s Board?
As of early 2025, the Board of Directors of Akamai Technologies includes a mix of independent directors and those with executive roles within the company. This structure is designed to provide both oversight and strategic guidance. The board's composition is regularly reviewed and updated, with changes disclosed in proxy statements filed with the SEC. These statements offer detailed information on each director's background, qualifications, and any affiliations with major shareholders. The current board members ensure that decisions are made with a broad perspective, not solely influenced by any single large shareholder.
Institutional investors exert their influence primarily through their voting power on matters such as director elections and executive compensation. Akamai operates primarily on a one-share-one-vote structure, which gives large institutional shareholders significant collective voting power due to their substantial holdings. While specific voting rights beyond the one-share-one-vote standard are not typically disclosed, the presence of independent directors helps to ensure decisions are made in the best interests of the shareholders. There have been no major proxy battles or activist investor campaigns publicly reported for Akamai in recent years.
| Board Member | Title | Affiliation |
|---|---|---|
| Dr. Tom Leighton | CEO and Director | Akamai Technologies |
| James D. Beer | Lead Independent Director | Former CFO, Microsoft |
| Roxanne S. Austin | Director | Board Member of various companies |
The Board of Directors plays a critical role in corporate governance, overseeing management and ensuring the company operates in the best interests of its shareholders. Understanding Growth Strategy of Akamai Technologies is crucial for investors. The board's role is essential in guiding the company's strategic direction and ensuring long-term value creation for Akamai shareholders. The composition of the board, including its independent members, is regularly reviewed and updated.
The Board of Directors at Akamai Technologies is composed of independent directors and executives, ensuring oversight and strategic direction. Institutional investors significantly influence the company through their voting power. Akamai operates on a one-share-one-vote structure, which gives substantial voting power to large shareholders.
- Board composition includes independent directors.
- Institutional investors hold significant voting power.
- Regular updates and disclosures in proxy statements.
- Focus on shareholder value and strategic guidance.
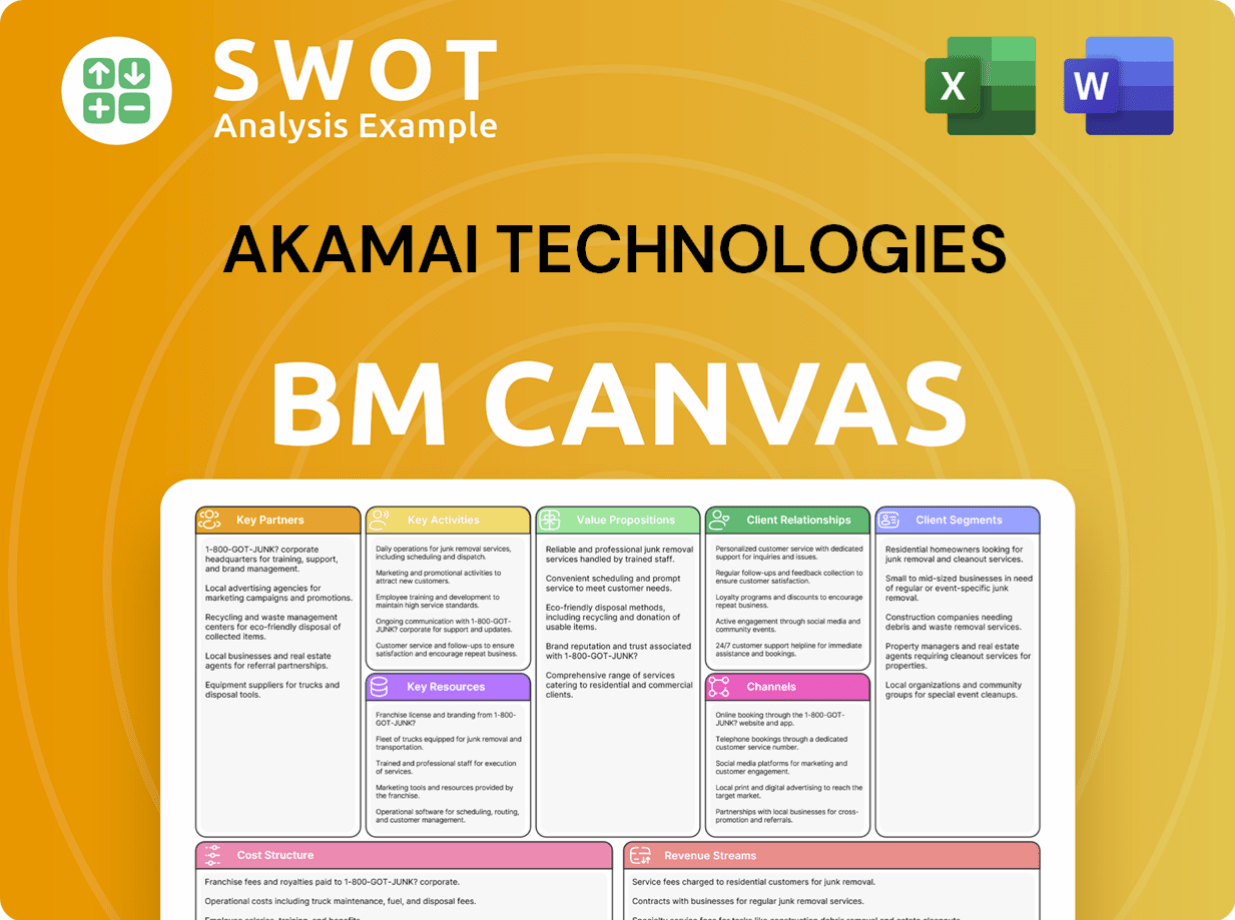
Akamai Technologies Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
What Recent Changes Have Shaped Akamai Technologies’s Ownership Landscape?
Over the past few years, the ownership structure of Akamai Technologies has seen continued evolution, significantly influenced by broader industry trends and the company's strategic initiatives. A key observation is the sustained presence of institutional investors. Major players like Vanguard and BlackRock have consistently held substantial stakes, reflecting Akamai's position as a stable, long-term investment within the technology sector. This consistent accumulation by institutional investors is largely due to Akamai's consistent performance, its critical role in internet infrastructure, and its expansion into high-growth areas like cybersecurity and edge computing.
Akamai has actively pursued strategic acquisitions, which have impacted its ownership profile through the issuance of new shares or the integration of acquired company shareholders. For instance, the acquisition of Linode in 2022, a leading Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS) platform, was a significant move that expanded Akamai's cloud computing capabilities and likely involved equity considerations. Share buybacks, when executed, have also subtly shifted ownership percentages by reducing the total number of outstanding shares, thereby increasing the proportionate ownership of remaining shareholders. The general trend of founder dilution over time is typical for mature public companies as new capital is raised and employee stock options are exercised. Industry-wide, there's a growing focus on environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors, influencing how large institutional investors allocate capital, which can indirectly impact Akamai's ownership as it addresses these concerns. Akamai's public statements and analyst reports continue to focus on its growth strategies, particularly in security and cloud, which may attract new investors and further shape its ownership landscape.
| Key Ownership Trends (2020-2025) | Details | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Institutional Ownership | Consistent holdings by Vanguard, BlackRock, and other large asset managers. | Reflects stability and long-term investment appeal. |
| Strategic Acquisitions | Acquisition of Linode in 2022, expanding cloud capabilities. | Potential for share issuance and changes in shareholder composition. |
| Share Buybacks | Ongoing, affecting the number of outstanding shares. | Increases proportionate ownership for remaining shareholders. |
Understanding Akamai's ownership structure is crucial for investors. The company's strategic moves, such as the acquisition of Linode, have expanded its capabilities and influenced its shareholder base. Institutional investors continue to play a significant role, attracted by Akamai's position in the market and its focus on growth areas like cybersecurity. For a broader view of the competitive landscape, consider exploring the Competitors Landscape of Akamai Technologies.
Institutional investors like Vanguard and BlackRock hold significant shares.
Share buybacks can subtly shift ownership percentages.
Acquisitions like Linode impact shareholder composition.
Focus on ESG factors influences investor decisions.
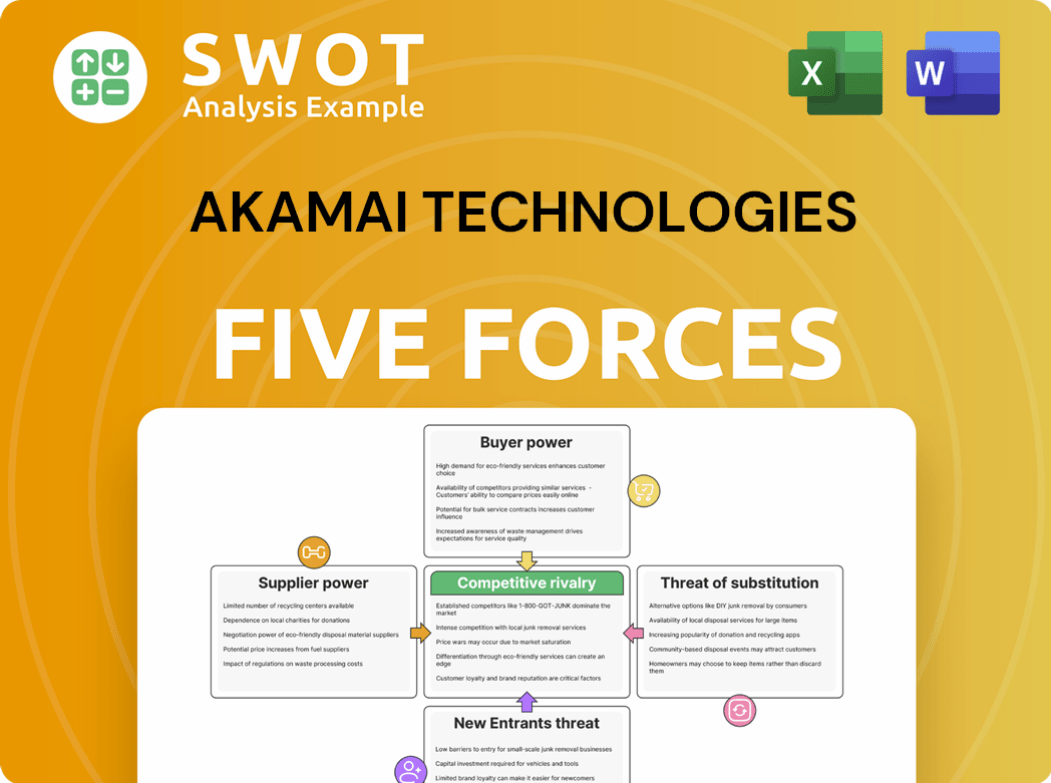
Akamai Technologies Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What are Mission Vision & Core Values of Akamai Technologies Company?
- What is Competitive Landscape of Akamai Technologies Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of Akamai Technologies Company?
- How Does Akamai Technologies Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of Akamai Technologies Company?
- What is Brief History of Akamai Technologies Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of Akamai Technologies Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.