Bourbon Bundle
Who Really Owns Bourbon Corporation?
Understanding the ownership of a company is paramount for investors and strategists alike. Bourbon Corporation, a key player in the marine services sector, experienced a significant ownership shift in 2020. This article unravels the complex ownership structure of Bourbon Corporation, exploring its evolution from its sugar industry roots to its current position in the offshore energy market.

The journey of Bourbon SWOT Analysis reveals how the company's ownership has influenced its strategic decisions. From its founding as 'Sucreries de Bourbon' to its present-day operations, the company's ownership has been a key driver in its transformation. This deep dive explores the influence of major stakeholders, the composition of the board of directors, and recent trends shaping the future of this important player in the whiskey industry, offering insights into who owns bourbon and its impact on the company's trajectory. Analyzing bourbon company ownership provides crucial insights for anyone interested in the bourbon brands and the wider distillery acquisitions landscape.
Who Founded Bourbon?
The story of the company, initially known as the 'Bourbon Group' and later as 'Sucreries de Bourbon,' began in 1948. It was formed on Reunion Island through the merger of several family-owned businesses. The primary goal was to revitalize the sugar industry in the region.
Early ownership details are not widely available, but the company's focus was on sugar production. Émile Hugot was the initial leader. The group diversified its interests in 1989, expanding into industrial fishing, mass distribution, and dairy products in La Réunion. In 1991, it expanded further into mainland France by acquiring a 50% stake in Compagnie Chambon.
A major shift in ownership occurred in 1998 when the company went public on the Second Market of the Paris Stock Exchange. This move transformed the company from a family-run entity to one with public shareholders. The company's early strategic direction was also shaped by acquisitions in the 1990s, such as Les Abeilles (towage) and Setaf-Saget (solid bulk transport) in 1996, which pushed the company towards marine services.
The initial focus of the company was on sugar production, reflecting its roots in the Reunion Island's economy. The company was led by Émile Hugot during this period.
In 1989, the company began to diversify its operations, expanding into industrial fishing, mass distribution, and dairy products. This marked a strategic shift beyond its initial sugar-centric business model.
The company expanded its footprint in 1991 by acquiring a 50% stake in Compagnie Chambon, marking its entry into mainland France. This acquisition was a key step in its growth strategy.
In 1998, the company went public on the Second Market of the Paris Stock Exchange. This transition from a family-owned business to a publicly traded company significantly altered its ownership structure.
Acquisitions in the 1990s, such as Les Abeilles and Setaf-Saget, were instrumental in shaping the company's strategic direction. These moves shifted the company's focus towards marine services.
The founding team's vision evolved from sugar production to diversification and, eventually, a strong emphasis on marine services. This evolution was reflected in its early business developments and the decision to go public.
Understanding the ownership of companies like this is crucial for anyone interested in the Target Market of Bourbon. The history of the company, from its family-owned beginnings to its public listing, highlights the dynamic nature of corporate ownership and the strategic shifts that drive growth. While specific details on early investors are limited, the evolution of the company's focus from sugar to marine services showcases its adaptability and strategic foresight. The company's journey reflects broader trends in the whiskey industry and the distillery acquisitions that shape its landscape. The early decisions and acquisitions laid the groundwork for its future, making it a significant player in the global market. The company's story is a testament to the importance of strategic planning and the ability to adapt to changing market conditions. The company's transformation demonstrates how diversification and strategic acquisitions can reshape a company's trajectory. The company's history provides valuable insights into the factors that influence corporate ownership and strategic direction.
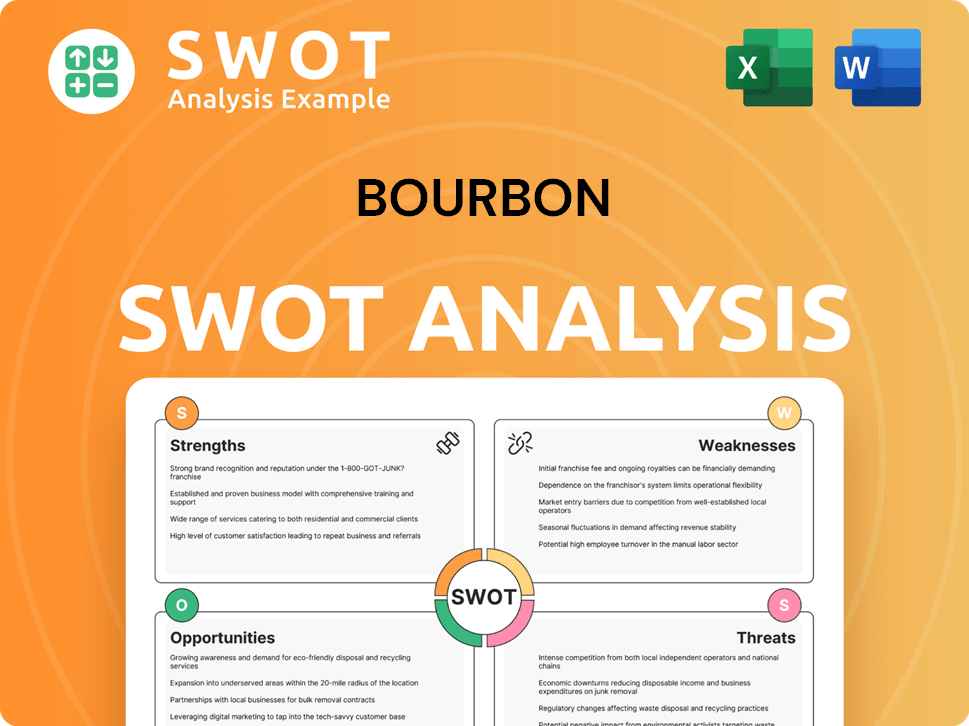
Bourbon SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
How Has Bourbon’s Ownership Changed Over Time?
The ownership of the Bourbon Corporation has seen dramatic shifts over time. Initially listed on the Paris Stock Exchange in 1998, the company shifted its focus to marine services, solidifying its presence on the SBF 120 index by 2006. However, a financial crisis in the oil industry led to significant restructuring, fundamentally altering the company's ownership and strategic direction. These changes have reshaped the landscape of the Growth Strategy of Bourbon.
The most significant changes occurred in 2019 and 2020. Facing financial difficulties, the company underwent reorganization proceedings. In January 2020, Société Phocéenne de Participations (SPP), backed by a consortium of French banks, acquired 100% of Bourbon Corporation's assets. This restructuring resulted in a 'total loss' for the former shareholders, and the former holding company was placed in compulsory liquidation in April 2020, with its shares delisted in June 2020.
| Year | Event | Impact on Ownership |
|---|---|---|
| 1998 | Initial Public Offering | Listed on the Second Market of the Paris Stock Exchange |
| 2005 | Rebranding | Bourbon Group became BOURBON |
| 2020 | Financial Restructuring | SPP, a consortium of French banks, acquired 100% of assets |
In 2024, the French banks sold their stake to American private equity groups Fortress Capital and Davidson Kempner (DK). This transition from bank-led ownership to private equity control suggests a strategic shift towards operational improvements and a potential future exit strategy within the competitive whiskey industry. This move is indicative of the dynamic nature of bourbon distilleries and the broader whiskey industry, where ownership can change rapidly.
The Bourbon Corporation's ownership has transformed significantly, from public listing to bank control and now private equity. This shift reflects the changing dynamics of the bourbon brands market.
- Initial public offering in 1998.
- Restructuring in 2020 with French banks taking control.
- Acquisition by American private equity firms in 2024.
- Focus on operational improvements and potential exit strategies.
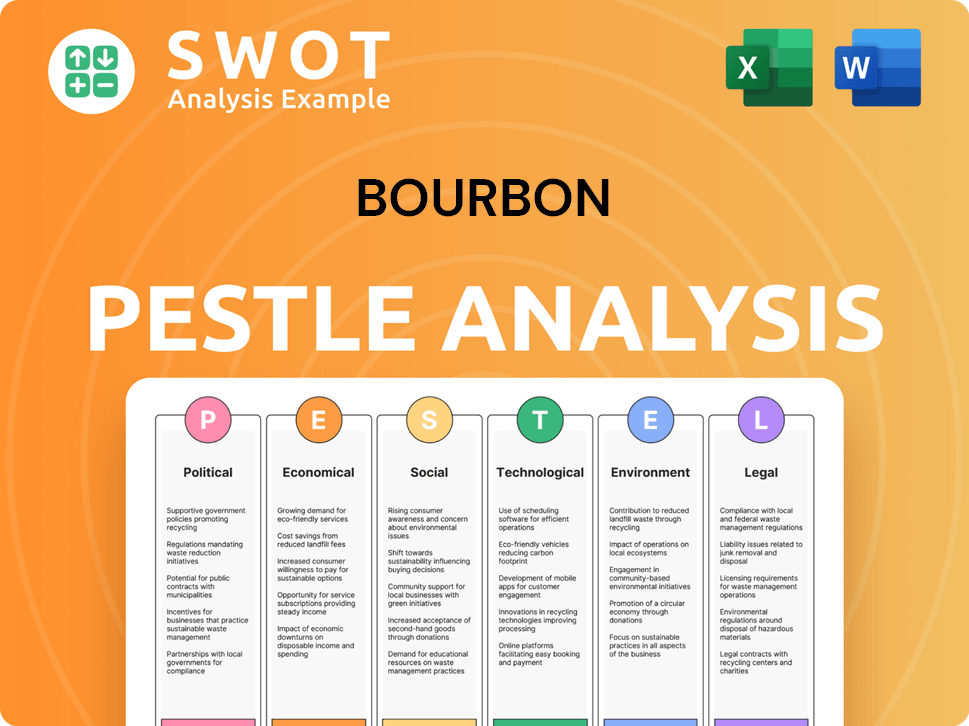
Bourbon PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
Who Sits on Bourbon’s Board?
The governance of the Bourbon Corporation is structured around a Supervisory Board and a Management Board. The Supervisory Board oversees the company's operations and holds supervisory authority. Currently, the board comprises eight members, each bringing diverse experience and expertise, particularly from the Oil & Gas and maritime sectors. Mr. Jean Peyrelevade, a former Chairman of major French financial institutions, serves as President of the Supervisory Board. Mr. Olivier Dubois, with a background in finance and executive management, is the Vice-President.
Other notable members of the Supervisory Board include Mr. Carsten Plougmann Andersen (former Vice-President of Maersk group), Mr. Jean Cahuzac (former CEO of Subsea 7), Mr. Yves-Louis Darricarrere (former member of Total's Executive Committee), and Mrs. Florence Weingarten (Group Chief counsel of Transdev). Additionally, ICIL Maritim (Global) Pte. Limited, represented by Liang Wang, and Martin Bretignière, an Employee Representative, are also members. The Management Board, established in 2021, is responsible for the strategic and operational management of the group, operating under the supervision of the Supervisory Board. It is composed of Gaël Bodénès, President of the Management Board and Group Chief Executive Officer, and Cyril Mathonnat, Group Chief Financial Officer.
| Board Member | Title | Background |
|---|---|---|
| Jean Peyrelevade | President of the Supervisory Board | Former Chairman of French financial institutions |
| Olivier Dubois | Vice-President | Finance and Executive Management |
| Carsten Plougmann Andersen | Member | Former Vice-President of Maersk group |
| Jean Cahuzac | Member | Former CEO of Subsea 7 |
| Yves-Louis Darricarrere | Member | Former member of Total's Executive Committee |
| Florence Weingarten | Member | Group Chief counsel of Transdev |
| Liang Wang | Member (ICIL Maritim (Global) Pte. Limited) | Maritime Industry |
| Martin Bretignière | Member (Employee Representative) | Employee Representative |
The voting structure within the Bourbon Corporation, particularly after its financial restructuring, is largely controlled by its major shareholders. Following Société Phocéenne de Participations (SPP)'s acquisition of 100% of Bourbon Corporation's assets in 2020, and its subsequent role as the new majority shareholder, French banks, along with ICBCL and Standard Chartered Bank, held significant voting power. The sale of the controlling consortium's stake to American private equity groups Fortress Capital and Davidson Kempner in 2024 further concentrated control within these private equity entities. This shift in ownership has significant implications for the future of the company and the broader Growth Strategy of Bourbon.
The Bourbon Corporation's ownership has shifted significantly, with private equity firms now holding substantial control. This impacts decision-making and strategic direction within the company, influencing the future of bourbon brands.
- Private equity firms now control a significant portion of the company.
- The shift in ownership affects strategic decisions.
- Major shareholders influence the voting structure.
- The ownership structure impacts the future of the whiskey industry.
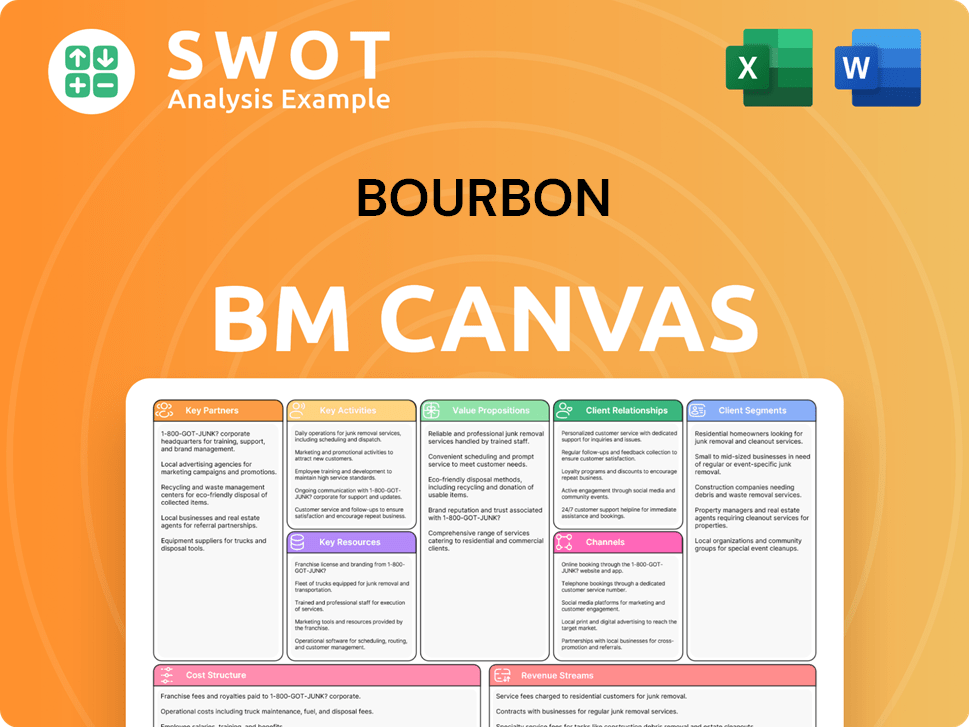
Bourbon Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
What Recent Changes Have Shaped Bourbon’s Ownership Landscape?
Over the past few years, the ownership of the Bourbon Corporation has undergone significant transformations. In January 2020, Société Phocéenne de Participations (SPP) acquired all of the company's assets, effectively making a consortium of French banks the majority shareholders. This acquisition was followed by ICBCL and Standard Chartered Bank acquiring approximately 18% and 10% of SPP's capital, respectively. This reshaped the ownership structure, leading to a complete loss for the former shareholders.
A major shift occurred in 2024 when the controlling stake of French banks in Bourbon was sold to American private equity groups Fortress Capital and Davidson Kempner (DK). This transition marked a move from bank-led ownership to private equity control. This change often means a focus on operational improvements, profit enhancement, and preparing the company for a future exit, such as a public listing or sale. Additionally, in mid-2024, senior management team members were found guilty of corruption, which they are reportedly appealing.
| Ownership Change | Date | Details |
|---|---|---|
| Acquisition by SPP | January 2020 | Consortium of French banks became majority shareholders. |
| Stake Acquisition | Post-2020 | ICBCL and Standard Chartered Bank acquired stakes in SPP. |
| Sale to Private Equity | 2024 | Fortress Capital and Davidson Kempner (DK) acquired control. |
The offshore marine services sector, where Bourbon operates, is seeing increasing institutional ownership and consolidation. Bourbon is strategically focusing on floating wind development, aiming to reduce greenhouse gas emissions by 25% by 2035. The company is also preparing for the Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD), which will apply to Bourbon for the 2025 financial year. These trends reflect the industry's move towards sustainability and stricter governance. The shift to private equity ownership often indicates a focus on improving the company's financial performance and future prospects, which could include a re-listing or sale in the future. For more insights into the company's strategic moves, you can read about the Marketing Strategy of Bourbon.
Recent changes include the 2020 acquisition by a consortium of French banks. This was followed by a 2024 shift to ownership by private equity firms.
The sector is seeing increasing institutional ownership and a focus on sustainability. Bourbon is adapting to these trends by focusing on renewable energy.
Private equity ownership often aims at operational improvements. This may lead to a future public listing or sale.
Bourbon is focusing on floating wind development and sustainability. They are also preparing for the CSRD.
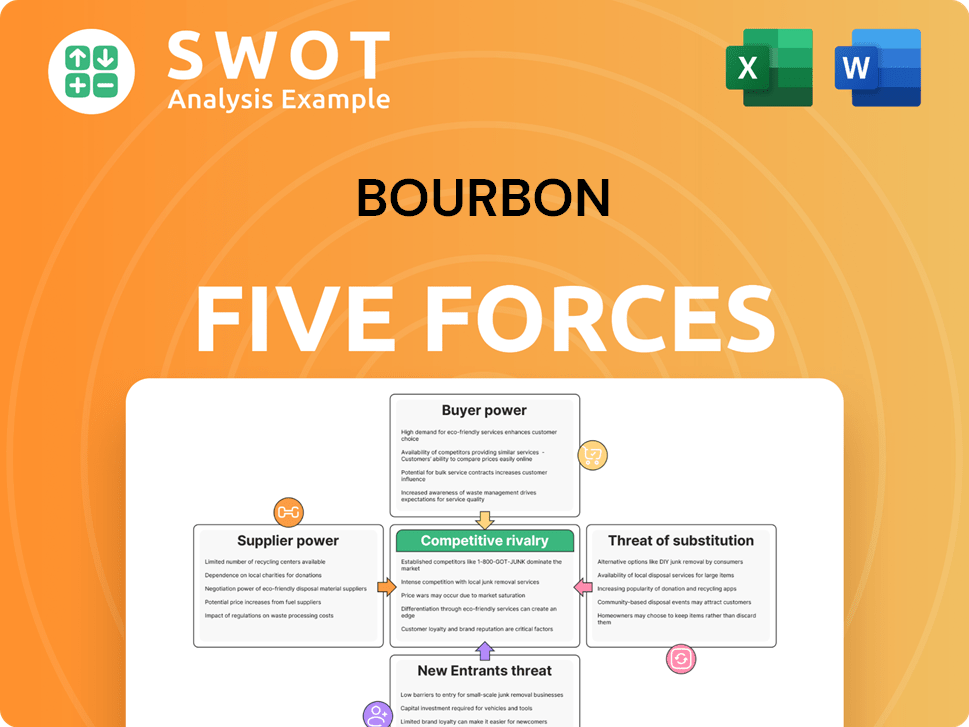
Bourbon Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What are Mission Vision & Core Values of Bourbon Company?
- What is Competitive Landscape of Bourbon Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of Bourbon Company?
- How Does Bourbon Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of Bourbon Company?
- What is Brief History of Bourbon Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of Bourbon Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.