Campbell Soup Bundle
Who Really Controls Campbell Soup Company?
Ever wondered who steers the ship at Campbell Soup Company, now officially known as The Campbell's Company? Understanding Campbell Soup SWOT Analysis is crucial for investors and stakeholders. This iconic food giant, with a history stretching back to 1869, has undergone significant transformations, making its ownership structure a key area of interest. From its humble beginnings to its current global presence, the story of Campbell's ownership is a fascinating one.

The evolution of Campbell's ownership reflects its strategic shifts and market adaptations. Knowing who owns Campbell's is essential for anyone analyzing the company's future prospects. This exploration will unravel the layers of Campbell's ownership, from its founders to the current major investors, shedding light on the forces shaping this food industry leader. Discover the history of Campbell Soup Company ownership and its impact on the company's trajectory.
Who Founded Campbell Soup?
The story of the Campbell Soup Company began in 1869 as Anderson & Campbell. This partnership was formed between Joseph A. Campbell and Abraham Anderson. They started with a modest investment of $400 to launch their canning business in Camden, New Jersey.
Initially, the company produced canned goods such as tomatoes, vegetables, and jellies. Over time, the business evolved, and ownership changed hands, shaping the Campbell's ownership structure we see today. The early years set the stage for the company's future growth and success.
Abraham Anderson left the company in 1876, and the name changed to Joseph A. Campbell Preserve Company. Later, Arthur Dorrance joined, leading to the Jos. Campbell Preserve Company in 1891. The arrival of John T. Dorrance in 1897 marked a significant turning point.
John T. Dorrance, a chemist, revolutionized soup production by developing a method to condense soup, making it more affordable and easier to transport. This innovation significantly boosted sales. By 1914, he became the president and eventually bought out the Campbell family, becoming the sole owner.
- The company officially became the Campbell Soup Company in 1922.
- John T. Dorrance's contributions were pivotal in transforming the company.
- His condensed soup innovation was a game-changer in the food industry.
- Dorrance's acquisition of the company marked a critical shift in Campbell Soup history.
Campbell Soup SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format

How Has Campbell Soup’s Ownership Changed Over Time?
The Campbell Soup Company's journey from a private entity to a publicly traded corporation in 1954 marked a pivotal moment in its ownership evolution. This transition, with its stock listed on the New York Stock Exchange, opened the doors to a wider array of investors, fundamentally changing the company's ownership structure. Over time, the company strategically expanded its portfolio through acquisitions, including Pepperidge Farm, Inc. in 1961, Pace Foods in 1995, and Snyder's-Lance in 2018, each move further diversifying its ownership base and market presence.
The evolution of Campbell's ownership reflects its growth and adaptation to market dynamics. The company's strategic acquisitions and its initial public offering have shaped its current ownership landscape. These changes have not only broadened the investor base but also influenced the company's strategic direction and financial performance, as detailed in the Marketing Strategy of Campbell Soup.
| Shareholder Type | Approximate Ownership (as of Feb 2024) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Institutional Investors | Approximately 54% | Includes major players like Vanguard and BlackRock. |
| General Public | Approximately 25% | Primarily individual investors. |
| Individual Shareholders | Significant, including Mary Alice Dorrance Malone | Mary Alice Dorrance Malone held approximately 18% as of February 2024. |
As of March 2025, Campbell Soup Company shareholders include a significant number of institutional owners. Vanguard Group Inc. and BlackRock, Inc. are among the major institutional shareholders, holding substantial shares. Mary Alice Dorrance Malone remains a key individual shareholder, with a notable percentage of ownership. The substantial holdings by institutional investors indicate their considerable influence on the company's strategic decisions and overall direction.
Understanding who owns Campbell's is crucial for investors and stakeholders.
- Institutional investors hold a significant portion of the company's shares.
- Individual shareholders, such as Mary Alice Dorrance Malone, also play a key role.
- The company's ownership structure has evolved significantly since its IPO in 1954.
- The Campbell Soup Company stock price and financial performance are influenced by these ownership dynamics.
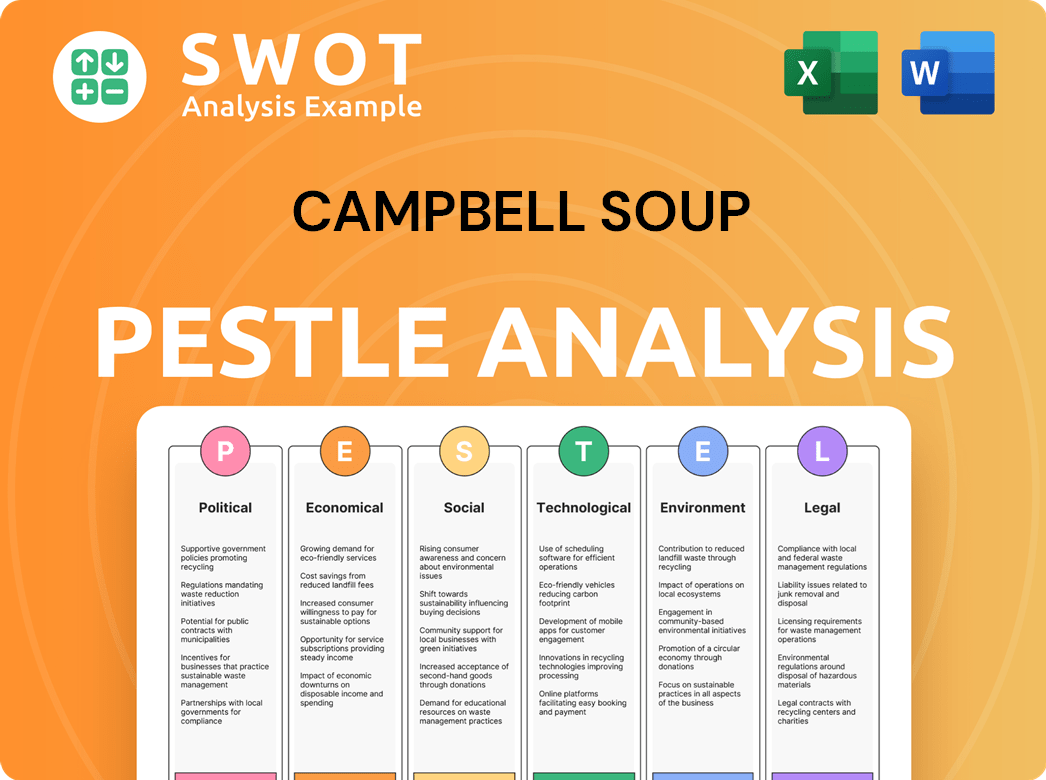
Campbell Soup PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
Who Sits on Campbell Soup’s Board?
The Board of Directors of the Campbell Soup Company plays a crucial role in corporate governance and oversight. At the 2024 Annual Meeting of Shareholders, which was held virtually on November 19, 2024, shareholders elected 12 director nominees to serve a one-year term. Shareholders who were recorded as of September 25, 2024, were eligible to vote at this meeting. This structure ensures the company's governance is regularly reviewed and updated by its shareholders.
The voting structure typically follows a one-share, one-vote system for most proposals. This includes items such as director elections and executive compensation, which require a majority of the votes cast to pass. However, certain special resolutions, like an amendment to the company's Restated Certificate of Incorporation to change the company's name, require approval from at least two-thirds of the votes cast. This setup balances shareholder influence with the need for decisive action on important matters.
| Director Name | Title | Relevant Experience |
|---|---|---|
| Keith R. McLoughlin | Chairman of the Board | Extensive experience in the consumer goods industry, including leadership roles at several major companies. |
| Mark A. Clouse | President and Chief Executive Officer | Deep knowledge of the food industry, with a proven track record in driving growth and innovation. |
| Other Directors (Names withheld for brevity) | Director | Diverse backgrounds including finance, marketing, and operations, providing a wide range of expertise. |
The Dorrance family, through their substantial shareholdings, has historically held considerable influence over the company's direction. While specific details on board members representing major shareholders are not explicitly detailed in recent public filings, the significant institutional ownership suggests the board would likely consider their preferences. The 2024 proxy statement also included a shareholder proposal for an independent diversity audit, which the company recommended shareholders vote against. For more details, you can read a Brief History of Campbell Soup.
The Dorrance family's ownership has historically given them considerable influence. Institutional investors also hold a significant stake, impacting board decisions. The voting structure generally follows a one-share, one-vote principle.
- Majority vote needed for director elections and executive compensation.
- Special resolutions require a two-thirds vote.
- Shareholder proposals, such as diversity audits, are subject to voting.
- The board considers the preferences of major shareholders.
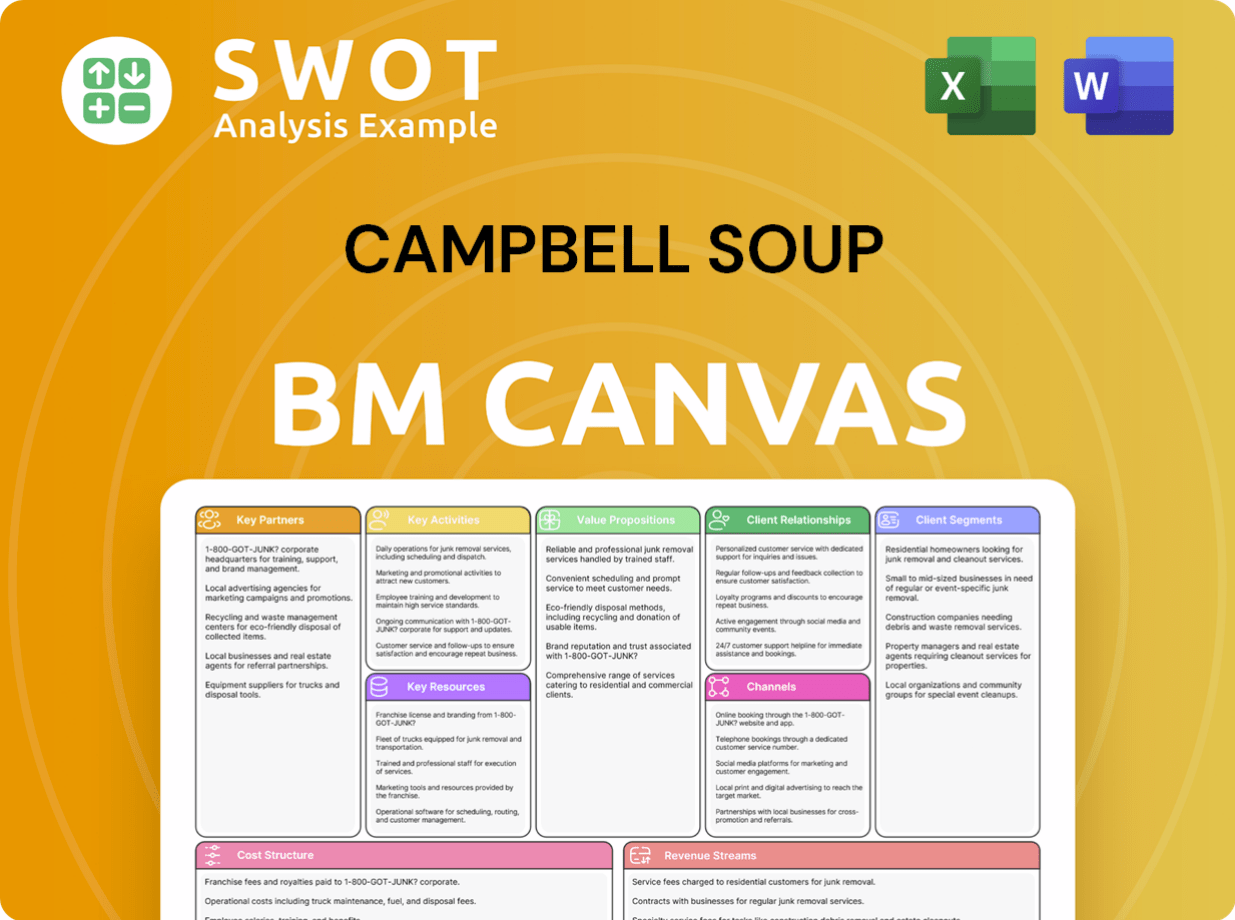
Campbell Soup Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
What Recent Changes Have Shaped Campbell Soup’s Ownership Landscape?
In recent years, Campbell Soup Company has undergone significant shifts in its ownership and strategic direction. A major development was the acquisition of Sovos Brands, finalized on March 12, 2024, for approximately $2.7 billion. This move brought premium brands, like Rao's pasta sauce, into the company's portfolio, aiming to boost revenue and expand its presence in higher-margin sectors. This acquisition is a key element in understanding the current landscape of Campbell's ownership and its future strategies.
The company also made strategic divestitures, including the Pop Secret popcorn business on August 26, 2024, and the noosa yogurt business on February 24, 2025, as part of its portfolio optimization efforts. Reflecting its diversified product offerings beyond soup, shareholders approved changing the company's name from Campbell Soup Company to The Campbell's Company on November 19, 2024. This change became effective after amending the company's certificate of incorporation in New Jersey. These actions highlight the evolution of Campbell's ownership and its adaptation to market trends.
| Key Development | Date | Details |
|---|---|---|
| Sovos Brands Acquisition | March 12, 2024 | Acquired for approximately $2.7 billion, including brands like Rao's. |
| Pop Secret Divestiture | August 26, 2024 | Divested as part of portfolio optimization. |
| Name Change | November 19, 2024 | Shareholders approved the name change to The Campbell's Company. |
| noosa yogurt business Divestiture | February 24, 2025 | Divested as part of portfolio optimization. |
Leadership transitions have also played a role in shaping the company's current state. Mick Beekhuizen became President and CEO on February 1, 2025, succeeding Mark Clouse, and Risa Cretella was appointed President of Meals & Beverages, also effective February 1, 2025. For fiscal year 2025, the company anticipates a 4% increase in net sales and a 2% rise in adjusted EBIT, which includes the impact of the Sovos Brands acquisition. The company continues its focus on cost savings, targeting approximately $250 million in annual ongoing savings by the end of 2028. This underscores the company's focus on strategic financial management within the context of Campbell's ownership.
The company expects a 4% increase in net sales and a 2% rise in adjusted EBIT for fiscal year 2025, reflecting the impact of recent acquisitions and strategic decisions. This is a key indicator of how the current ownership structure is impacting the business.
Focus on cost savings, targeting approximately $250 million in annual ongoing savings by the end of 2028. This initiative is crucial for maintaining and improving the company's financial health under its current ownership.
Mick Beekhuizen became President and CEO on February 1, 2025, succeeding Mark Clouse, and Risa Cretella was appointed President of Meals & Beverages, effective February 1, 2025. These changes reflect the evolving dynamics of Campbell's ownership.
Divestitures of Pop Secret and noosa yogurt businesses, along with the Sovos Brands acquisition, showcase the company's strategy to optimize its product portfolio. These actions are shaping who owns Campbell's and its future direction.
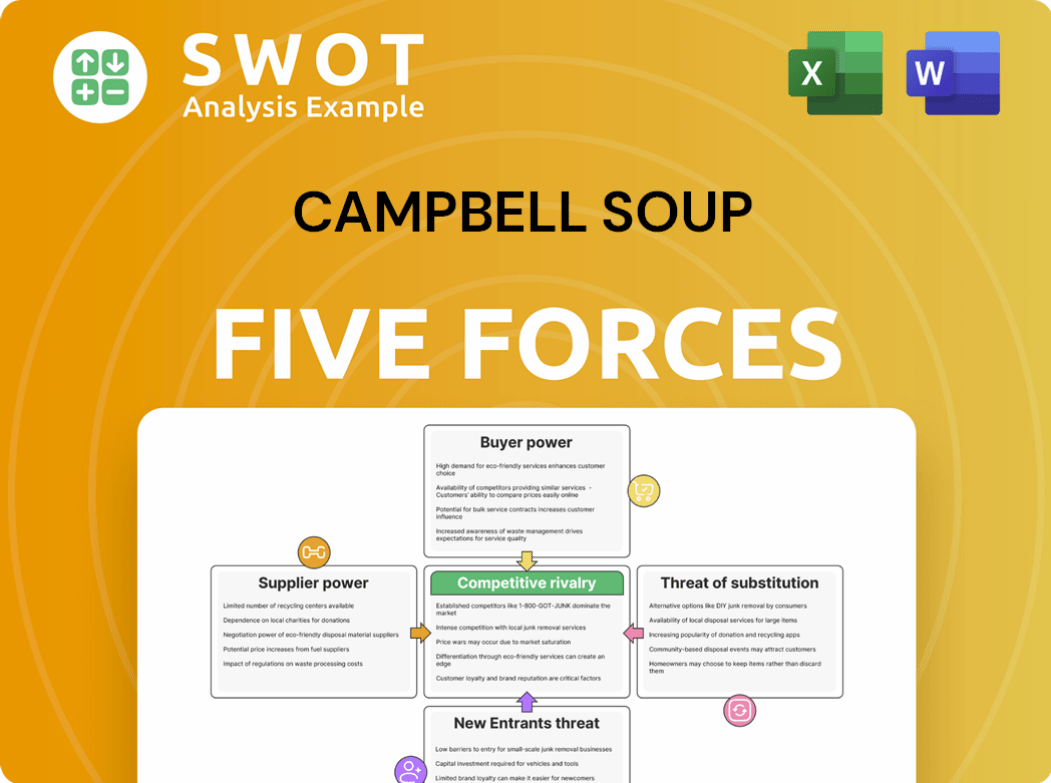
Campbell Soup Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What are Mission Vision & Core Values of Campbell Soup Company?
- What is Competitive Landscape of Campbell Soup Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of Campbell Soup Company?
- How Does Campbell Soup Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of Campbell Soup Company?
- What is Brief History of Campbell Soup Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of Campbell Soup Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.