Ciena Bundle
Who Really Owns Ciena?
Understanding the ownership structure of a company is crucial for investors and stakeholders alike. Knowing Ciena SWOT Analysis can provide insights into its strategic direction and market influence. Ciena Corporation, a leader in optical networking, has a fascinating ownership journey, from its founding in 1992 to its current position in the market.

This exploration into "Who owns Ciena" will uncover the evolution of Ciena's ownership, examining the key players and their impact. From its initial backers to its current major shareholders, we'll dissect the Ciena ownership structure and its influence on the company's trajectory. We'll also investigate the company's financial performance and market share, providing a comprehensive overview of this significant player in the tech industry. Learn about Ciena's history and the individuals and entities that have shaped its destiny.
Who Founded Ciena?
The genesis of the Ciena Corporation, initially named HydraLite, began on November 8, 1992. Electrical engineer David R. Huber spearheaded the venture, envisioning the application of fiber-optic technology for cable television. This marked the beginning of what would become a significant player in the telecommunications sector. Early support and resources were provided by Optelecom, Huber's former employer, and initial capital came from co-founder Kevin Kimberlin.
In 1994, Patrick Nettles, a telecom industry veteran, joined as the first CEO, taking charge of business operations. Nettles, along with Huber, changed the company's name to Ciena. The company's operational base was established in Dallas in February 1994. The founding team also included Larry Huang and Steve Chaddick, forming the core leadership alongside Huber and Nettles.
Early financial backing was crucial for Ciena's growth. The company secured $40 million in venture capital from firms such as Charles River Ventures and Sevin Rosen Funds. Sevin Rosen, in particular, invested $1.25 million in April 1994. The introduction of the MultiWave 1600 Transmission System in May 1996 marked Ciena's entry into the market, with Sprint Corporation as its first customer. By early 1997, a significant portion of Ciena's revenue, about 97%, was concentrated with Sprint and WorldCom, highlighting the early customer base.
Understanding the early stages of Ciena ownership provides insight into its foundational structure and strategic direction. The company's history reveals the roles of key individuals and the significance of early financial backing. The initial vision of David R. Huber, coupled with the expertise of Patrick Nettles, set the stage for Ciena's trajectory in the telecommunications industry.
- David R. Huber: The electrical engineer who founded the company, initially named HydraLite.
- Kevin Kimberlin: Provided initial equity capital, contributing to the company's early financial foundation.
- Patrick Nettles: Joined in early 1994 as the first CEO, crucial in shaping the company's business operations and renaming it Ciena.
- Early Investors: Firms like Charles River Ventures and Sevin Rosen Funds provided significant venture capital, fueling early growth.
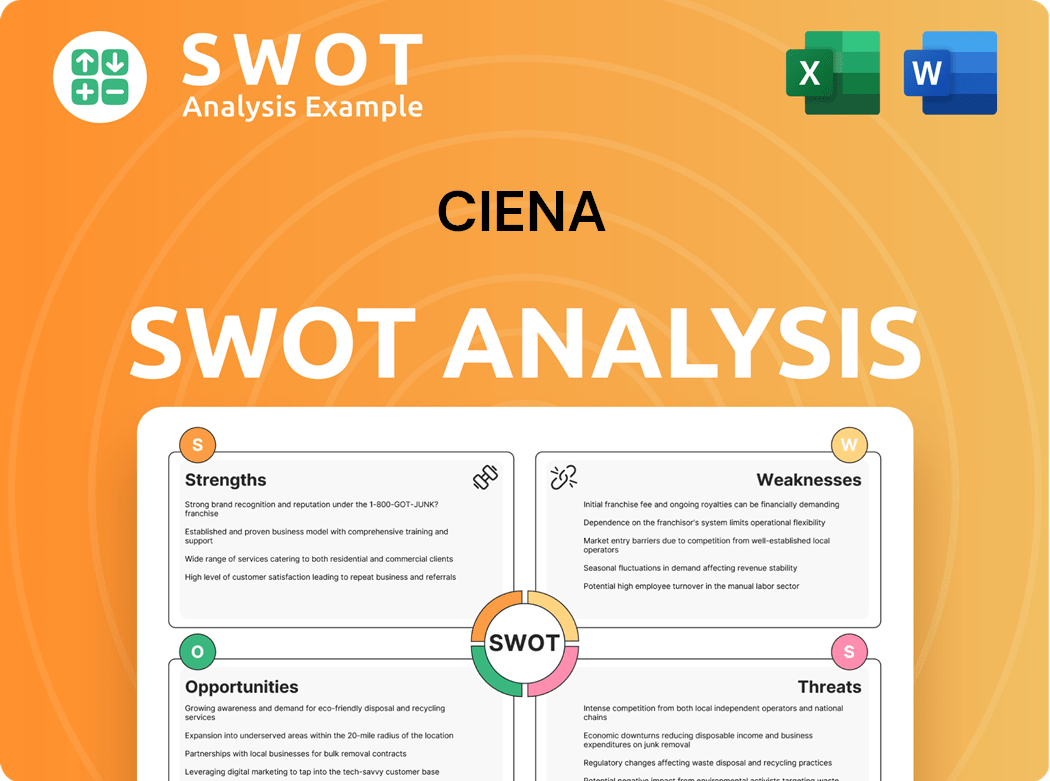
Ciena SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
How Has Ciena’s Ownership Changed Over Time?
The evolution of Ciena's growth strategy has been marked by significant shifts in its ownership structure. Initially, the company's initial public offering (IPO) in February 1997 on NASDAQ was a pivotal moment. This IPO was the largest venture-backed IPO at the time, valuing the company at $3.4 billion on its first day of trading. By June 2000, the company's stock price had risen significantly, trading around $120 per share, with a market capitalization approaching $20 billion.
Over time, the ownership of the
| Shareholder | Shares (as of December 31, 2024) | Percentage of Shares Outstanding (as of December 31, 2024) |
|---|---|---|
| FMR, LLC | 21.53 million | 15.15% |
| Institutional Investors (Total) | Approximately 100.95% (as of October 2024) | N/A |
| Mutual Funds | Increased holdings from 146.21% to 147.28% (as of October 2024) | N/A |
As of December 31, 2024, FMR, LLC was a significant institutional holder of the
Understanding the
- The IPO in 1997 was a major event, transitioning the company from a private to a public entity.
- Institutional investors, such as FMR, LLC, and BlackRock, Inc., hold a significant portion of the shares.
- Strategic acquisitions have shaped the company's focus and influenced its market position.
- The ownership structure continues to evolve, with institutional investors playing a key role.
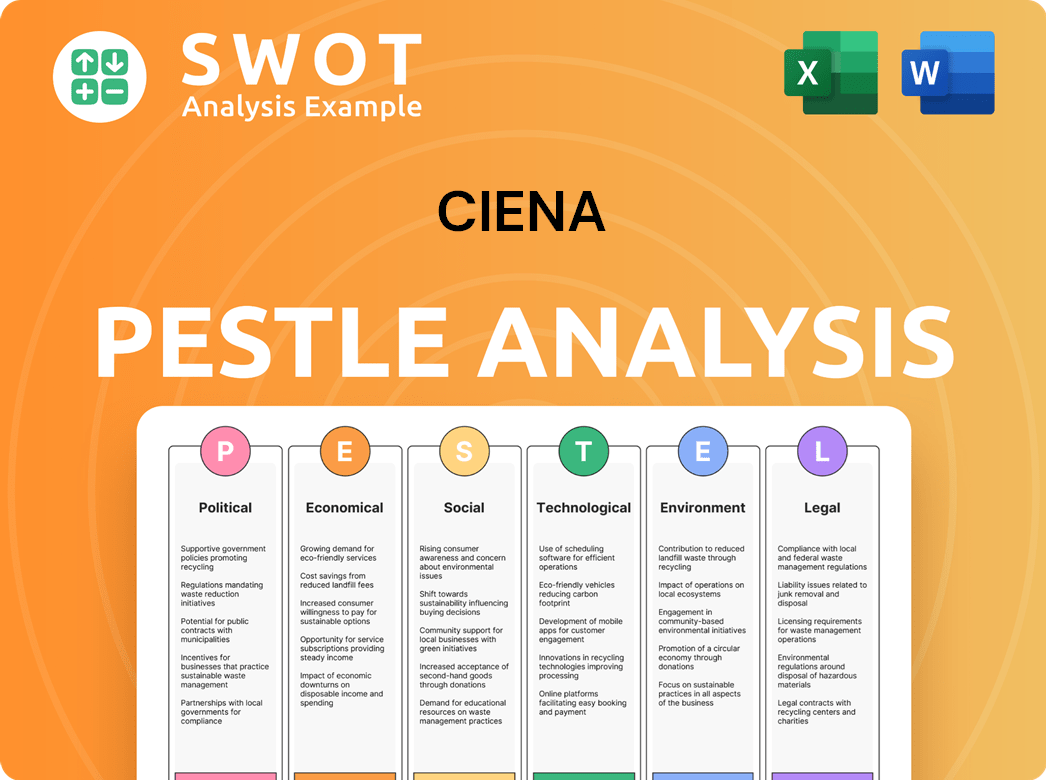
Ciena PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
Who Sits on Ciena’s Board?
The Board of Directors is vital to the governance of the Ciena corporation, guiding its strategic direction and representing the interests of Ciena shareholders. As of December 11, 2024, Lawton W. Fitt became the independent Chair of the Board. Patrick H. Nettles, Ph.D., previously the Executive Chair, stepped down from that role and plans to retire from the Board at the 2025 Annual Meeting of Stockholders. Ms. Fitt has served as a Director since November 2000 and chaired the Audit Committee from October 2004 until December 2024.
The composition of the Board and its committees is detailed in Ciena's filings, such as the DEF 14A filed on February 13, 2025. These documents provide insight into the individuals responsible for overseeing the company's operations and representing the interests of Ciena shareholders. The board's structure and the expertise of its members are crucial for the company's strategic decisions and overall performance. Understanding the board's makeup helps in evaluating the company's leadership and its approach to corporate governance.
| Director | Position | Since |
|---|---|---|
| Lawton W. Fitt | Chair of the Board | 2000 |
| Gary B. Smith | President and CEO | 2016 |
| David M. Anderson | Director | 2018 |
Ciena's voting structure generally follows a one-share-one-vote principle, typical for publicly traded companies. Information about special voting rights or founder shares is not readily available in recent public filings. Shareholders vote on matters like the election of directors and the ratification of the independent registered public accounting firm. The company's annual proxy statements provide detailed information on these voting matters. For more insights into Ciena's approach to the market, you can explore the Marketing Strategy of Ciena.
The Board of Directors is led by Lawton W. Fitt as Chair, with Gary B. Smith as President and CEO. The company's voting structure is straightforward, with one share generally equating to one vote.
- Lawton W. Fitt has been a Director since 2000.
- Shareholders vote on key matters, including director elections.
- The company's governance structure is transparent through its filings.
- Patrick H. Nettles, Ph.D., is retiring from the Board in 2025.
Ciena Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout

What Recent Changes Have Shaped Ciena’s Ownership Landscape?
Recent developments in the Ciena ownership structure reflect the company's strategic financial management. In October 2024, the Board of Directors authorized a stock repurchase program for up to $1 billion, running from fiscal year 2025 through 2027. This decision underscores Ciena corporation's confidence in its financial health and commitment to returning capital to Ciena shareholders. During the initial six months of fiscal year 2025, the company repurchased roughly 2.2 million shares for around $163.5 million. Repurchases in Q1 and Q2 of fiscal 2025 were approximately 1.0 million shares ($79.2 million) and 1.2 million shares ($84.3 million), respectively. Furthermore, in Q4 of fiscal 2024, Ciena repurchased approximately 2.1 million shares for $132 million.
Leadership changes are also underway. James E. Moylan, Jr., the Senior Vice President and Chief Financial Officer, plans to retire in August 2025 after more than 16 years of service. The company is actively seeking his successor. These actions, combined with the ongoing stock repurchase program, highlight Ciena company's dedication to its shareholders and its proactive approach to capital allocation. The company’s strategic focus continues to be on expanding market share, driven by increasing bandwidth demands from cloud and AI developments.
| Fiscal Quarter | Shares Repurchased (approx.) | Cost (USD millions) |
|---|---|---|
| Q4 2024 | 2.1 million | $132 |
| Q1 2025 | 1.0 million | $79.2 |
| Q2 2025 | 1.2 million | $84.3 |
Industry trends indicate a rise in institutional ownership, typical for established public companies like Ciena. The company's financial performance in fiscal Q1 and Q2 2025 has been strong, with Q2 2025 revenue reaching $1.13 billion, compared to $910.8 million in the second quarter of fiscal 2024. Fiscal Q1 2025 revenue was $1.07 billion, a 3.3% increase from the same quarter the previous year. Ciena is optimistic about accelerating revenue growth and expanding market share, leveraging its technological advancements and positive industry dynamics, especially in cloud and AI infrastructure. Further insights into the company’s strategic direction can be found in this article about Growth Strategy of Ciena.
The company authorized a $1 billion stock repurchase program. This program started in fiscal year 2025 and will continue through the end of fiscal year 2027. The program demonstrates Ciena's strong financial position.
James E. Moylan, Jr., CFO, will retire in August 2025. The company is in the process of finding his replacement. This change is part of the company's ongoing evolution.
Q2 fiscal 2025 revenue was $1.13 billion. Q1 fiscal 2025 revenue was $1.07 billion. These results reflect the company's market strength.
Increased bandwidth demands from cloud and AI drive market share expansion. Institutional ownership is a significant trend. Ciena is well-positioned for growth.
Ciena Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked

Related Blogs
- What are Mission Vision & Core Values of Ciena Company?
- What is Competitive Landscape of Ciena Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of Ciena Company?
- How Does Ciena Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of Ciena Company?
- What is Brief History of Ciena Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of Ciena Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.