Deere Bundle
Who Really Controls Deere & Company?
Unraveling the ownership of Deere & Company is key to understanding its future. Knowing who owns John Deere reveals the forces that shape its strategic decisions and long-term vision. This exploration will delve into the intricate ownership structure of this industrial giant, examining the key players and their influence.
From its origins with John Deere's groundbreaking plow to its current status as a global leader, Deere & Company's journey is intertwined with its ownership evolution. Understanding the Deere SWOT Analysis is crucial for investors and analysts. This analysis will examine the major shareholders, the company structure, and the impact of ownership on its operations, providing insights into the forces that drive this iconic company. This deep dive will explore who owns John Deere and how the company's stakeholders shape its future.
Who Founded Deere?
The story of Deere & Company begins with John Deere, a blacksmith who revolutionized agriculture. His invention of the self-scouring steel plow in 1837 was a pivotal moment, laying the foundation for a company that would transform farming practices. This innovation directly addressed the challenges farmers faced, making Deere's initial venture a success.
Initially, John Deere's business operated as a sole proprietorship, with Deere himself funding and managing all aspects of the operation. This early ownership structure meant complete control and personal investment in the company's success. As the business grew, the need for expansion and broader market reach prompted the inclusion of partners.
The evolution of Deere & Company from a sole proprietorship to a formally incorporated entity reflects its growth and increasing complexity. The transition to a corporate structure in 1868, with John Deere as president, marked a significant step. This move set the stage for future growth and potential external investment, shaping the company's trajectory.
John Deere, a blacksmith, founded the company in 1837. He invented the self-scouring steel plow, which was a major innovation.
Early operations were as a sole proprietorship. John Deere personally financed and managed the business.
As the business expanded, Deere brought in partners. This was to increase production and reach more markets.
The company was officially incorporated as Deere & Company. John Deere became the first president.
John Deere's son, Charles Deere, played an increasing role. This ensured continuity of family leadership.
Incorporation formalized the ownership structure. This prepared the company for future growth.
The initial ownership of Deere & Company was solely in the hands of John Deere, reflecting his entrepreneurial spirit and control. The shift to partnerships and, eventually, incorporation, marked a strategic evolution to support growth and expansion. This foundational structure set the stage for the company's future, including its eventual status as a publicly traded entity. Understanding the early ownership structure provides insights into the company's values and the transition from a family-run business to a major player in the agricultural and construction equipment industries. As of December 2024, the company's market capitalization is approximately $110 billion. The company's revenue for fiscal year 2024 was approximately $61.2 billion, with a net income of around $7.5 billion. The company's stock price has fluctuated, but as of early 2025, it remains a significant investment in the industrial sector.
- John Deere was the original John Deere owner and founder.
- Early ownership was a sole proprietorship.
- Partnerships were formed to expand the business.
- The company incorporated in 1868.
- Charles Deere, John Deere's son, played a key role.
Deere SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format

How Has Deere’s Ownership Changed Over Time?
The evolution of Deere Company ownership reflects its journey from a privately held enterprise to a publicly traded global entity. Initially, the company was closely held by its founder, John Deere, and early partners. The transition to public ownership, facilitated by an initial public offering (IPO), was a crucial step. This shift allowed the company to access broader capital markets, fueling its expansion and growth. While specific details about the IPO date and initial market capitalization from the 19th century are not readily available, the move to public markets was a defining moment in its history.
As a publicly traded entity, the ownership structure of John Deere has become more diversified. The majority of shares are now held by institutional investors, mutual funds, and individual shareholders. This transition has significantly altered the dynamics of the company, influencing strategic decisions and emphasizing shareholder value. The shift from a family-owned business to a publicly traded corporation has shaped its governance and financial strategies.
| Event | Impact on Ownership | Year |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Incorporation | Private ownership by John Deere and partners | 1868 |
| Initial Public Offering (IPO) | Transition to public ownership, broader access to capital | Historical, details not readily available |
| Growth and Acquisitions | Increased institutional and individual shareholder base | Ongoing |
In early 2025, the major stakeholders in Deere & Company include large institutional investors. Vanguard Group Inc. and BlackRock Inc. are among the largest institutional holders, reflecting their significant index fund strategies. Other key players often include State Street Corporation and Capital Research Global Investors. These institutional holdings typically represent a substantial percentage of the outstanding shares, often exceeding 70-80%. Individual insider ownership, including executives and board members, constitutes a smaller percentage. This ownership structure emphasizes shareholder value, consistent dividends, and strategic growth initiatives to appeal to a broad investor base. The company's market capitalization fluctuates, but as of early 2025, it remains a significant player in the agricultural and construction equipment industries.
Deere & Company's ownership is primarily held by institutional investors, with Vanguard and BlackRock being major shareholders.
- The company transitioned from private to public ownership through an IPO.
- Institutional investors hold a significant portion, often over 70% of shares.
- Individual insider ownership is a smaller percentage, typical of large public companies.
- The ownership structure influences company strategy, focusing on shareholder value.
Deere PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable

Who Sits on Deere’s Board?
The Board of Directors of the [Company Name] plays a crucial role in the company's governance and strategic oversight. As of early 2025, the board is composed of a mix of independent directors and executive management. The structure typically includes the Chief Executive Officer (who often also serves as Chairman), and a number of independent directors who bring external expertise and oversight. In recent years, the board has included individuals with backgrounds in finance, technology, global business, and manufacturing, ensuring a broad range of perspectives.
The board members are responsible for overseeing the company's operations, ensuring that it is managed effectively, and representing the interests of the shareholders. The board also sets the strategic direction of the company, approves major decisions, and monitors the performance of the executive management team. The composition of the board may change over time due to retirements, appointments, and other factors, but the overall structure and responsibilities remain consistent.
| Board Member | Title | Affiliation (Example) |
|---|---|---|
| John C. May | Chairman and CEO | Deere & Company |
| Denzil E. W. White | Lead Independent Director | Retired Executive |
| Joshua J. V. Rich | Independent Director | Finance Executive |
The voting structure of [Company Name] is generally based on a one-share-one-vote principle. This means that each share of common stock held by an investor typically grants one vote on matters brought before shareholders. There are no known dual-class shares or special voting rights that would grant outsized control to any specific individual or entity. This structure promotes a more equitable distribution of voting power among all shareholders. The board remains responsive to shareholder concerns and corporate governance best practices, regularly engaging with institutional investors on topics ranging from environmental, social, and governance (ESG) initiatives to capital allocation strategies. Understanding the Marketing Strategy of Deere can provide additional insights into the company's operations and stakeholder engagement.
The Board of Directors oversees [Company Name]'s strategic direction.
- The board includes independent directors and executive management.
- Voting is typically one share, one vote.
- The board is responsive to shareholder concerns.
- The board composition can change over time.
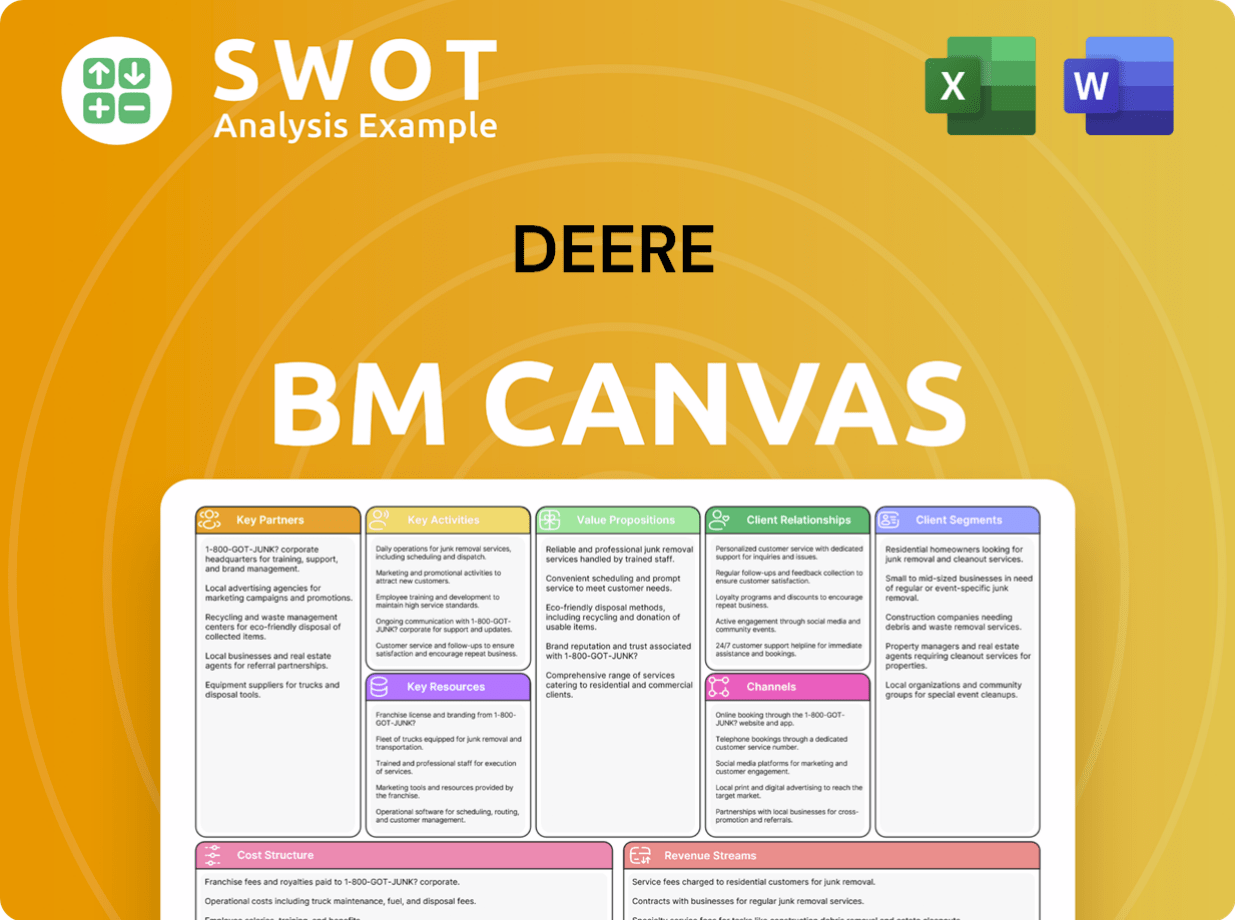
Deere Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
What Recent Changes Have Shaped Deere’s Ownership Landscape?
Over the past few years (2022-2025), the ownership of Deere & Company, often referred to as the John Deere owner, has remained largely stable, with institutional investors continuing to hold a significant portion of the shares. The company has focused on returning value to shareholders through share buyback programs. For example, in fiscal year 2024 and projected into 2025, these programs have been a key part of its capital allocation strategy. This approach aims to reduce the number of outstanding shares, potentially increasing earnings per share and benefiting existing shareholders. There have been no major changes in the company's ownership structure that would significantly dilute existing ownership.
Mergers and acquisitions have been strategic, mainly targeting technology and specific market segments. These moves, such as acquisitions in precision agriculture technology, have integrated new capabilities without fundamentally altering the overall ownership structure of the parent company. Leadership transitions, like CEO role changes, have been internal successions, maintaining continuity and not typically linked to major ownership shifts. Industry trends, such as the rise of passive investing through index funds, continue to influence Deere. These trends highlight the importance of strong corporate governance and consistent financial performance to attract and retain institutional holdings. The company consistently communicates its long-term growth strategies and capital allocation plans to the investor community, reinforcing its commitment to its current public ownership structure. The company's focus remains on delivering value to its shareholders through strategic initiatives and consistent performance.
| Metric | Value | Year |
|---|---|---|
| Market Capitalization (approx.) | $105 Billion | 2024 |
| Institutional Ownership (approx.) | 70% | 2024 |
| Share Repurchases (FY 2024) | $2.5 Billion | 2024 |
The company's commitment to its current ownership structure is evident in its consistent communication of long-term strategies and capital allocation plans to the investor community. This reinforces its dedication to delivering value and maintaining its public status. The primary stakeholders of Deere & Company continue to be institutional investors who value the company's strong performance and strategic direction.
The majority of Deere & Company is owned by institutional investors. These include large investment firms, mutual funds, and pension funds. The company is a public company, meaning its shares are traded on the stock market.
Deere & Company operates as a publicly traded corporation. This structure allows for diverse ownership and access to capital markets. The company's board of directors oversees operations and strategic direction.
Major shareholders include large institutional investors such as The Vanguard Group, BlackRock, and State Street Corporation. These firms hold significant portions of the company's outstanding shares.
As of late 2024, the market capitalization of Deere & Company is approximately $105 billion. This figure fluctuates based on the company's stock price and overall market conditions.
Deere Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked

Related Blogs
- What are Mission Vision & Core Values of Deere Company?
- What is Competitive Landscape of Deere Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of Deere Company?
- How Does Deere Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of Deere Company?
- What is Brief History of Deere Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of Deere Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.