Everest Bundle
Who Really Controls Everest Company?
Ownership is the lifeblood of any company, dictating its future and shaping its strategies. For Everest, a leading UK home improvement provider, understanding its ownership is key to unlocking its story. From its founding in 1964 to its recent acquisition, Everest's journey reveals the critical role of ownership in navigating market challenges and seizing opportunities.
This analysis dives deep into Everest SWOT Analysis, exploring the evolution of its ownership, from its founders to its current stakeholders. We'll uncover how changes in the Everest Company ownership structure, including the influence of key shareholders and management, have shaped its strategic direction and financial performance. Discover the answers to questions like: Who owns Everest? What is the Everest company owner's vision? and how has the Everest company history impacted its current standing in the market? This exploration provides a comprehensive understanding of Everest's ownership and its implications.
Who Founded Everest?
The company, founded in 1964, emerged from a collective of entrepreneurs who spotted an opportunity in the nascent market for factory-built double glazing. The initial ownership structure was likely a closely held private entity, typical of businesses during that period. Specifics on the exact equity split at the start are not publicly available.
The founders' vision was to revolutionize home improvement, offering superior insulation and security through innovative window and door designs. This directly challenged traditional carpentry methods. Early financial backing probably came from the founders themselves, possibly supplemented by small angel investments or loans from friends and family. These funds were crucial for scaling manufacturing and establishing a direct sales force.
Early agreements among the founders would have focused on operational control and profit-sharing. Vesting schedules, though common in later tech startups, might have been less formal. Buy-sell clauses were essential to manage potential founder exits or disputes, ensuring business continuity. The founding team's goal of a vertically integrated model—controlling manufacturing, sales, and installation—was intrinsically tied to their shared control.
Understanding the early ownership of the company provides context for its later development. The focus was on building a strong foundation for the business. The early structure was designed to maintain quality and customer satisfaction.
- The early ownership structure was likely a closely held private entity.
- The founders aimed for a vertically integrated model to control quality.
- Early funding came from founders and potentially small investments.
- Agreements focused on operational control and profit-sharing.
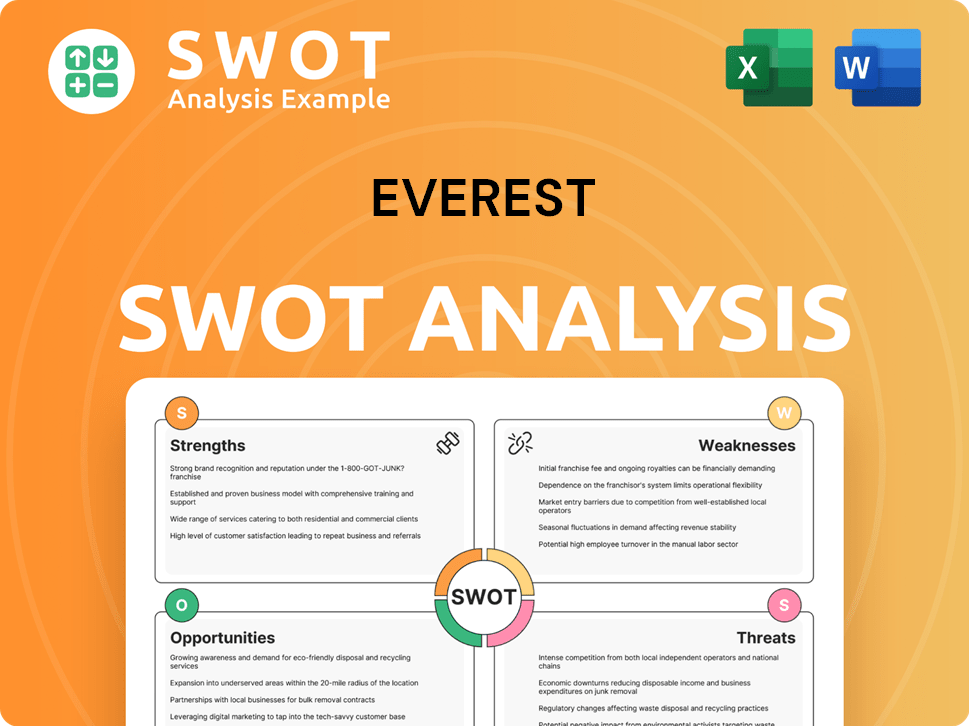
Everest SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
How Has Everest’s Ownership Changed Over Time?
The Everest Company ownership structure has seen notable shifts, particularly in recent years. Initially a private entity, the company's ownership details were not always publicly available. A critical juncture arrived in 2020 when the company entered administration. This led to its acquisition by Better Capital, a private equity firm, through its vehicle, Everest 2020 Limited. This transaction transferred ownership and control to Better Capital, aimed at restructuring and revitalizing the business.
Before the Better Capital acquisition, ownership belonged to Sun European Partners, a private equity firm that had acquired the company in 2012. Better Capital's involvement brought a new focus on stabilizing the company and implementing a turnaround strategy. As of early 2024, Better Capital remains the primary stakeholder, exercising significant control over strategic and financial decisions, although specific percentage holdings are not publicly disclosed. Other stakeholders may include lenders or investment vehicles involved in the restructuring. This change in Everest company owner was vital for the company's survival, influencing recent operational adjustments and market strategies. To learn more about the company's growth strategy, read Growth Strategy of Everest.
| Ownership Timeline | Key Events | Stakeholders |
|---|---|---|
| Pre-2012 | Private Company | Private Investors |
| 2012 | Acquired by Sun European Partners | Sun European Partners |
| 2020 | Entered Administration, Acquired by Better Capital | Better Capital (Everest 2020 Limited) |
| Early 2024 | Ongoing Operations under Better Capital | Better Capital, Lenders (potential) |
The Everest Company ownership has transitioned significantly, primarily from private investors to private equity firms. The most recent change involved Better Capital's acquisition in 2020, which continues to be the primary owner as of early 2024.
- Better Capital is the current primary stakeholder.
- Sun European Partners previously held ownership.
- The company's history includes private ownership.
- The 2020 acquisition was a crucial turning point.
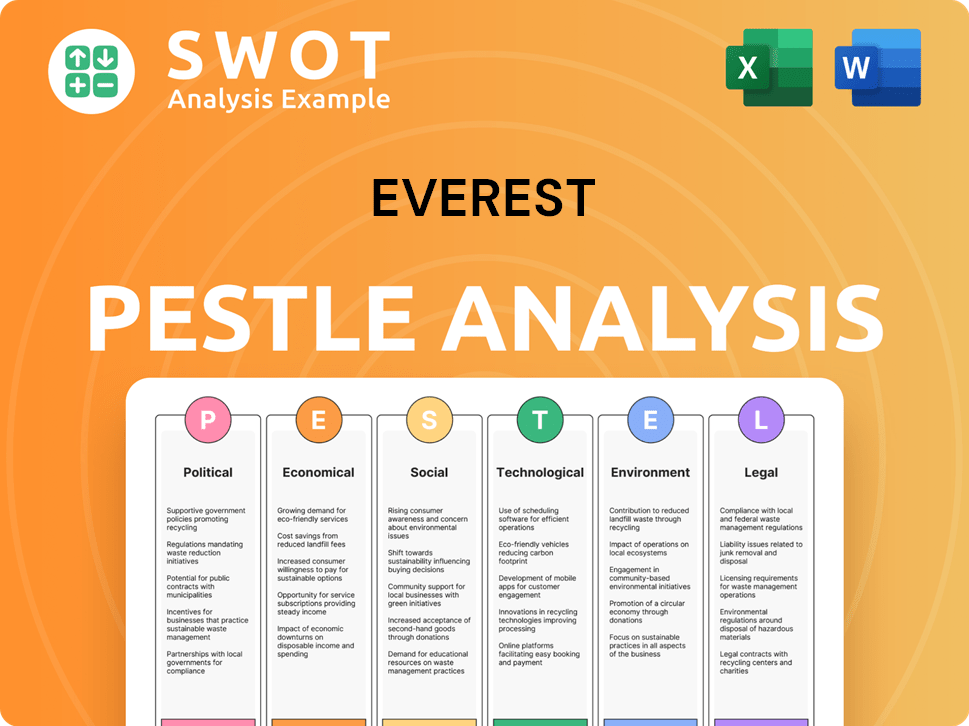
Everest PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
Who Sits on Everest’s Board?
The current board of directors for the Everest Company reflects its private ownership structure under Better Capital. While a comprehensive public list of board members and their affiliations isn't readily available for private companies, it's highly probable that the board includes representatives from Better Capital, independent directors with industry expertise, and potentially key executives of Everest. Given Better Capital's ownership, their representatives on the board would hold significant voting power, aligning with their investment objectives and strategic vision for the company. Information about the Everest Company owner is typically not disclosed to the public due to its private nature.
The Everest Company ownership structure, as a private equity-owned entity, typically grants substantial control to the primary investor. This means Better Capital, through its board representation and direct ownership, would effectively control major strategic decisions, including significant investments and executive appointments. The Everest Company management structure is designed to align with the financial and operational goals set by Better Capital, aiming to maximize the value of their investment. For more information on the company's operations, you can read about the Revenue Streams & Business Model of Everest.
Better Capital, as the primary owner, likely has significant influence over Everest's strategic direction.
- Board representation from Better Capital ensures alignment with their investment goals.
- Major decisions, such as investments and executive appointments, are likely controlled by Better Capital.
- The Everest Company ownership structure is designed to maximize the value of Better Capital's investment.
- Due to the private nature of the company, information about the Everest Company shareholders is not typically public.
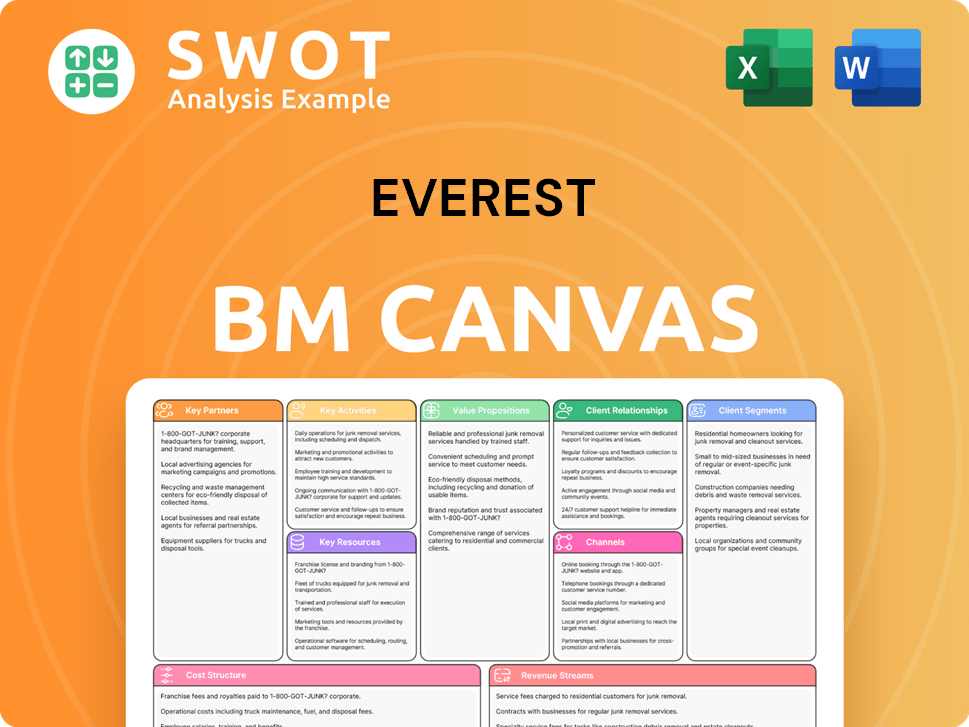
Everest Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
What Recent Changes Have Shaped Everest’s Ownership Landscape?
The recent history of the company's ownership, over the past few years, has been marked by a significant shift. In 2020, the company underwent administration. This led to its acquisition by Better Capital. This change was a direct result of financial difficulties, influenced by market conditions and earlier ownership challenges. The acquisition by Better Capital was a strategic move to stabilize and rebuild the business. The primary focus has been on improving operational efficiencies and fostering market recovery.
In the home improvement sector, there's a trend toward increased institutional ownership. Private equity firms often acquire companies to streamline operations and achieve economies of scale. For the company, the recent change of control is more about a complete ownership change rather than gradual dilution. Given that the company is privately held, the influence of activist investors is not a major factor. As of early 2024, there have been no public statements about future ownership changes or potential privatization, with the current focus on strengthening its market position.
The most significant recent development in the company's ownership is the 2020 acquisition by Better Capital. This followed a period of financial challenges, highlighting the dynamic nature of ownership in response to market pressures. The current ownership structure is focused on operational improvements and market stabilization.
The home improvement sector is seeing more institutional investment. Private equity firms are actively involved in acquisitions to optimize operations. The company's ownership structure reflects this trend, with a focus on strategic management and market positioning. This contrasts with the role of activist investors, who are typically more involved with publicly traded companies.
Everest Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What are Mission Vision & Core Values of Everest Company?
- What is Competitive Landscape of Everest Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of Everest Company?
- How Does Everest Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of Everest Company?
- What is Brief History of Everest Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of Everest Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.