Infosys Bundle
Who Really Owns Infosys?
Ever wondered who steers the ship at one of the world's leading IT giants? Understanding the Infosys SWOT Analysis is crucial, but first, let's dive into the heart of its control. The ownership structure of Infosys, a company that began in India, is a fascinating interplay of founders, institutional investors, and public shareholders. Knowing the answer to "Who Owns Infosys Company?" unveils the forces shaping its future.

The question of Infosys ownership is more than just a matter of shares; it's a window into the company's strategic direction and long-term vision. Examining the Infosys shareholders and Infosys parent company reveals how decisions are made and value is distributed. From the Infosys founder to the current institutional players, the evolution of Infosys ownership tells a compelling story of growth and influence, impacting the Infosys stock and its overall performance.
Who Founded Infosys?
The genesis of Infosys is rooted in the vision of seven co-founders: N. R. Narayana Murthy, Nandan Nilekani, S. Gopalakrishnan, S. D. Shibulal, K. Dinesh, Ashok Arora, and N. S. Raghavan. These individuals pooled their personal savings to establish the company, with an initial capital of just US$250. This humble beginning laid the foundation for what would become a global IT services giant.
In the early days, the ownership of Infosys was largely concentrated among the founders. While the precise equity distribution at the outset isn't fully detailed in public records, the founders collectively held the majority of shares. This structure reflected their shared commitment and vision for the company. N. R. Narayana Murthy, as the first CEO, played a crucial role in shaping the company's initial direction and culture.
The early ownership structure of Infosys was characterized by a tight-knit group of founders and their immediate families. There were no significant external investors or large-scale investments from angel investors during the initial phase. The founders primarily self-funded the venture, which allowed them to maintain greater control and align the company's values with their vision. Agreements among the founders emphasized building a strong, ethical, and meritocratic organization.
The company was founded by seven individuals, each contributing to the initial capital and vision.
The founders started with a modest initial investment of US$250, demonstrating their commitment.
Ownership was primarily held by the founders and their families in the early stages.
Early agreements emphasized building a strong, ethical, and meritocratic organization.
N. R. Narayana Murthy, as the first CEO, set the company's initial direction.
Some founders departed over time, but these transitions were generally amicable.
The evolution of Infosys's ownership structure has been a key part of its history. The initial tight-knit group of founders gradually saw their collective stake diluted as the company grew and eventually went public. While specific details of early vesting schedules are not widely publicized, the long-term commitment of the founders was evident in their sustained involvement. Over time, some founders departed, such as Ashok Arora, but these transitions were generally smooth and did not lead to major disputes. Today, understanding the Growth Strategy of Infosys provides further insights into the company's trajectory. As of the latest available data, Infosys has a market capitalization of approximately $75 billion USD, and the major shareholders include institutional investors and the founding families, reflecting the company's journey from a startup to a global IT leader. The current Infosys share price and stock performance continue to be closely watched by investors globally, highlighting the ongoing interest in Infosys ownership and its future.
The early ownership structure of Infosys was crucial to its initial success and culture.
- The founders' commitment and self-funding were instrumental.
- The focus on ethical practices and meritocracy set a strong foundation.
- The gradual dilution of the founders' stake occurred as the company expanded.
- The company's history and ownership structure are key factors for investors.
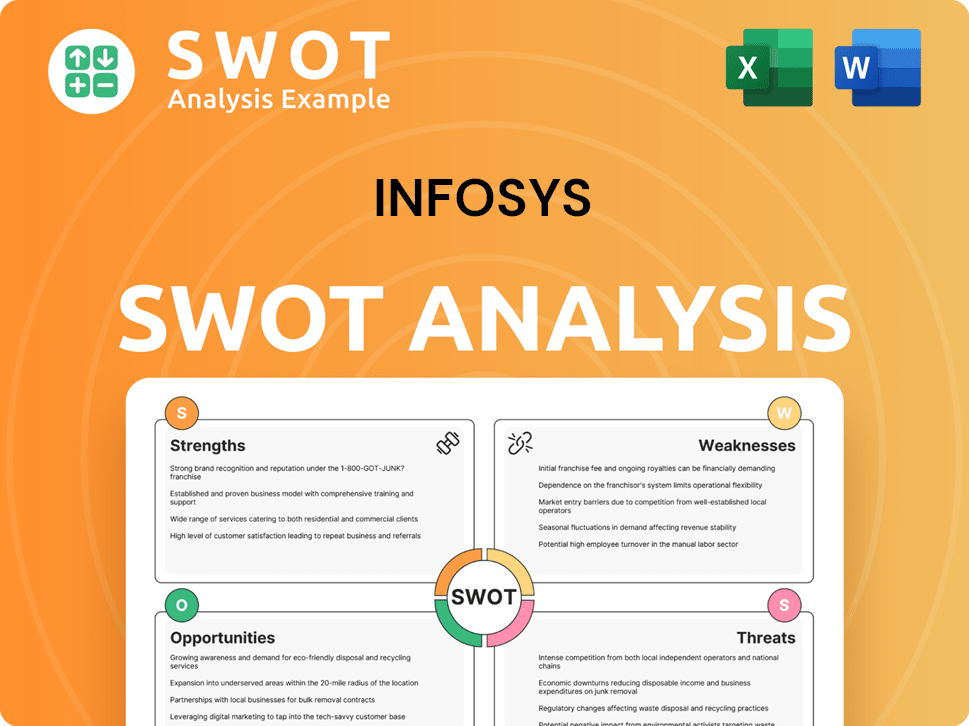
Infosys SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
How Has Infosys’s Ownership Changed Over Time?
The evolution of Infosys's ownership has been marked by key milestones. The company's initial public offering (IPO) in India in 1993 was a critical turning point, opening its shares to public shareholders. Initially, the IPO faced challenges but was supported by Morgan Stanley, which signaled early institutional interest. Further expanding its global presence, Infosys listed on the NASDAQ in 1999, becoming the first Indian company to achieve this, broadening its investor base internationally.
Today, the ownership of Infosys is primarily divided among promoters (founders and their families), institutional investors, and the public. The promoter group's stake has gradually decreased over time, a common trend for publicly traded companies. As of March 31, 2025, the promoter holding was approximately 14.78%. This shift reflects the company's growth and its increasing reliance on capital markets.
| Ownership Category | As of March 31, 2025 | Approximate Percentage |
|---|---|---|
| Promoters | Founders and their families | 14.78% |
| Institutional Investors | Mutual funds, FPIs, insurance companies | Over 50% |
| Foreign Portfolio Investors (FPIs) | Various | Around 33.78% |
| Domestic Institutional Investors (DIIs) | Various | Approximately 22.38% |
| Public | Retail investors | Around 28.76% |
Major stakeholders in Infosys include a wide array of institutional investors such as mutual funds and foreign portfolio investors. These investors collectively hold a significant portion of the company's shares. For instance, Foreign Portfolio Investors (FPIs) held around 33.78% of Infosys as of March 31, 2025, and Domestic Institutional Investors (DIIs) held approximately 22.38%. The public, including individual retail investors, holds the remaining shares, which was around 28.76% as of March 31, 2025. These shifts towards institutional ownership have generally been viewed as a sign of maturity and increased market confidence, influencing company strategy towards greater transparency and shareholder value creation. To understand more about the company's financial structure, you can explore the Revenue Streams & Business Model of Infosys.
Infosys's ownership structure has evolved significantly since its IPO in 1993.
- The promoter group's stake has decreased over time.
- Institutional investors hold a significant portion of the shares.
- Public shareholders also play a key role in Infosys ownership.
- The company's history includes a NASDAQ listing in 1999.
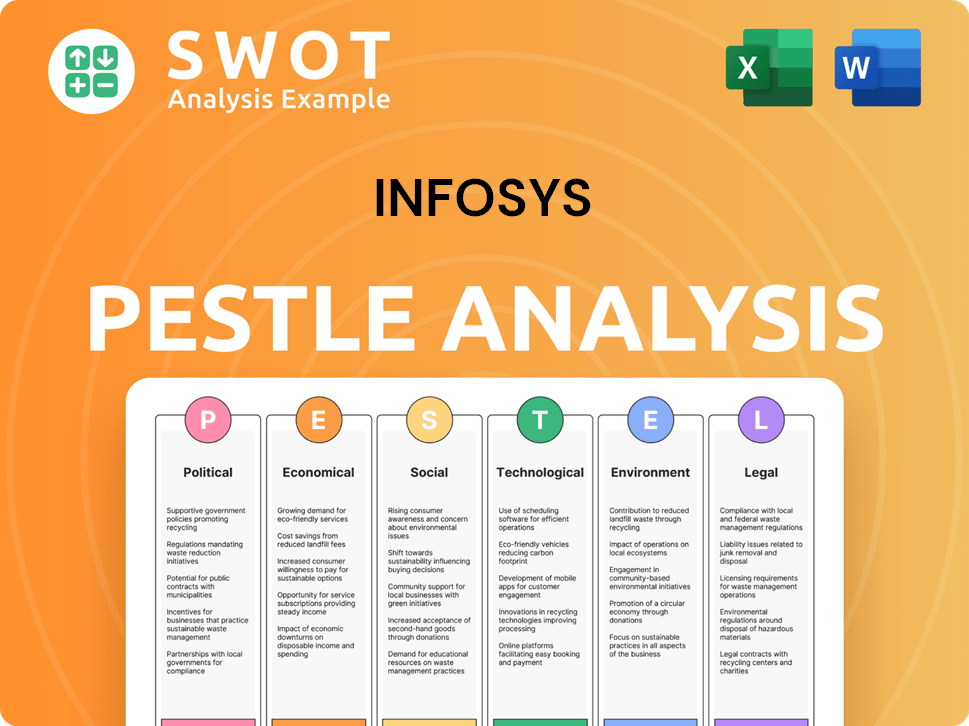
Infosys PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
Who Sits on Infosys’s Board?
The current Board of Directors at Infosys, as of early 2025, includes a mix of executive, non-executive, and independent directors. Key members include Salil Parekh, serving as the CEO & MD, and Nilanjan Roy, the CFO. Independent directors such as D. Sundaram, Chitra Nayak, and Bobby Parikh also play crucial roles. Nandan Nilekani currently holds the position of Non-Executive Chairman, providing strategic oversight. The board's composition reflects a commitment to good corporate governance, aiming to balance the interests of various stakeholders, including the founders, institutional investors, and the broader shareholder base. Understanding the Target Market of Infosys is also important in understanding the company's overall strategy.
The presence of independent directors is intended to ensure balanced decision-making and protect the interests of all shareholders. While founders like N. R. Narayana Murthy have had involvement in the past, the current structure emphasizes a diversified leadership approach. This structure is designed to maintain a balance between the influence of the founding members, the interests of large institutional investors, and the broader shareholder base. The company's commitment to good corporate governance is evident in its board composition and voting structure.
| Board Member | Role | Details |
|---|---|---|
| Salil Parekh | CEO & MD | Oversees the company's overall operations and strategic direction. |
| Nilanjan Roy | CFO | Manages the company's financial activities and reporting. |
| Nandan Nilekani | Non-Executive Chairman | Provides strategic oversight and guidance to the board. |
Infosys operates on a one-share-one-vote voting structure, typical for publicly traded companies. This structure ensures that voting power is directly proportional to the number of shares held, with no known dual-class shares or special voting rights. This approach promotes transparency and fairness among the Infosys shareholders. The company's history includes periods of public scrutiny regarding governance and leadership transitions, which have been addressed through internal processes and board decisions.
Infosys is a publicly traded company, meaning its stock is available for purchase on stock exchanges. The Infosys ownership structure is primarily based on a one-share-one-vote system. This structure ensures that voting power is directly proportional to the number of shares held by each shareholder.
- Infosys founder, N. R. Narayana Murthy, played a key role in the company's early years.
- The company has a significant number of institutional investors among its Infosys shareholders.
- Understanding the Infosys company ownership structure is crucial for investors.
- The current Infosys stock performance reflects the company's overall financial health.
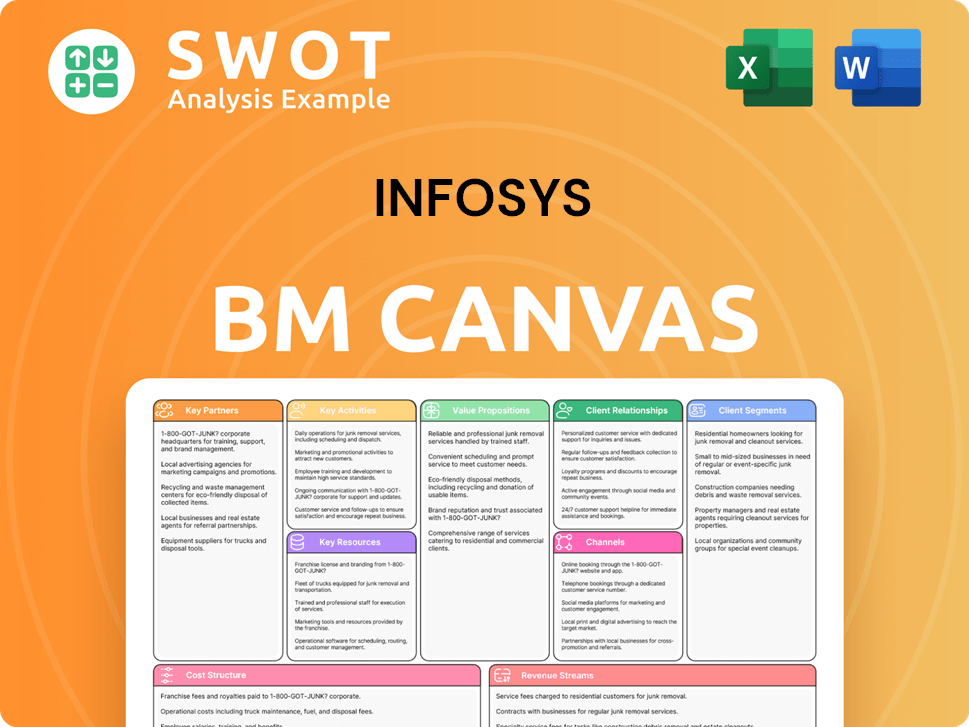
Infosys Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
What Recent Changes Have Shaped Infosys’s Ownership Landscape?
Over the past few years (2022-2024), the Infosys ownership structure has remained relatively stable. There haven't been any significant share buybacks or major secondary offerings that drastically changed the ownership profile. The company has consistently maintained a dividend payout policy, impacting shareholder returns but not the fundamental ownership percentages. This stability reflects the company's mature status and its position within the IT services sector.
A notable trend is the gradual dilution of the promoter group's holdings, a natural occurrence as the company's market capitalization grows. While the Infosys founder and key figures, like Nandan Nilekani, remain influential, their direct equity ownership represents a smaller percentage compared to the company's early days. Simultaneously, there's been an increase in institutional ownership, particularly from foreign portfolio investors. This reflects a broader industry pattern where stable technology companies become integral parts of institutional portfolios. The company has not experienced any major mergers or acquisitions that significantly altered its overall ownership structure.
| Shareholder Type | Approximate Ownership (as of late 2024) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Promoters | ~13-14% | Includes founders and related entities. |
| Institutional Investors | ~60-65% | Primarily foreign portfolio investors, mutual funds, and other institutional entities. |
| Public/Retail Investors | ~23-25% | Includes individual shareholders. |
Looking ahead, the focus remains on shareholder value creation through organic growth and strategic acquisitions, rather than major ownership shifts. Institutional investors are expected to remain the dominant shareholding group, reflecting Infosys's strong market position and performance. For a broader understanding of the competitive environment, you can explore the Competitors Landscape of Infosys.
The ownership structure of Infosys is primarily composed of institutional investors, promoters, and public shareholders. Institutional investors hold the largest share, followed by the promoters, and then the general public. This structure reflects a mature, publicly traded company.
The major shareholders of Infosys include institutional investors like mutual funds and foreign portfolio investors. The promoter group, including the founders, also holds a significant portion of the shares. Public shareholders make up the remainder of the ownership.
The ownership structure influences Infosys's strategic decisions and overall performance. Institutional investors often prioritize long-term value creation, which can influence the company's focus on sustainable growth. The promoter group's involvement ensures continuity and a focus on the company's core values.
Future trends suggest a continued focus on institutional ownership and stable ownership patterns. The company is expected to maintain its current dividend payout policy, which impacts shareholder returns. No major shifts in ownership are anticipated, indicating a focus on organic growth and strategic acquisitions.
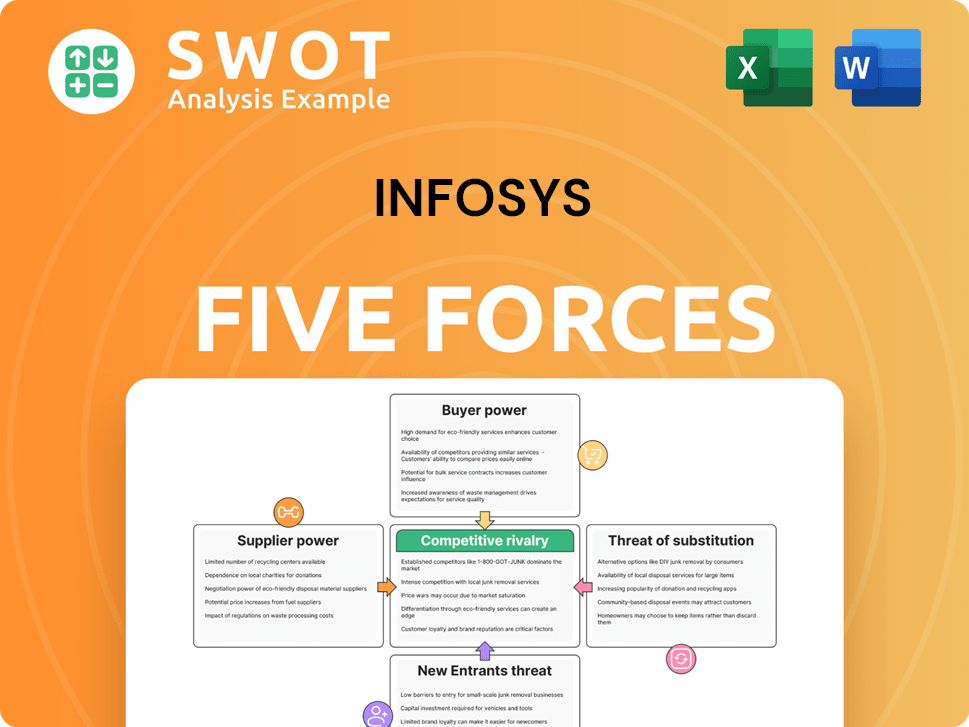
Infosys Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What are Mission Vision & Core Values of Infosys Company?
- What is Competitive Landscape of Infosys Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of Infosys Company?
- How Does Infosys Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of Infosys Company?
- What is Brief History of Infosys Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of Infosys Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.