Lennar Bundle
Who Really Owns Lennar Corporation?
Understanding the ownership structure of a giant like Lennar Corporation is crucial for investors and strategists alike. With the recent spin-off of Millrose Properties in February 2025, the landscape of Lennar SWOT Analysis and its strategic direction has been significantly reshaped. This deep dive explores the evolution of Lennar's ownership, from its founding to its present-day status as a leading homebuilder.
Founded in 1954, Lennar's journey from F&R Builders to a nationwide powerhouse offers valuable insights. This exploration will uncover who owns Lennar, examining the influence of major shareholders, the roles of key executives, including the Lennar CEO, and the impact of its publicly traded status on its strategic decisions. Discover the answers to questions like "Is Lennar a publicly traded company?" and "Who are the major shareholders of Lennar?"
Who Founded Lennar?
The story of Lennar Corporation, a prominent player in the homebuilding industry, begins with its founders and early ownership structure. Understanding the initial setup provides crucial context for analyzing the company's evolution and current standing. This foundational phase set the stage for Lennar's growth and its eventual position in the market.
Lennar's roots trace back to 1954 when Gene Fisher and Arnold Rosen established F&R Builders in Miami, Florida. This marked the initial venture into the homebuilding sector. However, the landscape of Lennar ownership shifted significantly in 1956.
A pivotal moment occurred when Leonard Miller, a young entrepreneur with 42 lots in Miami-Dade County, invested $10,000 and joined the company, effectively replacing Gene Fisher. This partnership between Miller and Rosen became central to the company's direction. The name 'Lennar,' a combination of their first names, was adopted in 1971, solidifying their roles.
Leonard Miller's $10,000 investment in 1956 was a crucial early financial move.
The collaboration between Leonard Miller and Arnold Rosen shaped the company's vision.
Lennar went public in 1971, raising $8.7 million.
Lennar was listed on the New York Stock Exchange in 1972.
Arnold Rosen's continued role as a director post-retirement indicates the founding team's lasting impact.
By 1969, F&R Builders had an equity base of $1 million.
The evolution of Lennar ownership from its founding to its public listing provides insight into the company's early trajectory. By 1969, F&R Builders had built an equity base of $1 million. In 1971, Lennar Corporation was formally established, with F&R Builders as its primary asset. The company's initial public offering in 1971 raised $8.7 million. Lennar's Lennar stock was subsequently listed on the New York Stock Exchange in 1972. While specific details on early agreements are not publicly available, the partnership between Miller and Rosen was key. Arnold Rosen retired in 1977 but remained a director. For further insights into the company's strategic growth, consider reading about the Growth Strategy of Lennar.
The early ownership structure of Lennar Corporation was critical to its initial success and future direction.
- Gene Fisher and Arnold Rosen founded F&R Builders in 1954.
- Leonard Miller joined in 1956, replacing Gene Fisher.
- The company went public in 1971, raising $8.7 million.
- Lennar was listed on the NYSE in 1972.
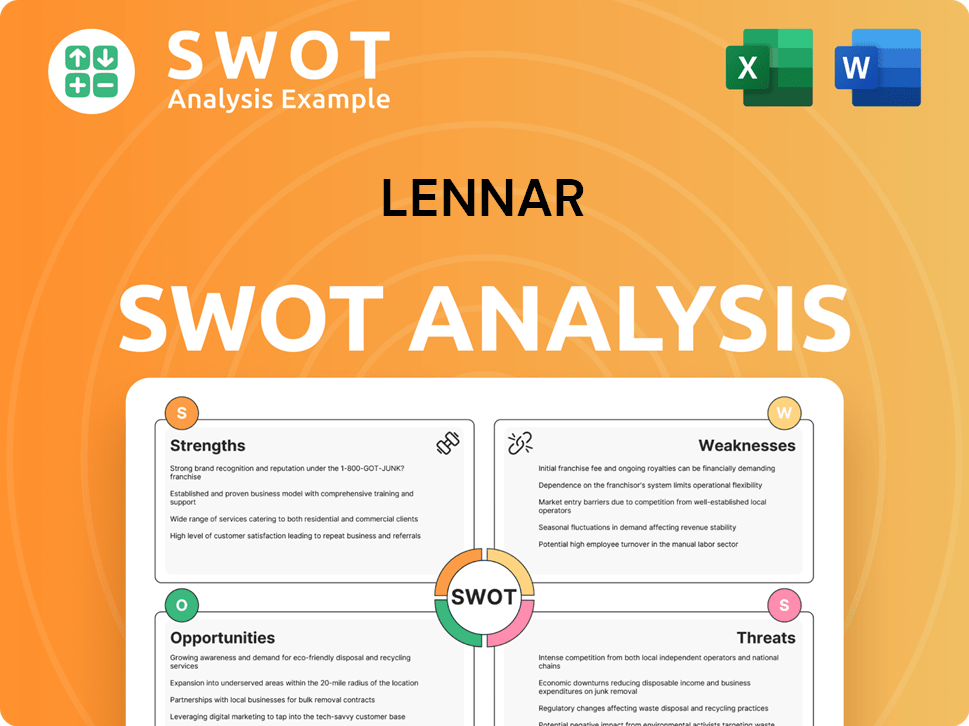
Lennar SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
How Has Lennar’s Ownership Changed Over Time?
The ownership structure of Lennar Corporation has evolved significantly since its initial public offering (IPO) in 1971. The company's stock was listed on the New York Stock Exchange in 1972. Throughout the 1980s and 1990s, Lennar expanded through organic growth and strategic acquisitions, including Pacific Greystone Corporation in 1997. A pivotal acquisition in 2000 was U.S. Home Corporation, which substantially increased Lennar's operations across multiple states. Further acquisitions of regional homebuilders occurred between 2002 and 2005. The 2018 merger with CalAtlantic Group, Inc., further solidified its position as a leading homebuilder, impacting the overall ownership landscape.
As of November 30, 2024, Lennar reported total assets of $41.31 billion and total equity of $27.87 billion. The company's structure includes two classes of common stock: Class A (LEN) and Class B (LEN.B) shares. As of December 31, 2024, there were 233,511,543 shares of Class A common stock and 32,009,014 shares of Class B common stock outstanding. In April 2024, the figures were 244,864,557 shares of Class A common stock and 33,283,143 shares of Class B common stock outstanding. The aggregate market value of Class A and Class B common stock held by non-affiliates was approximately $39.68 billion as of May 31, 2024, reflecting the market's perception of Lennar's value.
| Key Dates | Event | Impact on Ownership |
|---|---|---|
| 1971 | Initial Public Offering (IPO) | Began public ownership |
| 1972 | Listed on NYSE | Increased accessibility to investors |
| 1997 | Acquisition of Pacific Greystone Corporation | Expanded operations and shareholder base |
| 2000 | Acquisition of U.S. Home Corporation | Significant expansion of operations |
| 2018 | Merger with CalAtlantic Group, Inc. | Consolidated market position, changed shareholder composition |
| February 2025 | Millrose Properties spin-off | Strategic shift towards asset-light model |
Major stakeholders in Lennar Corporation typically include institutional investors, mutual funds, and individual insiders. While specific updated percentages for all major institutional holders are not readily available, public companies like Lennar see significant ownership by large asset managers and investment funds. For more insights into the company's strategic moves, consider reading about the Growth Strategy of Lennar. SEC filings (13D and 13G) provide detailed ownership reports, offering insights into major shareholding shifts. The strategic shift towards an 'asset-light, land-light' model, culminating in the Millrose Properties spin-off in February 2025, has significantly affected its strategy and governance by reducing capital intensity and balance sheet risk. This repositioning aims to enhance financial flexibility and potentially unlock greater shareholder value.
Lennar Corporation is a publicly traded company with a history of strategic acquisitions. The company has two classes of common stock, Class A and Class B. The market value of the company's stock held by non-affiliates was approximately $39.68 billion as of May 2024.
- Institutional investors and mutual funds are major shareholders.
- The company's stock symbols are LEN (Class A) and LEN.B (Class B).
- Lennar's headquarters are located in Miami, Florida.
- The company's business model focuses on homebuilding and financial services.
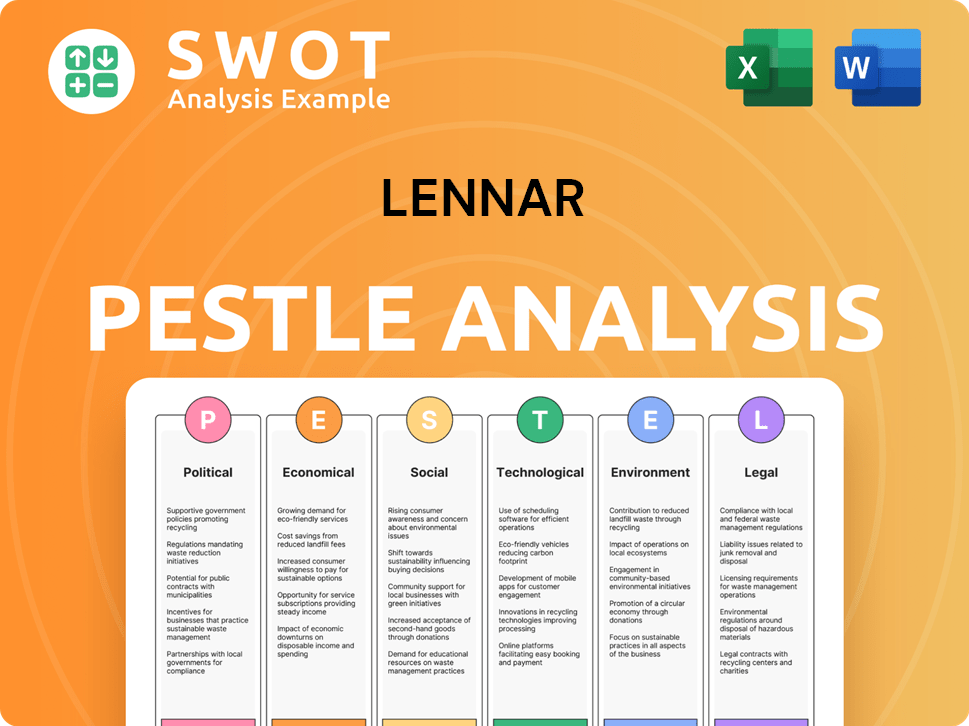
Lennar PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
Who Sits on Lennar’s Board?
The current Board of Directors of Lennar Corporation plays a crucial role in the company's governance and strategic direction. As of January 13, 2025, the Board determined to reduce its size from eleven members to ten members, effective upon the expiration of Sidney Lapidus's term at the 2025 Annual Meeting of Stockholders. Armando Olivera was appointed as Lead Director effective April 10, 2024. The Board includes a mix of individuals representing major shareholders, founders, and independent seats. Stuart Miller, the son of co-founder Leonard Miller, serves as Executive Chairman and Co-Chief Executive Officer and is a member of the board of directors. Jonathan M. Jaffe is also a Co-Chief Executive Officer, President, and Director.
Other independent directors include Amy L. Banse, Theron I. Gilliam, Sherrill W. Hudson, Teri Plummer McClure, Armando J. Olivera, Dacona Smith, Jeffrey Sonnenfeld, and Serena Wolfe. Serena Wolfe was appointed to the Audit Committee effective January 9, 2024, and Dacona Smith was appointed to the Compensation Committee effective the same date. Understanding who owns Lennar and the composition of its board is crucial for investors. The company's structure, including the presence of both Class A and Class B common stock, suggests potential differences in voting power, which is important for those interested in Lennar stock. For a broader understanding, consider reviewing the Competitors Landscape of Lennar.
| Board Member | Title | Appointment Date |
|---|---|---|
| Stuart Miller | Executive Chairman and Co-Chief Executive Officer | N/A |
| Jonathan M. Jaffe | Co-Chief Executive Officer, President, and Director | N/A |
| Amy L. Banse | Independent Director | N/A |
| Theron I. Gilliam | Independent Director | N/A |
| Sherrill W. Hudson | Independent Director | N/A |
| Teri Plummer McClure | Independent Director | N/A |
| Armando J. Olivera | Lead Director | April 10, 2024 |
| Dacona Smith | Independent Director | N/A |
| Jeffrey Sonnenfeld | Independent Director | N/A |
| Serena Wolfe | Independent Director | January 9, 2024 |
Lennar Corporation has Class A and Class B common stock. The existence of two classes of shares often implies different voting powers, with Class B shares typically held by insiders or founders carrying greater voting weight to maintain control. The company engages regularly with stockholders, speaking with those representing approximately 75% of its non-affiliated outstanding shares during fiscal 2024 on topics including executive compensation and corporate governance. There are no recent public reports of proxy battles or activist investor campaigns that have significantly shaped decision-making within the past year. The key executives at Lennar, including the Lennar CEO, play a vital role in the company's strategic direction.
The Board of Directors is reducing its size to ten members as of the 2025 Annual Meeting.
- Stuart Miller, son of the co-founder, is the Executive Chairman and Co-CEO.
- Armando Olivera serves as Lead Director.
- The company has Class A and Class B common stock, potentially affecting voting rights.
- Lennar headquarters is located in Miami, Florida.
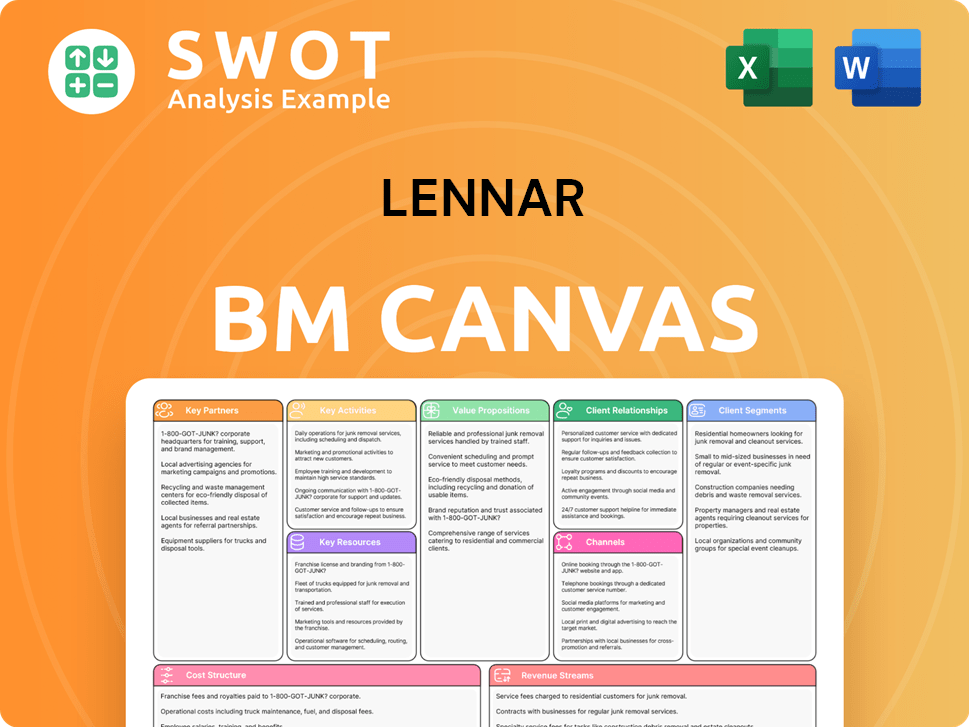
Lennar Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
What Recent Changes Have Shaped Lennar’s Ownership Landscape?
Over the past few years, strategic shifts have significantly influenced the ownership structure and operational model of Lennar Corporation. A pivotal move was the spin-off of Millrose Properties on February 7, 2025. This involved transferring approximately $5.6 billion in land assets and $1.0 billion in cash from Lennar's balance sheet. Approximately 80% of Millrose's stock was distributed to Lennar shareholders. Lennar temporarily retains the remaining 20% of Millrose's common stock, which it plans to dispose of later. This aligns with Lennar's goal to become an 'asset-light, land-light' homebuilder, reducing land ownership exposure and capital intensity. As of March 2025, about 98.0% of Lennar's lot position was controlled through land option contracts, a marked increase from 77% in Q1 2024, illustrating this strategic shift.
In February 2025, Lennar acquired Rausch Coleman Homes' homebuilding operations, expanding its reach, particularly in the Southeast and Texas. This acquisition is expected to add around 5,000 homes to Lennar's portfolio, with an average sales price of $230,000. Lennar also consistently returns capital to shareholders through dividends and share buybacks. In FY2024, the company repurchased $2.26 billion of common stock. In the first quarter of 2025, Lennar repurchased 5.2 million shares for $703 million, averaging $134.40 per share. During the fourth quarter of 2024, the company repurchased 3 million shares for $521 million. These buybacks reduce outstanding shares, potentially enhancing earnings per share.
| Metric | Details | Year |
|---|---|---|
| Cash and Cash Equivalents | $4.7 billion | FY24 |
| Homebuilding Debt-to-Total Capital Ratio | 7.5% | FY24 |
| Shares Repurchased Q1 2025 | 5.2 million shares | 2025 |
| Average Price per Share (Q1 2025) | $134.40 | 2025 |
Industry trends show a move towards asset-light strategies, with homebuilders aiming to decrease land ownership and increase control through options and joint ventures. This approach aims to boost cash flow, reduce capital expenditure, and mitigate risks. Lennar's strategic pivot exemplifies this industry trend, aiming for more predictable performance and enhanced shareholder value. The company's robust financial health, with $4.7 billion in cash and a homebuilding debt-to-total capital ratio of 7.5% as of FY24, supports its capital allocation strategy and future growth plans. If you're interested in learning more about the company, check out the [Lennar Corporation overview](0).
Lennar is a publicly traded company, so its ownership is spread among institutional investors, individual shareholders, and company insiders. The largest institutional shareholders include investment firms and mutual funds.
The current CEO of Lennar is Rick Beckwitt. He leads the company's strategic direction and oversees its operations.
Lennar's corporate headquarters is located in Miami, Florida. This location serves as the central hub for the company's administrative and executive functions.
Lennar's stock is traded on the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) under the ticker symbol LEN. Investors can monitor the stock's performance through financial news outlets and brokerage platforms.
Lennar Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What are Mission Vision & Core Values of Lennar Company?
- What is Competitive Landscape of Lennar Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of Lennar Company?
- How Does Lennar Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of Lennar Company?
- What is Brief History of Lennar Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of Lennar Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.