Lockheed Martin Bundle
Who Really Controls Lockheed Martin?
Unraveling the intricacies of 'Who owns Lockheed Martin?' is key to understanding the aerospace and defense giant's strategic moves and market influence. The 1995 merger of Lockheed Corporation and Martin Marietta was a pivotal moment, shaping the company's ownership and solidifying its dominance. This transformation moved Lockheed Martin into the realm of a publicly held entity, changing its ownership structure significantly.

From its humble beginnings in 1912, Lockheed Martin has evolved into a global powerhouse. Today, as a Lockheed Martin SWOT Analysis will reveal, the company is primarily held by institutional and individual investors. Understanding the Lockheed Martin ownership and the dynamics of its Lockheed Martin shareholders is vital. This exploration will examine the Lockheed Martin company structure, including its Lockheed Martin major shareholders and the influence of its Lockheed Martin executives and Lockheed Martin CEO and leadership.
Who Founded Lockheed Martin?
The story of Lockheed Martin's ownership begins with the foundational entities: Lockheed Corporation and Martin Marietta. These companies, prior to their 1995 merger, had distinct ownership structures rooted in the visions of their founders.
The Alco Hydro-Aeroplane Company, which later became Lockheed, was established in 1912 by brothers Allan and Malcolm Loughead. They initially held the primary equity, driven by their passion for aviation innovation. The Glenn L. Martin Company, also founded in 1912 by Glenn L. Martin, began with his direct ownership. Both companies evolved, seeking external capital to fuel expansion and technological advancements.
Early financial backing for these ventures likely came from a combination of personal funds and small private investments. The founders' control and strategic direction were paramount, especially in securing capital for research, development, and manufacturing. Any early ownership disputes or buyouts would have focused on maintaining control and funding growth during the volatile early decades of the aerospace industry. The founders' visions for technological advancement and air superiority were directly reflected in how control was distributed and how early capital was raised and deployed.
Founded as Alco Hydro-Aeroplane Company in 1912 by the Loughead brothers. Their initial ownership formed the base for the company's future.
The Glenn L. Martin Company was established in 1912 by Glenn L. Martin. He controlled the early equity, setting the stage for its growth.
Early funding came from personal funds and private investments. This was typical for aviation ventures of the time.
Founders prioritized control to guide technological advancements. This was crucial for early success and growth.
Capital was raised with a focus on research, development, and manufacturing. This helped shape the company's strategic direction.
Early ownership disputes often centered on maintaining control. This was critical during the early decades of the aerospace industry.
Understanding the early ownership of Lockheed and Martin Marietta provides context for the current Revenue Streams & Business Model of Lockheed Martin. The founders' visions shaped the companies' initial structures.
- The Loughead brothers and Glenn L. Martin were central to the foundational ownership.
- Early funding strategies focused on securing capital for growth and innovation.
- The founders' control was essential for guiding technological advancements.
- These early decisions influenced the company's trajectory and structure.
- The 1995 merger created the current corporate entity.
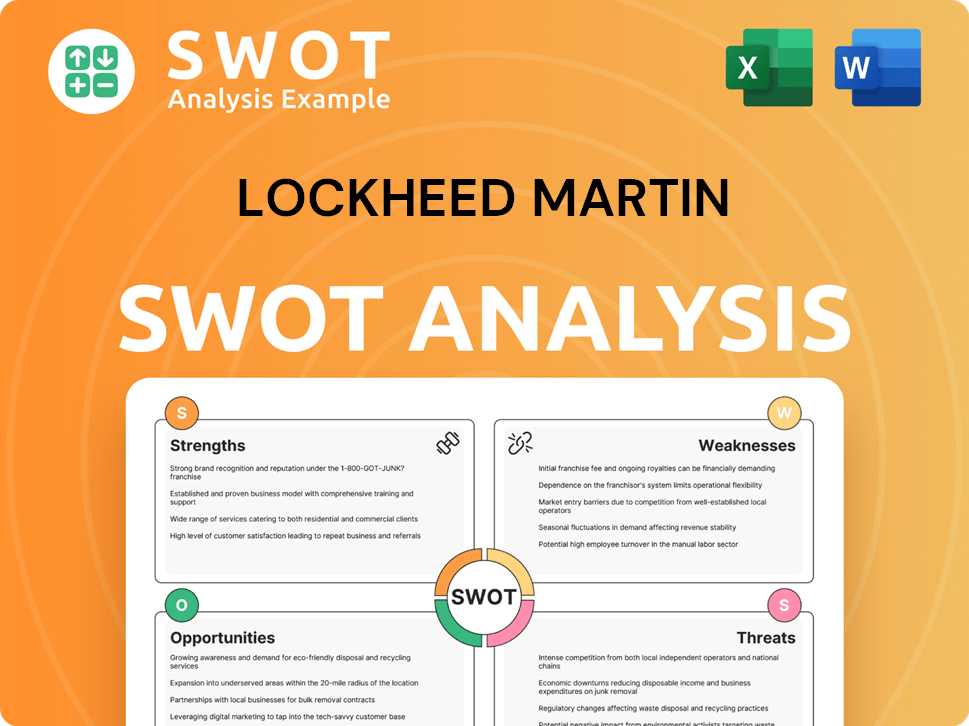
Lockheed Martin SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
How Has Lockheed Martin’s Ownership Changed Over Time?
The evolution of Lockheed Martin's ownership is a story of mergers and institutionalization. The pivotal moment was the 1995 merger, which created the current entity and transformed it into a publicly traded company on the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE: LMT). This event marked a shift from private or closely held ownership structures to a model dominated by public shareholders. The initial market capitalization post-merger was substantial, reflecting the combined scale of the defense giants.
Following the merger, the ownership of the company has largely transitioned to a broad base of institutional investors. This shift is typical for large-cap public companies, where ownership is dispersed among various investment entities. The company's ownership structure is now characterized by a significant presence of institutional investors, mutual funds, and index funds, which collectively hold a substantial portion of the outstanding shares.
| Ownership Milestone | Year | Details |
|---|---|---|
| Merger of Lockheed and Martin Marietta | 1995 | Formation of Lockheed Martin, a publicly traded company. |
| Institutional Ownership Growth | 1995-2025 | Gradual increase in the percentage of shares held by institutional investors. |
| Current Ownership Structure | Early 2025 | Dominated by institutional investors, mutual funds, and index funds. |
As of early 2025, the major stakeholders in Lockheed Martin are primarily large institutional investors. These include firms like Vanguard Group Inc., BlackRock Inc., and State Street Corp., which consistently rank among the top shareholders. These firms manage significant index funds and actively managed portfolios. For instance, as of the end of 2024, Vanguard Group Inc. held approximately 8-10% of the company's shares, while BlackRock Inc. and State Street Corp. held similar percentages. Individual insider ownership, including the Lockheed Martin executives and board members, represents a small fraction of the total shares, reflecting the diffused ownership structure. This shift to institutional ownership has generally promoted a focus on long-term shareholder value.
The Lockheed Martin parent company is publicly traded, with ownership primarily held by institutional investors. The company's structure is typical of a large-cap public firm, with a dispersed shareholder base.
- Institutional investors like Vanguard and BlackRock are key Lockheed Martin shareholders.
- Individual insider ownership is a small fraction of the total shares.
- The focus is on long-term shareholder value and strategic alignment.
- Understanding the Lockheed Martin company structure is crucial for investors.
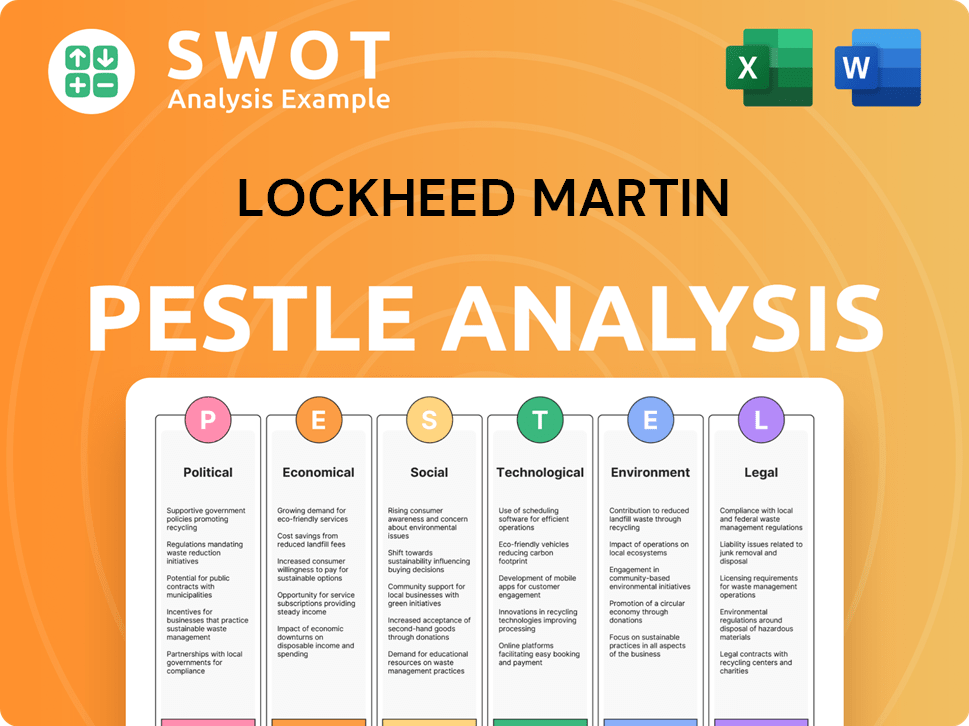
Lockheed Martin PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
Who Sits on Lockheed Martin’s Board?
The current board of directors of the company, as of early 2025, includes a mix of independent directors and those with extensive experience in the aerospace, defense, and government sectors. The board typically consists of around 10-12 members. The structure generally includes a Chairman, a Chief Executive Officer (who is also a board member), and several independent directors. For example, James Taiclet serves as Chairman, President, and CEO. Other directors often include individuals with backgrounds in finance, technology, military leadership, and public policy, reflecting the diverse expertise required to oversee a company of this complexity.
The board's role is to oversee strategic direction, risk management, and executive compensation. Board members are elected by a plurality of the votes cast, and their roles are primarily to represent the interests of all shareholders, ensuring sound corporate governance and long-term value creation. The company's governance emphasizes a strong, independent board.
| Board Member | Title | Relevant Experience |
|---|---|---|
| James Taiclet | Chairman, President, and CEO | Aerospace, Defense, Executive Leadership |
| Other Directors | Various | Finance, Technology, Military, Public Policy |
| Independent Directors | Various | Corporate Governance, Strategic Oversight |
The voting structure of the company is based on a one-share-one-vote principle. This means that each share of common stock generally entitles its holder to one vote on matters brought before shareholders. There are no dual-class shares or special voting rights that grant disproportionate control to any particular individual or group, reinforcing the widely held ownership model. For further details, you can explore the company's profile to understand more about the company's structure.
The company is a publicly traded company, and its ownership is widely distributed among various shareholders. The company does not have a single major shareholder with an outsized controlling stake.
- The company's stock is traded on the New York Stock Exchange.
- Institutional investors hold a significant portion of the company's stock.
- The company's stock ticker symbol is LMT.
- The company's investor relations site provides detailed information on ownership.
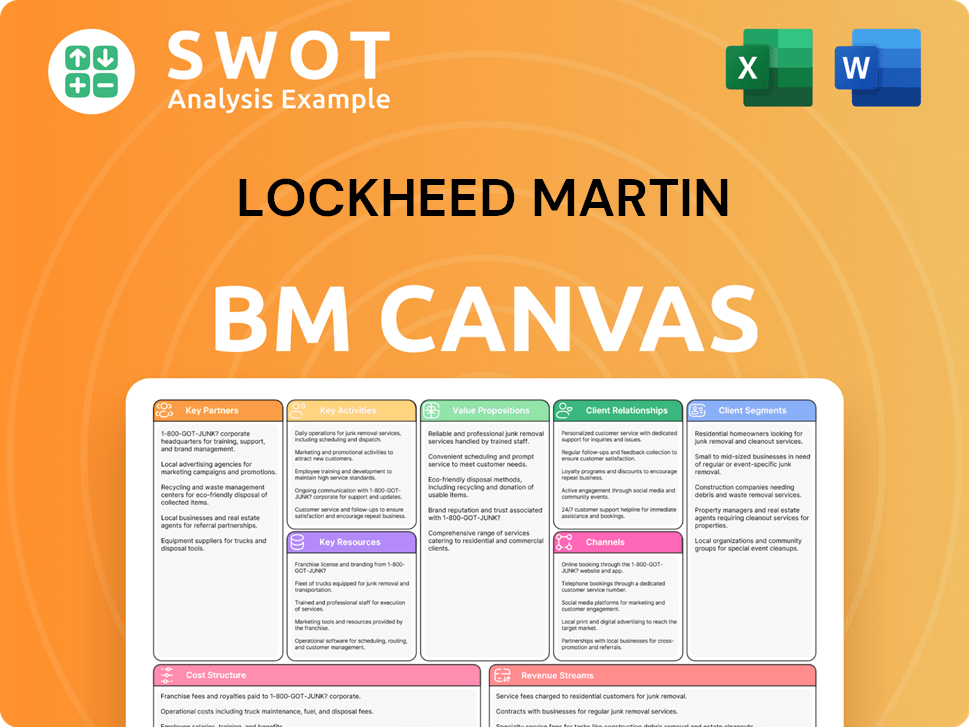
Lockheed Martin Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
What Recent Changes Have Shaped Lockheed Martin’s Ownership Landscape?
Over the past few years (2022-2025), the ownership of the Lockheed Martin parent company has largely remained stable. It continues to be a publicly traded company, with institutional investors holding a significant portion of the shares. There haven't been major shifts in control through significant share buybacks or large secondary offerings that would drastically alter the ownership percentages.
The company has maintained its share repurchase programs, which help to offset dilution from equity compensation and provide returns to shareholders. In 2024, Lockheed Martin allocated billions of dollars towards share repurchases. These actions have supported the stock price and shareholder returns, but haven't fundamentally changed the ownership structure. Mergers and acquisitions, while common for the company, haven't altered the overall ownership structure of the parent company.
The defense sector's trends, such as increased institutional ownership, are reflected in Lockheed Martin's profile. As a mature, stable company with consistent government contracts, it's favored by institutional funds seeking long-term value. The rise of activist investors hasn't significantly impacted Lockheed Martin, likely due to its strong market position and consistent performance. Public statements from the company and analysts focus on operational performance and contract wins, rather than impending ownership changes.
| Ownership Category | Approximate Ownership (2024-2025) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Institutional Investors | ~75-80% | Includes mutual funds, pension funds, and other institutional entities. |
| Individual Investors | ~15-20% | Represents shares held by individual shareholders. |
| Company Insiders (Executives and Board) | <1% | Includes shares held by the company's executives and board members. |
Institutional investors, such as mutual funds and pension funds, hold a significant majority of the Lockheed Martin shareholders. This indicates stability and investor confidence in the company's long-term prospects. Their ownership reflects the company's status as a mature and reliable investment within the defense sector.
Lockheed Martin continues to use share repurchase programs to return value to its shareholders. These programs often involve billions of dollars annually and can help boost the Lockheed Martin stock price. These buybacks also offset the dilution from employee stock options.
Changes in Lockheed Martin executives, such as the CEO, have not triggered major shifts in ownership. The company's governance structure manages these transitions effectively. The focus remains on operational performance and strategic goals.
The defense sector's trends, including increased institutional ownership, are well-reflected in Lockheed Martin’s profile. The company's strong market position and consistent performance make it a favored holding for large institutional funds. The company's focus is on innovation and contract wins.
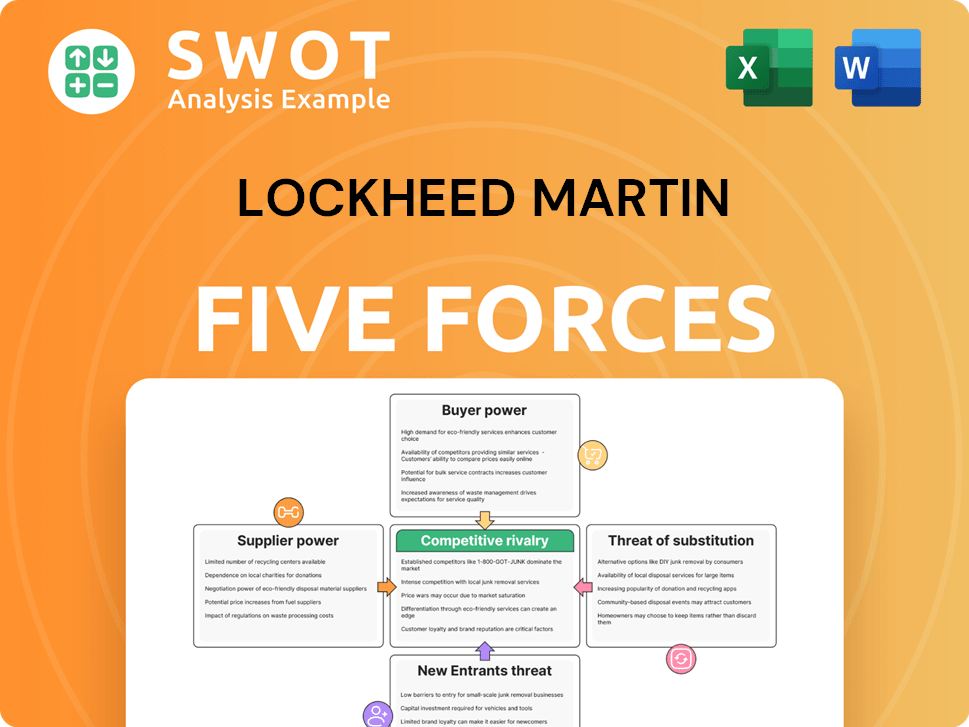
Lockheed Martin Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What are Mission Vision & Core Values of Lockheed Martin Company?
- What is Competitive Landscape of Lockheed Martin Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of Lockheed Martin Company?
- How Does Lockheed Martin Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of Lockheed Martin Company?
- What is Brief History of Lockheed Martin Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of Lockheed Martin Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.