Samsara Bundle
Who Really Owns Samsara?
Understanding a company's ownership structure is paramount for any investor or strategist. Samsara Inc., a leader in the IoT space, has experienced significant growth since its 2015 founding. Its innovative Samsara SWOT Analysis can provide valuable insights into its market position. This exploration unveils the key players behind this dynamic company.
As a public company, understanding the Samsara ownership is crucial. The Samsara company ownership structure reveals the influence of Samsara investors, the Samsara founder, and public shareholders. This analysis will provide a clear picture of who owns Samsara, including insights into Samsara's major shareholders and the evolution of its leadership team.
Who Founded Samsara?
The story of the company begins in early 2015 with its founders, Sanjit Biswas and John Bicket. Their prior experience as co-founders of Meraki, which was acquired by Cisco Systems in 2012 for $1.2 billion, provided a strong foundation for their new venture. This background played a crucial role in shaping the early stages of the company.
The company's initial focus was on sensor technology for industrial operations. While the exact initial equity distribution isn't public, Biswas and Bicket held significant stakes. Early funding rounds were crucial for the company's growth.
The company quickly gained momentum, achieving unicorn status by March 2018, with a valuation exceeding $1 billion. Further funding rounds in late 2018, backed by Andreessen Horowitz and General Catalyst, boosted its valuation to $3.6 billion, demonstrating the founders' vision.
Sanjit Biswas and John Bicket co-founded the company in early 2015. They met at MIT and had previous success with Meraki.
Andreessen Horowitz and General Catalyst were key early investors. These firms played a significant role in the company's early funding rounds.
By March 2018, the company achieved a valuation exceeding $1 billion. This marked a significant milestone in its growth trajectory.
Biswas and Bicket maintained significant influence, reflecting their vision for the company. This ensured their continued strategic direction.
Subsequent funding rounds, supported by Andreessen Horowitz and General Catalyst, increased the valuation to $3.6 billion. These rounds fueled further expansion.
The company's initial focus was on sensor technology for industrial operations. This strategic direction set the stage for its future innovations.
The company's early success was fueled by its founders' vision and the support of key investors. The company's journey from its inception to its current status is a testament to its founders' leadership and the strategic backing it received. For a deeper dive into the company's strategic approach, consider reading about the Growth Strategy of Samsara. The company's market capitalization as of May 2024 was approximately $28.5 billion. The company's leadership team, including the CEO and CTO, has been instrumental in guiding the company's direction. The company's headquarters is located in San Francisco, California. The company's stock is traded on the New York Stock Exchange under the ticker symbol "IOT."
The company's ownership structure is primarily influenced by its founders and early investors.
- Sanjit Biswas and John Bicket, the founders, held substantial stakes.
- Andreessen Horowitz and General Catalyst were among the key early investors.
- The company achieved a valuation exceeding $1 billion by March 2018.
- The founders' vision for bringing integrated hardware, software, and cloud computing to the industrial sector was evident from the start.
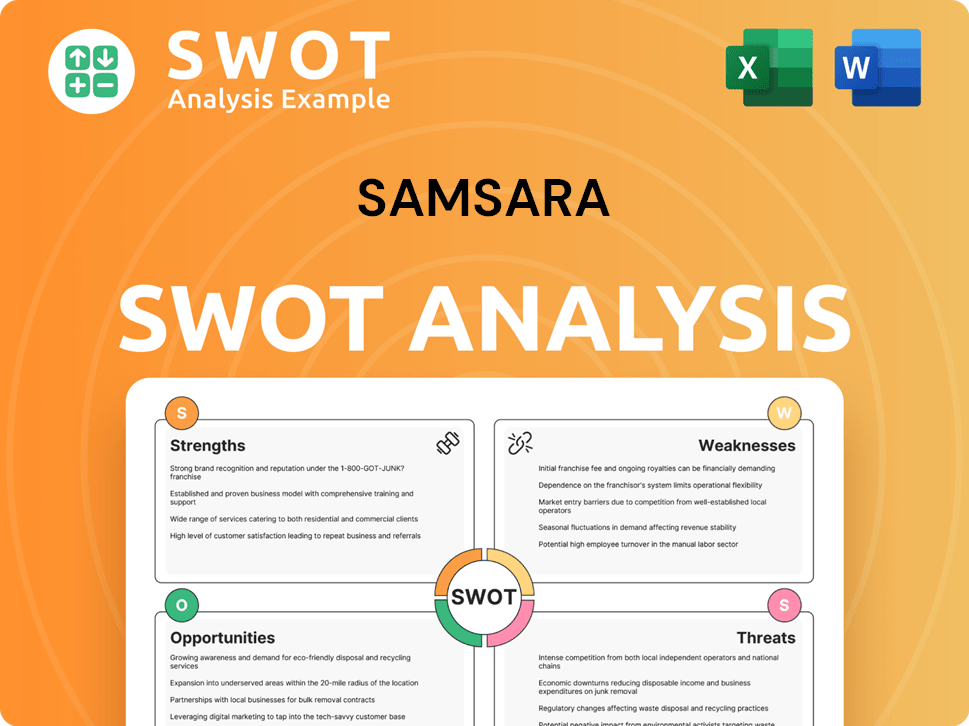
Samsara SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
How Has Samsara’s Ownership Changed Over Time?
The ownership structure of the company, now known as Samsara, underwent a significant transformation with its initial public offering (IPO) on December 15, 2021. The company began trading on the New York Stock Exchange under the ticker symbol 'IOT'. This move from private funding to a public market listing broadened the investor base, bringing in a variety of institutional and individual investors. The IPO generated $805 million through the sale of 35 million shares, priced at $23 each, which valued the company at $11.5 billion at the time.
Since its IPO, the company's market capitalization has increased substantially. As of June 12, 2025, the market capitalization reached $23.21 billion, marking a 101.65% increase. This growth reflects the company's performance and the increased interest from investors. The shift to a public company structure has also changed the composition of its major shareholders, with institutional investors now playing a key role in the company's ownership.
| Key Event | Date | Impact on Ownership |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Public Offering (IPO) | December 15, 2021 | Transitioned from private to public ownership; broadened investor base. |
| Market Capitalization Growth | June 12, 2025 | Increased company valuation; reflected investor confidence. |
| Institutional Investment | May 2025 | Significant institutional ownership; increased influence of large investors. |
As of May 2025, the company has a diverse ownership structure. There are 801 institutional owners and shareholders, collectively holding a total of 297,863,150 shares. Key institutional investors include Baillie Gifford & Co, Vanguard Group Inc., and BlackRock, Inc. Institutional ownership accounted for approximately 46.9% of the shares. Private equity firms hold a 12% stake, while individual insiders, including the founders, held about 39.6% of the shares. The general public owns about a 5.17% stake, demonstrating the broad distribution of ownership. The company's founders, Sanjit Biswas and John Bicket, continue to hold significant influence. To learn more about the company's journey, you can read a Brief History of Samsara.
The company's ownership structure has evolved significantly since its IPO, with a shift towards institutional investors.
- The IPO in December 2021 was a pivotal moment, opening the company to public investors.
- Major shareholders include institutional investors such as Baillie Gifford & Co and Vanguard Group Inc.
- Founders Sanjit Biswas and John Bicket still hold substantial influence.
- The company's market cap has grown significantly since its IPO, reaching $23.21 billion as of June 12, 2025.
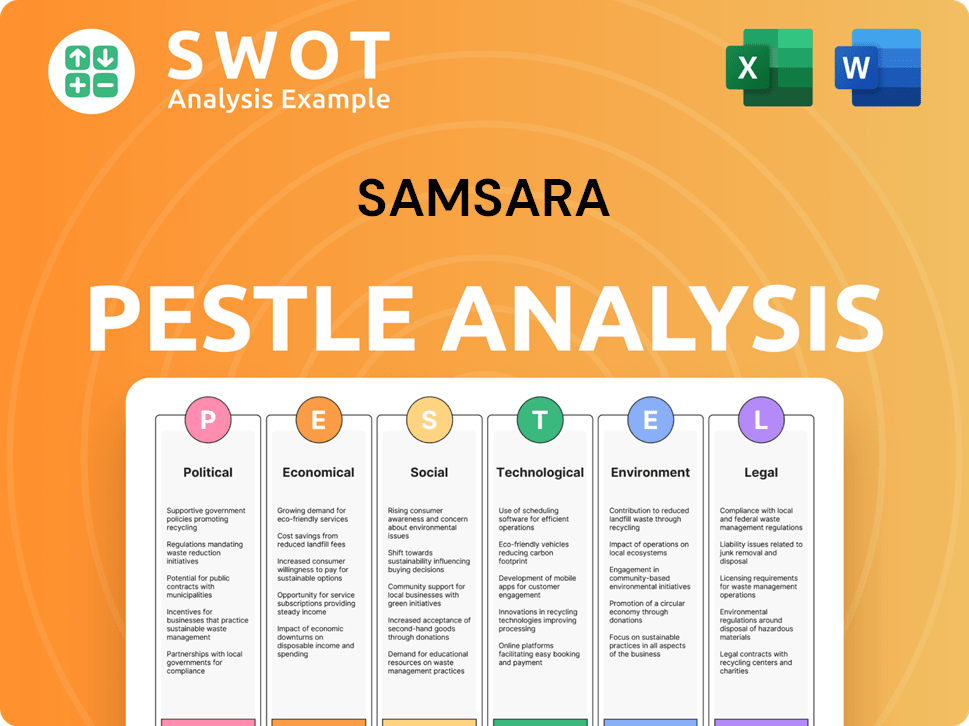
Samsara PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
Who Sits on Samsara’s Board?
The current board of directors of the company, plays a vital role in its governance and strategic decisions. As of July 2024, the board includes co-founders Sanjit Biswas and John Bicket, along with other elected directors. These individuals are elected to serve until the next annual meeting. Understanding the structure of Samsara ownership is key to understanding the company's direction.
The board's composition reflects a mix of founders and experienced investors, who bring diverse perspectives and expertise. This structure helps guide the company's growth and strategic initiatives. The board's decisions influence the company's performance and its ability to navigate the competitive landscape. The company's board of directors is crucial for understanding the company's trajectory.
| Director | Title | Affiliation |
|---|---|---|
| Sanjit Biswas | CEO, Co-founder | Samsara Inc. |
| John Bicket | CTO, Co-founder | Samsara Inc. |
| Marc Andreessen | Director | Andreessen Horowitz |
Sanjit Biswas, as CEO and co-founder, and John Bicket, as CTO and co-founder, possess significant voting power within the company. Through their ownership of 'super-voting' Class B shares, Biswas and Bicket together control 60% of the voting power in the company, providing them with a clear majority. Marc Andreessen, a well-known tech investor and a founding partner at Andreessen Horowitz, holds another 20% voting stake, further consolidating control among key early backers and founders. This dual-class share structure ensures that the founders and early investors retain substantial control over the company's direction, even with a broader public shareholder base. Understanding who owns Samsara is crucial for investors. For a deeper dive into the company's strategic moves, consider exploring the Marketing Strategy of Samsara.
The board of directors includes founders and experienced investors, ensuring a balance of expertise. The dual-class share structure gives founders and early investors significant control. The voting power is concentrated among key individuals, influencing strategic decisions.
- The founders, Sanjit Biswas and John Bicket, hold considerable voting power.
- Marc Andreessen of Andreessen Horowitz also has a significant voting stake.
- The company's ownership structure impacts its strategic direction.
- Understanding the board and voting power is important for investors.
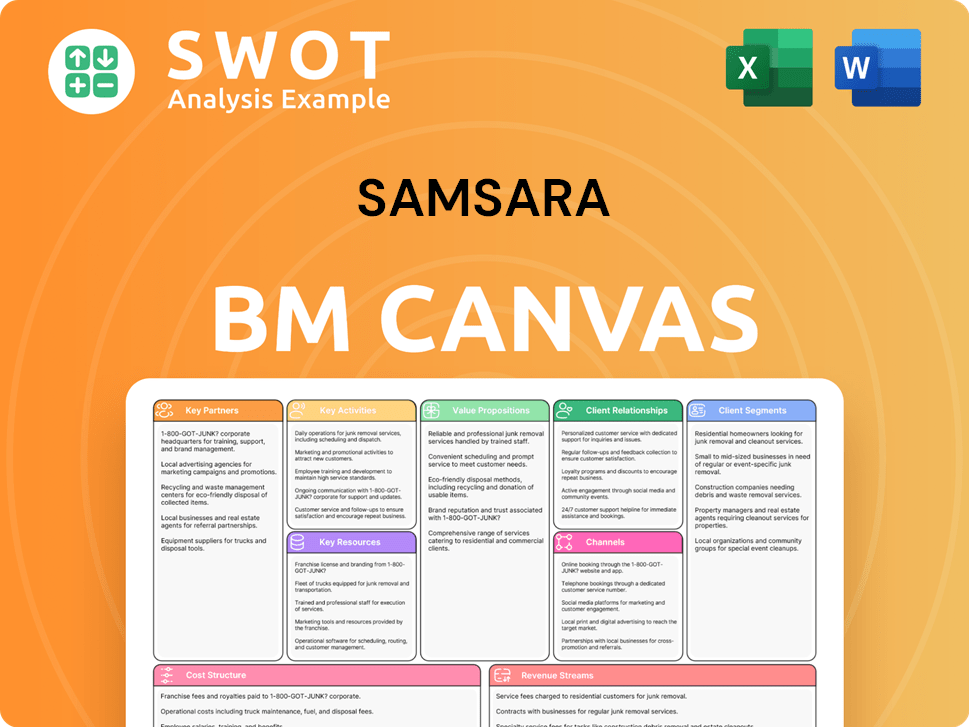
Samsara Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
What Recent Changes Have Shaped Samsara’s Ownership Landscape?
Over the past few years, the ownership profile of the Samsara company has shown dynamic shifts. As of May 2025, institutional ownership remains a significant factor, with 801 institutional owners holding a substantial number of shares. This indicates strong confidence from institutional
Financial performance in fiscal year 2025, ending February 1, 2025, demonstrated robust growth for the company. Revenue increased by 33% year-over-year, reaching $1.25 billion, and Annual Recurring Revenue (ARR) neared $1.5 billion, reflecting a 32% year-over-year increase. The customer base also expanded, with the number of customers with ARR over $100,000 growing by 36% year-over-year to 2,506. These figures highlight the company's ongoing expansion and market penetration. Despite some insider selling, the company has not experienced significant shareholder dilution.
| Metric | FY2025 (Ending Feb 1, 2025) | Change |
|---|---|---|
| Revenue | $1.25 Billion | +33% YoY |
| ARR | ~$1.5 Billion | +32% YoY |
| Customers with ARR > $100K | 2,506 | +36% YoY |
The company continues to focus on innovation, especially in AI-powered solutions, and international expansion. Approximately 13% of the total revenue was generated outside the United States in FY2025. There have been no major public announcements about planned successions or potential privatization as of early 2025, suggesting a focus on organic growth and market leadership. The company's leadership team, including the
The stock's performance reflects investor confidence and market conditions, with ongoing analysis crucial for potential investors. Understanding
Institutional investors play a significant role in
Monitoring insider transactions, such as those by the CEO, offers clues about the company's internal perspective and future outlook. This is crucial for understanding
The company's emphasis on AI and international expansion indicates its strategic direction. These initiatives are key to the company's future growth and market position. This is important for
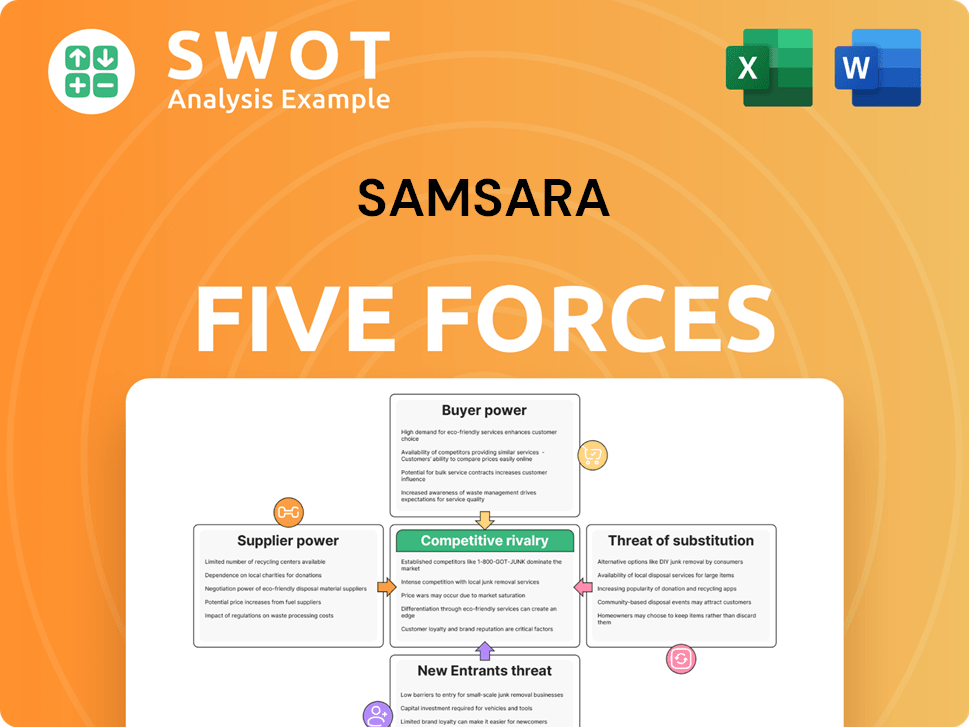
Samsara Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What are Mission Vision & Core Values of Samsara Company?
- What is Competitive Landscape of Samsara Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of Samsara Company?
- How Does Samsara Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of Samsara Company?
- What is Brief History of Samsara Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of Samsara Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.